Syntactic Analysis of Headline Structures in The Jakarta Post Online News
on
ISSN: 2302-920X
Jurnal Humanis, Fakultas Ilmu Budaya Unud
Vol 19.1 Mei 2017:67-73
Syntactic Analysis of Headline Structures in The Jakarta Post Online News
Amanda Ratri Yasmin1*, Ni Luh Ketut Mas Indrawati2, Ni Ketut Sri Rahayuni3 [123]English Department Faculty of Arts – Udayana University 1[amandaratriyasmin@yahoo.com] 2[mas.indrawati@yahoo.com]
3
3[ketut_srirahayuni@gmail.com]
*
Corresponding Author
Abstrak
Artikel ini berjudul “Analisis Sintaksis dari Struktur Judul Berita di Situs Online The Jakarta Post”. Penelitian ini terinspirasi oleh fenomena kehidupan sehari-hari, dengan berkembangnya teknologi masyarakat tidak lagi membaca berita dari koran tapi menggunakan gadget karena sekarang telah tersedia banyak layanan berita online. Hal pertama yang masyarakat baca dari berita adalah judulnya, tetapi sering kali judul berita melanggar aturan tata bahasa standar karena memiliki karakteristik yang unik. Penelitian ini bertujuan untuk mengetahui jenis struktur khusus yang dimiliki judul berita di situs online The Jakarta Post dan untuk mengetahui struktur judul berita di situs online The Jakarta Post.
Data penelitian ini diambil dari situs berita www.thejakartapost.com yang merupakan versi online dari koran The Jakarta Post. Penelitian ini merupakan penelitian deskriptif kualitatif dan metode yang digunakan untuk mengumpulkan data adalah metode dokumentasi dengan menggunakan teknik mencatat. Teori yang digunakan dalam menganalisis data adalah teori struktur khusus judul berita yang diusulkan oleh Swan (2005) dan Quirk (1985).
Hasil penelitian ini menunjukkan struktur khusus yang cenderung digunakan oleh penulis adalah: (1) penghilangan kata kerja bantu, (2) penghilangan artikel, (3) bentuk tenses sederhana, (4) bentuk masa depan, (5) penyingkatan, dan (6) penggunaan khusus dari tanda baca. Struktur khusus lainnya seperti untaian kata benda dan penggunaan as dan in jarang digunakan oleh penulis di The Jakarta Post.
Kata kunci: analisis sintaksis, judul berita, The Jakarta Post
Mass media cannot be separated from people’s life because it is human nature to be curious, especially about what is happening around them and that is exactly what the media provides. Moreover, people can be well-informed of what is happening around them instantly by reading online news in their gadget. There are lots of mass media that has digital version and The Jakarta Post was one of them.
This study is not concerned with the news as a whole, but it was concerned with the headlines of the news. The first thing that the readers will certainly read is the title because the readers will not read the whole news if the title does not interest them. However, the headlines will not be easily understood because the language has a different construction from the standard language and may have ignored the ungrammatical form. Thus, the news headline structure was an interesting object to be analyzed syntactically as it has its own characteristics.
-
a. What types of special structures occurred in the headlines of The Jakarta Post Online News?
-
b. How are the headlines of The Jakarta Post Online News structured?
-
a. To figure out types of special structures occurring in the headlines of The Jakarta Post Online News.
-
b. To find out the structure of headlines in The Jakarta Post Online News.
The data source of this study were taken from the online version of The Jakarta Post’s news available at www.thejakartapost.com. The data that were taken to be specific were only the headlines that were chosen randomly from the online-site published on October 2016. The method used to collect the data was the documentation method and used the note-taking techniques in the process of collecting data. The data were collected through some steps, first collecting the news from The Jakarta Post’s online-site published on October 2016 then identifying and selecting the headlines in order to find the suitable data followed by note taking. The collected data were analyzed descriptively based on the news headlines’ special structure theory proposed by Swan (2005). The data of this study were analyzed through these following steps: (1) classifying the suitable collected data based on the types of the special structures of headlines, (2) analyzing the data based on the theory used in this study to figure out how the headlines are structured presented in the form of descriptive text and tree diagrams.
As guidance to figure out the best explanation, the references which were concerned with English grammar, journalism and news writing style were used.
Headlines often leave out the auxiliary verb be in its construction, whether they are used to express the progressive or future aspect and the passive construction as well (Swan, 2005: 211). Here is an example of auxiliary verbs omission structures found in the website of The Jakarta Post:
TIFF showcasing 200 plus films in Tokyo (October 27, 2016)
TIFF is showcasing 200 plus films in Tokyo
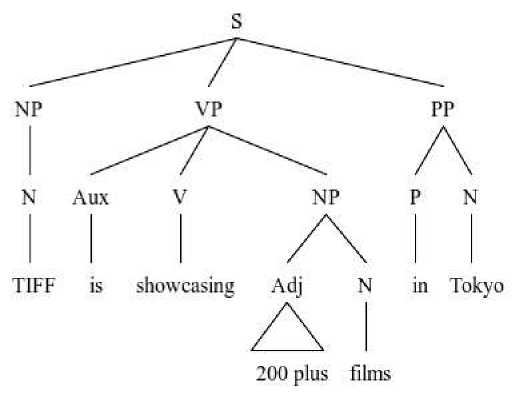
The auxiliary verb is is left out in the headline construction above. In this construction, the auxiliary verb is is needed as a helping verb to accompany the main verb showcasing.
According to Swan (2005: 211), headlines often leave out articles. News headlines have a tendency to avoid the use of the articles, regardless of their function as determiners or either they refer to the countable or uncountable, plural or singular matters. Here is an example of article omission structures found in the website of The Jakarta Post:
Balinese festival receives warm welcome in Netherlands (October 26, 2016)
Balinese festival receives a warm welcome in Netherlands
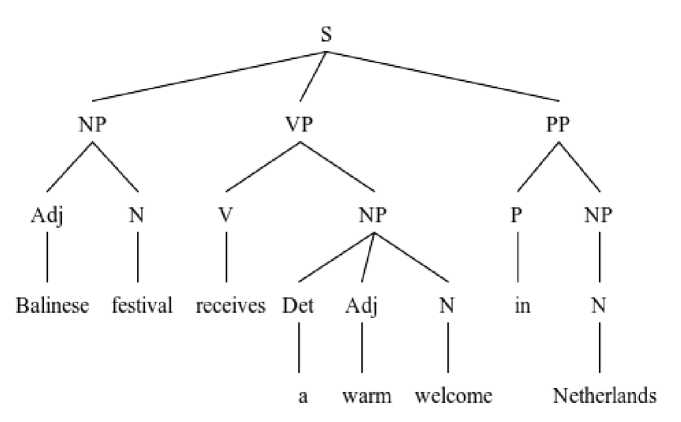
A is needed in front of the object of the sentence above. The function of article a is as a determiner in the construction above.
According to Swan (2005: 211), news headlines have a tendency to use simple tenses instead of progressive or perfect forms. The grammar rules are violated but it is acceptable. Here is an example of simple tense form structure found in the website of The Jakarta Post:
Foreign minister’s father passes away (October 27, 2016) Foreign minister’s father has passed away
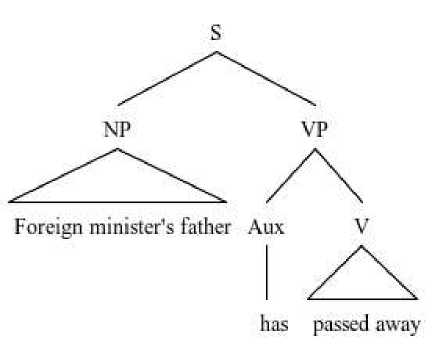
In the headline construction above, simple tense “passes away” is used instead of perfect tense “has passed away”. Even though this construction violated the grammar rules, it is acceptable because the writer believes that the reader understands what he/she is trying to say. It can be seen that the writer used a simple tense form in the news
headlines instead using a perfect form. Most headlines that should be written using the perfect form were written in the simple form.
News headline constructions refer to the future using the infinitive or the preposition for (Swan, 2005: 212). Here is an example of future form construction found in the website of The Jakarta Post:
Gili Islands to host ecofriendly festival (October 18, 2016)
Gili Islands are going to host ecofriendly festival
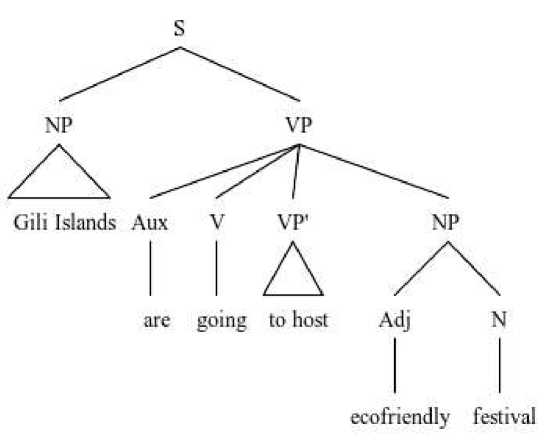
The infinitives form “to host” is used in the headline construction above to refer to a future plan of Gili Islands that will hold an eco-friendly festival. The writer makes the use of the infinitives form “to host” to represent a future action or plan. In the data found, the writer frequently used the to-infinitive form to refer future plans or movements. Although the preposition for can also be used to refer future, it is not common and rarely used by the writer.
News headlines are usually written as short as possible. Shortening is used in order to economize space without changing meaning in the news headline. Although sometimes shortening is not familiar, it is still acceptable because there is a tendency of abbreviating the long words. Here is an example of shortening structure examples found in the website of The Jakarta Post:
Hospital fire in Malaysia kills 6 (October 25, 2016)
Hospital fire in Malaysia kills 6 people
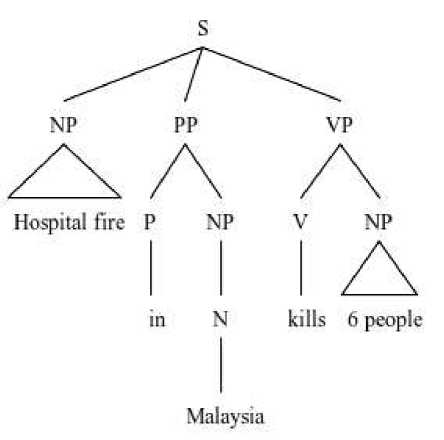
In the headline construction above the writer omits the word people. It is ambiguous in Standard English sentence to say “6” without further explanation. However, the writer believes people already know that the victim of the fire in hospital must be people. So, the writer omitted the word people to make it short.
Another way that the writer used in shortening was abbreviating the long words and taking the first letter of the word, for example, BI. B stands for Bank and I stands for Indonesia. So, the writer made the longer word shorter without changing the meaning and usually the shortened words are common abbreviations that most people know.
Some common punctuation marks usually found in headlines construction are colon (:), quotation marks (‘…’ “…”) and question mark (?). Colon (:) is used before explanations, while question mark (?) is often used when something is not certain. Quotation marks (‘…’ “…”) are used to show that the writer gives that a word has special meanings or it was said by somebody else. Here is an example of punctuation marks’ special use structures found in the website of The Jakarta Post:
Vienna Boys Choir finds Jakarta tour 'magical' (October 17, 2016)
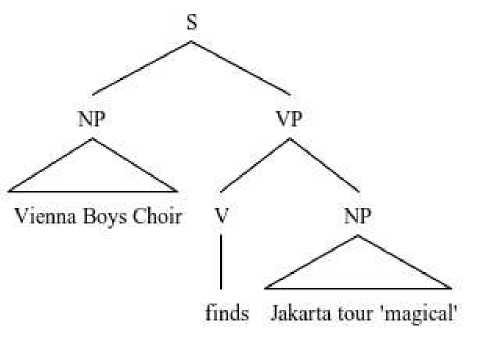
In the headline construction above, the writer used quotation mark in the word magical to make that word have some impact. The writer gives the word magical a special meaning that will be explained more in the article.
The result showed that the special structures that tend to be used by the writer are: the omission of the auxiliary verbs, the omission of articles, the simple tense form, the future form, shortening, and the special use of punctuation marks. Other special structures such as the strings of nouns and the use of as and in are rarely used by the writers in The Jakarta Post. So, in the news published on October 2016 those other special structures cannot be found.
Crystal, D. 1969. Investigating English Style. London: Longman
Gorrell, Robert M. and Charlton Laird. 1965. Modern English Handbook. Third Edition.
New Jersey: Prentice-Hall, Inc.
Hornby, A. S. 2010. Oxford Advanced Learner’s Dictionary. Eighth Edition. London: Oxford University Press
Quirk, et al. 1985. A Comprehensive Grammar of the English Language. New York: Longman
Swan, Michael. 2005. Practical English Usage. Third Edition. New York: Oxford University Press
Wekker, Herman and Liliane Haegeman. 1985. A Modern Course in English Syntax. London: Routledge
73
Discussion and feedback