Survey on LMS Moodle for Adaptive Online Learning Design
on
Journal of Electrical, Electronics and Informatics, Vol. 1 No.1, February 2017
Survey on LMS Moodle for Adaptive Online Learning Design
Linawati, NMAE Dewi Wirastuti, G. Sukadarmika
Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
Udayana University Bali – Indonesia
Abstract - The paper proposed usage of LMS Moodle for adaptive learning implementation because of its simplicity and its capabilities. LMS Moodle has wide range of features to satisfy many learning styles. Adaptive learning design in this paper recommended blended learning method which involves face-to-face activity and LMS Moodle utilization. In this initial design stage, only five LMS Moodle activities were chosen. The selected activities have met all learning styles requirements.
Index Terms - adaptive learning system, LMS, Moodle
-
I. INTRODUCTION
Since e-learning, mobile learning, technology based learning, web based learning, etc. have increased their popularity, more issues have to be addressed by education institutions, such as the uniqueness of learner’s style [Ahmed Abou Elfetouh S, 2013]. Traditional e-learning provides same learning process for all learners. It is namely one-size-fit-all learning style. Therefore recently many researches have proposed adaptive online learning to bring effective solutions for any types of learners style [Ahmed Abou Elfetouh S. 2013], [Despotović-Zrakić, M., 2012], [Nenad Stefanovic, 2013], [Andharini Dwi C., 2015], [Herman Dwi Surjono, 2011], [Bower, M., Craft, B., 2011], [Miroslav Minovic, 2010], [F. Kareal, 2006], [M. Prabhani Pitigala Liyanage, 2014].
Similar with other higher education of institutions, obviously Udayana University has developed and implemented e-learning since year 2008. The University utilizes LMS Moodle as its e-learning platform. Certainly its implementation without considering the uniqueness of a person as a learner. In addition e-learning implementation is applied only for local students. There is no elearning for overseas students. In fact students who study in Udayana University come from Indonesia and overseas. Therefore adaptive e-learning will be
designed for both all students in Udayana University. Then LMS Moodle will be selected as adaptive online learning platform. Thus this paper will discuss all features of LMS Moodle which fit to be implemented for adaptive online learning application.
-
II. RELATED WORKS
Each person has different learning style which depends on individual strengths, motivation, and preferences when receiving and processing information [Ahmed Abou Elfetouh S., 2013]. Then Table 1 shows briefly group of learning style according to Felder and Silverman's model. However Table 1 doesn’t conclude that a person strictly differentiated to be one of six learner’s styles. On the other hand, the six styles present which is dominant that their counterparts in one person. The style may appear powerfully, reasonably, or dimly.
TABLE 1
TYPES OF LEARNING STYLES MODIFIED OF FELDER-SILVERMAN MODEL [AHMED ABOU ELFETOUH S., 2013]
|
Type of Individua l Learning Style |
Style |
Explanation |
|
Processing |
Active |
Learning by doing |
|
Reflec tive |
Learning by thinking | |
|
Perception |
Sensiti ve |
Learners prefer deal with details. |
|
Intuiti ve |
Learners are keen to deal with principles and theories | |
|
Entry Channel |
Visual |
Learners prefer to see images, diagrams, graphs, etc. |
|
Verbal |
Learners easily to remember what they’ve heard, read or said. | |
|
Understan ding |
Seque ntial |
Learners easily to understand by subsequent a linear reasoning process when solving problems |
|
Global |
Learners easily to understand by having big intuitive leaps with the information | |
|
Realistic |
Traditi onal |
Learners can easily understand with simple concept or theory |
|
Advan ced |
Learners can easily get bored with just explanation of concept or theory | |
|
Behaviour |
Work in group |
Learners prefer to work together in peers or group |
|
Standalone |
Learners prefer to work alone |
Learner’s style then is set to be three clusters [Despotović-Zrakić, 2012]. The cluster describes the relationship between learning style and its characteristics as seen in Table 2. Classifying into cluster is to design course activity easily. They found that students who attended adapted online courses achieved better results than students who attended non-adapted online course. These related to students satisfaction analysis to the adapted online course.
TABLE 2
LEARNING STYLES CLUSTERS [DESPOTOVIĆ
ZRAKIĆ, 2012]
|
Cluster |
Characteristics |
Learning Style |
|
1 |
Multimedia materials Going through obligations sequentially Team work |
Visual Sequential Active |
|
2 |
Practical work No strict deadline Student choose topics |
Intuitive Active Global |
|
3 |
Written materials Going through obligations sequentially Team work |
Verbal Sequential Active |
Learning style models can be categorized as VAK (visual, auditory, kinesthetic) and Felder styles (global and sequential) [Herman Dwi Surjono, 2011]. When the learners prefer to follow logical stage by stage then they are categorized as sequential learners. Otherwise they are global learners who prefer to acquire in big leap. Visual, auditory, and kinesthetic learners concern to how human absorbs information using the channels of vision, hearing, and feeling. Auditory Learners use their listening channels to absorb information. Therefore they prefer to learn from listening to lectures, to involve actively in discussions. On the other hand Visual Learners use their visual channels to absorb information. They prefer to see information in pictures, tables, charts, maps or diagrams. Then Kinesthetic Learners use their feeling channels to absorb information. These learners prefer learning by doing and feeling. Activities in laboratory or excursion is best activity for kinesthetic learners.
Adaptive e-learning can be best implemented using LMS Moodle [F. Kareal, 2006]. The LMS Moodle appears to overcome basic e-learning barriers. The basic barriers are personal barriers (attitude towards e-learning, learning style or preferences), organizational barriers (lack of time for study, interpersonal barriers, registration system problems), technological barriers (Course Management Systems quality, Limitations of technical support,
Loss of data and inability to save or transfer data), content-suitability barriers (Content not audiencespecific, Poor content duality and limited rigor, Poorly constructed assessments), and instructional barriers (Lack of progress reports and feedback, Limited learner engagement, Poor instructional design, Limited reference materials, Access and navigation problems, Limited use of multimedia, Unclear or inconsistent instructions, Inability to save work, Information overload, Lack of instructor presence/interaction).
A framework for adaptive LMS Moodle is proposed in [M. Prabhani Pitigala Liyanage, 2014]. A questionnaire and a rule-based methods have been utilized to predict the learner’s style. There are four dimension of learners style, i.e. active or reflective, sensory or intuitive, visual or verbal, and sequentially or globally. Then they analysed learners’ behaviour using LMS Moodle into learner styles, such as content visit, content stay, forum visit, forum stay, and forum posts. When they mapped the behaviour to the style, they indicate the behaviour to be irrelevant behaviour, relevant positive behaviour, and relevant negative behaviour.
In addition, LMS Moodle could facilitate adaptive online learning [Despotović-Zrakić, 2012], [Nenad Stefanovic, 2013], and [Bower, M., Craft, 2011]. Table 3 and Table 4 presents Moodle suitability for adaptive online learning. According to [Despotović-Zrakić, 2012], the benefit of using LMS Moodle for adaptive online learning is no requirement for programming new software and without any programming knowledge. Thus the teachers can easily adjusting the contents, the activities, and the evaluation in LMS Moodle. However LMS Moodle has not yet provided real time adaptation features.
TABLE 3. LMS MOODLE FOR ADAPTIVE ONLINE LEARNING [DESPOTOVIĆ-ZRAKIĆ, 2012] [NENAD
STEFANOVIC, 2013]
|
Moodle Activities |
Coll abor ative Met hods | |||||||
|
Fo ru m |
C ha t |
Gl oss ar y |
Wo rks hop |
S ur ve y |
C h oi ce |
Les son | ||
|
Act ive |
Co ncr ete Pr obl em s |
Ye s |
Ma ny ter ms |
Exp eri me nt |
N o |
Y es |
Pro ble ms exa mpl e |
Face -to-Face |
|
Ref lexi ve |
To pic s for thi nki ng |
No |
Co nc ept s |
Une xpl ore d or new topi cs |
Y es |
Y es |
Pro vid ed topi cs |
Ema il |
|
Vis ual |
No |
No |
No |
Yes |
Y es |
Y es |
Illu stra tion |
Com bine d |
|
Ve rba l |
Ye s |
Ye s |
Ye s |
Yes |
Y es |
Y es |
Wri tten , mul tim edi a |
Com bine d |
|
Seq uen tial |
Ye s |
Fr eq ue nt |
Ye s |
Yes |
N o |
Y es |
Yes |
Com bine d |
|
Glo bal |
Gl ob al top ics |
No |
No |
Yes |
Y es |
R ar el y |
Rar ely |
Com bine d |
|
Sen siti ve |
Fa cts , ex am ple s |
Ye s |
Ye s |
Pra ctic al exa mpl es |
Y es |
Y es |
Fac ts, alg orit hm |
Com bine d |
|
Int uiti ve |
Ab str act top ics |
No |
No |
Une xpl ore d topi cs or new topi cs |
Y es |
N o |
Rar ely |
Com bine d |
TABLE 4. MAPPING OF LEARNING DESIGNER TLAS TO LMS MOODLE TOOLS [BOWER, M., CRAFT, 2011]
|
Learning Designers TLA |
Moodle Tools |
|
Tutor – supported class = Classes | |
|
Online presentation by tutor (synchronous) |
Web-conferencing, Virtual World |
|
Online presentation by student(s) (synchronous) |
Web-conferencing, Virtual World |
|
Online tutor – guided class guided class discussion (synchronous) |
Chat |
|
Online presentation by tutor (asynchronous) |
Page, Lesson, File, Label, URL |
|
Online tutor-guided class discussion (asynchronous) |
Forum |
|
TEL formative activity |
Choice, Survey |
|
Tutor – supported group = Tutor group | |
|
Online tutor – guided group discussion (synchronous) |
Chat |
|
Online tutor – guided group discussion (asynchronous) |
Forum |
|
Tutor – supported individual work = Tuition | |
|
Online individual tuition |
Web-conferencing, Virtual World, Skype |
|
Independent group work = Student group activity | |
|
TEL peer – assessed formative assignment |
Wiki, Folder, Forum |
|
TEL resource – based group activity |
Wiki, Folder, Database, Glossary |
|
Online student – only group discussion (synchronous) |
Chat |
|
Online student – only group discussion (asynchronous) |
Forum |
|
Online student group production (asynchronous) |
Wiki, Folder. Glossary |
|
Adaptive TEL group activity |
IMS content package, SCROM Package |
|
Independent individual work = Self-directed study | |
|
TEL resource – based individual activity |
File, Advanced Uploading of Files |
|
Adaptive TEL individual activity |
IMS Content Package, SCORM Package |
|
TEL – based formative assignment |
Advanced Uploading of Files, Quiz |
|
Summative Assessment | |
|
Essay |
Upload a Single File, Online Text |
|
Exam |
Quiz, Upload a Single File, Online Text |
|
Project Report |
Upload a Single File, Online Text |
|
Performance / Design |
Upload a Single File, Offline Text |
|
Dissertation |
Upload a Single File, Online Text |
|
TEL based summative assessment |
Quiz, Upload a Single File, Online Text |
-
III. RESULTS AND DISCUSSIONS
LMS Moodle has been implemented in Udayana University as e-learning platform. It can be accessed on http://elearning.unud.ac.id. The university has strongly supported its operation. However recently, the Moodle has been applied without concern on dissimilarity of personal learning style. Most lecturers just applied all the features of LMS Moodle in the form of blended learning. They put all subject contents with their references in the system. The contents and references can be content slides, web resources link, and lecturer notes. Then discussion has been done using ‘activity forum’ of the Moodle. In order to satisfy the uniqueness of learning styles in the University, learning process using Moodle will be designed to be adaptive online learning. From Table 3 and Table 4, the selection of the features of Moodle based on their simplicity and functionality to be applied in a classroom. There are six Moodle activities that will be combined with face – to – face in the class which is called a blended learning method.
TABLE 5. PROPOSED MOODLE ACTIVITIES
|
Lear ning Style |
Moodle Activities | |||||
|
Forum |
Surve y |
Lesson / Resour ces |
Assign ment |
Quiz |
Collab orativ e Metho ds | |
|
Activ e |
or group discuss ion
|
1. Onli ne form ative activ ity |
|
|
|
, Comb ined
Learni ng |
|
Refle xive | ||||||
|
Visu al | ||||||
|
Verb al | ||||||
|
Sequ ential | ||||||
|
Glob al | ||||||
|
Sensi tive | ||||||
|
Intui tive | ||||||
Definitely the proposed system will involve an administrator, teachers or lecturers, technical person, and students. An administrator has the highest access to the system which can modify the LMS Moodle. However the administrator has no capabilities to create course contents and manage the class. The teachers can set up and modify the contents, courses, assignment, discussion topics, and ability to explore all LMS Moodle features. On the other hand, the students have limited access to the system in comparison to administrator and teachers admission.
Mostly the course contents will be in multimedia form which include text, image, and illustrations. ‘Forum’ feature will be utilized by discussing at least two topics, for example in Industrial Technology course, i.e. (i) How green is industry in Indonesia?, and (ii) What kind of
innovated technology would you offer to industry in Indonesia to make them smarter and greener?. Then guideline for discussion below will be explained in Figure 1.
-
• Students’ comments or arguments must be relevant to the topic.
-
• Each topic will be open for two weeks.
-
• Teachers or Tutors will give response twice a week.
-
• Teachers and Students can read all comments.
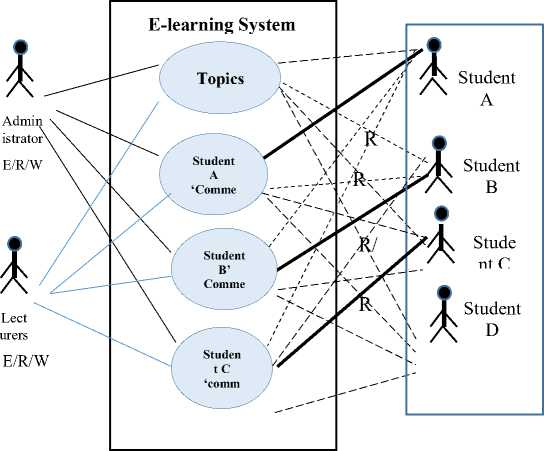
Figure 1. Use Case Diagram for Discussion using ‘Forum’
Feature
Then learning process will be completed with formative and summative evaluations. ‘Forum’, ‘Survey’, and ‘Quiz’ features will be applied for formative assessments. Then ‘Assignment’ and ‘Quiz’ features will be used for summative assessments.
-
IV. CONCLUSIONS
Survey on LMS Moodle features for adaptive online learning design has been done extensively. The LMS Moodle has broad range of activities which can be selected. In this paper, a blended learning method that is a combination between face-to-face in the classroom and LMS Moodle usage was selected for adaptive learning process. The proposed design selected only five Moodle activities, i.e. ‘Forum’, ‘Survey’, ‘Lesson or Resources’, ‘Assignment’, and ‘Quiz’. All selected activities be able to satisfy all learning styles.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The research project was funded by the Government of Indonesia through the Center of Research and Community Service (LPPM) of Udayana University under Project of Udayana Excellency (Hibah Unggulan Udayana) no 641-53/UN14.2/PNL.01.03.00/2016, date 15 June 2016. Therefore Authors would like to express their gratitude to the LPPM.
REFERENCES
-
[1] Ahmed Abou Elfetouh S., Hazem M. El-Bakry (2013), A Novel Adaptive Mobile E-Learning Model, International Journal of Computer Applications (0975 – 8887), Volume 63– No.14, February 2013, pp 12 – 25.
-
[2] Andharini Dwi C., Ari Basuki, Eka Mala Sari R, Yeni Kustiyahningsih (2015), Design an Adaptive E-learning Application Architecture Based on IEEE LTSA Reference Model, TELKOMNIKA, Vol.13, No.1, March 2015, pp. 284~289.
-
[3] Bower, M., Craft, B., Laurillard, D. & Masterman, L. (2011). Using the Learning Designer to develop a conceptual framework for linking learning design tools and system. In Cameron, L. & Dalziel, J. (Eds). Proceedings of the 6th International LAMS & Learning Design
Conference 2011: Learning design for a changing world (pp 61-71 ). 8-9 December 2011, Sydney: LAMS
Foundation.
http://lamsfoundation.org/lams2011sydney/papers.htm
-
[4] Despotović-Zrakić, M., Marković, A., Bogdanović, Z., Barać, D., & Krčo, S. (2012). Providing Adaptivity in Moodle LMS Courses. Educational Technology & Society, 15 (1), 326–338.
-
[5] F. Kareal and J. Klema (2006), Adaptivity in e-learning, Current Developments in Technology-Assisted Education, pp 260 – 264.
-
[6] Herman Dwi Surjono (2011), The Design of Adaptive ELearning System based on Student’s Learning Styles, International Journal of Computer Science and Information Technologies, Vol. 2 (5) , 2011, 2350-2353.
-
[7] M. Prabhani Pitigala Liyanage, K. S. Lasith Gunawardena, Masahito Hirakawa (2014), Using Learning Styles to Enhance Learning Management Systems, International Journal on Advances in ICT for Emerging Regions 2014 07 (02), pp. 1 – 10.
-
[8] Miroslav Minovic, Velimir Stavljanin, Milos Milovanovic, Dusan Starcevic (2010), User-centered Design of m-Learning System: Moodle on The Go, Journal of Computing Science and Engineering, Vol. 4, No. 1, March 2010, Pages 80-95.
-
[9] Nenad Stefanovic, Dusan Stefanovic, Branka Arsovic (2013), Adaptively in E-learning LMS Platform, vol. XVIII no. 3 (2013) METALURGIA INTERNATIONAL, pp 156 – 162.
-
[10] Siah Sim Tee, Tengku Siti Meriam Tengku Wook and Suhaila Zainudin (2013), User Testing for Moodle Application, International Journal of Software Engineering and Its Applications Vol.7, No.5 (2013), pp.243-252.
16
Discussion and feedback