Recommendation Decision Support System Smartphone Selection By Method Web-Based Simple Additive Weighting (SAW)
on
p-ISSN: 2301-5373
e-ISSN: 2654-5101
Jurnal Elektronik Ilmu Komputer Udayana
Volume 9, No 2. November 2020
Recommendation Decision Support System Smartphone Selection By Method Web-Based Simple Additive Weighting (SAW)
I Nengah Aryadi Suputraa1, I Gusti Agung Gede Arya Kadyanan, S.Kom, M.Koma2
aInformatics Department, Faculty of Math and Science, University of Udayana South Kuta, Badung, Bali, Indonesia 1aryadisuputra20@gmail.com
Abstract
Smartphones are already a must-have communication technology to make it easier to live your daily life. However, with so many choices can make consumers confused in determining the appropriate choice. The Simple Additive Weighting (SAW) method can help in the simple process that can be applied to decision-making cases such as in smartphone selection recommendations with a wide range of attributes. In the case of this study, the results were obtained that the Realme X3 Superzoom smartphone scored the highest preference with a value of 22. With this research, it is hoped that this decision support system can help potential consumers to more easily consider in the selection of smartphones that suit their wishes or needs
Keywords: Smartphone, Simple Additive Weight, Decision Support System, Recommendations, Web-based
The application of communication technology such as smartphones, is already a must-have to make it easier to live daily life. This is due to the high demand for the proper and rapid exchange of information. With the higher demand required, more and more companies are competing against each other to provide the level of security and comfort that consumers are most interested in. However, these circumstances can make consumers confused in determining their choice. This is also supported by the many factors to be considered in smartphone purchases.
In previous research, there is a smartphone selection recommendation system using Collaborative filtering and Content-based filtering methods combined using Mixed Hybrid and using rating as a reference in providing recommendations. The difference is that this study uses Simple Additive Weighting and provides a predictive value for the results of its recommendations. There is also a research system supporting mobile selection decisions with the web-based SAW method. A fundamental difference is found in the parameters of the criteria, sub-criteria, and data used in the system[1].
SAW is a weighted calculation method or method that provides certain weighted criteria so that each sum value of the weight of the result obtained will be the final decision [2]. The advantages of SAW with a simple and simple warking process can be applied to decision-making cases such as in smartphone selection recommendations with a wide range of attributes[3][4]
The hope is that this research can make it easier for consumers who want to buy a smartphone with some established criteria and provide the results in the form of desired smartphone data information to help in the decision-making to determine which smartphone to buy.
In this research, the system creation model used a linear sequential model or commonly called the waterfall model. The scope of the waterfall model process must complete a stage until it is completed before moving on to the next stage[5]. The waterfall model framework can be seen in Figure 1.
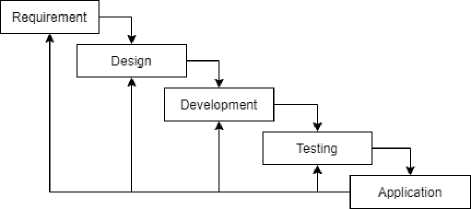
Figure 1 Waterfall diagram
Starting with the specification of needs, then to the planning and design stage. Specifications of requirements at the previous stage will be studied at this stage. Continued at the manufacturing and testing stage to make the application complete. The flowchart of the smartphone recommendation system can be seen in figure 2.
Star⅜
∕ Initialization criteria (C) and ∖ ∖ criteria weight ∕ ' '
( initialization smartphone y
; + ∕
/Price, internal memory, ∕ ∕ camera, processor, ram, ∕ ∕ operating system ∕
Calculating the price difference, internal memory, camera, processor, ram, operating system from input with prices, internal memory, camera, processor, ram. smartphone operating system
Normalization of the matrix
The sum of the normalized matrix multiplication with the criterion weight value
∕ Smartphone ranking ∕
Finish
Figure 2 Smartphone recommendation system flowchart
Figure 2 is the main process of the system. When the system starts (1), the initialization of the criteria and weights of each of the specified criteria (2) is performed. After that, the initialization of the smartphone was used in the study (3). Then enter the values of the initialized attribute (4), accompanied by calculating the difference from the previous value input with the value of the rule that has been created, then the difference value is converted back into the actual ilia according to the conduction of the difference value(5). If already, normalize the conversion result of the previous value on each criteria and alternative smartphone (6). The summation process of the
previous normalized matrix value with the weight value of each specified criterion (7). The process displays the result of the summation process of the previous normalized matrix value with the weight value of each criterion and makes the highest value of the process as the best smartphone (8). And the program is finished (9).
-
a. Criteria Table
Criteria data that contains code, criteria, descriptions, weights. The weight of the criteria determines how important those criteria are. The criteria attribute consists of benefit or cost, where the benefit means the greater the value the better, while the smaller the cost the better the value.
b. Criteria weight value
Table 1 Criteria Table
|
Code |
Criteria |
Description |
Weight |
|
C1 |
Price |
Cost |
5 |
|
C2 |
Internal memory |
Benefit |
4 |
|
C3 |
Camera |
Benefit |
3 |
|
C4 |
Processor |
Benefit |
4 |
|
C5 |
RAM |
Benefit |
4 |
|
C6 |
Operating System |
Benefit |
2 |
Table 2 Criteria weight value
|
Criteria |
Sub Criteria |
Weight |
|
Price |
<2 Million |
5 |
|
2-4 Million |
4 | |
|
4-6 Million |
3 | |
|
6-8 Million |
2 | |
|
>8 Million |
1 | |
|
Internal memory |
>128 GB |
5 |
|
64-128 GB |
4 | |
|
16-64 GB |
3 | |
|
4-16 GB |
2 | |
|
0-4 GB |
1 | |
|
Camera |
> 32 MP |
5 |
|
24-32 MP |
4 | |
|
16-24 MP |
3 | |
|
5-16 MP |
2 | |
|
0-5 MP |
1 | |
|
Processor |
Octacore |
5 |
|
Quadcore |
3 | |
|
Dual-core |
1 | |
|
RAM |
>8 GB |
5 |
|
6-8 GB |
4 | |
|
3-4 GB |
3 | |
|
2-3 GB |
2 | |
|
0-1 GB |
1 | |
|
> Android 9.0 |
5 |
|
Operating System |
Android 8.0 - Android 9.0 |
4 |
|
Android 7.0 - Android 8.0 |
3 | |
|
Android 6.0 - Android 7.0 |
2 | |
|
<Android 6.0 |
1 |
In this study, case studies will be used with the following:
-
a. Alternative data Options
The Alternate value records the value of each alternative based on all criteria data.
(xij max
l xij
min
i Xlj
Xij
Table 3 Alternative data Options
|
Criteria |
C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
C4 |
C5 |
C6 |
|
Oppo Reno |
4.999.000 |
128 |
64 |
OctaCore |
8 GB |
Android 10 |
|
XIAOMI NOTE 9 PRO |
3.899.000 |
128 |
64 |
OctaCore |
8 GB |
Android 10 |
|
Samsung Galaxy Tab A 8 plus |
4.499.000 |
32 |
8 |
OctaCore |
3 GB |
Android 9 |
|
Realme X3 SUPER ZOOM |
7.999.000 |
256 |
64 |
OctaCore |
12 GB |
Android 10 |
|
Vivo V19 |
4.999.000 |
128 |
48 |
OctaCore |
8 GB |
Android 10 |
b. Weight value of each criterion
Based on the table adjusts to the weight value of the criteria, thus obtaining results such as table 4.
Table 4 Weight value of each criterion
|
Alternative |
C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
C4 |
C5 |
C6 |
|
A1 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
5 |
4 |
5 |
|
A2 |
4 |
4 |
5 |
5 |
4 |
5 |
|
A3 |
3 |
3 |
2 |
5 |
2 |
4 |
|
A4 |
2 |
5 |
5 |
5 |
5 |
5 |
|
A5 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
5 |
4 |
5 |
c. Matrix Normalization
To normalize the table at the analysis stage, we need to understand formula 1, so that results such as table 5 and table 6 are obtained[3].
if j is a benefit attribute
(1)
if j is a cost attribute
Table 5 Matrix normalization
|
Alternative |
C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
C4 |
C5 |
C6 |
|
A1 |
0.66666666666667 |
0.8 |
1 |
1 |
0.8 |
1 |
|
A2 |
0.5 |
0.8 |
1 |
1 |
0.8 |
1 |
|
A3 |
0.66666666666667 |
0.6 |
0.4 |
1 |
0.4 |
0.8 |
|
A4 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
|
A5 |
0.66666666666667 |
0.8 |
1 |
1 |
0.8 |
1 |
d. Matrix Prefensi
Table 6 Matrix present value
|
Alternative |
C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
C4 |
C5 |
C6 |
|
A1 |
3.3333333333333 |
3.2 |
3 |
4 |
3.2 |
2 |
|
A2 |
2.5 |
3.2 |
3 |
4 |
3.2 |
2 |
|
A3 |
3.3333333333333 |
2.4 |
1.2 |
4 |
1.6 |
1.6 |
|
A4 |
5 |
4 |
3 |
4 |
4 |
2 |
|
A5 |
3.3333333333333 |
3.2 |
3 |
4 |
3.2 |
2 |
-
a. Admin login page
This page is a form that admins must input to access the system.
Figure 3 Admin login page
b.
Criteria setting page
On this page, admins can specify criteria that have benefit/cost attribute values. Admins can also choose the criteria of each attribute from very low to very high.
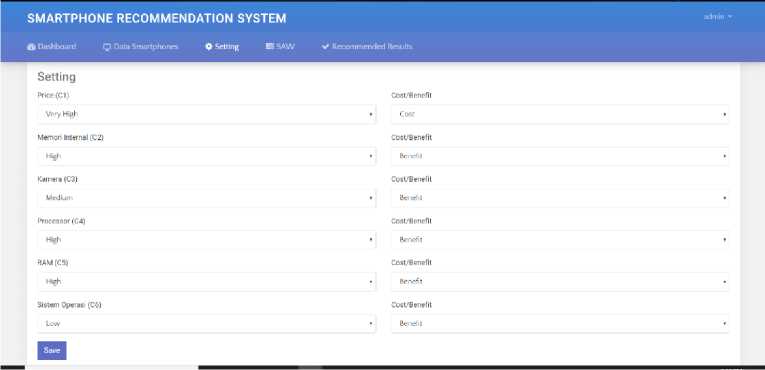
Figure 4 Criteria setting page
-
c. Matrix value page
On this page displays the matrix value that has been obtained.
SMARTPHONE RECOMMENDATION SYSTEM adπ*∙ *
ft Dashboard Q Data Smartphones φ Setting ≡ SAW ∙/ Recommended Results
MATRIX VALUE
Show 10 » entries Search:
# T Merk Price(Cl) InternaIMeniory(Cl) Camera (C3) Processor(CA) RAM{C5) Operating System (C6).
3 SamsijngGaIaxyTabABpIus 3 3 2 5 24
4 Realms X3 SUPER ZOOM 7 5 5 5 55
SlKJWingIio 5 of 5 CTIiries Previous Q Next
2020 © Wireless Sensor Network
Figure 5 Matrix value page
-
d. Matrix Normalization Page
This page displays matrix normalization based on formula 1.
SMARTPHONE RECOMMENDATION SYSTEM *"*∙~
ft Dashboard ∣□ Data Smartphones Φ Setting ≡ SAW √, Recommended Results
MATRIX NORMALIZATION
Show 10 r entries Search:
# ' Merk Price(CI) InternaIMemory(CZ) Camera (C3) Processor (C4) RAM(CS) OperatIngSystem(Cft)
1 OppoReno 0.66666666666667 O.R 1 1 Ofl1
2 XIAOMI NOTE 9 PRO 0.5 0.8 1 1 0.81
3 SamsungcalaxyTabASpIus 0.66666666666667 0.6 ∣ 0.4 1 0.40 8
4 Rcalme X3 SUPER ZOOM I 1 1 111
5 Viv⅛VI9 0.66666666666667 0.8 1 1 0.81

2020 © Wireless Sensor Network
Figure 6 Matrix Normalization Page
-
e. Recommended Results Page
The last page is the recommendation results page. On this page displays the order and results of smartphone recommendations.
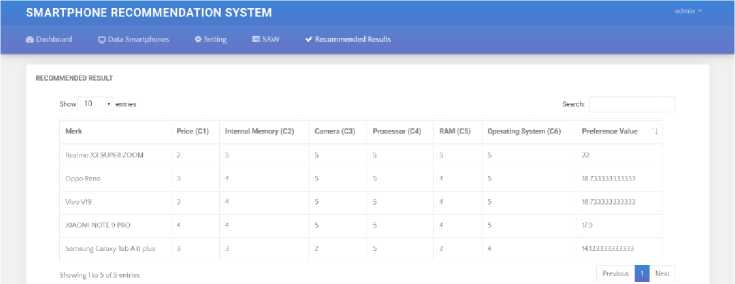
2020©Wireless Serrsor Network
Figure 7 Recommended Results Page
Based on the background and the above problems, it can be concluded that the system successfully calculates and processes by simple additive weighting method in determining the selection of smartphones to fit the specified criteria and weights such as price, internal memory,
RAM, camera, processor, and operating system. In this study obtained the results that the Smartphone Realme X3 Superzoom got the highest preference score (22). With this research, it is hoped that this decision support system can help potential consumers to more easily consider in the selection of smartphones that suit their wishes or needs.
Referencess
-
[1] A. Amijaya, F. Ferdinandus, and M. Bayu, “Sistem Pendukung Keputusan Pemilihan
Handphone Dengan Metode Simple Additive Weighting Berbasis WEB,” CAHAYAtech, vol. 8, no. 2, p. 102, 2019, doi: 10.47047/ct.v8i2.47.
-
[2] davis dalam Hartono, “Dalam Sistem Pendukung Keputusan Promosi,” Metod. yang
digunakan dalam menentukan promosi Promosi ini Simple Addit. Weight (SAW). Di mana Metod. ini adalah Metod. penghitungan tertimbang atau Metod. yang menyediakan Kriter. tertentu yang berbobot sehingga setiap nilai jumlah dari bobot dari has, no. 1, pp. 37–45, 2016.
-
[3] H. Harsiti and H. Aprianti, “Sistem Pendukung Keputusan Pemilihan Smartphone dengan
Menerapkan Metode Simple Additive Weighting (SAW),” JSiI (Jurnal Sist. Informasi), vol. 4, pp. 19–24, 2017, doi: 10.30656/jsii.v4i0.372.
-
[4] A. Mukhlasin, “PROSIDING SEMINAR NASIONAL SISFOTEK (Sistem Informasi dan
Teknologi) Sistem Pendukung Keputusan Pemilihan Smartphone Menggunakan Metode Simple Additive Weighting (SAW) Berbasis Web,” no. September, pp. 4–5, 2018, [Online]. Available: http://seminar.iaii.or.id.
-
[5] G. W. Sasmito, “Penerapan Metode Waterfall Pada Desain Sistem Informasi Geografis
Industri Kabupaten Tegal,” J. Inform. Pengemb. IT, vol. 2, no. 1, pp. 6–12, 2017.
This Page is Intentionally Left Blank
220
Discussion and feedback