Politeness Strategies Employed by the Trainers in Room Division Department BAPEPAR Nusa Dua
on
Politeness Strategies Employed by the Trainers in Room Division Department Bapepar Nusa Dua
I Gusti Ayu Vina Widiadnya Putri
Stiba Saraswati Denpasar
Abstract
This article tries to analyze and discuss the politeness strategies employed by the trainers in room division department when they practice on the job training in the hotel. Politeness strategy was needed when the trainers serve the guest. This research was done by observation and interview with the trainer and the guest about their conversation.
The analysis of politeness strategies that employed by the trainer focused on two discussions; (1) the kinds of politeness strategies used by trainer in room division department, and (2) the implications of politeness strategies used by trainer in room division department. This research used the theory from Brown & Levinson (1987) in his book entitled Politeness: Some Universals in Language Usages. The theory is supported by other theories that are considered relevant to the topic of discussion in this research.
Based on the analysis, it was found that there were two kinds of politeness stratgies that employed by the trainer in room division department Bapepar Nusa Dua, they were positive face and negative face. Beside that, there are three implications by using politness strategies such as: respect behaviour, togheterness, and cooperative interaction.
Keywords: Politeness strategies, trainer, guest
I INTRODUCTION
When we talk about language, there are many definitions of language, and one another look like similar. Language like other form of society activity has to be appropriate to the speaker using it. Language has special meaning to human beings when they do kinds of communication. According to Keyton (2011) communication is the process of transmitting information and common understanding from one person to another. So, it means that communication is an activity where two people contribute in conveying and receiving messages or information. Furthermore, Cheney (2011) explains there are some processes of communication, they are: the sender or the speaker is a person who has need or desire to convey an idea or concept to others. The receiver or the hearer is the individual to whom the messages or the information is sent. The information that sent could be in the form of verbal, nonverbal or written language. This is as the feedback for the receiver or hearer as they receive the information from the speaker. Thus, Grice (1975) states that communication should be explained in the form of social interaction whose success depends on interact presumption that communication is driven by certain norms and rules.
Considering the language used by people in communication, certainly the language used by people in certain places is concerned with social and cultural phenomena, (Trudgill, 1983). It means that the language used in the society deals with the social values or social norms which are developed there, because language and society bound each-other. In addition, language stays and walks together with culture that influences the language used. The language used in culture is a complex one due largely in part to the great difficulty in understanding people’s cognitive processes when they communicate. So, language and culture are supposed to be part of the communication among the society. Besides, language is also related with the place where and when the language is used (Hymes, 1994). Thus, people in society use the language based on their culture and social norms which are agreed and accepted by them.
Commonly, the speaker wants to have a good and polite behavior when they make communication with the hearer. This is due to how the speaker or people wants to keeps or have good relationship with the hearer. People live together in a society and do available conventions or norms in the social society where the politeness as a strategy to avoid conflict that might be happened and also in order to develop good relationship or togetherness in social interaction (Watts, 2003; Rash, 2004). It is very important if speaker uses politeness as a strategy in order to make communication with other people of social community running well. Seken (2007) stated that when talking about politeness in the communication, language will be seen as a behavior of human in the social interaction.
Politeness is the key point when people serve the client in hospitality industry. It is very important if the speaker uses politeness in communication. Moreover, when people obey all of the conventions, regulations, norms, values, in the society and keep the good relationship or togetherness in a
communication, then it means polite. I would like to analyze my discussion about politeness strategies used by trainer in room division department. The discussion focuses on the following points (1) what are the kinds of politeness strategies used by trainer in room division department; and (2) what are the implications of politeness strategies used by trainer in room division department.
II MATERIALS AND METHODS
Many social factors can into controlling the politeness. Politeness in speaking, courtesy, or etiquette is a procedure, custom, or custom prevailing in the society. It also as politeness is the rules of conducting establishment and agreed upon jointly by a particular community concluded as social behavior. Politeness is rules of behavior which is agreed together by the society where it is applied. In the real life that is occurred in the society politeness can be seen from the various facets of everyday interaction.
The researcher followed the descriptive qualitative as a design of this research study where all of aspect which related to the interaction between clerk or trainer and the guest involved and the strategy that related to the politeness are investigated in depth and explain in details. Descriptive-qualitative research was a research which investigated the quality of relationships, activities, situations, or materials (Fraenkel & Wallen, 1993). As the researcher following the descriptive qualitative research, the investigation is done by the observation to the interactive event.
-
2.1 POLITENESS STRATEGY
Practically, politeness is a strategy used in communication in order to avoid the conflict between the speaker and the hearer, especially used by the teacher and the student in classroom interaction in order to create harmonious relationship between teacher and students. Besides, to build students’ consciousness and motivation in employing their language to be polite and well accepted.
On the contrary, Brown & Levinson (1987) provide a slightly different perspective about politeness. As they followed the Goffman’s theory of face, they concerned on the FTA (Face Threatening Act) because every interlocutor and addressee have face and this face sometimes could be threaten. Face-threatening act (FTA) is acts that infringe on the hearer’s need to maintain his/her selfesteem and be respected. So, by conducting politeness in conversation interaction, one can avoid the effect of face threatening. In line with that, Brown and Levinson state that politeness is the speaker’s strategy to minimize the effect of an FTA (Face Threatening Act) in communication. As such, in an event of interaction, the threat to the face can concern either the speaker or the addressee, or even both, depending on the kind of act that is at issue (Brown & Levinson, 1987).
The rational actions take to preserve both kinds of face, for themselves and the people they interact with, add up to politeness. Politeness in interaction can be defined as a means employed to show awareness of another person’s face. In this sense, politeness can be accomplished in situation of social distance or closeness. Brown & Levinson also argue that in human communication, either spoken or written, people tend to maintain one another’s face continuously. In everyday conversation, people adapt conversation to different situations. For example showing awareness for another person’s face when that other seems socially distance is often described in term of respect and deference. The term of respect and deference here means speaker want to keep good relationship with hearer. The other example among friends, she/he takes liberties or says things that would seem discourteous among others and they avoid over formality with them. In both situations they try to avoid making the hearer embarrassed or uncomfortable. Thus, Brown and Levinson emphasized the application of politeness strategy in order to minimize the threat to the face and dealing with that FTA. Brown & Levinson (1987) claim that particular kind of act can threaten face, that is, the act that contras to what the face needs from the speaker. This is call face threatening act. FTA is seen as utterance or action that threatens person face. Some acts can threaten the hearers’ negative face. Negative face is the desire of every competent adult member to have freedom of action, freedom of imposition, and not to be impeded by others. Furthermore, some others can threaten positive face of the hearer. Positive acts is the need of every member that his wants to be appreciated and accepted, to be treated as the member of the same group, and to know that his or her wants are shared by others.
Basically, negative face as the basic claim to territories, personal preserves, right to nondistraction, such as: freedom from imposition, therefore, negative face emphasize other’s rights and freedom. In the other hand, positive face as the positive consistent self-image or personally aimed at establishing strong ties between individuals.
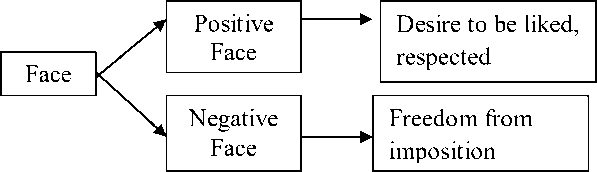
Figure 1. “face” according to Brown and Levinson (1987, p.68)
These to distinction of FTA may lead to do the FTA or not to do the FTA. The strategies of doing FTA depend on the circumstance whether the speaker wants to reserve the hearer face to any degree. In order to minimize the FTA, Brown & Levinson (1987) presented an anlysis strategy which leads to the theory of linguistic politeness. The figure showed the linguistic politeness strategy by Brown and Levinson, especially in dealing with FTAs (Face Threatening Act).
-
2.2 SPEECH ACTS
Conceptually, Austin (1962) defines speech acts as an utterance uttered by the people which are not intended to state the information only. The utterance is also intended to perform actions. Austin influences three categories of speech act called locutionary, illocutionary and perlucotionary act. Based on the categories, Searle (1976) focuses on illocutionary act which divided into some types, namely: Representative, Directive, Commisive, Expressive and Declarative. Furthermore, Clark (2004) enlarges those five categories of illocutionary act of Searle into: Representative, Directive, Need statement, Imperative, Embedded imperatives, Premision derictives, Question directives, Hint, Commisive, Expressive, Effective and Verdictive. Thus, the focus of the research study is on the application of politeness in the hotel which cannot be separated from illocutionary act because it is as the action that performed in the utterance spoken in the guest service interaction.
III RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
The discussion section has been parted as two discussions based on the finding in order to answer the research question of this research.
-
3.1 THE KINDS OF POLITENESS STRATEGIES USED BY TRAINER IN ROOM DIVISION DEPARTMENT
There were some politeness strategies employed by the trainer in room division department bapeppar Nusa Dua. The data collection was conducted by observing twenty trainers in room division department.
-
3.1.1 POSITIVE FACE
Positive acts need of every member that his wants to be appreciated and accepted, to be treated as the member of the same group, and to know that his or her wants are shared by others. In everyday conversation, the trainers adapt conversation to different situations. For example showing awareness for another person’s face when that other seems socially distance is often described in term of respect and deference. There are some utterances by the trainer when they serve the guest on the job training.
Data 1
Clerk : Receptionist, good afternoon, may I help you?
Guest : I want to make a reservation for me one single,
will arrive on eleven June, I will stay approximately a week.
Clerk : May I know who’s calling please?
Guest : My name is James Brown.
In that data, the clerk tried to use positive face. Positive acts need of every member that his want to be appreciated and accepted. The trainer or clerk only asks the guest about his job duty. He or she only asked the guest about the reservation information without asking anymore. The utterance are Receptionist, good afternoon, may I help you, May I know who’s calling please? It belongs to positive face in politeness strategies.
Data 2
Clerk : Are you traveling by plane? Could I have your flight detail? The airport representative will pick you up at the airport.
Guest : I’m flying by Garuda 2016 from Singapore arriving at the airport at four thirty five.
Clerk : certainly sir, shall I book you 2 double rooms?
In that data, showed the positive face used in the utterance. The clerk asked Are you traveling by plane? Could I have your flight detail? The airport representative will pick you up at the airport. That would be a formal utterance. The clerk only asked about flight detail to fill the reservation form. The trainers adapt conversation to these situations. The trainer only wanted to know about basic information on his or her duty.
Data 3
|
Reservation |
: May I know what date you will be arriving? |
|
Guest |
: I will be arriving on 19th of June 2016 |
|
Reservation |
: how about you will be departing? |
|
Guest |
: 22nd of June 2016 |
|
Reservation |
: Alright Sir, May I know about your name, Sir? |
|
Guest |
: My name is Hariyanto |
|
Reservation |
: Just A moment Mr, Hariyanto, I will check available room for that period, |
|
Guest |
: Yes Please |
In that data was showed that the clerk used positive face. The trainer asked about the reservation information to check the reservation form. The trainer only wanted to know about the reservation without talking anything. The trainer or clerk said May I know what date you will be arriving? and how about you will be departing? That utterance was belongs to positive utterance.
-
3.1.2 NEGATIVE FACE
Negative face as the basic claim to territories, personal preserves, right to non-distraction, such as: freedom from imposition, therefore, negative face emphasize other’s rights and freedom.
Data 4
|
Alan Robert |
: That’s right |
|
Trainer/clerk |
: May I see you passport, Sir? |
|
Alan Robert |
: Why do you need to see my passport? |
|
Trainer/clerk |
: It is for safety and security concern, sir. |
|
Alan Robert |
: well, just a minute, here it is. |
|
Trainer/clerk |
: Are you from Australia? |
|
Alan Robert |
: Yes. |
|
Trainer/clerk |
: Waoo,,, I would like to go to Australia, but I don’t have the money to go there. Hope I will go there some day |
In that data, the trainer tried to use negative face in their interaction with the guest. Negative face emphasizes the freedom. The trainer tried to make the communication in formal context of situation. The trainer said Waoo,,, I would like to go to Australia, but I don’t have the money to go there. Hope I will go there some day. It meant that utterance was informal condition and distraction utterance so the trainers just wanted to be friendly with the guest.
Data 5
|
Trainer/clerk |
: oh, yes Sir. I remember now. I am very sorry. |
|
Alan Roberts |
: Now, I would like someone to confirm my flight to HongKong. |
|
Trainer/clerk |
: will you go to Hongkong? |
|
Alan Roberts |
: Yes |
Trainer/clerk : There are many guests from Hongkong that leave in this Hotel. Hongkong is the best city for run the business.
In that data, the trainer used negative face in his utterance. The utterance is There are many guests from Hongkong that leave in this Hotel. Hongkong is the best city for run the business. That utterance was not the basic interaction for the guest’s information. That information was used for continuing his conversation so the guest was not stopping to talk something. The trainer tried to answer in freedom communication even though there was not really reasonable information.
Data 6
Alan Roberts : Okay, I want to get a bite to eat and drink coffee before I go to my room. Is
there a Coffee shop in this hotel?
Trainer/clerk : Yes there is coffee shop in the corner. Do you like coffee sir? I also like coffee and I love coffee especially luwak coffee. Have you tried it?
Guest : Never
Trainer/clerk : you should try it, sir
Guest : Maybe sometime.
Trainer/clerk : Yes just put the concierge desk, by the front door; you
passed it on Your way into the hotel. Here is your room key
Alan Roberts : Thank you
In that data, the trainer tried to use negative face in his utterance. The trainer just wanted to get similarity with the guest. That was not the basic point when the trainer handling guest in front desk, however the trainer possible to get best image from the guest as a friendly clerk in that hotel. The utterance is Do you like coffee sir? I also like coffee and I love coffee especially luwak coffee. Have you tried it? The trainer was free to answer the guest said as long as it didn’t make the guest offended. So that utterance was belong to negative face.
-
3.2 THE IMPLICATION OF POLITENESS STRATEGIES USED BY TRAINER IN ROOM DIVISION
DEPARTMENT
Politeness strategies have been given implication in their job training communication. There were some implications of using language in their interaction such as:
-
3.2.1 BEHAVIOR
Respect behavior. The trainers have respect to their guest and the guest also should be respect to the trainers. Positive face used by the trainer fulfills the respect behavior in their interaction. In interaction the trainers used greeting, thanking and also taking leave expression. They express respect behavior in order to create good relationship between the trainer and the guest in communication. Good relationship make good interaction atmosphere in the process serving guest
-
3.2.2 TOGETHERNESS
Meanwhile, the trainer has togetherness. Togetherness is behavior that should be fulfilled in the process of serving guest in hotel beside respect. Togetherness could make the trainers have more motivation in the serving guest process. Togetherness is one aspect in order to create good relationship between guest and the trainer, it is similar with respect. Togetherness perform when teacher appraising students’ idea, answer or responses. The trainers try to create togetherness in order to motivate the students for example by using joke and solidarity in group identity markers.
-
3.2.3 COOPERATIVE
Besides togetherness, the trainer has cooperative interaction. The Guest gave an instruction to the trainer then the trainer should be cooperated responding guest’s instruction. The guest can design their instruction by choosing politeness strategies at the time; however, the trainer also can respond the guest’s instruction by choosing the strategy of politeness.
In addition, sometimes negative face could be form by the guest and the trainer. In this case the guest feel disappointed when cooperate in their interaction is avoided by trainer. Also the trainer should decrease imposition to the guest. Less imposition performs by using negative politeness.
By implementing politeness strategy in the interaction processes become meaningful. It would create a good atmosphere which all the implication previously. Politeness strategies are much needed in serving guest interaction. The trainer should use politeness strategy in their interaction, there are some situations and condition of the interaction cannot be controlled by the trainer. Sometimes politeness strategy that employed by the trainer is uncontrolled, so that makes the guest fell uncomfortable.
IV CONCLUSION
Politeness strategies were also important in guest serving. The trainer should able to thoughtfully decide on politeness strategies to establish conductive interaction in giving service for the guest. In addition, trainer should be able to insert the topic of politeness into daily activities in guest serving on his or her duty. By this, the trainer can ask the guest by the politeness as well. Furthermore, by considering the politeness strategy in communication among trainer and guest, it is obvious that discussing of politeness strategy used by the trainer was also important in interaction. The politeness strategy can be chosen as politeness behavior of the trainer’s communication with their guest.
REFERENCES
Brown, P. & Levinson, S. C. (1987). Politeness: Some Universals in Language Usages. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Cheney, G. (2011). Organizational Communication in an Age of Globalization Issue, Reflection, Practice. Long Grove, IL: Waveland.
Fraenkel, J. R. and Nongman, E. (1993). How to Design and Evaluate Research in Education. New York: McGraw-Hill.
Grice, H. (1975). Logic and Conversation. In Leech, Principle of Pragmatics. New York: Longman.
Keyton, J. (2011). Communication and Organizational Culture: A Key to Understanding Work Experience. Thousand Oaks, CA.: Sage.
Seken, I. (2004). Being Polite in Balinese: An Analysis of Balinese Adat Leader's Spoken Discourse. Malang: University of Malang Unpublished Disertation.
Trudgill, P. (1983). Sociolinguisitcs: An Introduction to Language and Society. Haormondsworth: Penguin Book.
Watts, R. (2003). Key Topics on Sociolinguistics Politeness. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Discussion and feedback