The Role of Stakeholders in Ecotourism Development in Jatiluwih Tourism Village Area, Bali
on
E-Journal of Tourism Vol.10. No.2. (2023): 153-162
Analysis the Role of Stakeholders in Ecotourism Development In Jatiluwih Tourism Village Area, Bali
Yuvie Martadina*, Imam Ardiansyah
Hospitality & Tourism Program Study, Bunda Mulia University
*Corresponding Author: ayubangka3@gmail.com
DOI: https://doi.org/10.24922/eot.v10i2.102356
Article Info
Submitted:
June 12th 2023
Accepted:
September 20th 2023
Published:
September 30th 2023
Abstract
Jatiluwih is one of the tourist destinations in Bali. The development of the Jatiluwih ecotourism area certainly requires participation and synergy between stakeholders. This is useful for obtaining the objectives and results of good area management. In the development and management of the Jatiluwih, the stakeholders involved in it are considered not optimal. The purpose of this study is to find out how big the role and interests of stakeholders are in the development of ecotourism in Jatiluwih. Method of this research is qualitative and quantitative research methods. Analytical method for stakeholder using power-interest matrix grid. The number of participants in this study were 45 participants. Based on the results of research and field observations conducted by researchers, it was found that there were 15 stakeholders divided into four quadrants. The conclusion of this study is that there are 3 subject stakeholders are travel agents, tourists, and local communities. The 6 key player groups are the Ministry of Tourism and Creative Economy, Bali Tourism Office, Tabanan Regency Government, Jatiluwih Village Government, Jatiluwih tourist attraction Management, and Jatiluwih Subak. 3 context setter groups are accommodation, restaurants, and customary stakeholders, and 3 crowd groups are academics, Jatiluwih health center, and media. Suggestions for 15 stakeholders in Jatiluwih are that they should increase collaboration and cooperation to strengthen relations between one another so that they can develop the tourist area into a coordinated, beautiful, and neat tourist area, while still prioritizing tourism sustainability.
Keywords: ecotourism; stakeholders; tourism village; Jatiluwih; rice terrace.
INTRODUCTION
Background
Tourism is one of the industries in Indonesia that has the opportunity and potential to grow because of its beauty and natural wealth (Himawan, 2015). Tourism itself can be one of the sectors that help the Indonesian economy and also become a
source of livelihood for the surrounding community if tourism is developed properly and correctly. The diversity owned by Indonesia to develop tourism activities can be in various ways. Because Indonesia is rich in nature and culture ranging from natural beauty, cultural diversity, food, to history. So that in Indonesia a lot of thoughts arise to develop diverse
can be concluded that a stakeholder is a group of people or individuals who have an interest in developing a goal.
Based on observations made by researchers to one of the sources involved in the management of the Jatiluwih area, is Ms. Ayu Wulandari revealed that there are basic problems that exist in the Jatiluwih area. She revealed that there are major problems that exist in the management of Jatiluwih tourist area. For example, the development of Yeh Hoo waterfall attractions in tourist areas that have not received support from the government related to accessibility. The development of ecotourism areas by the management in the area is still experiencing problems in waste management, clean water supply, and maintenance of bamboo forest areas that are used as wildlife conservation areas.
Stakeholders have different interests and roles in an ecotourism area. Therefore, it is necessary to understand the role of each stakeholder so that the development of an ecotourism area can be carried out systematically and can achieve goals. So that a solution is needed, namely analyzing the roles and responsibilities of stakeholders so that they can be identified, maximize performance levels, and create good coordination and cooperation between stakeholders. Jatiluwih area has stakeholders with different roles and interest including in the development of ecotourism areas. Stakeholders who have different interests and roles support the running of a tourist area. So, a tourist area that is organized in its development aspects will get good results.
When a tourist decides to go on a tourist trip, they will find out about areas that can fulfill their desires and look for new things. Factors that influence a tourist trip can be the main focus in developing ecotourism attractions. So that it can be used as a guideline in developing tourist attractions. Ecotourism that has been well developed can be an attraction for tourists to visit. The purpose of this study is to determine how much the role and interests of 154 e-ISSN 2407-392X. p-ISSN 2541-0857
tourism. One of the tourism activities that is now becoming a public concern is Ecotourism activities. Ecotourism areas have begun to spread throughout Indonesia. Ecotourism is a form of responsible travel to natural places and contributes to the conservation of nature and the improvement of the lives of local communities. Ecotourism is a concept of nature-based tourism activities that simultaneously contributes to the maintenance and preservation of the environment so that the environment is maintained and beautiful. One of the tourist areas that has many tourist villages that present tourist attractions in the form of natural beauty and culture is Bali. One of the tourist village areas in Bali also included in ecotourism is Jatiluwih.
Jatiluwih is a tourist village area that is famous for its rice terraces that are neatly arranged in stages or often also called terraces. This tourism village has a lot of potential because is very attractive to tourists with beautiful and cool natural conditions because it is located in the highlands. This area is used by the community as one of their livelihoods by growing rice. The rice they grow has very good quality so that one of the results of brown rice is one of the reasons why Jatiluwih was awarded the UNESCO World Heritage Site in 2012 as an intangible culture (Herawati, 2015). Jatiluwih is also the only tourist village that received an award from UNESCO.
The existence of a tourist village area must be supported by optimal development in order to attract tourists. This must involve good collaboration between stakeholders in order to maximize the marketing of the tourist area. The ecotourism area that is being developed should have stakeholders who have identified their roles and contributions in the development of the ecotourism area. In developing an ecotourism area, participation and synergy between stakeholders are certainly needed. According to (Sulastri, 2017) stakeholders are all parties, both individually and in groups that can be give power and or influence decision making to achieve a goal. It http://ojs.unud.ac.id/index.php/eot
stakeholders involved in the management of Jatiluwih, and to determine the division of stakeholders based on 4 stakeholder elements. Therefore, the author wants to raise a topic with the discussion "Analysis of the Role of Stakeholders in Ecotourism Development in the Jatiluwih Tourism Village Area, Bali".
LITERATURE REVIEW
Ecotourism
Ecotourism is one of the naturebased tourism activities and makes an open space area for traveling activities while still paying attention to the preservation of nature and the environment. Ecotourism is a form of tourism activity that is responsible for nature and contributes to preserving nature and improving the welfare of local res-idents(Kristiana, 2019). According to (Tis-nawati et al., 2019), ecotourism is a type of tourism that focuses on natural resources and manages them as much as possible to minimize environmental damage. Protection of nature is an important focus in the development of ecotourism areas, so it can be concluded that ecotourism is a type of tourism that utilizes nature and resources as a selling point, but still preserves the environment and carries the concept of sustainable development.
In the decision of the Minister of Home Affairs No. 33 of 2009 related to the development of ecotourism, there are 4 types of ecotourism, namely marine ecotourism, forest ecotourism, mountain ecotourism, karst ecotourism. Jatiluwih tourism village area included to mountain tourism because this village is near from Puun hill in Tabanan.
Definition of Stakeholder
Stakeholders are parties that can influence by decisions taken. It can be defined as individuals, groups, or institutions that have concerns and the results of their activities (Widodo et al., 2018). It can be concluded that the definition of a
stakeholder is a group of people or individuals who have an interest in a place such as a tourist spot and provide their respective roles so that ecotourism area development activities can run well and in accordance with the objectives. Tourism development is inseparable from stakeholder intervention. According to(Rahim, 2012), the development of a tourism destination will essentially involve five interrelated stakeholders, namely the government, the private sector, media, academics and the local community. Each stakeholder has different inputs and roles in the destination development process. So, it needs a good understanding of the differences in these roles so that the development of ecotourism can be carried out and realized.
Stakeholder Classification
Ecotourism area management requires stakeholders who provide power and diverse interests so that there are differences related to interest, capacity and authority (Ardiansyah, 2021).
According to (Reed et al., 2009), analyzing the role of stakeholders begins with illustrating stakeholders in a two-by-two matrix that is divided into interest or interest in a problem and power (power) stakeholders in handling the problem. Interest is the how much attraction of stakeholders in the management and development of tourist areas, while power is the power possessed by stakeholders in making policies or influencing decision-making. From the grouping stakeholder of the level of power and interest, it' ll be found that there are 4 types of stakeholders, which is Subject, Key Player, Crowd, Context setter.
Subjects
Kuadran I
Key play ers Kuadran ∏
Crowd
Kuadran. IV
Context setterss
Kuadran III
T⅛gg> a (high)
I
N T
E S T (kepentingan)
Rendah (low) Rendah flow) POWER (pengaruh) Tinggi /high)
Figure 1. Power- Interest Matriks Grid Source : (Reed et al., 2009)
The matrix above illustrates the quadrant of each stakeholder. There is an axis (X) that represents the stakeholder's interest and an axis (Y) that represents the power exerted by the stakeholder on the tourist area. The management of questionnaire data will determine where the points and positions of the stakeholders involved are assessed from the level of power and interest. Quadrant I (Subject) illustrate that the stakeholders involved have a high interest, but the power given is small. Quadrant II (Key Player) illustrates that the stakeholders involved have high power and interest Quadrant III (Crowd) illustrates that power and interest tend to be low, and quadrant IV (Context Setter) illustrates that the power given by stakeholders is high but interests tend to be low. Grouping stakeholders based on quadrants serves to map and assess the relationship between stakeholders and where the quadrant position of each stakeholder is related to the management of Jatiluwih area.
METHODS
In this research, the object of research is Jatiluwih Tourism Village Area and the subject of research is stakeholders who have power and interest in Jatiluwih. This type of research is included in descriptive research with quantitative and quantitative approaches. According (Sugiyono, 2018), qualitative research is research that aims to understand the phenomena experienced by the subject and
describe in the form of words and language. The descriptive qualitative analysis method uses data containing empirical facts to illustrate the capacity of stakeholders in ecotourism management. While the descriptive quantitative research used in this study aims to measure how much power and interest between stakeholders based on the assessment of five instruments from each stakeholder who has an interest and power in the management of the Jatiluwih ecotourism area. Researchers used this type of research in order to describe and identify clearly the stakeholders involved in the development of ecotourism in the Jatiluwih tourism village, Bali.
Data collection in this research is by conducting observations, interviews, documentation, and questionnaires. So that the data sources obtained include primary and secondary resources. In filling out the questionnaire, the researcher used a simple random sampling method where each element had the opportunity to participate in filling out the questionnaire to be distributed by the researcher (Arieska & Herdi-ani, 2018). In distributing questionnaires for this study, researchers used 45 respondents from 15 stakeholder elements where researchers chose 3 people per element that were considered by researchers to have a high level of interest in the management of the Jatiluwih ecotourism area.
Participants will be asked to assess the level of stakeholder interest from the aspects of stakeholder involvement, benefits of area management, resources provided, management priorities, resource dependence. As well as the level of influence from the aspects of rules and policies, roles and participation, ability to interact and influence, authority in management, and the capacity of resources provided.
In this research, the statistical method used is to analyze the actor-ling-kage matrix stakeholder by making quadrants of power and interest. Actor-linkage matrix will present four quadrants with different classifications including subject, context setter, key player, and crowd. The
management consists of managers and oversees several divisions.
Identification of Stakeholders
In knowing the mapping and classification of stakeholder involvement in the development of ecotourism in the Jatiluwih area will be done by identification. Identification of stakeholders conducted by researchers is by observation to the object of research as well as by interviewing those who are considered by researchers to have high knowledge about the tourist area. Identification of stakeholders obtained from researcher observations at the research site and supported by statements from the manager there are 15 stakeholders who have a contribution in the management of Jatiluwih area. Stakeholders come from the government, local communities, farmer groups, academics, media, and the private sector. The success of cooperation in a tourist area in forming policies, upholding the same vision and mission, and jointly developing a tourist area is influenced by the level of importance and influence given by each stakeholder (Sulastri, 2017). A tourist area has stakeholders in its implementation who have a relationship to formulate operational policies and procedures for developing a tourist area. These stakeholders are classified into 5 groups (Yahya & Indonesia, 2015), there is :
-
1. Academics
-
2. Business (Private Sectors)
-
3. Community
-
4. Government
-
5. Media
data used are questionnaire answers from stakeholders who have a role in the development of ecotourism in Jatiluwih with an assessment of the Likerts scale 1-5. The results of the analysis will form an interest and strength matrix. The resulting matrix forms four quadrants that divide the categories of each stakeholder (Hudiyono & Fedora, 2019). The resulting matrix is known as the power-interest grid.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Jatiluwih Tourism Village
Jatiluwih is one of the ecotourism areas that presents natural beauty in the form of terraces or rice fields, the beauty of waterfalls, and bamboo forests. Jatiluwih is a village located in Penebel District, Tabanan Regency, Bali, precisely in Banjar Soka. In 1998, the Jatiluwih area was just a rice field area owned by residents whose community was referred to as subak. Initially, the Jatiluwih village government saw the potential of the beauty of the rice fields to become a tourist attraction. In early 2000, Jatiluwih area was made one of the tourist attractions in Tabanan Regency. Jatiluwih area is located in Jatiluwih village, Penebel district about 35 km from Tabanan district. Jatiluwih area is one of the best terraces among 9 (nine) terraces in Indonesia. Jatiluwih became one of the terraced areas that received an award from UNESCO, which is intangible cultural heritage.
Jatiluwih tourist attraction area was built with the cooperation of Jatiluwih village government and Tabanan local government. Administratively, the management status of the Jatiluwih area is under the Tabanan Regency Government. Based on the decision of the Tabanan Regent No. 11 of 2009 concerning the Management of Regional Tourism Areas, the management of Jatiluwih area was formed. The formation of management in the Jatiluwih area is due to the separation of the management of the tourist village with the Jati-luwih perbekel (village) area. Operational http://ojs.unud.ac.id/index.php/eot 157
Table 1. Identification of Stakeholder in Jatiluwih Tourism Village
|
Stakeholder Classification |
Stakeholder |
|
1. Ministry of tourism and creative economy | |
|
2. Bali Tourism Office | |
|
Govern- |
3. Tabanan Regency Government |
|
4. Jatiluwih Village Government | |
|
5. Jatiluwih Community Health Center | |
|
6. Jatiluwih DTW management | |
|
7. Jatiluwih's Subak | |
|
Community |
|
|
10. Travelers | |
|
11. Public | |
|
Business |
12. Accommodation |
|
(Private Sectors) |
13. Restaurant/Eatery |
|
Academics |
14. Academic (University & Researchers) |
|
Media |
15. National Media &Local Media |
|
Source: Primary Data Processed by Researcher (2023) | |
Level of Power-Interest Stakeholder
Reviewing the identification of stakeholders, the next step is to map the level of power and interest of stakeholders by creating a matrix. Making this matrix by giving statements to informants and expressed on a quantitative scale (score). The assessment given to informants that includes power and interest scores are five statements used in each category. In the interest category there are (1) Involvement, (2) Dependence, (3) Roles and Tasks, (4) Benefits, (5) Interests. As well as in the power category there are (1) Ability to negotiate or influence, (2) Position and role, (3) HR support, (4) Funding and management capabilities, (5) Interactive relationships with other stakeholders (Nurkhalis et al., 2018). http://ojs.unud.ac.id/index.php/eot
The results of the statements given to tourists so that the level of interest is obtained from the summation of X1-X5 and shared with 1-5 so that the average of each stakeholder's level of interest is obtained. Similarly, the results of the level of power operating the primary data are the same as the level of interest which is P1-P5. The data in the table below shows the high and low from power and interest between stakeholders in the Jatiluwih area.
Table 2. Value result interest of Stakeholder
|
Stakeholder |
Interest |
Average | ||||
|
X1 |
X2 |
X3 |
X4 |
X5 |
X | |
|
1 |
5 |
5 |
4 |
4 |
4 |
4,38 |
|
2 |
4 |
4 |
4 |
4 |
5 |
4,33 |
|
3 |
5 |
5 |
5 |
4 |
4 |
4,57 |
|
4 |
5 |
5 |
4 |
4 |
5 |
4,64 |
|
5 |
3 |
3 |
4 |
4 |
4 |
3,68 |
|
6 |
5 |
5 |
5 |
4 |
5 |
4,7 |
|
7 |
5 |
5 |
4 |
4 |
5 |
4,67 |
|
8 |
4 |
4 |
4 |
4 |
4 |
3,94 |
|
9 |
4 |
4 |
4 |
4 |
5 |
4,3 |
|
10 |
5 |
4 |
4 |
4 |
4 |
4,3 |
|
11 |
5 |
5 |
4 |
3 |
4 |
4,36 |
|
12 |
4 |
5 |
4 |
4 |
4 |
4,1 |
|
13 |
4 |
4 |
3 |
4 |
4 |
3,9 |
|
14 |
3 |
3 |
3 |
3 |
4 |
3,27 |
|
15 |
5 |
3 |
3 |
3 |
3 |
3,3 |
|
Source: |
Primary Data Processed searcher (2023) |
by Re- | ||||
From the table above, it shows that the stakeholders with the greatest interest score are the Management of Tourism Attraction Management with a value of 4.7 and Subak Jatiluwih with a value of 4.67. The results of the assessment are because the management is responsible for the Jati-luwih tourist area and organizes all operations in Jatiluwih. While Subak Jatiluwih is a farmer group that is responsible for the preservation of the terraced area which is one of the tourist attractions in the Jati-luwih area. The table above also shows stakeholders with the lowest interest score
in the management of ecotourism in the Jatiluwih area, is academics with a value of 3.27. The score obtained by the academics shows that the interests of these parties tend to be small, which is only interested in research and study purposes.
Table 3. Value result power of Stakeholder
|
Stake holder |
Power |
Average | ||||
|
P1 |
P2 |
P3 |
P4 |
P5 |
P | |
|
1 |
4 |
4 |
4 |
4 |
4 |
4,08 |
|
2 |
5 |
4 |
4 |
4 |
4 |
4,26 |
|
3 |
4 |
4 |
5 |
4 |
5 |
4,33 |
|
4 |
5 |
4 |
5 |
4 |
4 |
4,52 |
|
5 |
3 |
4 |
2 |
2 |
4 |
3,04 |
|
6 |
5 |
5 |
4 |
5 |
4 |
4,57 |
|
7 |
5 |
5 |
5 |
2 |
5 |
4,34 |
|
8 |
4 |
4 |
3 |
3 |
5 |
3,92 |
|
9 |
3 |
3 |
3 |
3 |
5 |
3,48 |
|
10 |
3 |
3 |
3 |
3 |
4 |
3,22 |
|
11 |
3 |
3 |
3 |
2 |
3 |
2,95 |
|
12 |
4 |
4 |
4 |
2 |
5 |
3,78 |
|
13 |
4 |
4 |
5 |
2 |
4 |
3,87 |
|
14 |
3 |
3 |
2 |
2 |
3 |
2,65 |
|
15 |
3 |
3 |
2 |
2 |
3 |
2,55 |
Source: Primary Data Processed by Researcher (2023)
The table above also presents the level of power score given by each stakeholder assessed by the informant who got the highest results, is Jatiluwih Tourism Attraction Management with a score of 4.57 and Jatiluwih Village Government with a score of 4.54. This shows that these
Classification of Stakeholder
Stakeholder classification is the mapping of the position of each stakeholder in accordance with the creation of a matrix of power-interestgrid. Stakeholder mapping in this matrix by tabulating the power category on the X axis of the matrix, and the interest category on the Y axis of the matrix. The results of the level of power and interest that have been obtained previously will be entered into the matrix calculation and obtained the quadrant of each stakeholder which is equivalent to the level of interest and power in the contribution in the Jatiluwih area.
Referring to the results of the table above, the results of stakeholder mapping on the power interest grid matrix are as follows.
two stakeholders provide a very high power in contributing to the development and management of the Jatiluwih area into one of the tourist areas that are more developed and can compete with competitors. Meanwhile, the smallest power score is the media with a score of 2.55. This is because the direct power of the media is relatively small because it only promotes and doesn’t contribute more. The media didn’t follow the process of management, implementation, funding, and development of the Jati-luwih ecotourism area.
Based on the matrix image above, the stakeholder classification is as follows. 1. Subject (Quadrant I)
In the picture above, stakeholders who have a high interest in the Jatiluwih area but provide a power that tends to be low are Travel Agents, Tourists, and Communities. Local communities tend to have a low power because they have not maximized the empowerment of human resources who participate in the development of ecotourism. However, with the support and guidance of key players, it is expected to increase the creativity of local 159 e-ISSN 2407-392X. p-ISSN 2541-0857
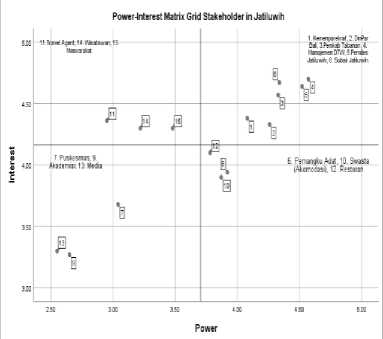
Figure 2. Power-Interest matrix grid
Source: Results of SPSS Output Ver. 25 Processed by Researchers (2023)
communities so that they can contribute more to the development of ecotourism in Jatiluwih.
-
2. Key Player (Quadrant II)
Key players are groups of stakeholders who have a high power and interest in the management of tourist areas. In the quadrant above, key players in the Jati-luwih area are the Ministry of Tourism and Creative Economy, Bali Tourism Office, Tabanan Regency Government, Jatiluwih Village Government, Jatiluwih DTW Management, and Jatiluwih Subak. Stakeholders in this quadrant are in control of the management and development of tourist areas. The existence of these stakeholders is very influential in achieving the goals of a tourist area and helps improve the standard of living of local communities.
-
3. Context Setter (Quadrant III)
Context setter is a classification of stakeholders who have a large level of power but the level of interest tends to be small. Mapping on the context setter obtained results, are customary stakeholders, accommodation providers, and restaurants. Customary stakeholders in the Jatiluwih area have a high power in policy considerations in it, because every event and activity that will be held must get approval and permission from customary stakeholders in Jatiluwih and Gunung Sari villages. However, the interest of customary stakeholders in the management of tourist areas tends to be small. For the accommodation and restaurants, judging from its presence in the Jatiluwih area has a high power on the management of this area. This refers to the increasing level of sales from accommodation and restaurants, there will also be an increase in tax payments and land rent that will be paid to the management. The fee will be used as a fund for the development of Jatiluwih area.
-
4. Crowd (Quadrant IV)
The last quadrant in the classification of stakeholders is the crowd. http://ojs.unud.ac.id/index.php/eot
Stakeholders in this quadrant have little power and interest in the management of tourist areas. Stakeholders who fall into this category are Jatiluwih community health center, media, and academics. Although the contribution made by these stakeholders tends to be low, their existence is needed as a reviewer of a tourist area. Because the crowd contributes to the management of tourist areas even though they do not directly participate.
CONCLUSION
Based on the results of research and field observations conducted by researchers, it was found that there are 15 stakeholders who have an attachment in managing the Jatiluwih area which is composed of government, community, academia, media, and private sector. Reviewing the division of stakeholder positions based on the creation of a power interest grid stakeholder matrix that refers to the level of strength and importance, it is obtained that the stakeholders with the greatest interest score are the Management of Tourism Attraction Management with a value of 4.7 and Subak Jatiluwih with a value of 4.67 while the stakeholders with the lowest interest score are academics with a value of 3.27. For the strength or power aspect, the highest score is obtained, namely Jatiluwih Tourism Attraction Management with a score of 4.57 and Jatiluwih Village Government with a score of 4.54 while the smallest power score is the media with a score of 2.55.
Reviewing the results of stakeholder mapping into 4 elements of stakeholder matrix division obtained results. Subject consists of 3 groups, there are Travel Agent, Tourist, Local Community. Key Player consists of 6 groups there are Ministry of Tourism and Creative Economy, Tourism Office, Tabanan Regency Government, Jatiluwih Village Government, Jatiluwih Tourism Attraction Management, and Subak Jatiluwih. Context Setter consists of 3 groups, there are Customary
REFERENCES
Ardiansyah, I. (2021). Analisis Stakeholder dalam Pengembangan Ekowisata di Taman Wisata Alam Gunung Pancar Kabupaten Bogor. Eduturisma, 6(1), 1–8.
Arieska, P. K., & Herdiani, N. (2018). Pemilihan teknik sampling berdasarkan perhitungan efisiensi relatif. Jurnal Statistika Universitas Muhammadiyah Semarang, 6(2).
Herawati, N. (2015). Pengembangan Pariwisata Berkelanjutan Berbasis Subak Sebagai Bagian Warisan Budaya Dunia UNESCO di Desa Manesta Kabupaten Tabanan. Jumpa, 2(1), 79–103.
Himawan, H. (2015). E-tourism: Antara konsep dan implementasi dalam mendukung industri pariwisata Indonesia. Seminar Nasional Informatika (SEMNASIF), 1(5).
Kristiana, Y. (2019). Buku Ajar Studi Ekowisata. Deepublish.
Nurkhalis, N., Arief, H., & Sunarminto, T. (2018). Analisis Stakeholders Dalam Pengembangan Ekowisata di Hutan Adat Ammatoa Kajang Sulawesi Selatan. Jurnal Pariwisata, 5(2), 107–119.
https://doi.org/10.31311/par.v5i2. 3811
Rahim, F. (2012). Pedoman Pokdarwis. Jakarta: Direktur Jenderal Pengembangan Destinasi Pariwisata Kementrian Pariwisata Dan Ekonomi Kreatif.
Reed, M. S., Graves, A., Dandy, N., Posthumus, H., Hubacek, K., Morris, J., Prell, C., Quinn, C. H., & Stringer, L. C. (2009). Who’s in and why? A typology of stakeholder analysis methods for natural resource management. Journal of
Stakeholders, Private Parties namely accommodation providers and restaurants. Crowd consists of 3 groups, there are Jati-luwih Health Center, Academics, and Media.
The results of the division or mapping of stakeholders above are expected to facilitate between stakeholders in establishing cooperation related to the development strategy and structuring of ecotourism areas in Jatiluwih and refers to the responsibilities and obligations of each stakeholder. Therefore, with a development strategy that has the same goal, it will improve the process of developing ecotourism in the Jatiluwih area.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
My praise and gratitude go to Gautama Buddha, the Great Teacher who has given me his blessings, health, materials, and the good people who surrounded me during this research. Without these blessings, I wouldn’t have been able to complete this paper properly.
In completing this research and paper, I have received great support from my family both materially and non-materially. I would also like to thank to the Head of Tourism Tabanan for taking the time to provide information to complete my data.
I also would like to thank Mr. Imam Ardiansyah, S.ST.Par,. M.M.Par as the supervisor in completing this research. Don’t forget to thank my friends and closest people who have supported and provided prayers for the smooth running of this research.
I would like to give many thanks to the Management of Jatiluwih tourist attraction, Jatiluwih Village Community, Jati-luwih Village Head, Mr. Regent of Tabanan, and many more parties who helped in the completion of this research.
This research will not be perfect if there is no intervention and assistance from these parties. The author recognizes the shortcomings in this research. The author expects criticism and suggestions to be input for further research.
http://ojs.unud.ac.id/index.php/eot 161
Environmental Management,
90(5), 1933–1949.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jen-vman.2009.01.001
Sugiyono, P. D. (2018). Metodologi kuantitatif, kualitatif dan R&D. Bandung: Alfabeta.
Sulastri. (2017). Peran Stakeholder Dalam Pengelolaan Objek Wisata Kebun Raya Massenrempulu Enrekang.
Tisnawati, E., Natalia, D. A. R., Ratrin-ingsih, D., Putro, A. R., Wirasmoyo, W., & Brotoatmodjo, H. P. (2019). Strategi Pengembangan Eko-Wisata Berbasis Masyarakat di Kampung Wisata Rejowinangun. Inersia: Jurnal Teknik Sipil Dan Arsitektur, 15(1), 1–11.
Widodo, M. L., Soekmadi, R., & Arifin, H. S. (2018). Analisis Stakeholders Dalam Pengembangan Ekowisata Di Taman Nasional Betung Keri-hun Kabupaten Kapuas Hulu. Jurnal Pengelolaan Sumberdaya Alam Dan Lingkungan (Journal of Natural Resources and Environmental Management), 8(1), 55–61. https://doi.org/10.29244/jpsl.8.1.5 5-61
Yahya, A., & Indonesia, M. P. R. (2015). Smart tourism. Konferensi Nasional Inovasi TIK Untuk Indonesia Cerdas.
http://ojs.unud.ac.id/index.php/eot
162
e-ISSN 2407-392X. p-ISSN 2541-0857
Discussion and feedback