The Effect of Ethics and Work Environment on Loyalty Through Employee Satisfaction and Commitment
on
160 Matrik: Jurnal Manajemen, Strategi Bisnis dan Kewirausahaan Vol. 15, No. 1, Februari 2021
MATRIK: JURNAL MANAJEMEN, STRATEGI BISNIS DAN KEWIRAUSAHAAN
Homepage: https://ojs.unud.ac.id/index.php/jmbk/index
Vol. 15 No. 1, Februari (2021), 160-166
The Effect of Ethics and Work Environment On Loyalty Through
Employee Satisfaction And Commitment
Sheila Ayu Pramesti Permatasari1), Ririn Tri Ratnasari2),
Bambang Hadi Santoso3)
1,2) Faculty of Economics and Business, Universitas Airlangga, Surabaya, Indonesia
3) Faculty of Economics and Business, STIESIA, Surabaya, Indonesia
email: dewi_hanggraeni@yahoo.com


SINTA 2
DOI : https://doi.org/10.24843/MATRIK:JMBK.2021.v15.i01.p14
ABSTRACT
This study aims to testing and analyzing whether work ethics and work environment variables had a affect on employee loyalty through job satisfaction and employee commitment to Nurul Hayat Surabaya employees. Data collection in this study used a questionnaire with a total sample of 75 employees at the Nurul Hayat Surabaya Foundation. Criteria for respondents in this study were employees of the Nurul Hayat Surabaya foundation who had worked more than one year. Sampling uses Non-Probability Sampling with saturated sampling technique or often also called a census. This research uses a quantitative approach with SEM Partial Least Squares analysis method. Exogenous variables in this study are work ethics and work environment, mediating variables used are employee satisfaction and commitment, while the endogenous variables used are employee loyalty.The findings of this study indicate that the intervening variable, namely job satisfaction, does not significantly influence endogenous variables, namely the employee loyalty of the Nurul Hayat Foundation in Surabaya and employee commitment has a significant effect on the endogenous variable, namely the employee loyalty of the Nurul Hayat Foundation in Surabaya. Exogenous variables of work ethics and work environment have a significant effect on endogenous variables, namely employee loyalty of Nurul Hayat Foundation, Surabaya. Suggestions for further research are expected to increase the scope of research subjects with the same characteristics of respondents.
Keyword: ethics, environment, loyalty, satisfaction, commitment
Pengaruh Etika Dan Lingkungan Kerja Terhadap Loyalitas Melalui Kepuasan Dan Komitmen Karyawan
ABSTRAK
Penelitian ini bertujuan untuk menguji dan menganalisis apakah variabel etika kerja dan lingkungan kerja berpengaruh terhadap loyalitas karyawan melalui kepuasan kerja dan komitmen karyawan pada karyawan yayasan Nurul Hayat Surabaya. Pengambilan data dalam penelitian ini menggunakan kuesioner dengan total sampel 75 karyawan di yayasan Nurul Hayat Surabaya. Kriteria responden dalam penelitian ini adalah karyawan yayasan Nurul Hayat Surabaya yang sudah bekerja minimal satu tahun. Pengambilan sampel menggunakan NonProbability Sampling dengan teknik sampling jenuh atau sering disebut juga sensus. Penelitian ini menggunakan pendekatan kuantitatif dengan metode analisis SEM Partial Least Squares. Variabel eksogen dalam penelitian ini adalah etika kerja dan lingkungan kerja, variabel mediasi yang digunakan adalah kepuasan dan komitmen karyawan, sedangkan variabel endogen yang digunakan adalah loyalitas karyawan. Hasil penelitian ini menunjukkan bahwa variabel intervening yaitu kepuasan kerja tidak berpengaruh terhadap variabel endogen yaitu loyalitas karyawan yayasan Nurul Hayat Surabaya dan komitmen karyawan berpengaruh terhadap variabel endogen yaitu loyalitas karyawan yayasan Nurul Hayat Surabaya. Variabel eksogen etika kerja dan lingkungan kerja berpengaruh terhadap variabel endogen yaitu loyalitas karyawan yayasan Nurul Hayat Surabaya.
Kata kunci: operational risk, internal fraud, perbankan
INTRODUCTION
Human resource management (HRM) is part of organizational management that focuses on the elements of human resources. Arifin and Fauzi (2007) explain that, HRM is the science and art of regulating the relationships and roles of the workforce to be effective and efficient in helping the realization of company, employee and community goals. The long-term success of an organization or company depends on its ability to measure the performance of its employees and use the information on the results of these measurements to base efforts to improve performance to always be in accordance with the standards set and demands for a change in the business environment to measure and use measurement results or feedback information is part of the performance evaluation process. This performance process is a complex process and is not easy to carry out properly (Ratnasari and Kirana, 2017; Herianingrum et al., 2019; Sedianingsih et al., 2019; Santoso et al., 2020).
The Islamic work ethic is a set of values or belief systems derived from the Quran and the Sunnah about work and hard work (Shukri and Owoyemi, 2012). Ali and Owaihan (2008) Islamic work ethics is an orientation that shapes and influences the involvement and participation of adherents in the workplace. Islamic work ethics views work as a means to enhance self-interest economically, socially and psychologically, to maintain social prestige, to advance the welfare of society and to reaffirm faith. The initial concept is derived from the Qur'an and Sunnah or the words of the Prophet Muhammad.
Marri (2012) states that Islamic work ethics is the orientation towards work and work as a virtue approach in human life. This Islamic work ethic was originally based on the Qur'an, the teachings of the Prophet which symbolized that hard work causes sin to be forgiven and the inheritance of the four Islamic caliphs. In addition, the people begins to see that the key to the success of a businessis when it touches on the spiritual aspect (Ratnasari et al., 2020). The introduction contains research background, brief description of literature review from previous researches (State of the art) to show the limitation of previous research, the expected goals, the renewal of reseach.
Islamic work environment is the existence of humans around to complement and complement each other in accordance with their respective roles by protecting nature (the environment) and other creatures created by Allah SWT, namely as a caliph (leader) who must use shari'ah values Islam in all its activities in order to achieve happiness in the world and the hereafter (Hasan, 2005; Mustika et al., 2020; Ratnasari and Nadira, 2020).
Job satisfaction is an employee's positive emotional response to a particular job (Zahednezhad et al., 2021). Job satisfaction with one's feelings about their work. This can be seen from the positive attitude of employees towards work and all things related in the conversation environment (Lailatirrohmah, 2014; Ratnasari et al., 2020). Companies that can provide an image that is liked by their employees, will effectively increase the positive attitude and employee satisfaction (Hayati and Ratnasari, 2020). Menurut Toropova et al. (2021), There is an influence between workplace conditions on job satisfaction. Job satisfaction is an important thing given by individuals in their work. Each individual worker has different differences, then the level of satisfaction is different, so the level of job satisfaction is also different - the high and low levels of job satisfaction can have different effects.
Yudha (2014) refers to employee commitment as another term of organizational commitment and organizational commitment to the behavioral dimension that can be used to assess employee's inclination to survive as a member of the company. Employee commitment does not just appear within.
Employee loyalty is a psychological condition that characterizes employee relations with the organization, and has implications for the decision to continue or stop membership in the organization (Hart and Thompson, 2007). These definitions indicate that loyalty is a feeling and behavior of employees who adhere to the organization where they work. Loyal employees
tend to have strong beliefs in accepting organizational values and goals and have a strong urge to remain in the organization (Chang et al. 2010; Ratnasari et al., 2020). Loyalty is an attitude of loyalty shown by someone through service and responsibility with the best behavior. In carrying out work activities employees will not be separated from loyalty and work attitude, so that the employee will always carry out the work well. Employees feel a deep pleasure towards the work done (Anwar, 2004). Employee loyalty can also be seen in the context of equality regarding reciprocity between employees and leaders (Gupta and Mikkilineni, 2018; Ratnasari et al. 2020).
The Relationship between Islamic Work Ethics to Job Satisfaction
Rokhman (2010) and Marri et al (2012) describes Islamic work ethic has a positive affect on job satisfaction. Haroon, Zaman and Rehman (2012) in their research stated that there is a relationship between Islamic work ethics and job satisfaction. Based on the description above, the following hypothesis can be formulated:
H1: Islamic Work Ethics has an effect on job satisfaction.
The Relationship between Islamic Work Environment to Employee Commitment
Zahroh (2018) states that there is a relationship between the work environment and employee commitment. Communication, social interaction, and compromise have a significant effect on performance (Ratnasari et al., 2018). The work environment is one of the factors that influence employee work commitment because one important role that must be emphasized by a company in order to achieve its goals is to create a work environment, both the physical work environment and the non-physical work environment. Like the perceptions of employees about the work environment they get so that employees can provide different assessments of all aspects of the work environment. If the perception shown by the employee is good, it will affect the employee's performance well because it can make the employees feel more comfortable and pleasant with a good working environment, while if the perception shown by the employee is bad then the performance of the employee will also decrease, the situation will affect employee work commitments (Wang et al 2014; Suseno and Sugiyanto 2010; Rahmawanti et al., 2014). Employee commitment is encouraged by the conditions of a fair work environment for employees, the higher the employee is valued, the higher the commitment of the employees at the company.
H2: Islamic work environment has an effect on employee commitment.
The Relationship between Islamic Work Ethics and Employee Loyalty
Ali and Al-Kazemi (2007) stated that there is a relationship between Islamic work ethics and employee loyalty.
H3: Islamic work ethics significantly has an affect on employee loyalty
The Relationship between Islamic Work Environment on Employee Loyalty
Kristanto (2017) states that the work environment has a positive effect on loyalty.
H4: Islamic work environment has an effect on employee loyalty.
The Relationship between Job Satisfaction and Employee Loyalty
Increasing the quantity and quality of Human Resources in Islamic-based companies the key. Empowerment of employees' abilities and knowledge is part of intellectual capital. the direction of business development no longer refers to the ability of physical capital. However, also in all abilities (Kinanti et al., 2020). Matzler and Renzl (2006) states that there is a relationship between job satisfaction and employee loyalty. Farrukh, M., Kalimuthuan, R., and
Farrukh, S. (2019) states that there is a relationship between job satisfaction and employee loyalty.
H5: Job satisfaction has an effect on employee loyalty.
The Relationship between Employee Commitments to Employee Loyalty
Suhendi (2010) states that employee loyalty in a company is shown by the commitment of employees within the company, commitment in the organization can be formed due to several factors, namely from themselves and the organization. Hardianty (2014) states that employee commitment has a significant effect on employee loyalty.
H6: Employee commitment has an effect on employee loyalty
RESEARCH METHODS
The approach used in this research is a quantitative approach. Yusuf (2014: 59) explains quantitative approach is an approach that focuses on proving hypotheses or questions that need to be answered, to guide the direction and achievement of research objectives.
The sampling technique used by the writer is nonprobability sampling. According to Sugiyono (2012: 84) nonprobability sampling is: "Sampling techniques that do not provide equal opportunities / opportunities for members of the population to be selected as samples". The type of nonprobability sampling used in this study is saturated sampling or often called census. According to Anshori and Iswati (2009: 106) saturation sampling is a sampling technique where all members of the population are used as samples.
Thus in this study using a saturated sample by taking all members of the population, namely all permanent employees of the Nurul Hayat Foundation in Surabaya who have worked for at least one year and obtained 75 permanent employees. This is intended so that respondents have a more complete perception and sufficient work experience so that they are able to give a good assessment.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
At this stage an estimation value for the path relationship in the structural model obtained by the bootstrapping procedure will be seen. Values that are considered significant are if the statistical t value is greater than 1.65 (significance level of 5%). Following are the bootstrapping test results derived from SmartPLS processed data:
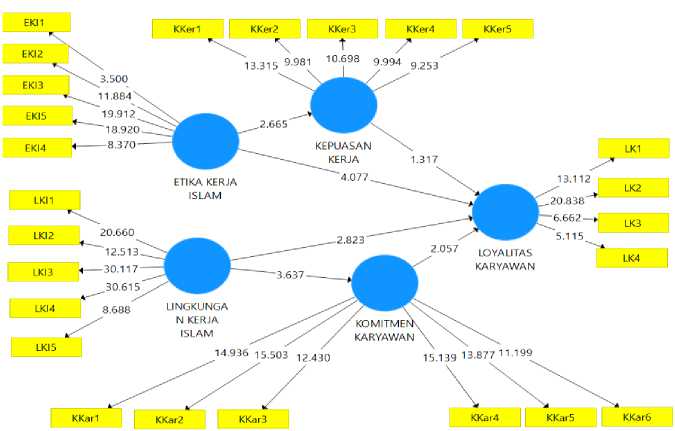
Figure 1. Bootstrapping Constructions
Source: SEM PLS Results
Table 1. Path Coefficient Value Results
|
Hypothesis |
Variable |
Original Sample (O) |
t statistic (|O/STERR|) |
KET |
|
H1 |
Islamic Work Ethics -> Job Satisfaction |
0,312 |
2,855 |
Significant |
|
H2 |
Islamic Work Environment -> Employee Commitment |
0,369 |
3,684 |
Significant |
|
H3 |
Islamic Work Ethics -> Employee Loyalty |
0,440 |
4,229 |
Significant |
|
H4 |
Islamic Work Environment -> Employee Loyalty |
0,345 |
3,530 |
Significant |
|
H5 |
Job satisfaction -> Employee Loyalty |
0,161 |
1,233 |
Not Significant |
|
H6 |
Employee Commitment -> Employee Loyalty |
0,273 |
1,859 |
Significant |
Source: SEM PLS Results
Based on Table 1 above, you can see the results of the hypothesis test showing, Hypothesis 1, namely the influence of Islamic work ethics on job satisfaction. There is an influence on Islamic work ethics variables on job satisfaction. The results of the calculation of the parameter coefficient between Islamic work ethics and job satisfaction indicate a positive influence (0.312) with a statistical T value of 2.855> 1.65. With results like this, the H1 research hypothesis is supported. Hypothesis 2, namely the influence of the Islamic work environment on employee commitment. There is an influence on the Islamic work environment variables on employee commitment. The results of the calculation of the parameter coefficient between the Islamic work environment and employee commitment shows a positive influence (0.369) with a statistical T value of 3.684> 1.65. With results like this, the H2 research hypothesis is supported. Hypothesis 3: the influence of Islamic work ethics on employee loyalty. There is an influence on Islamic work ethics variables on employee loyalty. The results of the calculation of the parameter coefficient between Islamic work ethics and employee loyalty shows a positive influence (0.440) with a statistical T value of 4.229> 1.65. With results like this, the H3 research hypothesis is supported. Hypothesis 4: the influence of the Islamic work environment on employee loyalty. There is an influence on Islamic work environment variables on employee loyalty. The results of the calculation of the parameter coefficient between the Islamic work environment and employee loyalty shows a positive influence (0.345) with a statistical T value of 3.530> 1.65. With results like this, the H4 research hypothesis is supported. Hypothesis 5 is the effect of job satisfaction on employee loyalty. There is no influence on job satisfaction variables on employee loyalty. The results of the calculation of the parameter coefficient between job satisfaction and employee loyalty showed a negative influence (0.161) with a statistical T value of 1.233 <1.65. With results like this, the H5 research hypothesis is not supported. Hypothesis 6 is the effect of employee commitment on employee loyalty. There is an influence on employee commitment variables on employee loyalty. The results of the calculation of the parameter coefficient between employee commitment and employee loyalty shows a positive influence (0.273) with a statistical T value of 1.859> 1.65. With results like this, the H6 research hypothesis is supported.
CONCLUSION
Based on the results of data processing using Part Least Square (PLS) and the discussion that has been done before, the following conclusions can be drawn: There is a influence of Islamic work ethics on job satisfaction and employee loyalty. There is an influence of the Islamic work environment on employee commitment and employee loyalty. But there is
no influence of job satisfaction on employee loyalty. Based on these results, the fifth hypothesis is rejected. There is an relationship of employee commitment on employee loyalty.
REFERENCES
Ali, A. J., & Al-Kazemi, A. A. (2007). Islamic work ethic in Kuwait. Cross Cultural Management: An International Journal, 14(2), 93–104.
https://doi.org/10.1108/13527600710745714
Chang, C. C., Chiu, C. M., & Chen, C. A. (2010). The effect of TQM practices on employee satisfaction and loyalty in government. Total Quality Management and Business Excellence, 21(12), 1299–1314. https://doi.org/10.1080/14783363.2010.530796
Anwar Prabu Mangkunegara. 2004. Manajemen Sumber Daya Manusia Perusahaan. Bandung: PT Remaja Rosdakarya.
Arifin, J., Fauzi, A. 2007. Aplikasi Excel dalam Aspek Kuantitatif Manajemen Sumber Daya Manusia. Jakarta: PT Elex Media Komputindo.
Hasan, Muhammad Tolhah. 2005. Islam Dalam Persepektif Sosio kultural. Jakarta: Lantabora Press
Hayati, A., & Ratnasari, R. T. (2020). Factors affecting muslim consumer decisions on choosing Islamic hotel. Hamdard Islamicus, 43(2), 619–638.
Herianingrum, S., Drasmawita, Fitri, Ratnasari, Ririn Tri, Fadlillah, Hanif. (2019). The Social Function Of Imi’s In The Exemption Of Micro Business Loans. Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling, 35(88), 819-831
Kinanti, R. A., Ratnasari, R. T., Robani, A., Widiastuti, T., & Sukmana, R. (2020). Intellectual capital and islamic sosial reporting index: The case of Indonesian islamic banking. Humanities and Social Sciences Reviews, 8(4), 728–736.
https://doi.org/10.18510/hssr.2020.8472
Kirana, K.C., Ratnasari, R.T. 2017. Evaluasi Kinerja Sumber Daya Manusia (SDM). Yogyakarta: Gosyen Publishing.
Marri, M. Y. K., Sadozai, A. M., Zaman, H. M. F., & Ramay, D. M. I. (2012). The Impact of Islamic Work Ethics on Job Performance and Organizational Commitment: A study of agriculture sector of Pakistan. Proceedings of 5th Asia-Pacific Business Research Conference, 2(12), 1–12.
Matzler, K., & Renzl, B. (2006). The relationship between interpersonal trust, employee satisfaction, and employee loyalty. Total Quality Management and Business Excellence, 17(10), 1261–1271. https://doi.org/10.1080/14783360600753653
McShane, Steven L., dan Glinow Von, Mary Ann. 2016. Organizational Behavior. 3rd edition. USA: McGrawHill.
Mustika, H., Eliyana, A., Agustina, T. S., & Ratnasari, R. T. (2020). Knowledge sharing behavior between self-leadership and innovative behavior. Journal of Security and Sustainability Issues, 9(May), 148–157. https://doi.org/10.9770/JSSI.2020.9.M(12)
Muttie ur, R., Rabbia, I., Namra, T., Zara, I., Uzma, N., & Ume, S. (2012). The Impact of Job Stress on Employee Job Satisfaction: A Study on Private Colleges of Pakistan. Journal of Business Studies Quarterly, 2(3), 50–56.
Pi, W., & Huang, H. (2011). Effects of promotion on relationship quality and customer loyalty
in the airline industry: The relationship marketing approach. African Journal of Business Management, 5(11), 4403–4414. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJBM10.1426
Ratnasari, R. T., Gunawan, S., Qudzi Fauzi, M., & Fitrisia Septiarini, D. (2018). Patient Intimacy and Innovation Development to Improve Health Service Performance. International Journal of Engineering & Technology, 7(2.29), 338.
https://doi.org/10.14419/ijet.v7i2.29.13649
Ratnasari, R. T., Gunawan, S., bin Abu Talib, J., Herianingrum, S., Widiastuti, T., & Septiarini, D. F. (2020). The Moderating Effects of Gender between Patient Intimacy, Trust, and Loyalty. International Journal of Innovation, Creativity and Change, 12(10), 1–16.
Ratnasari, R. T., Gunawan, S., Mawardi, I., & Kirana, K. C. (2020). Emotional experience on behavioral intention for halal tourism. Journal of Islamic Marketing.
https://doi.org/10.1108/JIMA-12-2019-0256, Vol. ahead-of-print No. ahead-of-print.
Ratnasari, R. T., Gunawan, S., Septiarini, D. F., Rusmita, S. A., & Kirana, K. C. (2020). Customer satisfaction between perceptions of environment destination brand and behavioural intention. International Journal of Innovation, Creativity and Change, 10(12), 472–487.
Ratnasari, R. T., Rahmandani, R. (2020). The Correlation of Financial Development on Energy Consumption: A Study Case in Indonesia. Test Enginearing & Management, 83 (March - April), 3560-3564.
Ratnasari, R. T., Ula, U. F., & Sukmana, R. (2020). Can store image moderate the influence of religiosity level on shopping orientation and customers’ behavior in Indonesia? Journal of Islamic Accounting and Business Research, 12(1), 78–96.
https://doi.org/10.1108/JIABR-01-2017-0006.
Santoso, A., Erdawati, Ratnasari, R. T., Palupiningtyas, D., & Balaka, M. Y. (2020). Determinants of social media use by handicraft industry of Indonesia and its impact on export and marketing performance: An empirical study. International Journal of Innovation, Creativity and Change, 12(9), 1–21.
Sedianingsih, Ratnasari, R. T., Prasetyo, A., & Hendarjatno. (2019). Antecedents of recommendation and repurchase intention on medical tourism. Opcion, 35(Special Issue 23), 1277–1300.
Shukri Ahmad, & Musa Yusuf Owoyemi. (2012). The Concept of Islamic Work Ethic: An Analysis of Some Salient Points in the Prophetic Tradition. International Journal of Business and Social Science, 3(20), 116–123. http://repo.uum.edu.my/7440/
Toropova, A., Myrberg, E., & Johansson, S. (2021). Teacher job satisfaction: the importance of school working conditions and teacher characteristics. Educational Review, 73(1), 71–97. https://doi.org/10.1080/00131911.2019.1705247
Zahednezhad, H., Hoseini, M. A., Ebadi, A., Farokhnezhad Afshar, P., & Ghanei Gheshlagh, R. (2021). Investigating the relationship between organizational justice, job satisfaction, and intention to leave the nursing profession: A cross-sectional study. Journal of Advanced Nursing, 77(4), 1741–1750. https://doi.org/10.1111/jan.14717

Discussion and feedback