Web Based Home Learning Application For Basic School Children
on
p-ISSN: 2301-5373
e-ISSN: 2654-5101
Jurnal Elektronik Ilmu Komputer Udayana
Volume 10 No. 1, August 2021
Web Based Home Learning Application For Basic School Children
Gregorius Ericco Jansena1, I Komang Ari Mogia2
aInformatics Department, Faculty of Science and Mathematic, Udayana University Jimbaran, Bali, Indonesia 1Ericcojansen07@gmail.com 2Arimogi@cs.unud.ac.id
Abstract
Currently, technological developments, especially in the field of information technology and computers, are developing very rapidly. In current conditions, the world is shocked by the presence of a deadly virus called the Covid-19 virus. Because of the virus, all human activities are disrupted and even stopped, one of which is teaching and learning activities in schools. With the development of technology like now, we can take advantage of this technology to help students in the learning process at school. Web design is an alternative way to keep the learning process going. With this distance learning process students can still learn and receive the material given.
Keywords: E-Learning, Website, Web Based Learning Method, Basic School Children, Technology
Along with the development of today's technology, it is growing rapidly. There have been many online activities such as buying and selling online, ordering tickets online, etc. In conditions like now the world is shocked by the presence of a very dangerous virus, namely Covid-19 or better known as the corona virus. Because of the virus in all activities such as work, vacation, and learning at school, it becomes obstructed and even stops because they have to follow health protocols that should not be in the crowd Many parties are confused in carrying out activities without direct contact with other people, especially teaching and learning activities in schools. The school is confused about how they can continue to teach their students so that they can learn and learn subject matter without having to meet in person. There is no other way to undergo learning activities except by creating an online learning system. This system can provide information, items, and items carried by the teacher. With the above problems, the author took the initiative to create a web-based online home study system. There are several studies that discuss the use of e-learning learning models, namely Ananda Hadi Elyas's research entitled Using E-Learning Learning Models to Improve Learning Quality. This study aims to see the use of e-learning learning models in improving the quality of learning. The method used in this research is library research (library research). From the discussion it can be denied that the Learning model with virtual classes (e-learning) is a new breakthrough in the field of learning and learning, because it is able to teach how to teach and materials, so as to provide a more consistent quality standard of learning.
XAMPP is an open source software that is used as a stand-alone server (localhost), which consists of a MYSQL database, Apache HTTP server. The name XAMPP stands for X (the placeholder for any operating system), Apache, MySQL, PHP and Perl. This program is available under the GNU General Public License and is free, is an easy-to-use web server that can serve dynamic web page displays.
Source : https://id.wikipedia.org/wiki/XAMPP
Sublime Text is software that is used as a text editor. Sublime text is usually used by programmers, especially by a web developer. This application must be used by a web developer to do their job for coding. Many web developers who use this application, with the presence of colors in coding writing can help a programmer in finding errors in writing coding.
HTML (Hypertext Markup Language) is the standard markup language for documents designed to be displayed in internet browsers. This can be helped by technologies such as Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) and scripting languages such as JavaScript and VBScript. Internet browsers receive HTML documents from a web server or from local storage and turn the documents into multimedia web pages. HTML describes the structure of web pages semantically and the initial cues are included for the appearance of the document.
Source : https://id.wikipedia.org/wiki/HTML
CSS (Cascading Style Sheet) is a rule for arranging several components in a web so that it will be more structured and uniform. Generally, CSS is used to format the appearance of web pages created in HTML and XHTML. CSS can control image size, body color in text, table color, border size, border color, hyperlink color, mouse over color, space between paragraphs, spacing between text, left, right, top, bottom margins, and other parameters. CSS is a style sheet language used to adjust the appearance of documents. With CSS allows us to display the same page with different formats.
Source : https://id.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cascading_Style_Sheets
PHP (Hypertext Prepocessor) is a programming language used for web programming. PHP is the most popular programming language used in creating dynamic websites. A dynamic website is a web whose content can change at any time or according to data stored on the server.
Source : https://id.wikipedia.org/wiki/PHP
SQL (Structured Query Language) is a special programming language for a database management system that uses special instructions in manipulating data to execute commands. SQL plays an important role as instructions that are useful in database management. SQL is a programming language that is important to understand because it can be a relationship for several tables with a database or between databases itself.
Source : https://bootup.ai/blog/pengertian-mysql/
ERD is a diagram that explains the relationship between data objects that have relationships between relations. ERD is used to construct data structures, relationships between data, and to describe it used notations, symbols, charts, and so on. The following
is the ERD database used in this web-based online teaching and learning application system:
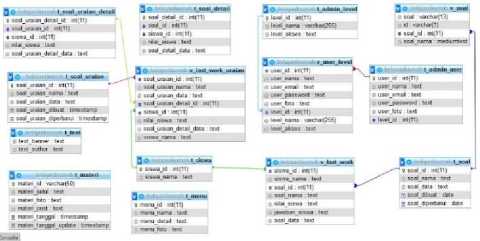
Figure 1. Entity Relationship Diagram online teaching and learning application database
Figure 1 is an ERD image of the online teaching and learning system. Where in the figure there are 14 tables used to store data including data on the number of students, admin data, practice questions, materials, etc. The tables are connected to each other between the primary key and foregn key between the tables.
-
a. Homepage
The homepage is the page that will appear first when someone opens the website.
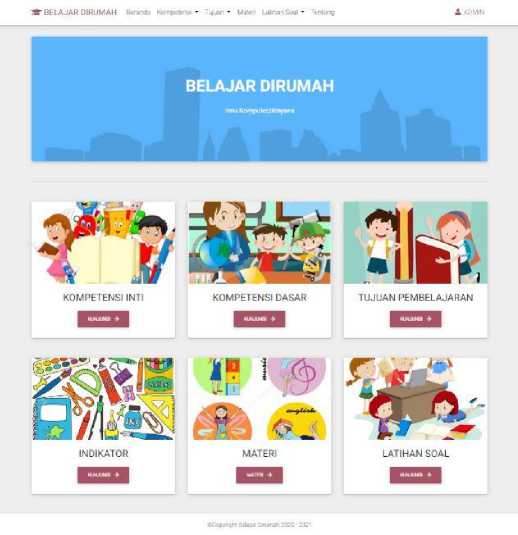
BELAJAR DIRUMAH
Figure 2. Homepage (Students)
On the student homepage, this online teaching and learning website, there are several menus, namely the home menu, competencies, objectives, materials, practice questions, about, and a login page for the admin (teacher). Students can access the menu as needed.
-
b. Core Competencies
Core competencies are the level of ability to achieve Graduate Competency Standards (SKL) that a student must have at each grade level. This menu can only be filled in by the teacher (admin), while students can only read it.
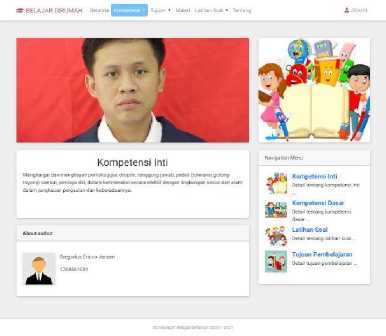
Figure 3. Core Competencies
-
c. Basic Competencies
Basic competence is the minimum learning goal that students must achieve for a subject in each education unit which refers to the core competency. This menu can only be filled in by the teacher (admin), while students can only read it.
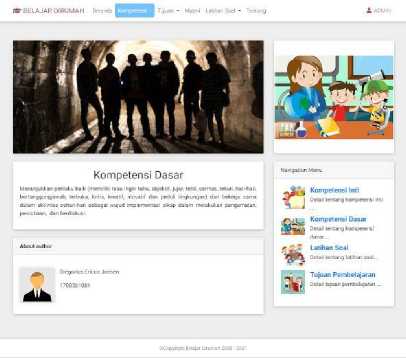
Figure 4. Basic Competencies
-
d. Learning Objectives
Learning objectives are the attainment of behavior or competence in students after participating in learning activities, attaining behaviors or competencies in students after participating in learning activities. This menu can only be filled in by the teacher (admin), while students can only read it.
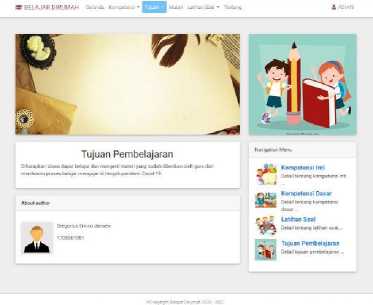
Figure 5. Learning Objectives
-
e. Indicator
Indicators are markers of achieving specific basic competencies that can be used as a measure to determine the achievement of learning objectives. This menu can only be filled in by the teacher (admin), while students can only read it.
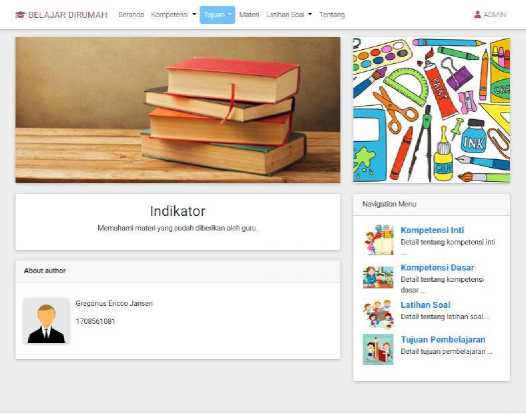
H⅛ji⅛hl Be⅛ja∣ Diiunaft 2020 - 2021
Figure 6. Indicator
-
f. Theory
This page contains materials or modules that the teacher will give to students. Then students can read and perform it.
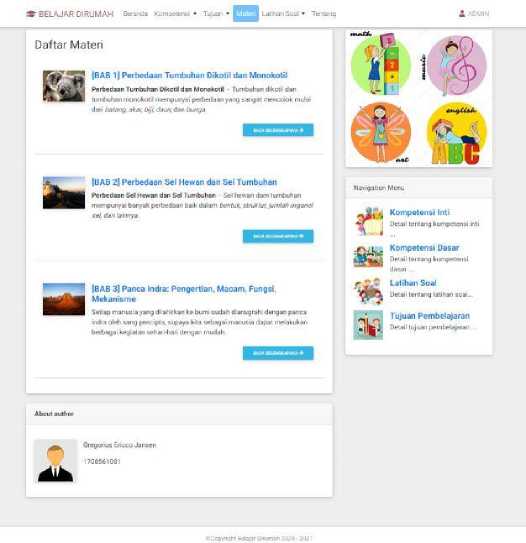
Figure 7. Theory
-
g. Exercises
This menu contains practice questions consisting of multiple choice questions, descriptions, and assessments of the questions that have been worked on.
3.3.
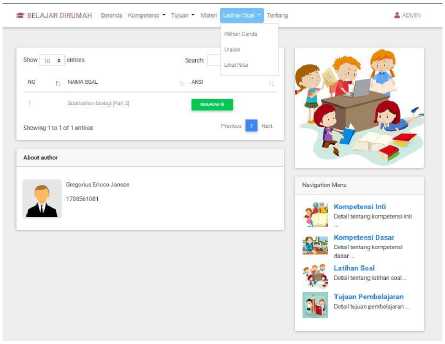
Figure 8. Exercises
Website Design (Teacher or admin)
-
a. Homepage
The homepage is the page that will appear first when someone opens the website.
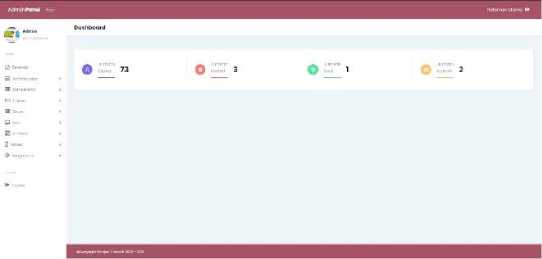
In the
Figure 9. Homepage teacher
teacher or admin homepage, this online teaching and learning website has
several menus, namely administrator, competence, objectives, students, questions, about,
material, settings. These menus are used by the teacher to edit core competencies, basic competencies, objectives, students, practice questions, materials, and other settings.
-
b. Core Conpetencies
Core competencies are the level of ability to achieve Graduate Competency Standards that must be possessed by a student at each grade level. On this menu the teacher can edit the core competencies which will be displayed on the student page on the core competency menu.
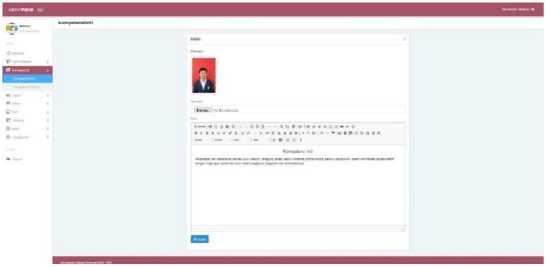
Figure 10. Core Competencies
-
c. Basic Competencies
Basic competence is the minimum learning goal that students must achieve for a subject in each education unit which refers to the core competency. On this menu the teacher can edit the basic competencies which will be displayed on the student page in the basic competency menu.
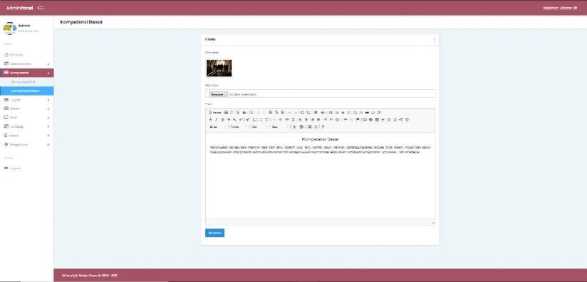
Figure 11. Basic Competencies
-
d. Indicator
Indicators are markers of achieving specific basic competencies that can be used as a measure to determine the achievement of learning objectives. On this menu the teacher can edit the indicators that will be displayed on the student page on the indicator menu.
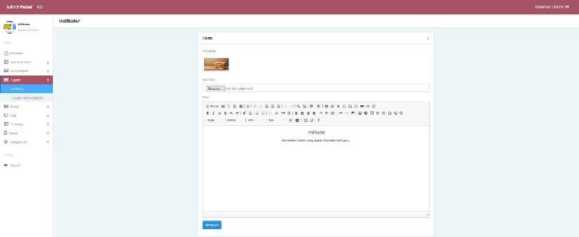
Figure 12. Indicator
-
e. Learning Objectives
This menu is useful for teachers to change learning objectives which will be displayed on the learning objectives website page.
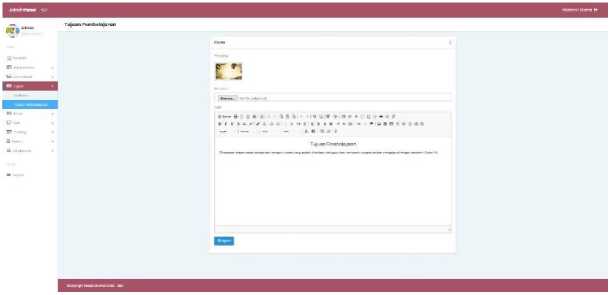
Figure 13. Learning objectives
-
f. Question (Multiple Choice)
This menu is used for the teacher to practice multiple choice questions. The teacher can make questions, multiple choice answers, along with answer keys to check students' answers.
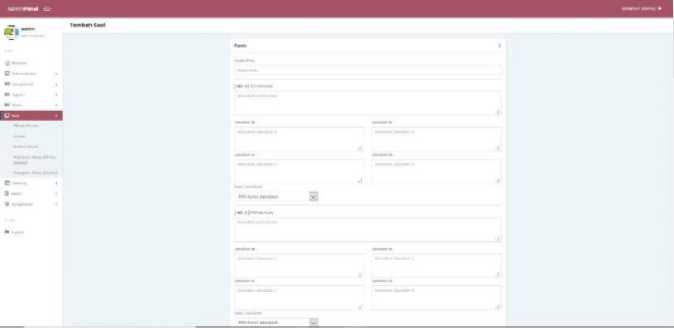
Figure 14. Multiple Choice
-
g. Questions (essay)
In this menu it is used for the teacher to make practice description questions. The teacher is only asked to enter the questions that will be given to students.
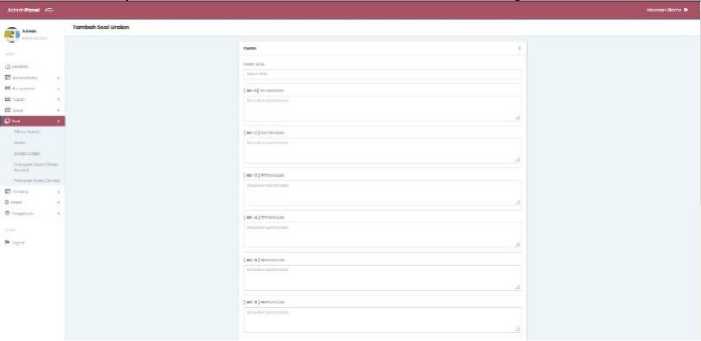
Figure 15. Essay
-
h. About
This page contains the online teaching and learning website page. Starting from the purpose of the web created, benefits, etc. admin or teacher can change this "about" page as you wish.
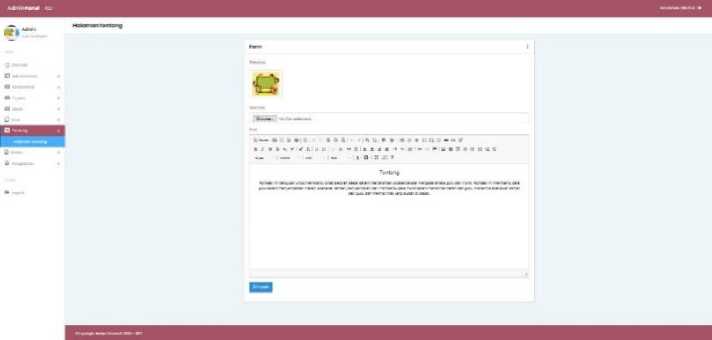
Figure 16. About
-
i. Theory
On this "material" page is used by the teacher to distribute lesson material to students.
Figure 17. Theory
From the discussion above, it can be concluded that this application can simplify the teaching and learning process in elementary schools. Teachers can easily distribute course material, provide practice questions to students, multiple choice questions or descriptions. The menu for multiple choice questions is also equipped with an answer key feature. That way the teacher does not need to check student work because the questions automatically check student work with an answer key that is already available. Students can also easily accept the material and practice questions provided by the teacher. That way the teaching and learning process can be carried out without having to violate health protocols in the midst of a pandemic like now.
References
-
[1] Ariani. Diana, “Komponen Pengembangan E-Learning”, Jurnal Pembelajaran Inovatif, Vol. 1, no. 1, 58 - 65, 2018.
-
[2] Elyas. A. H, “Penggunakan Model Pembelajaran E-Learning Dalam Meningkatkan Kualitas Pembelajaran”, Jurnal Warta Edisi : 56, 2018.
-
[3] Silahuddin, “Penerapan E-Learning Dalam Inovasi Pendidikan”, Jurnal Ilmiah CIRCUIT, Vol. 1, no. 1, 48 – 59, 2015.
This page is intentionally left blank
38
Discussion and feedback