The Non-verbal Resources of Linguistic Landscape in Dali Ancient City Tourist Attraction, China
on

e-Journal of Linguistics

Available online at https://ojs.unud.ac.id/index.php/eol/index
Vol. 16, No. 1 January 2022, pages: 01-10
Print ISSN: 2541-5514 Online ISSN: 2442-7586
https://doi.org/10.24843/e-jl.2022.v16.i01.p01
The Non-verbal Resources of Linguistic Landscape in Dali Ancient City Tourist Attraction, China
-
1 Lu Xing
Center for Language Education and Cooperation, Beijing, China
Email: 124360898@qq.com
-
2 I Made Suastra Department of Linguistic, Faculty of Humanities, Udayana University, Indonesia, Email: made_suastra@unud.ac.id
Article info
Received Date: 5 July 2021
Accepted Date: 19 July 2021
Published Date: 31 January 2022
Keywords:*
Linguistic Landscape; Non-verbal
Resources; Dali Ancient City
Abstract*
The aim of this study is to call for more attention to the non-verbal resources of linguistic landscape research and also provide a certain reference for implement of various countries in the other scenic area of the world. The data collection technique is the comprehensive photographing of signs in various shops, hotels, restaurants at the streets of survey areas. The equipment used is a digital camera. The sampling technique is carried out by random sampling. In order to get the diversity, a wide range of signs is selected. Through analyze, the non-verbal resources of the linguistic landscape of Dali ancient city tourist attraction is that official signs appropriately use the non-text marks to better promote local culture. The use of colors highlights text messages and makes people visually comfortable, in line with Chinese aesthetic habits. Most of the signs have radically abandoned traditional shapes and used non-traditional shapes that are more distinctive and can convey cultural information, which are worthy of promotion. Since the combined sign is formulated in accordance with the official sign standard, the shape and color are more in line with the official standard. The non-text marks on the signs are customized privately, which is more diverse than the unified official watch signs. The nonverbal resources of private signs pay more attention to the transmission of information, and more use of phone numbers combined with brand logos makes the linguistic landscape an advertising effect and maximizes the mass communication of private brands. In addition, in order to comply with the official requirements, the color and shape of the signage do not differ much from store to store. It is worth mentioning that the official signage has a more long-term development perspective, by using the QR code which is very popular nowadays, but the scope of the implement is limited.
Linguistic landscape is the product of the development and progress of human society, and it carries the crystallization of human civilization and wisdom. The linguistic landscape of a region can not only reflect the aesthetic characteristics of the locals, but also reflect the deeper cultural connotations behind it, thus showing the language status and national characteristics of a region.
It is considered that there are two important functions of linguistic landscape: information function and symbolic function. (Rodrigue Landry, Richard Y. Bourhis. 1997:24) Information function mainly refers to the language characteristics of a region, the social status of language, the use and the diversity of language. Information such as status, its symbolic function is mainly because it can reflect the value and status of language, whether it is dominant or subordinate, and it symbolizes the strength or weakness of the use of a certain national language.
Linguistic landscape includes language resources and non-verbal resources. Language resources mainly convey code information. Non-verbal resources are supplementary explanations of code information, and have additional functions such as decoration, beautification of the linguistic landscape, and attracting more attention. The language resources on the public signs is mainly showing the literal information while the non-verbal resources been used can reflect more symbolic meaning of a region and leave the image of a place to readers. It not only reflects the aesthetic of the locals, but also shows the cultural identity, as well as the language and ecological environment of a region. Therefore, the exploration and research of the non-verbal resources of linguistic landscape is very necessary and valuable.
At present, many scholars treat the linguistic landscape as a whole for research, or conduct multilingual research, translation research, and grammar research on language of linguistic landscape, but few people pay attention to non-verbal resources which is a part of linguistic landscape and play an important role in symbolic function.
Dali is located in the west of Yunnan Province, China. It is where the state government of Dali Bai Autonomous Prefecture is located. It was also the capital of the ancient Nanzhao Kingdom (AD 738-902) and the Dali Kingdom (AD 937-1094) (AD 1096-1253). The city has positioned the tourism industry as a permanent basic industry, and strives to build an international cultural tourism city. This study selects the non-verbal resources of linguistic landscape in the most representative historical and cultural districts of Dali as the research object, and analyzes the important role of non-verbal resources.
This research mainly adopts quantitative as basic research methods. Use a digital camera to photograph all the public signs on the streets within the scope of investigation. The photos were downloaded to the database and sorted. Analysis is then carried out to clarify the non-verbal situation at the time of data collection.
Photo 1 below shows the survey area in this study. The eight streets are located in the core part of the tourist attraction in the Dali ancient city, with the largest population flow and the most representative.
The data collecting of this study is not confined to any particular type of sign. In order to get the diversity of linguistic landscape, a wide range of signs has been selected rather than a specific sign, which could enhance the reliability. The method of data collecting is the comprehensive photographing of signs in various shops hotels restaurants governments at the streets of survey areas. In order to understand the characteristics of non-verbal resources, the data analysis is carried out under the framework of linguistic landscape.
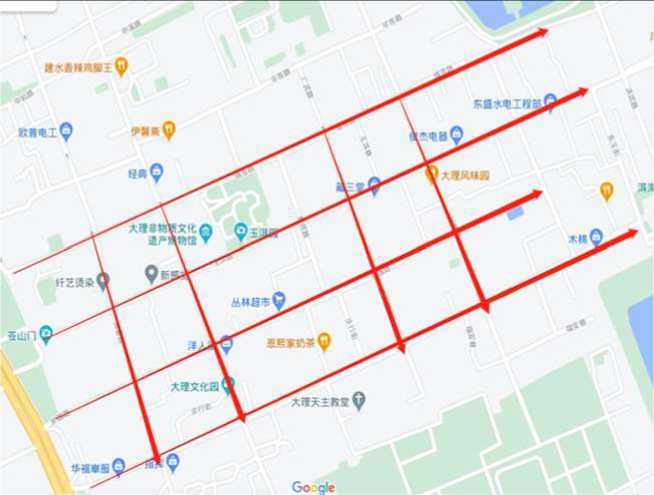
Photo 1 Research Area
According to the classification methods commonly used in linguistic landscape research, the collected samples can be divided into official signs and private signs. In this research, a special type of sign was added as a combination of official and private signs, private signs set up on official signs. This kind of sign belongs to the government, but the theme is private, so it is classified into the third category.
After delineating the scope of language resource collection, a digital camera was used to photograph and record all public signs in the area, and a total of 1722 linguistic landscapes were counted. A total of 235 official signs are counted, which refer to signs of an official nature established by the government, such as street signs, street names, building names, etc., which are also often called top-down signs. A total of 1185 private signs are counted. They are signs set up by private individuals or companies for commercial or information introduction, such as store names, billboards, posters, etc., which are usually called bottom-up signs or unofficial signs, etc. There are a total of 302 official and private combination signs which are special signs. The official selects the location and presentation method of the sign, and private individuals apply for the use of the official signage form to set up the sign and provide language services.
The trademarks, pictures, photos, paintings, and even some complex reliefs on the linguistic landscape are all belong to the research range of non-verbal resources. This study mainly analyzes non-verbal resources involving three aspects: non-text marks on signs, the color of the signs, and the style of the signs.
The non-text marks on the signs refer to all the non-verbal texts that appear on the public signs, but also have the function of transmitting information and expressing the meaning of symbols, such as patterns, trademarks, and signs. Chinese characters are hieroglyphs, and hieroglyphs are derived from pictures. With the development of society, the nature of pictures has weakened and the symbolic nature has increased. Based on hieroglyphs, Chinese characters have gradually developed into ideograms, and many new Chinese character-making methods are still
based on the original on the pictographs, the pictographs are used as the basis to combine, subtract, or add or delete symbolic symbols. Since ancient times, China has said that "calligraphy and calligraphy have the same origin". This is because the earliest source of text is pictures, and calligraphy and painting are like brothers. Growing from the same root, there are many internal connections. The origin of Chinese characters is primitive pictures. The "picture" form used by primitive people to express them in life has gradually changed from primitive pictures into a kind of "ideographic symbols". Nowadays, people are accustomed to putting some symbols or signs and words together on the signs. These non-text signs can convey information intuitively and vividly, and can enhance the effect of text expression.
|
Non-text marks Signs |
Logo |
Telephone number |
Photo or picture |
Other marks |
Two and more combined |
|
Official signs |
— |
— |
76 |
127 |
32 |
|
Private signs |
136 |
98 |
15 |
405 |
531 |
|
Combined signs |
— |
24 |
165 |
— |
113 |
Table 1 Non-text Mark Statistics
The non-text marks used by official signs are relatively uniform. The essential pictures used on the official signs are cartoons of male and female Bai (One of 55 ethnic minorities) costumes with the most Dali characteristics, because Dali is the main settlement of the Bai people in China. This design also reflects the awareness of the publicity and protection of ethnic minority culture by the official signs in the area, and also highlights the important characteristics of this scenic spot that distinguish it from other scenic spots. There are also the national flag, peace dove and some tourist attractions with Dali style hung on the signs.
It can be found that the diversity of private signs, which stems from the diversity of service purposes and the diversity of means used by different shop owner to achieve service purposes. The most commonly used non-text forms of are trademarks and phone numbers. The pairwise combination method displays as much information as possible on the limited exhibition board to achieve the greatest possible attraction to the utmost extent. As non-text marks, phone numbers are the most displayed form of private signs. Whether it is a pure phone number or combined with other signs, phone numbers seem to be an indispensable choice for private signs.
The important way of displaying non-text marks of combined signs is photos. Models in ethnic costumes in the photo show the theme of the advertisement and also the combination of trademark and phone number or the combination of picture and phone number, etc., a combination of two or more forms. It is worth mentioning here that the QR code that is rarely seen on both official and private signs appears in the combined signs. QR code is a popular encoding method on mobile devices in recent years, which can store more information and represent more data types.
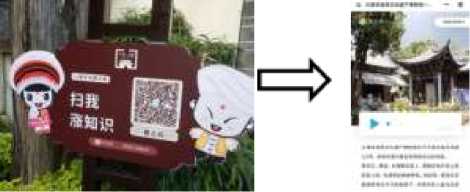
Photo 2 QR Code and Details after Scanning (Introduction of the Area)
The background color of the sign is also an important part of the non-verbal resources. As a symbol, color is related to people's customs and traditions, historical precipitation, appreciation habits and other factors. Appropriate background color and text color matching make language and readers get closer. This close emotion is complex, rational and sensual, and cold text gives people a sense of life temperature through color. In the same way, improper color matching not only fails to stimulate people's interest in browsing, but also greatly affects the quality of


language services and fails to achieve the expected service goals of t
he linguistic landscape.
|
Background colors Signs |
Red |
Yellow |
Black |
White |
Green |
Blue |
Other colors |
Two colors and more |
|
Official sign |
127 |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
108 |
|
Private Sign |
337 |
288 |
392 |
15 |
6 |
21 |
— |
126 |
|
Combined sign |
213 |
16 |
— |
— |
— |
27 |
— |
46 |
Table 2 Statistical of Background Color of Each Signs
It can be seen that the background colors of official signs are relatively uniform and those of private signs are relatively rich. The colors of combined signs are used based on the standards and requirements of official signs. Private signs use black background the most, followed by red and yellow. It should be noted that the focus of this research is not on professional art or color research, so there is no further subdivision of background colors, such as shades, etc. As long as they are of the same color, they are all classified into one category, and gold is also classified as yellow. In fact, many red backgrounds use crimson, not bright red, and are classified as red here.
Photo 3 Different Effects with Different Background Color
The most sensitive thing in human vision is the perception of color. The color of red is warm, strong and outgoing, and it is a very stimulating color. Red is easy to attract people's attention, it is also easy to make people excited, excited, nervous, impulsive, and it is also a color that can easily cause people's visual fatigue. Because red is easy to attract attention, it is also widely used in various media. In addition to having a better visual effect, it is also used to convey the corporate image and meaning of vitality, positivity, enthusiasm, warmth, and progress. In addition, red is often used as the color of warning, danger, prohibition, fire prevention, etc. When people see the red label on some occasions or objects, they can understand the meaning of warning danger without having to read the content carefully. Big red is generally used for eyecatching, such as red flags and a little red in the green bush; light red is generally gentle and tender, such as: new house decoration, children's clothing, etc.; dark red can generally be used as a foil, and there are relatively deep and warm feel. Red and light yellow are the best match, big red repels green, orange, and blue (especially the darker blue), and it is a neutral match with cream and gray. Black is noble and stable. Black also has a solemn image. It is also commonly
used in space design for some special occasions. Most daily necessities and clothing designs use black to create a noble image. It is also a main color that will always be popular. It is suitable for many colors. Match. Black and white is extremely opposite colors, and they always show their power through the presence of each other. (Zhao Meng, 2009)
The shape and style of signs are also an important part of non-verbal resources. In the traditional sense, the shapes of public signs are simple geometric edge shapes, such as squares, circles, trapezoids, and so on. They mainly rely on the words, patterns and colors in the signs for publicity, and their outer edges do not have the function of transmitting information and attracting attention. As the sole carrier of language and non-verbal resources in the linguistic landscape, it remains to be questioned whether it can fully play its due role if the shape is the same. To be sure, the style of billboards must be more than a few simple geometric shapes. Personalized sign styles are related to language service content. The shape of the sign and the service goal of the sign are complementary to each other.
This study divides the shape of signs into traditional and non-traditional shapes. Traditional shapes include linguistic landscape signs composed of various geometric figures, such as rectangles, squares, circles, and trapezoids. Non-traditional modeling is summarized as all geometric figures mentioned in non-traditional modeling, such as irregular shapes or cartoon
modeling.
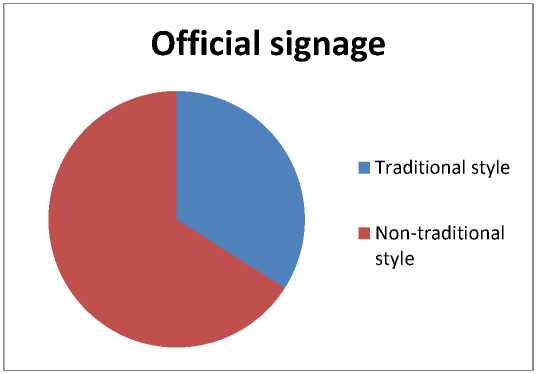
Photo 5 the Proportions of Official Signs
The non-traditional shapes of official signs accounted for 66% of the total, mainly because of the irregular shapes of road name signs and the shapes of some public service advertisement signs. The road nameplates of the tourist attractions in the ancient city of Dali uniformly use a butterfly shape. On the one hand, it breaks the square style of the traditional road nameplates and is more beautiful and lively. On the other hand, this shape also shows another important cultural symbol besides the Bai people in the ancient city of Dali. In addition, there are also some signs shaped like flying flags. Most of these signs are hung on street lights and are equipped with the Chinese national flag. The use of such signs can display public service advertisements more vividly and show the authority and charity of the text.


Photo 6 Non-traditional Shape of Official Signs
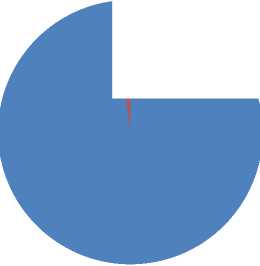
In sharp contrast with official signs, the traditional shapes of private signs possess absoluteness. Ninety-eight percent of private signs are traditional geometric shapes, rectangular or square, and even a few irregular shapes are fine-tuned on the basis of traditional shapes. The unification of private signage is not only affected by the size of the store door, but the most important reason is that it is restricted by the use of signs in tourist attractions.
Private signage
-
■ Traditional style
-
■ Non-traditional style
Photo 7 the Proportions of Private Signs
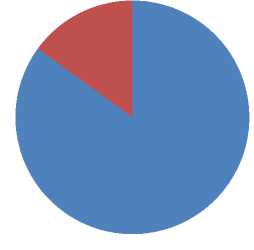
The traditional shape of combined signs accounts for 85% of the total. Multifunctional billboards and most signs are traditional square or rectangular shapes. Only a small part of the signs are non-traditional, but they are actually the same as the non-traditional shapes of official signs. This further illustrates that the combined signage is based on the requirements of official signs and the language service content of private signs as the core.
Combination signage
-
■ Traditional style
-
■ Non-traditional style
Photo 8 Proportions of Combined Signs
4. Conclusion
In general, non-verbal resources as a part of linguistic landscape are indispensable. Language is the core of linguistic landscapes while non-verbal resources are the presenting method and important symbolic of linguistic landscape used in a region. The sign designers transmit certain information, promote a certain product, and provide certain services through linguistic landscape and the viewer receive information through both language and non-verbal resources to find products that meet their own needs.
This study uses quantitative analysis to study the current situation of non-verbal resources of 1722 linguistic landscape in the 8 core blocks of Dali Ancient City. Through observation, it is found that the official signs of Dali ancient city scenic area appropriately use the non-text marks to better promote local culture. At the same time, the use of colors highlights text messages and makes people visually comfortable, in line with Chinese aesthetic habits. Most of the signs have radically abandoned traditional shapes and used non-traditional shapes that are more distinctive and can convey cultural information, which are worthy of promotion. Since the combined sign is formulated in accordance with the official sign standard, the shape and color are more in line with the official standard. The non-text marks on the signs are customized privately, which is more diverse than the unified official watch signs.
The non-verbal resources of private signs pay more attention to the transmission of information, and more use of phone numbers combined with brand logos makes the linguistic landscape an advertising effect and maximizes the mass communication of private brands. In addition, in order to comply with the official requirements, the color and shape of the signage do not differ much from store to store. It is worth mentioning that the official signage has a more long-term development perspective, by using the QR code which is very popular nowadays, but the scope of the implement is limited.
Due to the limited time and scope of the investigation, this research also has certain limitations, but the results can provide a reference for future language landscape research. It is hoped that in future research, scholars will not only pay attention to language, but also the importance of non-verbal resources.
References:
Landry, R. & R.Y. Bourhis (1997). ‘Linguistic Landscape and Ethnolinguistic Vitality: An Empirical Study’ Journal of Language and Social Psychology, 16, 23-49.
Zhao Meng. (2014) The Use and Matching of Colors in Advertising Design, Intelligence, 249-250.
Husband, Charles & Verity Saifullah Kahn. (1982) The viability of ethnolinguistic vitality: Some creative doubts. Journal of Multilingual and Multicultural Development 3(3). 193-205.
Antonio Bruyel-Olmedo, Maria Juan-Garau. (2015) Minority languages in the linguistic landscape of tourism: the case of Catalan in Mallorca. Journal of Multilingual and Multicultural Development, 598-619.
Backhaus, Peter. (2009) Rules and regulations in linguistic landscaping: A comparative perspective. In Elana Shohamy & Durk Gorter (eds.), Linguistic landscape: Expanding the scenery, 157-172. New York, NY & London: Routledge.
Collins, J. & S. Slembrouck (2007). ‘Reading Shop Windows in Globalized Neighborhoods: Multilingual Literacy Practices and Indexicality’ Journal of Literacy Research, 39:3, 335-356.
Shan Zhiqiang. (2017) Language Code in Geographical Investigation, Language Strategy Research, (2) 22-25.
Feng Xiaohui. (2014) The translation and translation of Shijiazhuang language, language and landscape guided by the promotion of city image, Science and Technology Vision, (18)28-31.
Fang Jia. (2015) Investigation and Research on the English Translation of Public Signs of Road Names from the Perspective of Language Landscape: Taking Urban Roads in Changzhou as an Example, Journal of Jiangsu University of Technology, (1) 55-59.
Biography of Authors


Lu Xing is a Doctor candidate of Linguistics in Udayana University, Denpasar, Indonesia. He was born in Henan, China, in 1989. By 2012, he finished his Bachelor Degree from Tianjin Foreign Study University, major in Enalish Language and Culture. In 2016 he got his Master Degree from Beihua University, major in Education: Chinese Teaching. After that, he continued to Doctoral study program of Linguistics in Udayana University, Denpasar, Indonesia. As visiting scholar he went to many different countries and universities to teach Chinese language.
Email: 124360898@qq.com
Prof. Drs. I Made Suastra is senior lecturer at faculty of humanities, undergraduate Udayana University from 1993 until now.
Email: made_suastra@unud.ac.id
Discussion and feedback