Influence Of Financial Technology (E-Wallet) On MSMEs’ Turnover In Denpasar
on
pISSN : 2301 – 8968
JEKT ♦ 15 [1] : 307-315 eISSN : 2303 – 0186
Influence Of Financial Technology (E-Wallet) On MSMEs’ Turnover In Denpasar
Ketut Shanti Cintya Devi, Ida Bagus Putu Purbadharmaja
ABSTRAK
UMKM merupakan sektor yang mampu menopang pertumbuhan ekonomi di Indonesia. Keberadaan UMKM membantu pemerintah dalam menyerap tenaga kerja. Kemajuan teknologi saat ini mendorong para pelaku UMKM untuk mampu beradaptasi dengan teknologi. Perkembangan teknologi dalam sistem pembayaran dikenal dengan Fintech. Penggunaan teknologi merupakan sebuah pilihan yang didasari oleh beberapa faktor sehingga tujuan dari penelitian ini adalah untuk mengetahui pengaruh lokasi usaha, tingkat pendidikan, dan jenis usaha terhadap omzet UMKM yang telah menggunakan produk Fintech yaitu E-wallet sebagai alat transaksi. Penelitian ini dilakukan di Kota Denpasar dengan menargetkan UMKM kategori sedang dengan jumlah sampel 89 responden, instrumen yang digunakan adalah kuesioner dan observasi. Analisis data yang digunakan dalam penelitian ini adalah 2SLS. Hasil penelitian ini menyatakan bahwa secara simultan variabel jenis usaha, tingkat pendidikan, lokasi usaha, dan keputusan penggunaan E-wallet berpengaruh terhadap omzet UMKM. Secara parsial variabel bebas yang mempengaruhi omzet UMKM adalah jenis usaha, tingkat pendidikan, dan keputusan penggunaan E-wallet.
Kata kunci: UMKM, Fintech, E-wallet, Transaksi
Klasifikasi JEL: M29, O39, O33, G53
Influence Of Financial Technology (E-Wallet) On MSMEs’ Turnover In Denpasar
ABSTRACT
MSME is a sector that is able to support economic growth in Indonesia. The existence of MSMEs helps the government in absorbing labor. Current technological advances encourage MSME actors to be able to adapt to technology. Technological developments in the payment system are known as Fintech. The use of technology is a choice based on several factors, so the purpose of this study is to determine the effect of business location, education level, and type of business on the turnover of MSMEs that have used Fintech products, namely E-wallet as a transaction tool. This research was conducted in Denpasar City by targeting medium category MSMEs with a sample of 89 respondents, the instruments used were questionnaires and observations. Analysis of the data used in this study is 2SLS. The results of this study indicate that the variables of type of business, education level, business location, and decisions on the use
of E-wallet have an effect on MSME turnover. Partially the independent variables that affect the turnover of MSMEs are the type of business, education level, and the decision to use E-wallet.
Kata kunci: MSMEs, Fintech, E-wallet, Transaction
Klasifikasi JEL: M29, O39, O33, G53
INTRODUCTION
Economic development in Indonesia currently shows that the informal sector is one of sector that had an important role, it can be shown through people's income in national income (Putra and Sudibia 2018). In line, the informal sector in the form of Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) has been
successfully developed evenly into every single areas (Utari and Dewi 2014). The various advantages possessed by MSMEs currently have helped the state in overcoming unemployment, absorbing labor, creating new job opportunities, and being able to increase GDP. The role of MSMEs in Indonesian economy is shown in Figure 1 which illustrates that the ability of MSMEs to absorb labor is relatively stable from years which is in line with (Putra and Mustika 2014) states that the role of MSMEs in Indonesia is as one of the important pillars in terms of employment.
Reflecting on the monetary crisis occurred in 1997-1998 which caused large scale companies bankrupt. However, MSMEs tend to survive and continue to grow (Jam’iyatuzzulfiyyah 2021).
Figure 1. Contribution of MSMEs Per Capita to GDP and Labor Absorption from 2010-2020 (in percent)
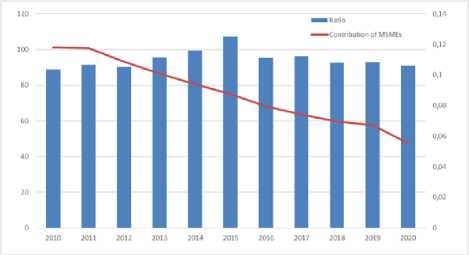
Source: Ministry of Cooperatives and Small and Medium Enterprises (data processed), (2021)
The important role of MSMEs currently as important as adapting technology in the field of information and communication to all sectors. The development of this technology had an impact of new innovations, one of the innovation shown in Indonesia’s payment system . The importance of this technology is also in line with the theory
of economic growth by Robert Solow which states that the level of output growth in the long run is the result of a combination of three factors, these factors are labor, capital, and technological change. So, in this case, it illustrates that all forms of business including MSMEs are required to be able to adapt to technological developments, which the technology is the form of payment transactions, financing and financial transactions (Trimulato 2020). The existence of technology is able to change the pattern of work, production, and distribution processes to be efficient. This combination of technology and finance is called Financial technology (Fintech). One of these fintech products is an electronic wallet (E-wallet). E-wallet is starting to be known in Indonesia as a transaction tool in the form of a server based whose existence is able to realize a reduction in cash circulation in the community and encourage people's transaction patterns to become a less cash society (Ferdiana and Darma 2019).
Bank Indonesia as the Central Bank of Indonesia is build the less cash society program in order to make an easier, free
Increase from
Period Amount last period (%)
|
2016 |
51.204.580 | |
|
2017 |
90.003.848 |
56,89 |
|
2018 |
167.205.578 |
53,83 |
|
2019 |
292.299.320 |
57,20 |
|
2020 |
432.281.380 |
67,62 |
|
charge, and spread transaction | ||
process throughout Indonesia. The role of Fintech for MSMEs is considered capable of increasing sales volume, improving performance and increasing customer loyalty (Taufik, Polindi, and Aguspriyani 2021). The shifting in transaction patterns can be shown in Table 1 which shows an increase in the amount of electronic money circulating in Indonesia from years it also shows there is an increase in using e-wallet as a transaction tool. The increase in the use of e-wallet is also due to the ease of transactions provided by BI policy of issuing the Quick Response Code Indonesian Standard (QRIS), besides that financial technology has been
supported by Bank Indonesia and OJK by issuing Bank Indonesia regulation No. 18/40/PBI/2016 and OJK 13/POJK.02/2018. This regulation protects security in the transaction process through fintech so that electronic transactions through fintech products are carried out in Indonesia with guaranteed safety.
Table 1. Amount of Electronic Money Transaction in Indonesia 2016-2020
The role of Bank Indonesia and OJK in issuing policies to facilitate transaction processes is currently able encourage and mobilize people to start adapting in the use of fintech. This shows that the combination of technological developments with the government role can shift the transaction pattern of the community to a less cash society. In addition to the role of the government, there are also internal factors that affect the willingness of the community, in this case the MSME owners to use ewallet as a transaction tool. Research conducted by Angelia and Gultom (2020) states that the type of sub-sector
and scale of business determine how the influence of the use of technology on economic performance, in line with this, this study was only carried out on a medium-scale business by giving consideration that technology readiness in medium-scale of business is easier to reach. on medium-scale MSMEs which is stated in the research that adaptation to technology for small and micro-scale enterprises has a negative effect (Angelia and Gultom 2020).
The use of technology is a society’s choice, according to (Ruli, Hilmawati, and Kusumaningtias 2021) and (Marpaung 2021) stating that the level of education or knowledge possessed is a motivating factor for someone to use fintech. In addition, research conducted by (Ihsan and Siregar 2019) states that in using and conducting transactions with e-wallet there is an e-service quality factor that has a significant influence on trusting the technology, it can encourage someone to make transactions with e-wallet. Based on the factors that have been mentioned, in this study the independent variables are
business location, education level and type of business with the decision to use e-wallet as an instrument variable where the dependent variable in this study is MSME turnover which is influenced after using e-wallet as an instrument. transaction tools in running their business. based on all the factors and the economic impact caused, this research is entitled Influence Of Financial Technology (E-Wallet) On Msmes’ Turnover In Denpasar.
RESEARCH METHOD
Aim of this research is to show the benefits obtained from the use of ewallet in MSMEs. To reach the aim of this research, data collection process conducted in Denpasar by conducting survey to 89 respondents out of 492 MSMEs with medium category that the sample size determined by Slovin formula with 10% margin of error.
The design of this study is an associative causality type of research because this
Table 2. First Stage Least Square as Testing Instrument for Instrumental Variables Candidate.
research analyze the effect of several independent variables on one dependent variable is using two stage least square (2SLS) regression analysis.
This study aims to obtain evidence of how much influence the use of e-wallet had on MSMEs turnover through independent variables: business location (X1), education level (X2), type of business (X3) and E-service quality (IV) as instrumental variables, and the turnover of MSMEs as the dependent variable (Y). Because this research using instrumental variables and 2SLS, there is a need to measure the candidate of instrumental variables (Wooldridge 2013).
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
This research had 89 respondents and had 89 valid respondents. Respondents in this study consisted of medium category MSMEs who knew and used ewallet in transacting in their business. This estimation is done to prove the suitability of the IV used.
|
Decision |
Coef. |
Std. Err. |
t |
P>t |
[95% Conf. |
Interval] |
|
eservice |
.3596154 |
.0658357 |
5.46 |
0.000 |
.2287599 |
.4904709 |
|
_cons |
.625 |
.056263 |
11.11 |
0.000 |
.5131712 |
.7368288 |
The results of the first stage least square estimation show that e-service quality has a significance value of less than 0.05 and a positive coefficient. These results are in line with research conducted by (Ihsan and Siregar 2019) which states that consumers go through an evaluation process before deciding to use service technology by looking at the Table 3. Estimation of Two Stage Least Square
e-service quality factor. E-service quality will show the ease of using applications that can be enjoyed by users. E-service quality can influence person in their decision to use technology. The result as shown in Table 2 that e-service quality meets the requirements of IV and can be used as an instrumental variable in this research.
|
Omzet |
Coef. |
Std. Err. |
z |
P>z |
[95% Conf. |
Interval] | |
|
Decision |
.6317355 |
.1274206 |
4.96 |
0.000 |
.3819957 |
.8814752 | |
|
businesstype |
.0381372 |
.0139487 |
2.73 |
0.006 |
.0107982 |
.0654761 | |
|
educlevel |
.2761297 |
.0813184 |
3.40 |
0.001 |
.1167485 |
.4355108 | |
|
businessloc |
.0066415 |
.0344301 |
0.19 |
0.847 |
-.0608403 |
.0741233 | |
|
_cons Prob > chi2 = R-squared = |
0.0000 0.7257 |
.0532667 |
.0736117 |
0.72 |
0.469 |
-.0910095 |
.1975429 |
Through the results of the regression in table 2, the results of the F-test are obtained as indicated by Prob > chi2 = 0.0000. Where the p value <0.05 means that with a significance level of 5 percent this model is appropriate and
significant, which means there is at least one of the independent variables are simultaneously affect the turnover of medium category MSMEs in Indonesia. Denpasar City.
The value of R-squared = 0.7257 means that the diversity of the independent variable data is able to explain the diversity of the dependent variable data by 72.57 percent while the remaining 27.43 percent is explained by variables outside the model.
The 2SLS estimation results shows each difference in the type of business is able to provide a difference in turnover of 3.8 percent for MSMEs in Denpasar City with a significance level of 0.006 which means it is significant at the 5 percent level. This result is in line with research conducted by Sanistasya, Raharjo, and Iqbal 2019 which states that different types of businesses can affect the number of different turnovers in each category of MSMEs.
The relationship between education level on MSME turnover is shown by the 2SLS estimation results in Table 2 shows 28 percent which means if the respondent states that education level is an important factor to be able to use ewallet as a transaction tool, then the turnover increases by 28 percent with a
level of significance 0.001 which means significant at the level of 5 percent. Research conducted by Utari and Dewi 2014 states that the level of education has a positive and significant effect on the income of MSMEs.
The relationship between business location on MSME’s turnover is shown by the 2SLS estimation results in Table 2 which shows 0.6 percent with a significance level of 0.847 which means that the business location has no significant effect at the 5 percent significance level (0.847> 0.05). The results of the 2SLS estimation are in line with research conducted by Damariyah (2012) which states that the business location has a positive and insignificant effect on turnover, so this means that the business location does not affect the turnover obtained by MSMEs.
CONCLUSION
F-test result showed the independent variables which is type of business, education level, business location, and the decision to use e-wallet affect the turnover of MSMEs in Denpasar City.
However, the T-test result showed the independent variables that influence the turnover of MSMEs in Denpasar City are the type of business, education level, and the decision to use e-wallet where these variables are significant at 5 percent. The type of business affects the decision of business owners in using ewallet as a transaction tool, the tendency to use e-wallet when a transaction is carried out by someone only on several occasions. The use of e-wallet as a transaction tool is dominant for consumers in the culinary and fashion business fields. The education level variable provides an overview of the capabilities of human resources in Denpasar City. The ability of MSME owners to adapt to technology is certainly as an obstacle in the application of financial technology to their business. Thus, the level of education is considered important in the adaptation process which MSMEs absorb technological developments.
However, currently there are still many people who are refused to use ewallet due to lack of understanding in
using the cash less system and also because of transactions by using ewallet are subject to administrative fees and the risk of cyber crime. So, in order to optimizing the usage of e-wallet in Indonesia, we need accommodative regulations from Indonesian
government through BI and OJK in supporting the optimization of fintech which can strengthen its position as one of digital financial ecosystem foundations. This fintech optimization should be supported by the modernization of the legal framework to provide a legal landscape that can improve the supervision of the monetary and financial system in Indonesia.
REFERENCES
Angelia, Febri, and Yohanna Gultom. (2020). “Peran Pemanfaatan Teknologi Informasi Dan
Ekonomi Kreatif Di Indonesia.” Jurnal Kebijakan Ekonomi 15(2):1– 26.
Biantong, Juan Salao, and Iwan Krisnadi. (2021). “Pengaruh Manajemen Strategis Mengenai Penggunaan E-Payment
Terhadap Peningkatan Intensitas
Transaksi Pada Industrsi
UMKM.”
Dwi, Aksami Ni Made, and Jember I. Made. (2019). “Analisis Minat Penggunaan Layanan E-Money Pada Masyarakat Kota
Denpasar.” E-Jurnal Ep Unud 8(10):2439–70.
Ihsan, Mohammad, and Ade Perdana Siregar. (2019). “Pengaruh EService Quality Terhadap Keputusan Pengguna Jasa Ojek Online Go-Ride Dalam Aplikasi Go-Jek Melalui Kepercayaan Konsumen Di Kota Jambi.” J-MAS (Jurnal Manajemen Dan Sains) 4(1):170. doi:
Inggiharti, Nonika. (2020). “Pengaruh Electronic Wallet Terhadap Kegiatan Keuangan Indonesia (Perbandingan Aplikasi
Perusahaan Financial Technology Terhadap Aplikasi Electronic Wallet Milik BUMN).” University Of Bengkulu Law Journal 5(1):74– 88. doi: 10.33369/ubelaj.5.1.74-88.
Jam’iyatuzzulfiyyah. (2021). “Analisis Peran Usaha Mikro, Kecil Dan Menengah Terhadap Penyerapan Tenaga Kerja Di Indonesia.” Jurnal Inovasi Penelitian 1(8):6.
Putra, I. made sedana, and I. Ketut Sudibia. (2018). “Pengaruh Faktor Sosial, Ekonomi Dan Demografi Terhadap Pendapatan Usaha
Sektor Informal Di Desa Darmasaba.” Piramida Jurnal Kependudukan Dan Pengembangan Sumber Daya Manusia XIV(1):49– 58.
Sanistasya, Poppy Alvianolita, Kusdi Raharjo, and Mohammad Iqbal. (2019). “The Effect of Financial Literacy and Financial Inclusion on Small Enterprises
Kalimantan.” Jurnal Economia 15(1):48–59. doi:
10.21831/economia.v15i1.23192.
Utari, Tri, and Putu Martini Dewi. (2014). “Pengaruh Modal,
Teknologi Terhadap Pendapatan Usaha Mikro Kecil Dan Menengah (Umkm) Di Kawasan Imam Bonjol Denpasar Barat.” Ekonomi Pembangunan 3(12):576– 85.
Wardani, Ayu Putu Yulia Kusuma, and Nyoman Ari Surya Darmawan. (2020). “Peran Financial
Technology Pada UMKM: Peningkatan Literasi Keuangan Berbasis Payment Gateway.” Jurnal Ilmiah Akuntansi Dan Humanika 10(2):170. doi:
315
Discussion and feedback