Welfare of Employment and Unemployment Due to Covid-19 in Gianyar Regency
on
pISSN : 2301 – 8968
JEKT ♦ 15 [1] : 293-306 eISSN : 2303 – 0186
Welfare of Employment and Unemployment Due to Covid-19 in Gianyar Regency
Ni Made Itarini, Ni Nyoman Yuliarmi, A.A. I.N Marhaeni
ABSTRAK
Pekerja selalu menginginkan kesejahteraan yang berkelanjutan. Kementerian Ketenagakerjaan menggunakan Indeks Pembangunan Ketenagakerjaan (IPK) untuk mengukur keberhasilan pembangunan ketenagakerjaan. Indikator IPK yang mengalami penurunan dari tahun 2019-2020 yaitu indikator kesejahteraan yang disebabkan oleh Covid-19 sejak awal tahun 2020. Tujuan penelitian ini adalah menganalisis pengaruh tingkat kesehatan, kreativitas, dan networking terhadap produktivitas dan kesejahteraan, serta menganalisis hubungan tingkat kesehatan, kreativitas, dan networking terhadap kesejahteraan melalui produktivitas pekerja yang dirumahkan dan di PHK akibat Covid-19 di Kabupaten Gianyar. Penelitian menggunakan data primer dimana pengumpulan data dilakukan dengan metode accidental sampling dikombinasikan dengan snowball sampling. Teknik analisis yang digunakan adalah analisis Partial Least Square. Hasil penelitian menunjukkan bahwa tingkat kesehatan, kreativitas, dan networking berpengaruh positif dan signifikan terhadap produktivitas dan kesejahteraan, serta produktivitas memediasi pengaruh tingkat kesehatan, kreativitas, dan networking terhadap kesejahteraan pekerja yang dirumahkan dan di PHK akibat Covid-19 di Kabupaten Gianyar.
Kata kunci: tingkat kesehatan, kreativitas, networking, produktivitas, kesejahteraan Klasifikasi JEL: I15, O35, A13, O49, I31
ABSTRACT
Workers always want sustainable prosperity. The Ministry of Manpower uses the Employment Development Index (EDI) to measure the success of labor development. The EDI indicator which has decreased from 2019-2020 is the welfare indicator caused by Covid-19 beginning of 2020. The purpose of this study is to analyze effect the level of health, creativity, and networking on productivity and welfare, and examine the levels of health, creativity, and networking with productivity that affect on the welfare of employment and unemployment due to Covid-19 in Gianyar Regency. This research uses primary data collected under the accidental sampling method combined with snowball sampling. The analysis technique used is Partial Least Square analysis. The results showed that the level of health, creativity, and networking had a positive and significant effect on productivity and welfare, and productivity mediates effect the level of health, creativity, and networking on welfare of employment and unemployment due to Covid-19 in Gianyar Regency.
Kata kunci: level of health, creativity, networking, productivity, welfare JEL Classification: I15, O35, A13, O49, I31
INTRODUCTION
Continuous improvement of worker welfare is highly expected by every worker. Various efforts have been made by the government to maintain the welfare of workers. The Ministry of Manpower uses the Employment Development Index to measure the success of national and regional employment development in each province. Manpower development has four main objectives, namely the utilization of the entire national workforce in the process of national or economic development, equal distribution of employment opportunities throughout Indonesia, protection of workers throughout Indonesia, and safeguarding the welfare of all workers and their families.
This EDI measurement can be used as a reference in measuring the welfare of workers in accordance with the objectives of labor development. Figure 1 below shows the achievements of the
indicators used in the measurement of employment.
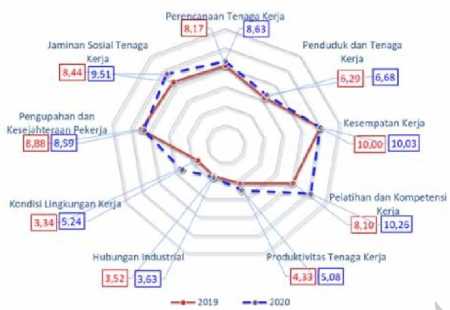
Source: Ministry of Manpower, 2020
Figure 1. Comparison of the Values of the Main Indicators of the National
Employment Development Index, 2019
2020
Based on Figure 1, it shows that the indicators of worker welfare have decreased from 2019-2020 as a result of the Corona Virus Disease 2019 (Covid-19) pandemic at the beginning of 2020. The pandemic has affected the global labor market and the world of work and has implications for the welfare of workers worldwide. This Covid-19 outbreak has caused many emotional impacts such as confusion,
extraordinary sadness, extraordinary fear of death, and increased anxiety (Farhan, 2020). This has led to a large number of studies taking into account the widespread negative impact of pandemics on well-being (Jemberie et al, 2020; Patrick et al, 2020; Sibley et al, 2020).
The government's policy to suppress the spread of Covid-19 is by issuing Government Regulation No. 21 of 2020 regarding the policy of Large-Scale Social Restrictions. Social Distancing causes various events to be cancelled, religious events are limited, tourist attractions are temporarily closed, causing many workers to have to work from home and even lose their jobs. Many companies are threatened with their business so that various efforts are made to reduce losses by reducing the number of workers. Several sectors affected during the Covid-19 pandemic were transportation, tourism, trade, health and the household sector (Susilawati et al., 2020). The results of the Central Statistics Agency (BPS)
survey (2020) noted that the accommodation and food/drink business sector was the sector that experienced the most income decline, which was 92.47 percent.
Gianyar Regency is one of the famous tourism areas in Bali Province. One of the tours offered by Gianyar Regency is cultural tourism. The pressure on the tourism sector caused by Covid-19 is believed to have an impact on the welfare of the Balinese people, especially workers. According to Sugihamretha (2020), Covid-19 has had a major impact on the tourism sector because social distancing policies have resulted in travel restrictions, cancellation of large events and reluctance to travel internationally and domestically, resulting in reduced tourist visits.
According to Rifai and Ratih Damayanti (2020) workers whose working hours are reduced (employment) is the status of returning workers temporarily not working anymore or reducing working hours, but will be called to work again if
the company operates again, while workers who are laid off (unemployed) are termination of employment relationship due to a certain matter which results in the termination of the rights and obligations between the worker and the entrepreneur. Based on the Circular Letter of the Minister of Manpower No. SE-05/M/BW/1998 of 1998 concerning Workers' Wages reduced by working hours addressed to the Regional Office of Manpower, employment and unemployment have different statuses, the status of workers whose working hours are reduced (employment) is still the same, status as workers so that they are entitled to monthly wages and benefits, while workers who laid off (unemployment) are only entitled to severance pay.
In general, welfare theory can be classified into three types, namely classical utilitarian, neoclassical welfare theory and new contractarian approach (Albert and Hahnel, 2005:77). The classical utilitarian approach emphasizes that a person's pleasure or satisfaction can be measured and
increased. According to Todaro (2003: 90), one of the factors that represents a person's level of life is said to be prosperous, namely an increase in productivity. Termination of employment or the workers whose working hours are reduce causes a decrease in worker productivity so that their welfare is also threatened (Syauqi, 2018). One of the most important things to keep productive during a pandemic is health (Rahmawati, et al, 2020). Health is very important during a pandemic, because if the immune system is weak, the Covid-19 virus is very easy to infect so that it will interfere with worker productivity. In addition to maintaining health, creativity while at home is also very important to stay productive. Productivity will be high if it is accompanied by a variety of creativity (Muthor, 2019). Overall creativity starts with a creative idea. According to Hendrawan, et al (2019), creative behavior can trigger the development of small businesses in strengthening the people's economy in MSME businesses which will affect the productivity and welfare of workers.
The pandemic requires everyone to make every effort to meet the needs of the economy. The strategy that can be used to increase productivity is by network expansion (Utomo and Susanta, 2017). Networking is one component of social capital. Social networks are very important to be formed during the covid-19 pandemic because through a network one can have access to people who can support productivity. Networks during a pandemic can be built through social media because the pandemic prohibits people from gathering through social distancing policies.
RESEARCH METHOD
This study uses two types of data, namely primary data and secondary data. Primary data were obtained from workers whose working hours were reduced (employment) and were laid off (unemployment) in Gianyar Regency. Primary data is the main data used for analysis. Primary data in this study is supported by secondary data. Samples were obtained by accidental sampling
method combined with snowball sampling. The total sample is 203 workers whose working hours were reduced (employment) and were laid off (unemployment) in Gianyar Regency. The research location is in Gianyar Regency and the object of research is employment and unemployment.
Testing the effect of the level of health, creativity, and networking on the productivity and welfare of employment and unemployment in Gianyar Regency using welfare as the dependent variable and productivity as a mediating variable. The independent variables in this study were the level of health, creativity, and networking. The characteristics of the research sample used are gender, marital status, latest education, number of dependents, source of income, average income, and perceptions of income adequacy.
The analytical technique used to analyze the effect of the level of health, creativity, and networking on the productivity and welfare of
employment and unemployment in Gianyar Regency is Partial Least Square.
RESULT AND DISCUSSION
The results of the Partial Least Square analysis in this study are shown in Table 1.
Based on Table 2, it shows that all statement indicators in the variables of health, creativity, networking, Table 2. Partial Least Square Analysis
productivity and welfare have a Pearson correlation value greater than 0.30 so that all indicators are declared valid. The convergent validity AVE value is greater than 0.5, so it can be stated that the data in the study is valid. The value of discriminant validity is greater than the correlation of each construct, so it can be said that the model is valid.
|
Variable |
Indicators |
Pearson Correlation |
AVE |
Discriminant Validity |
Cronbach Alpha |
Composite Reliability |
|
Level of |
X1.1 |
0.959 | ||||
|
Health (X1) |
X1.2 |
0.978 |
0,915 |
0,957 |
0,961 |
0,970 |
|
X1.3 |
0.952 | |||||
|
X2.1 |
0.953 | |||||
|
Creativity |
X2.2 |
0.975 |
0,887 |
0,942 |
0,956 |
0,959 |
|
(X2) |
X2.3 |
0.955 | ||||
|
Networking |
X3.1 |
0.938 | ||||
|
(X3) |
X3.2 |
0.933 |
0,875 |
0,936 |
0,919 |
0,955 |
|
X3.3 |
0.920 | |||||
|
Productivity |
Y1.1 |
0.963 | ||||
|
(Y1) |
Y1.2 |
0.975 |
0,892 |
0,944 |
0,960 |
0,961 |
|
Y1.3 |
0.953 | |||||
|
Welfare (Y2) |
Y2.1 |
0.944 | ||||
|
Y2.2 |
0.948 |
0,910 |
0,954 |
0,945 |
0,968 | |
|
Y2.3 |
0.956 |
Source: Primary data, processed (2022)
The value of Cronbach's alpha and Composite reliability on each variable is greater than 0.70, so it can be stated that the data is reliable.
Table 3. R-square Test Result
|
Variable |
R Square |
Adjusted R Square |
|
Productivity |
0,855 |
0,853 |
|
Welfare |
0,869 |
0,866 |
Source: Primary data, processed (2022)
Based on the R2 in Table 3, the Q-Square
value is 0.981, this shows that the productivity, while the remaining 2 variation in the welfare variable can be percent is explained by other variables explained by variations in the level of outside the mode health, creativity, networking and
Tabel 4. Path Coefficients (Mean, STDEV, T-Statistics, P-Values)
|
Variable |
Original Sample Sample Mean Standard Deviation T Statistics P Values |
|
X1 - Y1 X2 - Y1 X3 - Y1 X1 - Y2 X2 - Y2 X3 - Y2 Y1 - Y2 |
0.309 0.301 0.101 3.051 0.002 0.385 0.380 0.107 3.589 0.000 0.281 0.291 0.128 2.185 0.029 0.241 0.248 0.072 3.327 0.001 0.173 0.173 0.083 2.088 0.037 0.218 0.234 0.092 2.383 0.018 0.349 0.325 0.120 2.916 0.004 |
Source: Primary data, processed (2022)
Table 4 shows that the level of health, significant impact on the welfare
|
creativity, |
and networking has a employment and unemployment in |
positive and significant effect on the Gianyar Regency. This is indicated by productivity of employment and comparing the t-count value which is unemployment in Gianyar Regency. The greater than the t-table which is 1.65 and level of health, creativity, networking, by comparing the P-Values value which and productivity have a positive and is smaller than alpha 0.05.
Table 5. Indirect Effects (Mean, STDEV, T-Statistics, P-Values)
|
Variable |
Original Sample |
Sample Mean |
Standard Deviation |
T Statistics |
P Values |
|
X1 → Y1 → Y2 |
0.108 |
0.099 |
0.051 |
2.098 |
0.036 |
|
X2 → Y1 → Y2 |
0.134 |
0.123 |
0.058 |
2.309 |
0.021 |
|
X3 → Y1 → Y2 |
0.098 |
0.093 |
0.054 |
1.825 |
0.069 |
Source: Primary data, processed (2022)
Based on Table 5 shows that there is an indirect relationship between the level of health, creativity, and networking on welfare mediated by productivity with a t-count value of 2.098 which is greater
than the t-table which is 1.65 with a p-value (p-value divided by two) is less than 0.05.
Workers whose working hours were reduced (employment) and were laid off
(unemployment) due to Covid-19 represent a relatively healthy level of health during the pandemic. The level of health in this study is measured by three indicators, namely the frequency of illness in the last three months, the frequency of experiencing injuries in the last three months, and the level of ownership of infectious diseases, this means that the majority of workers have infectious diseases while working hours were reduced or laid off. The infectious diseases referred to by the respondent are flu, cough, and Covid 19, because the respondent feels more susceptible to these diseases so it is necessary to implement strict health protocols, maintain body immunity by consuming vitamins, and keep a distance to be protected from these infectious diseases. The lowest appreciation of respondents is the frequency of respondents being sick in the last three months. This means that workers who have reduce working hours or laid off have not felt sick in the last three months, because few respondents answered strongly with this statement. Some respondents, did not state that they were sick if the
condition they experienced was only a mild headache or just weakness, even though headaches accompanied by a weak body were a reflection of a sick body condition. Respondents who only experience mild headaches tend not to have their body checked, respondents only let the pain they feel until it goes away by itself. This is inseparable from the economic disruption experienced by workers, respondents feel unable to pay for their health because the pandemic which has an impact on the employment sector causes workers whose working hours were reduced or laid off so that their income is reduced.
The creativity of the respondents whose working hours were reduced (employment) and were laid off (unemployment) is high. This can be seen from the activities that many respondents did while being sent home or in layoffs, namely selling food and selling canang or offerings as religious facilities. Some respondents also developed their creativity by making cloth masks, making carvings, and making incense. Creativity in this study
is measured by three indicators, namely the level of ownership of ideas, the level of ability to experiment, and the level of ability to produce products. The highest appreciation from respondents is that respondents are able to produce products while reduce of working hours and were laid off, this means whose working hours were reduced (employment) and were laid off (unemployment) workers are able to produce products from the development of their ideas so that the resulting products can add to the respondent's income to support their welfare. The lowest appreciation from respondents is the level of ability to experiment, this means that workers who are reduce of working hours or laid off have not been able to experiment. Respondents should try to develop their ideas by experimenting before making a product to be marketed. Respondents in this study felt that the experiments carried out were a waste of time and resources, because respondents felt that they were in a pinch had to produce products to be marketed as quickly as
possible so that they could quickly earn income. A product that begins with an experiment will be of higher quality than a product without an experiment, because with an experiment, the respondent will know the weaknesses and strengths of the product.
The highest appreciation for networking is the statement of ownership level of access with capital owners, this means that while whose working hours were reduced (employment) and were laid off (unemployment) workers have access to capital owners, namely neighbors or friends of respondents who are trusted to have capital or from financial institutions. The statement that has the lowest appreciation is the level of closeness to the business owner, this means that workers feel less close to the business owner so that respondents whose working hours were reduced and were laid off can expand their network to business owners. The majority of respondents in this study establish relationships with the people around them, because the social distancing
policy makes it difficult for respondents to build networking, so that the opportunity to respond to network with business owners becomes difficult. Some respondents also develop their network through social media, such as establishing good relationships with online shop actors or influencers.
Workers whose working hours were reduced (employment) and were laid off (unemployment) due to Covid-19 represent that their welfare is high while being employment were reduced working hours or laid off due to COVID-19. The statement that has the highest appreciation value is the statement of income from work after reduce working hours or being laid off to be able to pay for health, this means that workers who are reduce working hours or laid off are able to finance their health from the income earned while reduce working hours or laid off. The statement that has the lowest value is the income from work after reduce working hours or laid off to be able to finance their daily needs, this means that workers who are laid off or laid off
are less able to finance their daily needs so they must increase their income from the work they do while being reduce working hours or laid off. Workers who are reduce working hours or laid off in Gianyar Regency tend to experience shortages in meeting their daily needs. Based on a survey conducted, respondents who experienced layoffs tend to experience shortages in meeting their needs, this is because the level of income earned only relies on income from work carried out during the pandemic, in contrast to workers who reduce working hours still earn income from the company where they work and income from their work. While workers who reduce working hours so that their income is higher than workers who have been laid off. Respondents who experienced layoffs met their food needs by utilizing plantation products in their fields in the form of vegetables so that they could reduce the respondent's food expenditure.
The productivity of workers whose working hours were reduced and were laid off due to Covid-19 is relatively
high while working hours were reduced or being laid off. The statement of the respondent who has the highest appreciation is the statement of the level of ability to produce products in a standard period of time, this means that as long as workers are working hours were reduced or laid off workers are able to produce products within a standard period of time. The statement that has the lowest appreciation value is the level of the respondent's ability to produce products with efficient use of resources, this means that workers whose working hours were reduced or laid off are less able to produce products with efficient use of resources. Workers whose working hours were reduced or laid off develop their productivity by carrying out various activities that are adapted to sectoral conditions in their area. Respondents have not been able to produce products with efficient use of resources because workers whose working hours were reduced or laid off feel they are still in the learning process to increase their productivity by doing various things that are able to produce
products so that workers can increase their income to support welfare. Respondents stated that they will continue to learn through trainings that are in accordance with the activities they do because respondents feel that if their abilities continue to be honed, they can produce products using more efficient resources. Respondents whose working hours were reduced tend to have more time to study and train themselves than respondents who were laid off, because respondents who were laid off were no longer working so they would be more focused on their daily activities compared to respondents whose working hours were reduced because they had to divide their time between work and carry out their activities at home because respondents whose working hours were reduced are still working at the company where they work.
CONCLUSION
Based on the results of the study, it can be concluded that the level of health, creativity, and networking has a
positive and significant impact on the productivity of workers whose working hours were reduced (employment) and laid off (unemployment) due to the Covid-19 pandemic in Gianyar Regency. The level of health, creativity, networking, and productivity has a positive and significant impact on the welfare of workers whose working hours were reduced (employment) and laid off (unemployment) due to the Covid-19 pandemic in Gianyar Regency. Productivity is indirectly able to mediate the level of health, creativity, and networking on the welfare of workers whose working hours were reduced (employment) and laid off (unemployment) due to the Covid-19 pandemic in Gianyar Regency.
Workers whose working hours were reduced or laid off feel that their income is insufficient to meet their daily needs, so during the Covid-19 pandemic, workers whose working hours were reduced and laid off must try to meet their needs. One of the things that workers can do is to expand their rice field plantations by diverting the
plantations in their yard by planting vegetables so that their daily needs can be fulfilled. Workers whose working hours were reduced or laid off can improve their abilities by continuing to learn and through training that is in accordance with the activities carried out to support their productivity so that workers are able to produce products with efficient use of resources. In particular, workers whose working hours were reduced should better manage their time between work and doing activities at home so that their productivity can be maintained. Workers whose working hours were reduced or laid off should immediately check their health if they feel sick, even if it is only a light headache or weakness, because the slightest pain that is felt indicates that the body is not in good condition so that the pain that is felt can be prevented as early as possible with treatment. One of the health services that workers can use is the Healthy Indonesia Card, which is one of the government's programs to maintain the level of public health.
REFERENCE
Farhan, Adib. 2020. Covid-19 Outbreak : Spoiled Students & Mental Health -Restrictions of the Truth?
Jemberie, W. B., Williams, J. S., Eriksson, M., Grönlund, A. S., Ng, N., Nilsson, M. B., et al. 2020. Substance Use Disorders and COVID-19: Multi-Faceted
Problems Which Require MultiPronged Solutions. Front.
Psychiatry 11:714. Doi:
10.3389/fpsyt.2020.00714
Patrick, S. W., Henkhaus, L. E., Zickafoose, J. S., Lovell, K., Halvorson, A., Loch, S., et al. 2020. Well-Being of Parents and Children During the COVID-19 Pandemic: a National Survey.
Pediatrics 146:e2020016824.
Doi: 10.1542/peds.2020-016824
Sibley, C. G., Greaves, L. M., Satherley, N., Wilson, M. S., Overall, N. C., Lee, C. H., et al. 2020. Effects of the COVID-19 Pandemic and Nationwide Lockdown on Trust, Attitudes Toward Government, and Well-being. Am. Psychol. 75, 618–30. Doi: 10.1037/amp0000662
Sulistiawati, Asri., Djuara P Lubis., dan Eko Sri Mulyani. 2014. Social Network Analysis in Farmers Group (Gapoktan) of Tani Berkah. Jurnal Sosiologi Pedesaan, Vol 2 No 2, hlm : 76-82
Sugihamretha, I.D.G., 2020. Respon
Kebijakan: Mitigasi Dampak
Wabah Covid-19 Pada Sektor Pariwisata. Jurnal Perencanaan Pembangunan Indonesia, Plan. 4, 191–206.
https://doi.org/10.36574/jpp.v4i 2.113
Rifai, Ahmad dan Gusti Ayu Ratih Damayanti. 2020. Kajian Hukum Terhadap Hak Pekerja yang Dirumahkan pada Masa Pandemi Covid (19) Berdasarkan Undang -Undang Nomor 13 Tahun 2003 Tentang Ketenagakerjaan. Jurnal Hukum Saraswati. Vol 2 No 2 pp: 214-230
Albert, M. & Hahnel, R. 2005. Traditional Welfare Theory,
www.zmag.org/books/1/html (diakses: 30-8-2021).
Todaro, Michael P. 2003. Pembangunan Ekonomi di Dunia Ketiga. Jakarta: Erlangga.
Syauqi, Teuku Muhammad. 2018. Pengaruh Produktivitas Kerja
Pegawai Terhadap Kesejahteraan Pegawai Kecamatan Medan
Selayang. Jurnal Warta Edisi : 57
Rahmayanti, Rini., Fitri Wahyuni., Velga Yazia., Delvi Handayani., dan Hidayatul. 2020. Pentingnya Menjaga Kesehatan di Masa Pandemi Covid-19 pada Remaja di Panti Aisyiyah Lubuk Minturun. Jurnal Pengabdian
Masyarakat. Vol 2 No 2 pp: 158164
Muthor. 2019. Pengaruh Kemampuan Kerja dan Kreativitas Terhadap Produktivitas Pegawai pada Dinas Komunikasi dan
Informatika Kabupaten Sumenep. Jurnal Manajemen dan Administrasi Publik. Vol 2 No 2 pp: 221-234
Hendrawan, Andi., Ferri Kuswantoro., dan Hari Sucahyawati. 2019. Dimensi Kreativitas dan
Pengembangan Usaha Mikro Kecil dan Menengah (UMKM). Jurnal HUMMANSI (Humaniora, Manajemen, Akuntansi), Vol 2 No 1 pp: 25-36
Utomo, Pranoto, and Hari S. Nugraha. 2017. Pengaruh Jaringan Bisnis, Teknologi Produksi, dan
Penjaminan Mutu Terhadap
Kinerja Pemasaran (Studi Pada IKM Gitar Di Kecamatan Baki, Kabupaten Sukoharjo). Jurnal Ilmu Administrasi Bisnis. Vol. 6, No. 2
306
Discussion and feedback