Android Based Application for Rhizome Medicinal Plant Recognition Using SqueezeNet
on
Journal of Electrical, Electronics and Informatics, p-ISSN: 2549–8304 e-ISSN: 2622–0393
10
Android Based Application for Rhizome Medicinal Plant Recognition Using SqueezeNet
Krisna Hany Indrani1*, Duman Care Khrisne2, I Made Arsa Suyadnya3
-
1,2,3 Department of Electrical Engineering Faculty of Engineering, Udayana University Bali - Indonesia
Abstract— Rhizome is modification of stem that grows below the surface of the soil and produce new bud and roots from its segments. Besides being used as spices, rhizome also used by people as ingredients of traditional medicine to treat various diseases. This proves that rhizome has many benefits. However, the ability to recognize types of rhizome can only be done by certain people because rhizome has variety of types, aromas, and different colors. This study was designed to build an Android based application to recognize the types of rhizome, so that people can recognize types of rhizome without having special knowledge. The application was built using Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) methods with SqueezeNet architecture model. This study used 9 class of rhizome with Zingiberaceae Family, namely Bangle, Jahe, Kunyit Kuning, Kencur, Lengkuas, Temu Kunci, Temu Ireng, Temu Mangga, and Temulawak. Testing is carried out to know the performance of application such as accuracy level of application in recognize types of rhizome. Based on the results of testing with 54 rhizomes sample images, the application is capable of recognizing rhizomes types by obtaining a top-1 accuracy value of 41% and top-5 accuracy value of 81%.
Index Terms— Rhizome, Medicinal Plants, Convolutional Neural Network, SqueezeNet, Tensorflow, Android
-
I. INTRODUCTION
Rhizome is modification of stem that grows below the surface of the soil and produce new bud and roots from its segments. Rhizome has many benefits such as raw materials for herbs, cooking spices or spices, aromatherapy (essential oils), fragrances, even as a basic ingredient in the beverage industry. In addition, rhizome also used by people as ingredients of traditional medicine to treat various diseases. Rhizome have a role in storing the results of plant metabolic processes so that these plants contain many active compounds that are beneficial to human body [1]. Rhizome which are commonly used as medicine mostly from Zingiberaceae family.
Rhizome has variety of types, aromas, and different colors. People usually recognize rhizomes based on its aroma and color, however not all people have this knowledge. Its because rhizome has similar characteristic and shape each other, so it’s hard for people to recognize rhizome types. Some people usually recognize rhizome by comparing rhizome image that will be identified with rhizomes images on book or internet or bring it to the researcher. This certainly requires a lot of time and cost. Therefore, this study tried to build a mobile application to help people to recognize rhizome without having special knowledge.
The proposed approach in this study is a deep learning approach that recognize the image of rhizome. One of the methods used is Convolutional Neural Network with architecture model namely SqueezeNet. This study tried to
utilize SqueezeNet architecture model because this model has techniques for compressing parameters while maintaining accuracy [2]. Therefore, this model has a small model size and can be used on devices with limited memory such as mobile devices.
-
II. RELATED WORKS
From the research that has been conducted, there are several studies related to this research, such as rhizome identification system using One Minus Correlation Coefficient method [3]. Another research is done by [4] and [5], using Convolutional Neural Network method with Smaller VGGNet-like they try to recognize classify Indonesian herbs and spices and also dragon fruit ripeness. [6] also use Convolutional Neural Network method with GoogleNet architecture to recognize plant leaf. Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) is deep learning method that has best performance in natural image processing. However, the research taken by [3], [4], and [6] only based on desktop. In addition, the CNN method used by [4] and [6] has a large model size, so it is not suitable for devices with limited memory such as mobile devices. Therefore, this study tried to build an Android based application that can recognize medicinal plant rhizome and utilize another architecture from CNN such as SqueezeNet. SqueezeNet firstly introduced by [2]. It has 50 times less parameters and 2 times faster training time. Therefore, this
model has a small model size and suitable for mobile devices.
Fig. 1. General system overview
-
III. PROPOSED APPROACH
This study proposed the use of CNN model to recognize medicinal plant rhizomes image. This study uses SqueezeNet architecture to create the model. With this approach, object inside image automatically recognized from classification process.
-
A. SqueezeNet
SqueezeNet is an artificial neural network architecture using the CNN method. SqueezeNet is capable to reach AlexNet accuracy level (ILSVRC 2012 winner) with 50× less parameters and 2× faster training time. SqueezeNet replaces many 3×3 convolution layers with 1×1 and fewer filter to minimize the dimensions of activation map. SqueezeNet also replaces the fully-connected layer with global average pool layer to determine predictions by taking the average of the last convolution layer [2]. This model has a small model size so it can be used on mobile devices.
-
B. Tensorflow Lite
Tensorflow Lite is a machine learning library designed specifically for deploying model on mobile and embedded devices. Tensorflow Lite provides tools to convert Tensorflow models to Tensorflow Lite format for use on mobile and embedded devices. These tools can also be used to optimize binary size and model performance by using a quantized model. Tensorflow Lite supports Android (Java / C ++ API), iOS (C ++ API) and Linux (Python / Java / C ++ API) platforms [7].
-
C. Top-N Accuracy
Top-N Accuracy is the correct predicted class contained in Top-N. Top-N Accuracy commonly used are Top-1 Accuracy, Top-3 Accuracy, and Top-5 Accuracy. This study uses Top-1 Accuracy and Top-5 Accuracy to test the application performance. Top-1 Accuracy is a prediction class with the highest probability that is classified correctly. Top-5 Accuracy is the 5 highest prediction class where one of the class is correctly classified. The equation used to calculate the accuracy value is refer to (1) as follows [8]:
. am oun to f correct d a t a xaaa, /A\
Accuracy = ------j----------× 100% (1)
Total Data '
Training Image
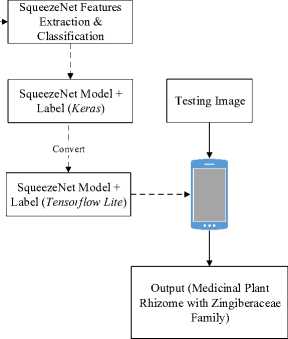
Our proposed approach is to use a Squeeze-Net to build an artificial neural network model. This model’s goal is to classify rhizome images. To make this model run on mobile applications, we first need to change the model generated by the library (we use Tensorflow with a Keras Backend) in the form of a .h5 file into a .tflite file type (tensorflow lite model file). After getting the model we have to test the performance of the model using Top-N Accuracy. General system overview of medicinal plant rhizome recognition is shown in Figure 1. Generally, this system consists of two process, namely training process (training and validation) that is drawn with dotted arrow line and testing process that is drawn with black arrow line.
-
IV. RESULT
-
A. Dataset
Dataset in this study is created by searching images in Google Image Search and directly take pictures in Bokashi Farm. This study also uses augmentation data to multiply the dataset. As the results, this dataset has 5454 images from 9 classes. Then we have to split the image dataset into training data and testing data. Data structure of this study can be seen in Figure 2. Training data is used for training process with SqueezeNet model and testing data is used for rhizome application testing.
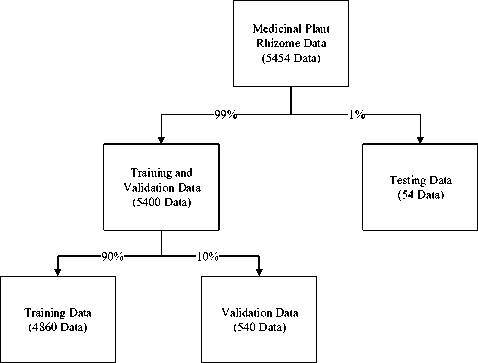
Fig. 2. Data structure
-
B. SqueezeNet Model Performance
After collect the dataset, we have to train our SqueezeNet model using training data. This study used 200 epoch and learning rate value is 1e-3, according to [9] research that best performance of SqueezeNet is obtained when changing learning rate value from 4e-2 to 1e-3. SqueezeNet performance chart during the training process is shown in Figure 3.
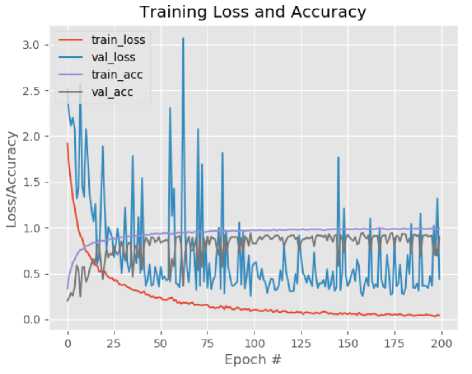
Fig. 3. SqueezeNet performance chart on training process
The model training process consist of training and validation process that aim to train the model in order to recognize the types of medicinal plant rhizomes. The time needed to complete the training process with 200 epochs is 8,8 hours using Graphics Processing Unit (GPU).
According to training process chart, best model is obtained at epoch 159 with train_loss = 0.0492, val_loss = 0.2537, train_acc = 0.9863, val_acc = 0.9481. Therefore, the model with epoch 159 then will be used to build an Androidbased medicinal plant rhizome application.
-
C. Application Performance
The application was build using Tensorflow library with Keras backend. SqueezeNet model with Keras format (.h5) must be converted to Tensorflow Lite format (.tflite) using Tensorflow Lite Converter so it can be used on mobile
application. Tensorflow Lite provides a converter using quantized models to optimize the model by increasing performance and reducing the binary size of the model but slightly reducing the accuracy of the model. This application uses a floating-point model because SqueezeNet model has produced a small model size after training process, that is 6.589 KB. Then after converting using Tensorflow Lite Converter, the model size becomes 2.173 KB. The model (.tflite) and label (.txt) results then entered into assets in Android Studio software. How medicinal plant rhizome application works can be seen in Figure 4.
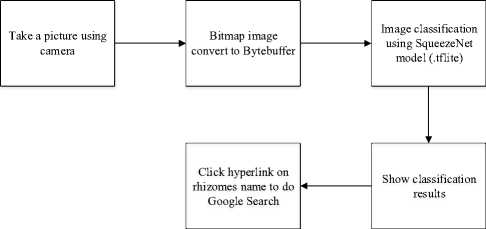
Fig. 4. Medicinal plant rhizome application procedure
TABLE I. TEST DATA CLASSES, IMAGE AMOUNT OF EVERY CLASS, AND DATA CORRECTLY RECOGNIZED
|
Class |
Data |
CR | |
|
Top-1 Accuracy |
Top-5 Accuracy | ||
|
Bangle (Zingiber purpureum) |
6 |
2 |
6 |
|
Jahe (Zingiber officinale) |
6 |
5 |
6 |
|
Kencur (Kaempferia galanga) |
6 |
3 |
6 |
|
Kunyit Kuning (Curcuma domestica) |
6 |
5 |
5 |
|
Lengkuas (Alpinia galanga) |
6 |
1 |
4 |
|
Temu Ireng (Curcuma aeruginosa) |
6 |
3 |
5 |
|
Temu Kunci (Boesenbergia pandurata) |
6 |
3 |
6 |
|
Temu Mangga (Curcuma amada) |
6 |
0 |
6 |
|
Temulawak (Curcuma xanthorriza) |
6 |
0 |
0 |
|
Total |
54 |
22 |
44 |
CR : Correctly Recognized
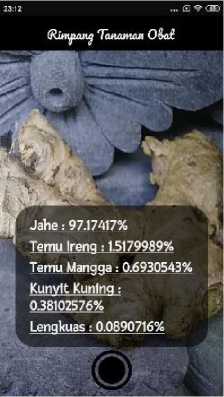
(a)
Fig. 5. Medicinal plant rhizome application
(b)
First, the application takes a picture of medicinal plant rhizomes using camera, bitmap image input is converted into a bytebuffer so that it can be read by the model, then the model classifies by matching the image input values that are close to the label values, then the application display the classification results namely the rhizome name and its probability value. User can also do google search to know more detail information about classified rhizome by clicking
hyperlink on rhizome name. The results of rhizome recognition android based application is shown in Figure 5.
Application testing is carried out to determine the performance of the application which is the application accuracy value in recognizing the medicinal plant rhizomes. The application was tested using 54 testing data of medicinal plant rhizome images with 6 data each class. The test data class, image amount of every class, and data correctly recognized described in Table I.
According to the data in Table I, from the correctly recognized (CR) data, we can calculate the testing accuracy value by using equation (1) as follows:
-
a) Top-1 Accuracy
- × 100% = 41% (2)
54
-
b) Top-5 Accuracy
- × 100% = 81% (3)
54
Based on the calculation (2) and (3) shows the application is capable to recognize medicinal plant rhizomes by obtaining a top-1 accuracy value of 41% and top-5 accuracy value of 81%.
-
D. Application Testing
Application testing is carried out by comparing the similar application performance, that is accuracy value. The result of application testing is shown in Table II.
TABLE II. APPLICATION TESTING RESULTS
|
App Name |
Testing Data |
CR |
|
Medicinal Plant Rhizome |
54 |
44 |
|
PlantSnap |
3 | |
|
PlantNet |
1 |
CR : Correctly Recognized
According to correctly recognized (CR) data in Table II, we can calculate the testing accuracy value by using equation (1)
|
as |
follows: |
|
a) |
Medicinal Plant Rhizome |
|
- × 100% = 81% (4) 54 | |
|
b) |
PlantSnap |
|
- × 100% = 6% (5) 54 | |
|
c) |
PlantNet |
|
- × 100% = 2% (6) 54 |
Based on the calculation (4), (5), and (6) shows medicinal plant rhizomes application obtain better accuracy value, which is 81% compared to other similar application. This is due to the medicinal plant rhizome application is specifically made to recognize medicinal plant rhizome with Zingiberaceae family, while similar application is made to recognize plants in general. The results of application testing with similar application can be seen in Figure 6.
V. CONCLUSION
This study is capable to build Android based application that can recognize medicinal plant rhizome using
Convolutional Neural Network method with SqueezeNet architecture model. Through this application, the user can recognize medicinal plant rhizome without having special knowledge. The application is tested using testing data to determine the application performance. Based on application testing with 54 testing data, the application capable to recognize medicinal plant rhizome by obtaining a top-1 accuracy of 41% and top-5 accuracy of 81%. This application also tested with similar application and obtain better accuracy value which is 81% compared to other similar application.

(a)
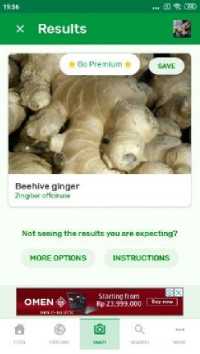
(b)
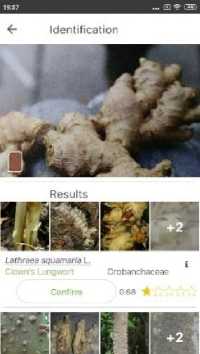
(c)
Fig. 6. Application testing with similar application
REFERENCES
-
[1] L. Hakim, Rempah & Herba, no. 164. 2015.
-
[2] F. N. Iandola, S. Han, M. W. Moskewicz, K. Ashraf, W. J.
Dally, and K. Keutzer, “SqueezeNet: AlexNet-level accuracy with 50x fewer parameters and <0.5MB model size,” pp. 1–13, 2016, doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-24553-9.
-
[3] D. P. Sari and A. Fadlil, “Sistem Identifikasi Citra Rimpang
Pada Tanaman Famili Zingiberaceae (Temu - Temuan) Menggunakan Metode Fungsi Jarak One Minus Correlation Coefficient,” J. Sarj. Tek. Inform., vol. 2, no. 2, pp. 288–297, 2014, doi: 10.12928/jstie.v2i2.2638.
-
[4] D. C. Khrisne and I. M. A. Suyadnya, “Indonesian Herbs and
Spices Recognition using Smaller VGGNet-like Network,” in 2018 International Conference on Smart Green Technology in Electrical and Information Systems (ICSGTEIS), 2018, pp. 221– 224, doi: 10.1109/ICSGTEIS.2018.8709135.
-
[5] I. M. Wismadi, D. C. Khrisne, and I. M. A. Suyadnya,
“Detecting the Ripeness of Harvest-Ready Dragon Fruit using Smaller VGGNet-Like Network,” J. Electr. Electron.
Informatics, vol. 3, no. 2, p. 35, 2020, doi: 10.24843/jeei.2019.v03.i02.p01.
-
[6] W.-S. Jeon and S.-Y. Rhee, “Plant Leaf Recognition Using a
Convolution Neural Network,” Int. J. Fuzzy Log. Intell. Syst., vol. 17, no. 1, pp. 26–34, 2017, doi: 10.5391/ijfis.2017.17.1.26.
-
[7] Anonim, “Deploy machine learning models on mobile and IoT
devices,” 2019. .
-
[8] P. A. Wicaksana, I. M. Sudarma, and D. C. Khrisne,
“PENGENALAN POLA MOTIF KAIN TENUN GRINGSING MENGGUNAKAN METODE CONVOLUTIONAL NEURAL NETWORK DENGAN MODEL ARSITEKTUR ALEXNET,” J. Spektrum, vol. 6, no. 3, pp. 159–168, 2019.
-
[9] A. Rosebrock, “Training SqueezeNet on ImageNet,” in Deep
Learning For Computer Vision With Python, 1st ed., pyimagesearch.com : pyimagesearch, no. Mm, 2017, pp. 121129.
Discussion and feedback