Breast Cancer Classification Using Artificial Neural Network and Feature Selection
on
p-ISSN: 2301-5373
e-ISSN: 2654-5101
Jurnal Elektronik Ilmu Komputer Udayana
Volume 8, No 2. November 2019
Breast Cancer Classification Using Artificial Neural Network and Feature Selection
Frisca Olivia Goriantoa1, I Gede Santi Astawaa2
aInformatics Department, Udayana University
Bali, Indonesia 1fgorianto@gmail.com 2santiastawa@gmail.com
Abstract
Breast cancer is still one of the leading causes of death in the world. Prevention can be done if the cancer can be recognized early on whether the cancer is malignant or benign. In this study, a comparison of malignant and benign cancer classifications was performed using two artificial neural network methods, which are the Feed-Forward Backpropagation method and the Elman Recurrent Neural Network method, before and after the feature selection of the data. The result of the study produced that Feed-Forward Backpropagation method using 2 hidden layers is better after the feature selection was performed on the data with an accuracy value of 99,26%.
Keywords: Feed-Forward Backpropagation, Elman Recurrent Neural Network, Feature Selection, Hidden Layer
Cancer is one of the most common causes of death in the world, including in Indonesia. Nowadays, breast cancer is the most threatening type of cancer for women throughout the world. Breast cancer is a malignant tumor that is formed from breast cells that grow and develop uncontrollably that it can spread between tissue or organs near the breast or other body parts[1]. Breast cancer can be fatal if it is detected too late. That is why it is good to know whether a growing tumor is a malignant or benign tumor.
Classification is the process of finding a set of models that describe and differentiate classes of data[2]. The purpose of classification is to produce model that can be used to predict the class of data that does not have a class label. In general the classification algorithm uses all the features contained in the data to build a model, even though not all of the features are relevant to the results of the classification. If this happens to data that has a very large size and dimensions, it makes the algorithm performance ineffective and inefficient. One thing to deal with this problem is to reduce irrelevant features.
An Artificial Neural Networks (ANN) is an information processing system that works similar with neural networks[3]. This study uses ANN because with its ability to obtain meaning from complex or inaccurate data, can be used to extract patterns and trends that are more complicated for use by humans or other computer techniques[4].
In previous studies, an initial diagnosis of breast cancer was carried out using Genetic Algorithm which were implemented on the Backpropagation Neural Network[5]. This method has advantages in terms of accuracy but requires a long computational time. In addition there is also breast cancer classification study that use a combination of Neural Network and Association Rule methods[6]. However, this method is considered to be still not optimal due to the average results of the accuracy which shows less than the maximum number.
This study will compare Neural Network methods in diagnosing breast cancer. The methods to be compared are Feed-Forward Backpropagation (FFBP) and Elman Recurrent Neural Network (ERN). The data to be used in this study is the Wisconsin Breast Cancer Data Set with a total of 699 records and 10 attributes. In this data there are two classes of cancer represented by the numbers 2 (benign) and 4 (malignant). This study aims to find out which method is better in diagnosing breast cancer based on the highest accuracy value.
The data used consists of 699 records and there are 19 missing data which means that one of the attributes is unknown. Therefore preprocessing data is done by deleting 19 missing data so that the data becomes 680 records with 237 Malignant class records and 443 Benign class records.
ANN processes information in the same way as the human brain. This network consists of a large number of highly interconnected processing elements(neurons) that work in parallel to solve certain problems. Neural networks learn by example. The examples that will be used for training must be chosen carefully because if the training examples used are not right then the network will function incorrectly too.
-
2.1. Feed-Forward Backpropagation (FFBP)
One of the artificial neural network training algorithms that is widely used in the field of pattern recognition is backpropagation. This algorithm is generally used in multi-layer feed-forward type ANN, which is composed of several layers and the signal is flowed in the direction from input to output. The backpropagation training algorithm basically consists of three stages[3] : a. Input training data values so that output values are obtained b. Backpropagation of the error value obtained
-
c. Adjust connection weights to minimize error values.
The three stages are repeated continuously until you get the desired error value. After the training is completed, only the first stage is needed to utilize the ANN. To train a network a set of data pairs is needed as follows:
{P1,t1},{p2,t2 },-,{pn,tn} (1)
where pn is the nth network input value and tn is the target, that is, the output value that should be generated. For each input that enters the network, the output produced by the network will be compared to the target.
This algorithm will manage or adjust network parameters to minimize the mean square error, namely:
where x, e, t and a are weight vector and bias, error vector, target vector and output vector.
If the network has several outputs, then the above equation can be developed into:
F(x) = E(eτe) = E[(t — a)τ(t — a)](3)
Mean square error is calculated by :
-
2.2. Elman Recurrent Neural Network (ERNN)
ERNN is often referred to as a modification of Feed-Forward and has a more optimal performance in learning time series data. Elman Recurrent Neural Network (ERNN) has a feedback connection (feedback) from the previous input, so it is expected to improve the performance of ANN. According to [7], Elman said that ERNN is a modified feed- forward with the main difference is the additional layer of context neurons that provide the unit's hidden pattern is fed back to him alone. This recurrent network has two inputs, which are real input and contextual input. There is feedback that can cause iteration processes to be much faster, so that makes the parameter update speed and convergence faster .
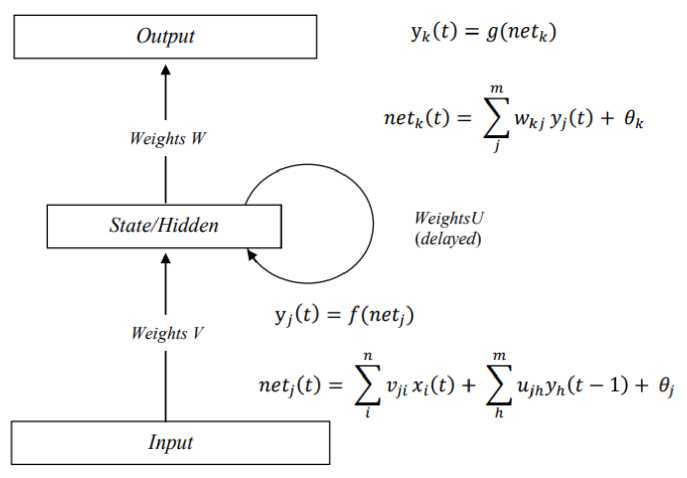
Picture 1. Recurrent ANN Layer
After preprocessing the data, ANN calculations will be performed using MATLAB. ANN is carried out using the Feed-Forward Backpropagation and Elman Recurrent Neural Network methods for the Wisconsin Breast Cancer Data Set. The data is divided in two with a ratio of 60:40 for training data and testing data. Out of a total of 680 records, 408 records are used for training data and 272 records are used for testing data.
Feature selection of the data is based on the correlation value using IBM SPSS Statistics. Correlation can take any value in the range of [-1, 1]. The correlation coefficient sign indicates the direction of the relationship, while the value of the correlation (how close to -1 or +1) indicates the strength of the relationship[8]. A value of -1 means perfect negative linear relationship, 0 means no relationship, and +1 means perfect positive linear relationship.
In addition to feature selection, this study also made a comparison based on the number of hidden layers used in each method both after and before feature selection. The number of hidden layers to be compared is 1, 2, and 3 hidden layers.
Table 1. Classification Accuracy Before Feature Selection
|
Number of Hidden Layers | |||
|
Method |
1 |
2 |
3 |
|
FFBP |
97,43% |
98,16% |
97,79% |
|
ERNN |
98,53% |
98,16% |
97,06% |
Table 2. Attributes Correlation Values
|
Attribute |
Correlation with Class |
|
Sample code number |
-.083 |
|
Clump Thickness |
.714 |
Uniformity of Cell Size .822
|
Uniformity of Cell Shape |
.823 |
|
Marginal Adhesion |
.706 |
|
Single Epithelial Cell Size |
.694 |
|
Bare Nuclei |
.824 |
|
Bland Chromatin |
.761 |
|
Normal Nucleoli |
.721 |
|
Mitoses |
.426 |
In Table 2, it can be seen that the correlation value of the Sample code number attribute is close to 0, which means that this attribute is less related to the class of data so that in the next calculation this attribute will be removed from the data. Then do the classification process again using Feed-Forward Backpropagation and Elman Recurrent Neural Network.
Table 3. Classification Accuracy After Feature Selection
|
Number of Hidden Layers | |||
|
Method |
1 |
2 |
3 |
|
FFBP |
98,90% |
99,26% |
98,53% |
|
ERNN |
97,06% |
96,32% |
97,79% |
Breast cancer classification is done by comparing the two methods of ANN, the Feed-Forward Backpropagation and Elman Recurrent Neural Network on the data before and after feature selection based on the attribute correlation values and by the different number of hidden layers. It can be seen in Table 1 and Table 3 that the number of hidden layers affects the accuracy of the classification even though the difference is not much.
In this study it can be concluded that the classification of breast cancer using neural network, the best method is using the Feed-Forward Backpropagation after removing irrelevant feature and using two hidden layers because it produces the highest accuracy value, which is 99.26 %.
In the FFBP method it can be seen that the average accuracy increases after the selection of irrelevant features. Whereas in the ERNN method that the average accuracy value decreases after the feature selection is done. However, the range of accuracy values that occur is not too large with a range between 96.32% to 99.26% so that it can be concluded that the ANN used in this study is quite stable.
References
-
[1] (2018). InfoDatin Pusat Data dan Informasi Kementerian Kesehatan RI. Available:
http://www.depkes.go.id/resources/download/pusdatin/infodatin/infodatin%20tuberkulosi s%202018.pdf
-
[2] A. J. J. F. H. U. Indriani, "Klasifikasi data forum dengan menggunakan metode naïve
bayes classifier," 2014.
-
[3] L. V. Fausett, Fundamentals of neural networks: architectures, algorithms, and
applications. prentice-Hall Englewood Cliffs, 1994.
-
[4] V. Sharma, S. Rai, A. J. I. J. o. A. r. i. c. s. Dev, and s. engineering, "A comprehensive
study of artificial neural networks," vol. 2, no. 10, 2012.
-
[5] A. M. Zamani, B. Amaliah, and A. Munif, "Implementasi Algoritma Genetika pada
Struktur Backpropagation Neural Network untuk Klasifikasi Kanker Payudara."
-
[6] M. Karabatak and M. C. J. E. s. w. A. Ince, "An expert system for detection of breast
cancer based on association rules and neural network," vol. 36, no. 2, pp. 3465-3469, 2009.
-
[7] J. B. Habarulema, "A contribution to TEC modelling over Southern Africa using GPS
data," Rhodes University, 2010.
-
[8] "SPSS Tutorials: Pearson Correlation,"
117
Discussion and feedback