Application of Levine’s Model in Nursing Care of Patient with Diabetic Foot: A Case Study
on
Journal of a Sustainable Global South, p-ISSN: 2579-6062
Application of Levine’s Model in Nursing Care of Patient with Diabetic Foot:
A Case Study
Ida Ayu Agung Laksmi1, Heri Kristianto2, Tony Suharsono3
Nursing Study Program
Institute of Health Science Bina Usada Bali
Denpasar
Master Degree of Nursing Study Program
Medical Faculty of Brawijaya University
Malang
Master Degree of Nursing Study Program
Medical Faculty of Brawijaya University
Malang
Abstract
Diabetic foot is such a life threatening condition for people with Diabetes Mellitus which it can be result in hemodynamic instability and loss of consciousness. In order to improve quality of nursing care in patient with diabetic foot, nurses should apply a nursing model approach. Levine conservation theoretical model is one of comprehensive model theory that can be applied in patients with critical diabetic foot in Emergency Department (ED). This case study describes a nursing care using Levine's Conservation Model to care for a patient with diabetic foot. This study was a case study with a single case design. Data were collected using physical assessment, written communications with the patient, interviews patient family members, and observing the patient during intensive care in the ED of Lawang General Hospital on December 21th, 2015. Levine's Conservation Model used as the nursing guideline successfully identified patient issues including ineffective breathing pattern as a major priority of energy conservation problem and damage tissue integrity as a problem of structural conservation. Both of conservation problem were caused by patient's personal integrity conservation maladaptive that caused by ineffective therapeutic regimen management. Levine’s conservation model is useful to investigate nursing problem and applicable to solve the emergency condition of damage tissue integrity in patients with diabetic foot.
Index Terms— diabetic foot, nursing care, levine’s conservation model.
Diabetic foot is one of the complications of diabetes mellitus with prevalence about 15% of the total number people with DM [1]. Diabetic foot ulcers increased the risk of mobility disability and contribute to almost 85% of amputations [2].
Diabetic foot infection is a life-threatening condition due to a combination of neuropathy, ischemia, and hyperglycemia. Poor quality treatment of diabetic foot and
hyperglycemia condition can cause hemodynamic instability and loss of consciousness [3]. Therefore, it is not uncommon patients with diabetic foot was taken to the emergency room (ER) to receive emergency treatment.
Emergency service is a part of the health services that provide treatment of individuals with acute life- or limbthreatening medical and potentially surgical needs [4]. Nursing theories and models are guidelines for nurses in providing holistic services to patients that can be outlined through the nursing care process which includes assessment, determination of nursing problems, interventions, implementation and evaluation in all situations including emergency situations. The application of nursing theories in
nursing care will give an improvement the nursing care’s quality [5]. One of the nursing models that can be applied in providing nursing care for patients with diabetic foot is the theory of conservation of Myra E. Levine.
Applications Levine's theory model conservation is particularly useful for identifying activities within each component of nursing. Levine conservation model is one of the guidelines for the nurse to provide nursing intervention. The conservation model is based in the belief that the nurse creates the environment in which a patient is to heal by conserving the patient’s energy through nursing interventions, conserving or restoring the patient’s structural integrity by promoting healing, conserving the patient’s sense of identity, and by conserving the patient’s social integrity by facilitating and maintaining relationships [6]. According to Hendrich [7], Levine’s Conservation nursing model is very applicable to use in medical cases (medical) or trauma (surgical) commonly found in the ER. Therefore, the authors are interested to apply for Levine’s Model in Nursing Care of Patient with Diabetic Foot.
The methodology used in this study is a single case study with a nursing care approach in emergency care. This case study is taken from an emergency case with first priority triage in the ER of Lawang Hospital on December 21th, 2015. The research applied the nursing process according to Levine’s Conservation Model to emphasize problem patients based on conservation of energy, structural integrity, personal integrity, and social integrity.
-
A. Case
Mrs. N is a 55-year-old mother who arrived at the emergency room at Lawang Hospital on Monday, 21 December 2015 at 2:20 pm with loss of consciousness. Previously Mrs. N is a poly-surgical patient who is waiting to get wound debridement treatment after diabetic foot surgery, but suddenly Mrs. N is unconscious and taken to the ER. The initial assessment results in the ER are E2V3M4 with Blood Pressure (BP): 130 / 60 mmHg, Heart Rate (HR): 132 rpm, Respiratory Rate (RR): 32 bpm, Temperature (T): 36.4 and the Blood Sugar (BS) > 600mmol / L.
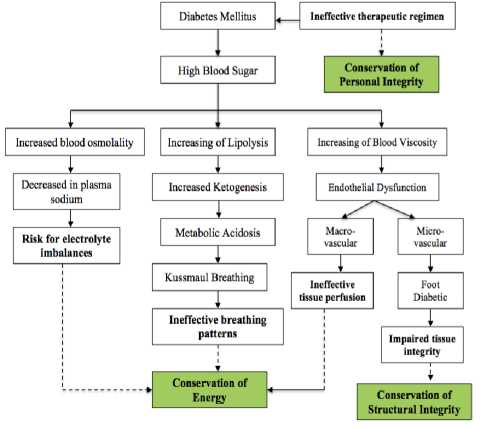
Fig. 1. Data Analysis (source: Levine’s Conservation Model Theory)
-
B. Nursing Diagnosis
Based on Figure 1, it can be concluded some nursing diagnosis (Trophic-Gnosis) as follows :
-
1. Ineffective breathing patterns
-
2. Ineffective cerebral tissue perfusion
-
3. Risk for electrolyte imbalances
-
4. Impaired tissue integrity
-
5. Ineffective therapeutic regimen management
-
C. Nursing Intervention
Planning in Levine concept called by”hypothesis”. The essence of Levine’s Theory is “currently nursing intervention by a nurse can affect a person’s adaptation and improve the social welfare conditions, when the nurse is able to act as a therapeutic [8].
-
D. Implementation
The first action was given to Mrs. N administered O2 with 10 lpm NRM mask therapy and installed a bedside monitor to evaluate oxygen saturation and vital signs. Then checked the blood sugar with a finger stick as a form of energy conservation hypothesis immediately after the patient comes to the emergency room at 2:20 p.m. At 2:25 pm was installed intravenous access by taking blood for lab tests complete blood profile and electrolyte levels, followed by hydration with 0.9% NaCl loading dose and urine catheter for monitoring the patient's fluid balance as energy conservation hypothesis of risk of electrolyte imbalance. Then, continued with the collaboration of insulin drip (novorapid) (25 units / 5 hours) in 100 ml 0.9% NaCl at 2:45 pm and evaluation of the level of consciousness, vital signs and blood glucose levels first 15 minutes. At 2:50 we did aseptic wound care.
The wound was irrigated with 0.9% NaCl high pressure to minimize bacteria in the wound. At 3:30 pm, condition of patient began to stabilize with GCS E4V5M6, HR: 100 rpm, RR: 24 bpm, BP: 130/80 mmHg, T: 36.50 C, urine output of 150 cc, and BS decreased to 435 mmol /L and
monitored every 1 hour. At 4:30 BS decreased to 300 mmol/L, HR: 90 rpm, RR: 22 bpm, BP: 130/80 mmHg, T: 36.50 C, urine output of 150 cc. At 5:30 pm BS decreased to 247 mmol/L, HR: 92 rpm, RR: 22 bpm, BP: 130/80 mmHg, T: 36.50 C, urine output of 200 cc. At 7:30 pm, we continued with the provision of health education (HE) on the management of diabetes and how importance of treatment with diabetic foot to patient and family.
-
E. Discussion
Levine conservation model is one of the guidelines for the nurse to provide nursing intervention with four dimensions–energy, structural integrity, personal integrity, and social integrity [8]. Conservation of energy refers to balancing energy input and output includes adequate rest, nutrition and exercise. Conservation of structural integrity refers to maintaining or restoring the structure of body preventing physical breakdown and promoting healing. Conservation of personal integrity recognizes the individual as one who strives for recognition, respect, self-awareness, selfhood and self-determination. Conservation of social integrity is recognized as someone who resides with in a family, a community, a religious group, an ethnic group, a political system and a nation [9]. These components influence one another.
Based on nursing care in Mrs. N above, we could use four principles conservation to assess patient in ER. We found problem on energy conservation and structural as actual problems that can be life-threatening emergency. Problems in energy conservation and structural experienced Mrs. N caused by an inadequate conservation of the personal integrity of the patient. This is supported by data gaps in the form of ineffectiveness therapeutic regimens carried out by Mrs. N at home. It can be caused by the less of understanding about the importance of diabetes treatment and the less family and social system support.
The essence of Levine's theory is "nurse's intervention at this time can influence adaptation and improve conditions of social welfare, that's when nurses are able to act as a therapy [9]. Nursing interventions in Levine model theory focuses on the theory of conservation is defined as the activity of maintaining and preserving the integrity of the body that explains the functions of a complex system, although there are obstacles in the process [6]. Efforts in maintaining and preserving the integrity of the body both physiologically (energy) or anatomical (structural) was the main reason the patient came to the emergency room. n emergency settings the priority actions are energy and structural conservation, but do not rule out the possibility of conservation of personal and social integrity so that HE can be given if an adaptation of the patient or family is maladaptive.
According to the above case, we also found maladaptive data on the conservation of the patient's personal integrity, so that Health Education and discharge planning were given to change the patient's adaptation response to be adaptive.
One hypothesis based on conservation theory that is very applicable is infection control management in the integrity of damaged tissue so that wound care is given with the principle of aseptic and high pressure irrigation.
Levine conservation model to initiate development of a framework of medical-surgical nursing were based on nursing therapeutic interventions with the goal of conservation function. By applying a model of conservation Levine, nurses can implement patient care plans either supportive or with therapeutic to help patients achieve integrity. This is in accordance with the principle of handling emergency patients by providing measures that could solve patient problems [10].
In addition, the Levine’s conservation model is also very suitable for discharge planning of patient at ER. Discharge planning is the process of assessment, preparation, and a dynamic and systematic coordination to facilitate the supervision of health and social services before and after return [11]. Other study developed a model discharge planning to individuals and family in diabetic foot management based on four principles of conservation in a holistic manner in order to reduce the number of patient visits to the hospital [12].
Levine proper conservation model theory was applied to the case Mrs. N particularly in addressing Impaired tissue integrity by infection control management and wound care as the hypotheses of structural conservation issues. Besides this, conservation model aims to help patients in solving actual problems in the ER patients. Discharge planning on diabetic foot is provided by focusing holistically on energy, structural, personal, and social management methods to reduce receptivity or recurrence in patients to the ER. As a suggestion, further research is needed to develop a Levine application conservation model in other emergency situations of diabetes.
This article is the result of a class assignment in Master of Nursing Program, Medical Faculty of Brawijaya University. The authors thank any parties that support this study, especially to Institute of Health Science Bina Usada Bali. We are also very grateful to the Emergency Department of the Lawang Hospital for allowing to carry out this project.
References
-
[1] Dinker R. Pai S.S., “Diabetic Foot Ulcer – Diagnosis and Management. Clin Res Foot Ankle”, 2013.
-
[2] Wong, E., Backholer, K., Geraon, E., Harding, J. et.al., “Diabetes and risk of physical disability in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis” The Lancet Diabetes and Endocrinology, 2013. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2213-8587(13)70046-9
-
[3] Pendsey S., “Understanding diabetic foot ulcers”, Int J Diabetes Dev Ctries, 2010.
-
[4] Hirshon J.M., Risko N., Calvello EJ, de Ramirez S, O’Neil J. Health systems and services: the role of acute care. Bull World Health Organ. 2013;
-
[5] Gabriel AM. Quality Healthcare from the Nurses’ Perspective.
University of Saskatchewan; 2013.
-
[6] Alligood M. Nursing theorists and theirworks. 8 th. St Louis
Missouri: Mosby Elsevier.; 2014.
-
[7] Hendrich A.L., “Empirical data mining: Conservation of nursing energy and care capacity in medical-surgical hospital work environments”, Loyola Univ Chicago, 2011.
-
[8] Fawcett J., DeSanto-Madeya S., “Contemporary Nursing Knowledge: Analysis and Evaluation of Nursing Models and Theories”, Philadelphia: Davis Company, 2013.
-
[9] Schaefer K., “The conservation models. In: Alligood M, editor. Nursing theorists and their works”, Philadelphia: Elsevier Missouri, 2014.
-
[10] Mock V., St. Ours C., Hall S, Bositis A., “Tillery M, Belcher A, et al. Using a conceptual model in nursing research - Mitigating fatigue in cancer patients”, J Adv Nurs, 2007.
-
[11] Nursalam, Effendi F., “Nursing Management Applications in Professional Nursing Practice”, Jakarta: Salemba Medika, 2014.
-
[12] Rias Y.A., Rosa E.M., Yuniarti F., “Action Research: Pengembangan Model Konservasi Discard Planning Terstruktur terhadap Individual and Family Self Management Diabetic Foot Ulcer”, Muhammadiyah J Nurs, 2016.
Discussion and feedback