Decision Support System for the Selection of Outstanding Students Using the AHP-TOPSIS Combination Method
on
LONTAR KOMPUTER VOL. 10, NO. 1 APRIL 2019
DOI : 10.24843/LKJITI.2019.v10.i01.p05
Accredited B by RISTEKDIKTI Decree No. 51/E/KPT/2017
p-ISSN 2088-1541
e-ISSN 2541-5832
Decision Support System for the Selection of Outstanding Students Using the AHP-TOPSIS Combination Method
Varindya Ditta Iswari1, Florentina Yuni Arini2, Much Aziz Muslim3
-
1,2,3Computer Science Department, Semarang State University Semarang, Indonesia
1varindya2@students.unnes.ac.id 2floyuna@yahoo.com 3a212muslim@yahoo.com
Abstract
This research develops a decision support system for the selection of outstanding students by combining AHP and TOPSIS methods. AHP method was used because it could be implemented to this data and do the priority ranking process for each criterion based on pairwise comparison matrix. The TOPSIS method was used because the concept of the chosen alternative does not only have the shortest distance from the positive ideal solution, but also has the longest distance from the negative ideal solution. The purpose of this study was finding out the workings of the TOPSIS method and the AHP-TOPSIS combination method, as well as to find out the comparison of the best methods between TOPSIS and the combination method of AHP-TOPSIS in the selection of outstanding students. The concept of TOPSIS is simple and easy to understand and has the ability to measure decision alternatives while AHP is not chosen because the AHP method is widely used in the case of criteria weighting and priority determination of each criterion. However, if the two methods were combined the results will be better because in AHP there is an eigenvector concept which is used to do the priority ranking process for each criterion based on pairwise comparison matrix, then the results of the weighting criteria are processed by the TOPSIS method for ranking process. The application of the TOPSIS method on the selection of outstanding students can be analyzed with the results of the presentation using Hamming Distance incompatibility is 93%. Meanwhile, the application of the AHP-TOPSIS combination method gets the presentation results using Hamming Distance incompatibility is 91%. Based on these results in this study it can be concluded that the AHP-TOPSIS combination method is better than the TOPSIS method.
Keywords: Decision Support System, AHP, TOPSIS, Outstanding Students, Hamming Distance
The development of information technology has allowed decision makers to be carried out more quickly and carefully. Decision Support System (DSS) is designed to support all stages of decision making starting from identifying problems, selecting relevant data, and determining the approach used in the decision-making process, evaluating alternative choices. In the early 1970s, Scott Morton revealed the concept of SPK with the term "Management Decision System" in which this system helped decision making using data and models to solve an unstructured problem [1]. Decision support system applications are widely used to provide solutions to problems in decision making [2]. The result obtained by decision support system can be based on the criteria that setting up [3].
One school program that can develop the potential of students is the existence of a selection program for outstanding students. Academic achievement becomes very important for a student [4]. Senior High School 2 of Demak is a school which has a selection program for outstanding students to increase student learning interest and as a reward for students who have a good academic record. The selection of outstanding students is also needed by the school for external purposes, such as providing data on outstanding students to the City and Provincial
Government Offices [5]. However, in determining this outstanding student, it is still seen based on the academic value which is calculated manually and the recommendation of the guardian teacher where tend to subjective.
Analytical Hierarchy Process (AHP) used a multi-purpose, criteria, sub-criteria, and alternative hierarchical structure. The relevant data were obtained using a set of pairwise comparisons [6]. AHP had the advantage of explaining the process of decision making because it could be described graphically, so that it was easily understood by all parties involved in decision making. AHP was a decision support tool that could be used to solve complex decision problems. This used a multi-purpose, criteria, sub-criteria, and alternative hierarchy structure [7].
The concept of the alternative chosen by Technique for Order Preference by Similarity to Ideal Solution (TOPSIS) is the best alternative that has the shortest distance from the positive ideal solution and the farthest distance from the negative ideal solution. TOPSIS has the shortest geometric distance from the positive ideal solution and compares an alternative set with the weight of each criterion [8]. This method is widely used to solve practical decisions. There are several methods in MADM (Multiple Attribute Decision making) to help choose a department including AHP, SAW (Simple Addictive Weighting) TOPSIS.
The TOPSIS method is very simple and easy to implement, so it is used when users prefer a simpler approach [9]. The concept of TOPSIS is easy to understand and has the ability to measure decision alternatives while AHP is not chosen because the AHP method is widely used in the case of criteria weighting and priority determination of each criterion. However, if the two methods are combined the results will be better because in AHP there is an eigenvector concept which is used to do the priority ranking process for each criterion based on pairwise comparison matrix, then the results of the weighting criteria are processed by the TOPSIS method for the ranking process [10].
Some researches had been conducted using AHP and TOPSIS. Purnomo conducted a study to compare the analysis using AHP, TOPSIS, and AHP-TOPSIS methods in the case study of acceptance decision support systems for accelerated program students" [11]. For the parameters used are the results of school ranking and student report card rankings acceleration with the aim of taking the suitability of the results with school provisions. Other parameters are student report grades and also as a parameter to determine the recommendation method. The results obtained from the hamming distance values of the three methods against the results of school ranking, obtained the AHP-TOPSIS method to be the best with 96.02%. The parameters used in this study can be added by another parameter. It can be obtained different result and option for decision making. Then, Herman conducted a study about decision support systems for determining the best employees using AHP and TOPSIS combination methods [12]. This research was conducted at PT. South Pacific Viscose. The HRD department has difficulty in making decisions in determining the best employees because of the large data and the long process. The decision support system for determining the best employee is done using the Analytical Hierarchy Process method to determine the weight of each criterion, and the use of the Technique for Order Preference by Similarity to Ideal Solution method to rank alternatives in the form of employee data. In this research discussed with another criterion like Skill and Attitude to determining of outstanding students using the AHP-TOPSIS combination method
The purpose of this research was to determine the workings of the TOPSIS method and the AHP-TOPSIS combination method and find out the comparison of the best method between TOPSIS and the combination method of AHP-TOPSIS in the selection of outstanding students.
Analytic Hierarchy Process is a multicriteria decision making with the support of a methodology that has been recognized and accepted as a priority that can theoretically provide different answers in decision-making problems and rank alternatives to the solution [13]. Because of its superiority, this method has been successfully used in various fields. As mentioned earlier, this method calculates both tangible and intangible factors in and this attribute is suitable for the subjectivity features in actual problems [14]. In AHP, there are three bases. The first base is a
model structure. The second base is an alternative comparison and assessment criteria. The third base is the synthesis of priority. Those bases made AHP can determine the relative cases in multi-criteria decision problem [15].
In solving a problem, the AHP method is used by structuring the criteria hierarchy by drawing consideration from interested parties to develop weight. AHP is an approach used to handle a complex system that is also related to determining a decision from the choices considered from several alternatives. This method was first developed by Saaty in 1980. The hierarchical model stated by Saaty is a functional hierarchy model with the main input being human perception. In general, the steps in using the AHP method for solving a problem are as follows:
1. Make a Pairwise Comparison Matrix
|
1 ⋯ 1 — 1 ∙ r2n (1) = [ ]= ⎢⋯ ⋯ ⋯ ⋯⎥ ⎢⎢ 1 1 ⎥⎥ |
2. Normalize Decision Matrix
⅞= rι i+ r2 i+ ∙∙∙+ rnl (2)
Description:
̅ = Number of matrix columns
i = Variable column to-i
-
= Variable line to-n
-
r = Pairwise Comparison Matrix Index
-
3. Determining Criteria Weight
Xj = r i'+ r2 i + ∙+ nni, (3)
Description:
̅ = Number of Matrix Columns
i = Variable Column to-i
j = Variable Line to-j
= Variable Line to-n
= Normalization of The Decision Matrix
Then calculate the weight of the criteria
Wl = n (4)
Description:
|
X J n w |
= Number of Matrix Rows = Variable Line to-i = Variable Line to-j = Number of Criteria = Criteria Weight |
TOPSIS (Technique for Others Reference by Similarity to Ideal Solution) is a multicriteria decision-making method that was first introduced by Yoon and Hwang (1981). TOPSIS has an alternative principle that is chosen must have the closest distance from the positive ideal solution and the farthest distance from the negative ideal solution. Positive ideal solutions are meant as the overall best value of each attribute, while negative ideal solutions are defined from all the worst values.
TOPSIS can be used to consider the distance between positive ideal solutions and the distance of negative ideal solutions by taking proximity relative to positive ideal solutions [16]. The stages of the TOPSIS method explained as follows:
-
1. Make a normalized pairwise comparison matrix
=
(5)
1I γ2
∑ X
Where i=1,2,..m; and j=1,2,..n;
Description:
= Normalized Matrix Elements [i][j]
= Decision Matrix Element X
-
2. Make a weighted normalized decision matrix
ytj = wirlj (6)
Where i=1,2,..m; and j=1,2,..n;
Description:
= Normalized Matrix Elements [i][j]
= Decision Matrix Element X
Where:
;
;
;
-
4. Determine the matrix of positive and negative ideal solutions with the distance between the values of each alternative
= ∑ ( - )
(8)
(9)
= ∑ ( - )
Description:
= Alternative distance to-i with positive ideal solution
= Elements of a positive ideal solution [i]
= Elements of normalized weighted matrix [i][j]
= Alternative distance to-i with negative ideal solution
= Elements of negative ideal solution [i]
-
5. Determine preference values for each alternative
=
= +
Description:
= The proximity of each alternative to the ideal solution
= Alternative distance to-i with positive ideal solution
= Alternative distance to-i with negative ideal solution
A larger Vi value indicates that the alternative to-i is preferred.
In this research, the system was made based on the website to determine the results of the selection of outstanding students using TOPSIS and AHP TOPSIS methods. The system was developed by using the Framework laravel and Database Management System (DBMS) MySQL XAMPP. The Data Flowchart Diagram was made to describe the need and function used in the system. In DFD there are two roles that involved, Teacher and Admin. Two of those roles have different capability. The DFD of this research can be seen in Figure 1.
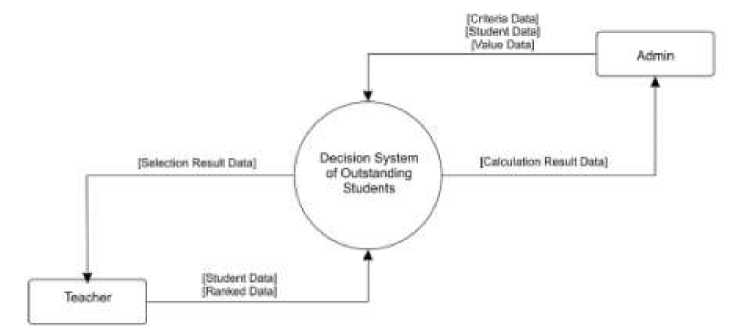
Figure 1. DFD of the selection of outstanding students
The developing of the system needed data related to the selection of outstanding students. These data were used to test the system. As an output, which method was better for the selection of outstanding students from each method. The data used in this study obtained from the data of students in Senior High School 2 of Demak numbered 100 samples which data consisting of Knowledge Value, Skill Value, Attitude Value, and Achievement. This type of data was frequently used for the decision maker in this school to select the outstanding students. Those values are referenced to academic and non-academic ability. In fact, those values are also used in the competition of outstanding student in Demak district.
This system was made based on the website using the PHP programming language and MySQL database. The interface was made with responsive design by displaying the website would follow the monitor screen used by the user. In the first stage was the determination of weight which weighted by the AHP method which consists of determining the criteria hierarchy structure, pairwise comparison matrix, normalizing the matrix, determining the criteria weight and the final weight value.
Method calculations and data processing were performed on the system. Before performing calculations, the system was designed based on the prototype that had been made. Data was entered into the database. Then the data started to appear and then processed on the system. The user had to enter the login process to find out the access rights to the Decision Support System of this outstanding student, if the user logged in as Admin then it would enter the Admin Dashboard. If the user is logged in as a Teacher, it would enter the Teacher Dashboard.
Criteria in the selection of outstanding students were obtained from the school, then the criteria were given weight by those responsible for the selection process. Weight criteria presented in Table 1.
|
Table 1. Weight Criteria | |
|
Criteria |
Degree of Interest Criteria |
|
Achievement Achievement Achievement Knowledge Value Knowledge Value Attitude |
2x Attitude 2x Knowledge Value 5x Skills Value 3x Skills Value 2x Attitude 2x Skills Value |
The next stage was the calculation using AHP, which determining pairwise comparison matrix, presented in Table 2.
Table 2. Pairwise Comparison Matrix
|
Criteria |
Achievement Value |
Attitude Value |
Knowledge Value |
Skills Value |
|
Achievement Value |
1 |
2 |
2 |
5 |
|
Attitude Value |
0.5 |
1 |
0.5 |
3 |
|
Knowledge Value |
0.5 |
2 |
1 |
3 |
|
Skills Value |
0.2 |
0.3333 |
0.3333 |
1 |
|
TOTAL |
2.2 |
5.333333 |
3.833333 |
12 |
Then after determining pairwise comparison, the next step was calculating matrix normalization by dividing the matrix value by the sum of the total values in the column. The normalization result was presented in Table 3.
Table 3. Normalization Result
|
Criteria |
Achievement Value |
Attitude Value |
Knowledge Value |
Skills Value |
|
Achievement Value |
0.4545 |
0.3750 |
0.5217 |
0.4167 |
|
Attitude Value |
0.2273 |
0.1875 |
0.1304 |
0.2500 |
|
Knowledge Value |
0.2273 |
0.3750 |
0.2609 |
0.2500 |
|
Skills Value |
0.4545 |
0.3750 |
0.5217 |
0.4167 |
The next step was determining criteria weight, by adding up all rows. Criteria weight was
|
presented in Table 4. |
Table 4. Criteria Weight |
|
Criteria |
Achievement Attitude Knowledge Skills Value Value Value Value e g |
|
Achievement Value Attitude Value Knowledge Value Skills Value |
0.4545 0.3750 0.5217 0.4167 1.767951 0.2273 0.1875 0.1304 0.2500 0.795208 0.2273 0.3750 0.2609 0.2500 1.113142 0.4545 0.3750 0.5217 0.4167 0.323684 |
After that stages, the next step was the final AHP stage by dividing the criteria weight by the number of criteria. The final weight value was presented in Table 5.
Table 5. Final Weight Value
|
Criteria |
Achievement Value |
Attitude Value |
Knowledge Value |
Skills Value |
Weight |
Final Weight |
|
Achievement Value |
0.4545 |
0.3750 |
0.5217 |
0.4167 |
1.767951 |
0.441988 |
|
Attitude Value |
0.2273 |
0.1875 |
0.1304 |
0.2500 |
0.795208 |
0.198802 |
|
Knowledge Value |
0.2273 |
0.3750 |
0.2609 |
0.2500 |
1.113142 |
0.278286 |
|
Skills Value |
0.0909 |
0.0625 |
0.0869 |
0.0833 |
0.323684 |
0.080921 |
After the AHP process was finished, the ranking was carried out using the TOPSIS method with the stages of determining the normalized performance rating, normalized weight rating, positive and negative ideal solution, positive and negative distance, then the output of the final output, namely preference value. The first stage was making a normalized performance rating by making the normalized decision matrix. The Normalized Performance Rating was presented in Table 6.
Table 6. Normalized Performance Rating
|
Achievement Value |
Attitude Value |
Knowledge Value |
Skills Value | |
|
A1 |
0.1031 |
0.1025 |
0.0998 |
0.0966 |
|
A2 |
0.0993 |
0.1002 |
0.0994 |
0.0977 |
|
A3 |
0.0993 |
0.1002 |
0.1001 |
0.0981 |
|
A100 |
0.0993 |
0.1025 |
0.1003 |
0.0995 |
Furthermore, the making a normalized weight rating, by multiplying the decision matrix result with the weight that has been generated in the previous process. The normalized weight rating was presented in Table 7.
Table 7. Normalized Weight Rating
|
Achievement Value |
Attitude Value |
Knowledge Value |
Skills Value | |
|
A1 |
0.049736 |
0.009049 |
0.015719 |
0.026256 |
|
A2 |
0.047903 |
0.008846 |
0.015656 |
0.026555 |
|
A3 |
0.047903 |
0.008846 |
0.015766 |
0.026663 |
|
A100 |
0.047903 |
0.009049 |
0.015798 |
0.027044 |
The next steps to find positive ideal solutions and negative ideal solutions were presented in Table 8 and Table 9.
|
Table 8. Positive Ideal Solution | |||
|
Achievement Value |
Attitude Value |
Knowledge Value |
Skills Value |
|
Vi |
y? |
yt |
yt |
|
0.052099910780595 |
0.0090492291474562 |
0.016474948500217 |
0.028266960409512 |
|
Table 9. Negative Ideal Solution | |||
|
Achievement Value |
Attitude Value |
Knowledge Value |
Skills Value |
|
yi |
yi |
yi |
yi |
|
0.047902973523269 |
0.0086431174003509 |
0.014017881611083 |
0.024652051049449 |
Then the distance between the values of each alternative with the positive and negative ideal solution matrix was presented in Table 10 and Table 11.
|
Table 10. Positive Distance | |
|
Alternatives |
Positive Distance |
|
A1 |
0.003194 |
|
A2 |
0.004611 |
|
A3 |
0.004553 |
|
A100 |
0.004424 |
Table 11. Negative Distance
|
Alternatives |
Negative Distance |
|
A1 |
0.002998 |
|
A2 |
0.002519 |
|
A3 |
0.002673 |
|
A100 |
0.003009 |
Then determine the proximity of each alternative to the ideal solution and get the results of ranking, can be seen in Table 12.
Table 12. Result of Ranking
|
Alternatives |
Proximity of each Alternative |
|
A1 |
0.484173127 |
|
A2 |
0.353295933 |
|
A3 |
0.369914199 |
|
A100 |
0.404816359478 |
From the V value (preference) it can be seen that A22 has the greatest value, so it can be concluded that from the sample of students at SMA 2 Demak, A22 is recommended to be an outstanding student.
In a comparative analysis method, it used Hamming Distance with the aim of measuring how well the results method using the system and the manual calculation (the implementation of methods on Excel) in terms of the differences number in position on the data. Hamming distance incompatibility was applied because the results of a decision support system with results based on manual calculations would certainly be different. For example, the results given to Alternatives A1 on the system was 0.484173127 while A1 in the manual results was 0.469552974 therefore, Alternatives A1 was included in the data with a position of Hamming Distance incompatibility.
The results of the comparison between the TOPSIS method and the AHP-TOPSIS combination proved that the AHP-TOPSIS combination method is better than the TOPSIS method. By the comparison using Hamming Distance incompatibility, the accuracy of the TOPSIS method had 93% obtained from incompatibility of 93 data divided by the data number which is 100 then it multiplied by 100%. The AHP-TOPSIS method had 91% obtained from incompatibility of 91 data divided by the data number then multiplied by 100%. It meant in Hamming Distance of AHP-TOPSIS smaller than the result which obtained by TOPSIS referencing that smaller presentation of hamming distance showed the better result of selecting the outstanding students.
The implementation of the AHP-TOPSIS method in the selection of outstanding students obtained 91% using Hamming Distance incompatibility. Then, the implementation of the TOPSIS method in the selection of outstanding students obtained 93% using Hamming Distance incompatibility. Based on these results it can be concluded that the AHP-TOPSIS combination method is better than the TOPSIS method. The hamming distance of AHP-TOPSIS smaller than TOPSIS method which it showed that the distance of each criterion similar and obtained as decision making a result of an outstanding student.
References
-
[1] E. Turban, J. E. Aronson, and T. P. Liang, “Decision Suport System and intelligent
system.” Prentice Hall, New Jersey, 2005.
-
[2] P. O. Rahmanda, R. Arifudin, and M. A. Muslim, “Implementation of Analytic Network
Process Method on Decision Support System of Determination of Scholarship Recipient at House of Lazis Charity UNNES,” Scientific Journal Informatics, vol. 4, no. 2, pp. 199– 211, 2017.
-
[3] A. Nurzahputra, A. R. Pranata, and A. Puwinarko, “Sistem Pendukung Keputusan
Pemilihan Line-up Pemain Sepak Bola Menggunakan Metode Fuzzy Multiple Attribute Decision Making dan K-Means Clustering,”Jurnal Teknologi dan Sistem Komputer, vol. 5, no. 3, pp. 106–109, 2017.
-
[4] K. B. Leng, S. J. K. C. C. Tong, J. Kempas, and T. K. Putri, “The Relationship between
Self-Concept, Intrinsic Motivation, Self-Determination and Academic Achievement among Chinese Primary School Students,” International Journal of Psychological Studies, vol. 3, no. 1, pp. 90–98, 2011.
-
[5] S. F. Ng et al., “A study of time use and academic achievement among secondary
school students in the state of,” International Journal of Adolescence and Youth, vol. 3843, pp. 1–16, 2016.
-
[6] J. Chen, H. Nie, and K. Li, “Evaluation and Selection Model of Strategic Emerging
Industries in Guangdong Province of China Based on AHP-TOPSIS,” International Journal of Business and Management, vol. 10, no. 11, pp. 161–168, 2015.
-
[7] I. Engineering, E. Triantaphyllou, and S. H. Mann, “Using The Analytic Hierarchy
Process For Decision Making In Engineering Applications: Some Challenges,” Inter1I Journal of Industrial Engineering: Applications and Practice, vol. 2, no. 1, pp. 35–44, 1995.
-
[8] S. Gurung and R. Phipon, “Multi-criteria decision making for supplier selection using
AHP and TOPSIS method,” International Journal of Engineering Inventions, vol. 6, no. 2, pp. 13–17, 2016.
-
[9] G. Kabir and M. A. A. Hasin, “Comparative Analysis of TOPSIS and Fuzzy TOPSIS for
the Evaluation of Travel Website Service Quality,” International Journal for Qaultity Reseach, vol. 6, no. 3, pp. 169–185, 2012.
-
[10] M. Zeydan and C. Çolpan, “A new decision support system for performance measurement using combined fuzzy TOPSIS / DEA approach,” International Journal of Production Reseach, vol. 47, no. 15, 2009, pp. 4327–4349.
-
[11] E. Nur, S. Purnomo, S. Widya, and R. Anggrainingsih, “Analisis Perbandingan Menggunakan Metode AHP , TOPSIS , dan AHP-TOPSIS dalam Studi Kasus Sistem Pendukung Keputusan Penerimaan Siswa Program Akselerasi,” ITSMART: Jurnal Teknologi Informasi, vol. 2, no. 1, 2013.
-
[12] I. H. Firdaus et al., “Sistem Pendukung Keputusan Penentuan Karyawan Terbaik,” Seminar Nasional Teknologi Informasidan Komunikasi 2016 (Sentika), pp. 18–19, 2016.
-
[13] P. T. Kazibudzki, “On Some Discoveries in the Field of Scientific Methods for Management within the Concept of Analytic Hierarchy Process,” International Journal of Business and Management, vol. 8, no. 8, pp. 22–30, 2013.
-
[14] K. Eylem and H. A. Burhan, “An Application of Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) in a Real World Problem of Store Location Selection,” Advances in Management & Applied Economics, vol. 5, no. 1, pp. 41–50, 2015.
-
[15] C. A. Josaputri, E. Sugiharti, and R. Arifudin, “Decision Support Systems for The Determination of Cattle with Superior Seeds using AHP and SAW Method,”Scientific Journal of Informatics, vol. 3, no. 2, pp. 21–30, 2016.
-
[16] S. Kusumadewi, S. Hartati, S. Harjoko, A. Wardoyo and Retantyo. “Fuzzy Multi-Attribute Decision Making ( Fuzzy MADM ),” Yogyakarta: Graha Ilmu, p. 78-79.
48
Discussion and feedback