Performance Assessment of OFDM System using Reed-Solomon Codes over Fading Channels
on
Journal of Electrical, Electronics and Informatics, Vol. 2 No. 2, August 2018
48
PERFORMANCE ASSESSMENT OF OFDM SYSTEM USING REED-SOLOMON CODES OVER FADING CHANNELS
N.M.A.E.D. Wirastuti1*, I.M.A. Suyadnya2, and D.C. Khrisne3
-
1Telecommunication System Lab., Department of Electrical Engineering
Udayana University
Badung, Bali, Indonesia
-
2,3Computer Lab., Department of Electrical Engineering
Udayana University
Badung, Bali, Indonesia
Abstract This paper study the performance of Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) system over AWGN and Rayleigh fading channels. OFDM performs multi-carrier transmission where all the subcarriers are orthogonal to each other. The channel coding was applied to improve the OFDM system performance. Reed Solomon (RS) codes was chosen that an efficient channel coding algorithm and has intense error correction ability. Adding the benefits of multicarrier OFDM system and Reed Solomon codes to achieve the expected system performance. The coded OFDM system was modeled over and simulated using Matlab. The bit error rate (BER) and energy bit (Eb) per noise power density (No) was performed during system simulations. QPSK modulation was used to modulate the random bits. From the simulation results It can be seen that BER vs. EB/No parameter for Coded OFDM system lower than uncoded OFDM. This was because RS codes succeed to correcting the error generated along data transmission.
Index Terms—discrete Fourier transforms, fast Fourier transform, channel coding, OFDM
Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) technology is one of the technologies used in supporting and realizing the demand for fast communication services. OFDM is a transmission or modulation technique that uses multiple (multi-carrier) orthogonal frequencies. The main principle of OFDM is that its modulation scheme divides a series of high-speed information data into several low-speed data series arranged in parallel, thereby widening the duration of the symbol and being able to reduce the influence of Inter Symbol Interference (ISI), especially in mobile communication environments [1].
In wireless communication, the transmitted data will certainly get noise from the channel which can cause damage to the data. Therefore, it is necessary to have a channel coding technique to achieve the expected Quality of Service (QOS). Channel coding techniques is one of ways
in correcting errors from transmitted data and reducing the error rate of bits. By adopting coding technique to the OFDM systems, it combines the benefits of multicarrier and coding. This paper studies the use of Reed Solomon or RS codes in assessing the performance of OFDM systems over Rayleigh fading channel.
RS codes are the most well-known and the most widely-used in the telecommunication that codes having non-binary symbols. RS codes form a prime class of linear block codes efficient in correcting random symbol errors and burst errors [2,3,4]. So that RS Codes are popular linear block codes in many practical systems [2].
There were many researches of using RS codes to improve the performance of OFDM system. In [5], it applied RS codes to the clipped and filtered OFDM systems for compensation of clipping distortion. Among the four codeword arrangements considered in [5], the cyclic-time arrangement which distributes symbols of each codeword over time and frequency in a symbol-wise manner seems most attractive from the viewpoint of implementation and resulting decoding error performance. Other research has shown a study of the performance of a basic OFDM system
in a frequency selective propagation environment using different types of Reed-Solomon coding schemes [6]. The results for the OFDM system in the urban and suburban channels developed in [6] indicated a relatively poor performance. After the use of concatenated schemes proved that most of the fading effects can be removed. reducing almost totally the effects of the multipath channel [6]. A joint solution to the design problem of a good error correcting code for an OFDM scheme with a low Peak to Average Power Ratio (PAPR) in the case of impulse noise was investigated in [7]. The complexity was reduced since the whole RS-OFDM system can be seen as one large RS code, such that low complexity RS decoders can be applied in practice [7].
The remainder of this paper is organised as follows. Section 2 presents the system model used in this study. Section 3 describes the simulation results and analysis the performance of uncoded OFDM system and RS OFDM system. Finally, in section 4, a conclusion is drawn.
-
A. An Efficient OFDM Implementation
In practice, an OFDM transmitter and receiver can be implemented efficiently using the IFFT and FFT,
respectively, that are typically employed in the baseband OFDM basic structure [8], as shown in Figure 1. A type of modulation (M -qpsk, M -qam) is used to modulate the input data stream, b bps, and resulting an M-ary symbol stream, R, where each symbol has in-phase (I) and quadrature (Q) components.
A set of N parallel M-ary symbols, S(i)=S(0), S(1),…, S(N-1), is the output of a serial-to-parallel converter. These output symbols are transmitted over N sub-channels and correspond to the symbols transmitted over each of the subcarriers. The number of sub-carries (N) and modulation type used will determine the number of bits on an OFDM block.
Each sub-carrier transmits one symbol during each OFDM block. Thus, the N symbols output from the serial-to-parallel converter are the discrete frequency components of the output OFDM modulator, x(n). x(n) is generated by converting its frequency components into time samples by performing an IFFT on the N sub-channels. Each subchannel modulates a separate carrier through the IFFT modulation block, which actually generates the OFDM block, performing the multi-carrier modulation [9].
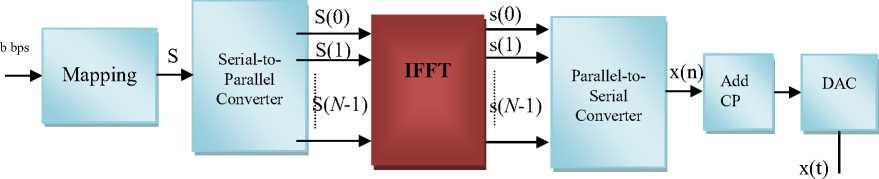
Radio
Channel
y(t)
bˆ bps

De
Mapping

Parallel-to-Serial Converter
R(0)
R(1)
R(N-1)
r(0) rr((01)) r(N-1)
Serial-to-Parallel Converter
y(n)
Remove CP

ADC
Figure 1 N-sub-carriers OFDM with IFFT/FFT implementation
-
B. Reed-Solomon Codes Implementation
The implementation of Reed-Solomon Codes in OFDM system can be seen in Figure 2. In OFDM system, the Reed Solomon codes are modelled by adding Reed Solomon encode blocks at the beginning of the transmission and the Reed Solomon block decodes at the end of the transmission. In the encoding block, the transmitted messages divided into separate data blocks. The encode block is a systematic
code which means that the encoding process does not change message symbols and protection symbols are added to a separate place on the data block. Then in the decode block, there is reception of data that has been encoded with Reed Solomon which has been damaged by noise. The function found in this decode block is to find the location of the error and calculate the number of errors.
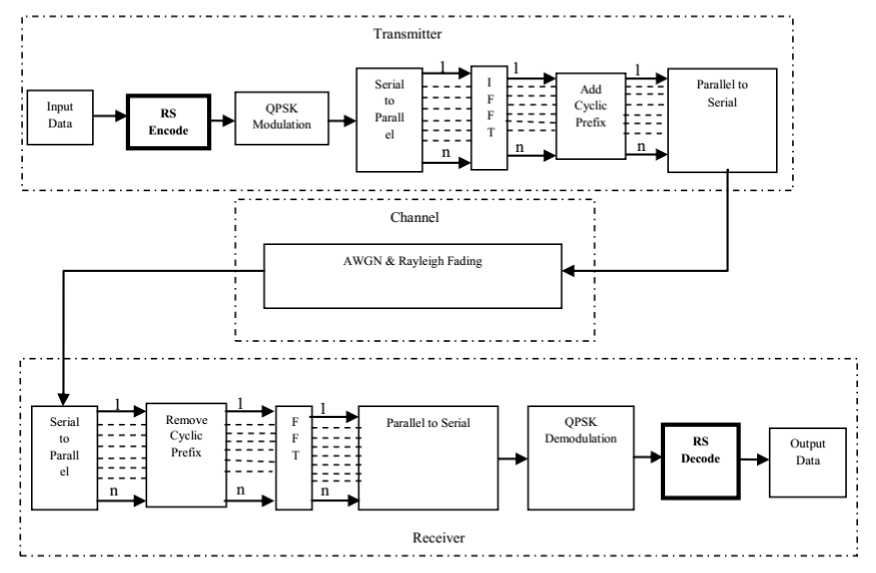
Figure 2 RS Codes Implementation in OFDM System
OFDM is known consist of IFFT and cyclic prefix (CP) on the transmitter and CP is eliminated and FFT on the receiver. CP forms the convolution channel seen as cyclic and IFFT/ FFT diagonalizes the channel.
The parameter used in the simulation can be seen in Table 1.
Table 1 Simulation parameter
|
Parameter N frame |
Values 5000 |
|
FFT Size N of data subcarriers Guard periode type N bits per OFDM symbol N symbol N Cyclic prefix Total symbol |
64 64 Cyclic prefix 64 1 ¼ (N of data subcarriers) N of data subcarriers + N cyclic prefix |
Perbandingan Sistem Uncodeti OFDM dengan Coded OFDM RS Melalui Kanal AWGN
0 2 4 S 8 10 12 14 16 18 20
EWNo1 dB
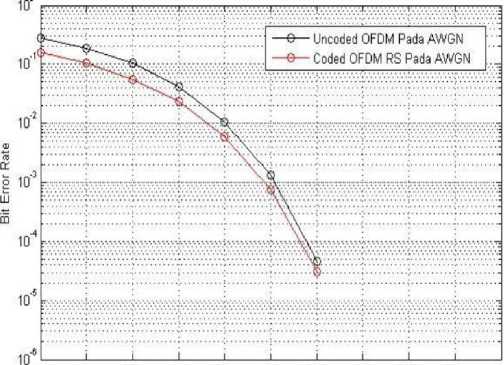
Figure 3 BER vs. Eb/No of OFDM System-RS codes over AWGN channel
The simulation was based on DFT-OFDM model as seen in Figure 2. The performance of OFDM system with and without RS codes over AWGN and Rayleigh fading channels were observed. The parameters used for simulation can be seen in Table 1. The performance of OFDM system with and without RS codes over AWGN channels can be seen in Figure 3. Figure 4 shown performance assessments of OFDM System using RS codes over Rayleigh fading channels.
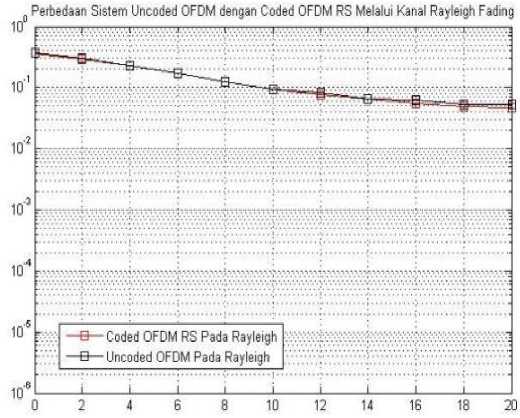
Figure 4 BER vs. Eb/No of OFDM System-RS codes over Rayleigh fading channel
From Figure 3, it can be seen that by using the Reed Solomon codes, the error is smaller than the uncoded OFDM system. The average difference in the error value obtained is equal to 0.1725. In both OFDM systems, bit detection errors do not occur when the Eb/No value reaches 12 dB.
Figure 4 shows the performance of Reed Solomon codes on OFDM system through the Rayleigh Fading channels. By using the Reed Solomon coding technique, the BER is smaller than uncoded OFDM system. With an average error value of OFDM coded system of 1.5199 and the average error of the uncoded OFDM system is 1.5840, the difference is obtained error of 0.0641. Performance of the COFDM system with techniques Reed Solomon encoding has a smaller error value than the uncoded OFDM system. This is caused by the ability of Reed Solomon coding to detect and correct the error. Reed Solomon coding is able to change the error symbol with its actual symbol un-regardless of what error occurred in the symbol caused by one-bit or all bit error in the symbol.
The performance of OFDM system was assessed using Reed Solomon codes over AWGN and Rayleigh fading channels. The results shown that Reed Solomon codes were able to improve the performance OFDM system. It due to advantages of RS codes that efficient in correcting random symbol errors.
Acknowledgment
The author(s) would to thank Lembaga Penelitian dan Pengabdian kepada Masyarakat (LPPM), Universitas Udayana, for their financial supports.
References
-
[1] A. Luise, “Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing for Wireless Networks”, Report Submitted to University of California, 2000.
-
[2] I. G. Reed and G. Solomon, "Polynomial codes over certain finite fields," J. Soc.Ind. Appl. Maths., pp. 8:300-304, June 1960.
-
[3] T. K. Moon, Error Correction Coding: Mathematical Methods and Algorithms. John Wiley & Sons, July 2005.
-
[4] S. Lin and D. J. Costello, Error Control Coding, 2nd ed. Prentice Hall, June 2005.
-
[5] Masakawa, T., & Ochiai, H. Design of Reed-Solomon Codes for OFDM Systems with Clipping and Filtering. 2007 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference.
-
[6] Arijon, I. M. Performance of an OFDM system in frequency selective channels using Reed-Solomon coding schemes. IEE Colloquium on Multipath Countermeasures, 1996.
-
[7] Van Meerbergen, G., Moonen, M., & De Man, H. (n.d.). Combining Reed-Solomon Codes and OFDM for Impulse Noise Mitigation: RS-OFDM. IEEE International Conference on Acoustics Speed and Signal, 2006.
-
[8] S. B. Weinstein, P. M. Ebert, “Data Transmission by Frequency Division Multiplexing using the Discrete Fourier Transform”, IEEE Transactions on Communications, Volume 19, No. 5, pp. 628 –634, October 1971.
-
[9] N.M.A.E.D. Wirastuti, J.M. Noras, S.M.R. Jones, Evaluation of the Very Fast Fourier Transform applied to OFDM, Proceeding of 2nd IEE/EURASIP Conference on DSPenabledRadio, London, UK, 19-20 Sept. 2005, p. 12, ISBN: 0 86341 560 1.
Discussion and feedback