Influence of Patient Characteristics on The Type of Insulin Therapy Obtained by Diabetes Type 2 Outpatient in Denpasar Municipality
on
139
Influence of Patient Characteristics on the Type of Insulin Therapy Obtained by Diabetes Type 2 Outpatient in Denpasar Municipality
Luh Putu Febryana Larasanty1, I Gusti Ngurah Agung Dewantara Putra1, Rhyce Dewata Sari1, Komang Dede Saputra1, I Gusti Agung Gede Minanjaya1, I Made Arya Wiraguna1, I Made Wiracana1
. Pharmacy department, Faculty of Mathematic and Basic Sciences Udayana University Bali, Indonesia
ABSTRACT
This study aims to investigate the influence of patient characteristics on the choice of insulin therapy in type 2 diabetes mellitus outpatients in Denpasar municipality. This is a descriptive analysis study using the patient's medical records as research material. Patients who meet inclusion and exclusion criteria are being recorded based on their medical records. Characteristics that are taken are age, gender, fasting blood glucose level (FBG), 2-hour postprandial blood glucose level (2-hours PPG) and HbA1c values of patients. Types of insulin therapy gained from patient medical records and drug use report in pharmacy. Characteristics data and type of insulin analyzed using correlation test to determine the effect of the patient characteristics on the selection of insulin therapy. 43 patients became the research subject. Males gendered patients (72.09%) and the patients aged less than 65 years (90.70%) are the dominant characteristics of the research subjects. The average value of FBG of patients is 212 mg / dL; 2-hours PPG 280 mg / dL and HbA1c 10.1%. There is a correlation between sex, age, HbA1c value and FBG with the type of insulin obtained by patients (p <0.05). Based on the results of statistical tests, age and gender have a strong correlation on insulin choice, HbA1c and FBG level has a moderate influence and 2-hours PPG have a weak correlation. Patient characteristics had an influence on the type of insulin choice for diabetes mellitus type 2 outpatient in the Denpasar municipality.
Keywords: characteristics, glucose level, HbA1c, insulin, type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Insulin is one of the recommended therapy for type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) patients with HbA1c value above 9% or if diabetes is not well controlled despite adequate oral glycemic therapy [1]. Insulin can be grouped into four types based on its working onset, i.e., long-acting insulin, intermediate-acting insulin, short-acting insulin and rapidacting insulin. Insulin therapy is given in order to mimic the body's physiological insulin secretion pattern [2]. The guidelines therapy recommend the use of long-acting insulin as an initial therapy for T2DM patients. However, several studies have shown the concurrent use of long-acting insulin, and shortacting insulin or fast-acting insulin provides better glycemic control than single-basal insulin use [3].
The choice of insulin type should be adjusted to the characteristics of the patient or referred as an appropriate patient on the rational use of medicine. Patients’ appropriateness is the ability to adjust the selection of therapy to the clinical condition and background of the patient's illness. Freemantle et al. (2011) showed that the characteristics of patients play an important role in determining the type of insulin that will be given as patient therapy [4]. Age, sex, fasting blood sugar, 2 hours postprandial blood sugar level and HbA1c values are part of the characteristics of DM type 2 patients. The aim of this study is to determine the effect of patient characteristics on the selection of insulin therapy in type 2 diabetes outpatient in Denpasar municipality.
-
A. Study Design
This is a descriptive analytic research using patient medical records as research material. The study took place from April 2016 until September 2016 at a general hospital in Denpasar Municipality.
-
B. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
The subjects of the study were outpatients with a diagnosis of type 2 diabetes mellitus with inclusion and exclusion criteria as follows:
-
a. Patients with type 2 DM who are pregnant or breastfeeding.
-
b. Patients who use oral contraceptives and other drugs can affect blood glucose levels of patients such as loop diuretics, thiazide, and cortisone.
-
c. Patients with type 2 diabetes with comorbidities.
-
d. Patients undergo a change in the type of insulin therapy regimen during the treatment period.
Patients who met the inclusion and exclusion criteria were recorded according to their medical records. Characteristics taken were age, sex, fasting blood glucose (FBG), two postprandial blood glucose (2PPBG) and HbA1c value of patients by means of research tool in the form of data collection sheets. This type of insulin therapy is obtained based on patient treatment records and drug use reports on pharmaceutical installations. Characteristic data and type of insulin were then analyzed by using correlation test to determine the effect of characteristics on the choice of patient insulin therapy type.
TABLE I
Demographics Data of T2DM Outpatient in Denpasar Municipality
|
Characteristics |
Quantity |
Percentage |
|
Gender | ||
|
Male |
31 |
72.09 |
|
Female |
12 |
27.91 |
|
Age | ||
|
< 65 y.o |
39 |
90.70 |
|
≥ 65 y.o |
4 |
9.30 |
-
A. RESULTS
43 patients met the inclusion and exclusion criteria and became the research subject. Table 1 shows patient's age and gender as a demographics data. The results showed that T2DM outpatient who more dominant were male (72.09%) and aged <65 years (90.70%). The mean FBG level of the patient was 212 mg / dL while the mean 2PPBG level of the patient was 280 mg./dL (Figure 1). The mean HbA1c value of the patient was 10.1% (Figure 2)
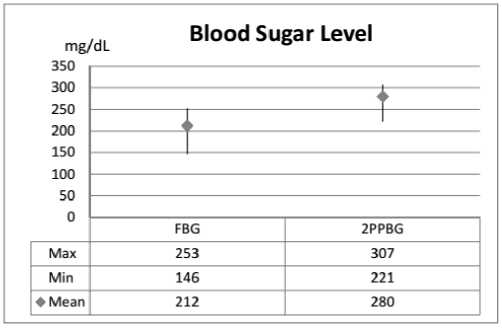
Fig.1. Blood glucose level of T2DM outpatient in Denpasar Municipality
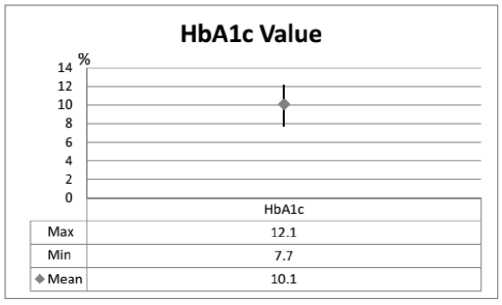
Fig.2. HbA1c value of T2DM outpatient in Denpasar Municipality
Type of insulin therapy obtained by the patient is divided into 5 groups i.e. 3 groups of single insulin therapy and 2 groups of insulin therapy combination. The most commonly used in single insulin therapy is insulin aspart (novorapid®) as much as 32.56% of the total insulin obtained by the patient. The most widely used of insulin combination is combination of aspart insulin and insulin glargine (combination of novorapid® and lantus®) as much as 39.53% (Table 2). The correlation test in table 3 showed that there was a correlation between selection of insulin type with the patient characteristic i.e. on age, gender, FBG and patient HbA1c value (p <0,05). Gender and age have a strong effect, FBG and HbA1c have moderate effect. The 2 post prandial blood glucose levels have a no correlation based on the statistic calculation and have weak effect on insulin selection for the patient.
TABLE II
Insulin Therapy Obtained by the T2DM Outpatient in Denpasar Municipality
|
Insulin Type |
Working Onset |
Quantity (%) |
|
Insulin Aspart (Novorapid®) |
Rapid acting |
14 |
|
insulin |
(32.56) | |
|
Insulin Detemir (Levemir®) |
Long acting |
5 |
|
insulin |
(11.63) | |
|
Premixed Insulin (Novomix®) |
Mixed acting (Rapid acting + |
6 |
intermediate (13.95)
acting insulin)
17
Combination of Insulin Aspart Rapid acting (Novorapid®) and Insulin insulin + long Glargine (Lantus®) acting insulin
(39.53)
|
Combination of Insulin Aspart |
Rapid acting |
1 |
|
(Novorapid®) and Insulin |
insulin + long |
(2.33) |
|
Detemir (Levemir®) |
acting insulin |
TABLE III
Correlation Test Results of Insulin Type and T2DM Outpatient Characteristics
|
Test Parameters |
p Value |
r Value |
|
Gender and insulin therapy |
0.000 |
0.742 |
|
Age and insulin therapy |
0.008 |
0.565 |
|
Fasting blood glucose and insulin therapy |
0.016 |
-0.365 |
|
2 hours postprandial blood glucose and insulin therapy |
0.508 |
-0.104 |
|
HbA1c value and insulin therapy |
0.001 |
-0.478 |
-
B. DISCUSSION
Patient characteristic is one of the parameters used in the selection of drug therapy, including the selection of insulin therapy in type 2 diabetes patients. The results showed that age and gender have a strong influence on the choice of insulin type. The results of Freemantle (2012) showed that the average age of insulin therapy was started at age 61 years and was dominated by male gender [4]. That results is similar with the results that obtained in our study, where age <65 years with male gender is a dominant influence factor. The results of the correlation test give a positive value indicating that the higher the age of the patient, the type of insulin obtained more complicated, in this case indicates the combination of therapy. The proportion of patients receiving combination insulin is also greater. This may be due to the higher chance of insulin resistance in men compared to women [5], thus male patients need more insulin to obtain more adequate glycemic control [6] (NIDDK, 2016).
Fasting blood sugar and HBA1c values have a moderate effect on the type of insulin obtained by the patient. The results of the correlation test give a negative value indicating that the higher the FBG level of the patient will tend to get a single insulin type. This is consistent with the therapeutic guideline for type 2 DM patients. Whenever FBG increases, the recommended insulin type is a single basal insulin [7]. Increased HbA1c values indicate poor glycemic control. Patients generally receive insulin when the HbA1c value is above 9% and the recommended initial insulin type is basal insulin. If basal insulin does not provide adequate control, mixed insulin may be given to control both FBG and 2PPBG [1]. Two hours postprandial blood glucose values do not have a
significant effect on the choice of insulin therapy. This can be due to the range of 2PPBG distributed evenly across all types of insulin therapy. Based on guidelines for insulin therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes, elevated levels of 2PPBG can be treated with single insulin using short-acting insulin or fastacting insulin [7].
The patients’ characteristics had an influence on the choice of insulin therapy in type 2 diabetes mellitus outpatients in the Denpasar municipality. Age (r = 0,565) and gender (r = 0.742) had a strong influence, fasting blood sugar (r = -0.365) and HbA1c (r = -0.478) had moderate impact and blood sugar level 2 hours posstprandial (R = -0.104) has a weak effect on the choice of insulin therapy obtained by the patient.
Acknowledgment
Authors would like to thank all patients who are willing to participate in this research. The authors would like to thank the Directorate of Research and Community Service of the Ministry of Research, Technology and Higher Education through the Institute of Research and Community Service of Udayana University to provide research grants for this study.
References
-
[6] Petznick, A., “Insulin Management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus” American Academy of Family Physicians, vol. 84, no. 2, 2011, pp 183190.
-
[7] Soegondo, S., Soewondo, P., Subekti, I., “Konsensus Pengelolaan dan Pencegahan Diabetes Melitus Tipe 2 di Indonesia”, Jakarta : Perkumpulan Endokrinologi Indonesia, 2006.
-
[8] van Brunt, K., Curtis, B., Ivanyi, T., Balogh, E., Chalkiadaki, C., MacLachlan, S., et al, “Basal-bolus Therapy in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in the UK: Patient Characteristics, Treatment Patterns and the Effect of Switching to Premixed Insulin”, Diabetes Therapy, vol. 4, no. 4, 2016, pp 793-807.
-
[9] Freemantle, N., Balkau, B., Danchin, N., Wang, E., Marre, M., Vespasiani, G, et al, “Factors Influencing Initial Choice of Insulin Therapy in a Large International Non-Interventional Study of People with Type 2 Diabetes”, Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism, vol. 14, 2012, pp. 901–909.
-
[10] Geer, E.B., Shen, W., “Gender Differences in Insulin Resistance, Body Composition, and Energy Balance”, Gender Medicine, vol. 6 Suppl 1, 2009, pp. 60-75.
-
[11] The National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (2016) “Prediabetes and Insulin Resistance” [Online] available : https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/diabetes/types/prediabetes-insulin-resistance (access on 17 Desember 2016).
-
[12] Pearson, T.L. (2007) “Initiating Insulin in the Type 2 Diabetes Patient” [Online] available : http://www.medscape.org/viewarticle/567952 (access on 16 Desember 2016)
Discussion and feedback