Prepositional Phrase and Its Translations Found in the Novel “Budha, a Story of Enlightenment”
on

e-Journal of Linguistics

Available online at https://ojs.unud.ac.id/index.php/eol/index
Vol. 15, No. 1, January 2021, pages: 111-125
Print ISSN: 2541-5514 Online ISSN: 2442-7586
https://doi.org/10.24843/e-jl.2021.v15.i01.p14
Prepositional Phrase and Its Translations Found in the Novel “Budha, a Story of Enlightenment”
I Made Juliarta
Universitas Bali Dwipa, Bali, Indonesia, madejuliarta330@gmail.com
Article info
Received Date: 4 December 2020
Accepted Date: 7 December 2020
Published Date: 31 January 2021
Keywords:*
prepositional phrases, translation, simple preposition, complex preposition.
Abstract*
The novel “Budha, A Story of Englightenment” is one of popular novels with New York Times Best Selling authors. This novel tells story as an icon of peace and serenity. The sentences with prepositional phrase and their translations from English into Indonesian are found in this novel. Therefore, the author is interested in analyzing the translation process occured in translating the source text into target text. The source text is analyzed and viewed to find out the translation of prepositional phrase. The translation is the proccess of transferring form from the first language into second language using semantic structure. This study aims at analyzing the source text and get the meaning and its translation. It is stated that a prepositional phrase is a group of words consisting of a preposition, its object, and any words modifying the object. A prepositional phrase also modifies a verb or a noun. There are two kinds of prepositional phrases which are called adverbial phrases and adjectival phrases. There are some complex prepositional phrases. Those are as for, except for, according to, by means, on the part of, etc. This present study is intended to: (i) identify the types of lexical and syntactical forms of the English prepositional phrases found in the data source “Budha, A Story of Englightenment”, (ii) analyze the types of shifts of prepositional phrases that were applied in the translation from source text into target text in the novel “Budha, A Story of Englightenment”
The translation can be meant as the proccess of transferring the form from the first language into the second language by using semantic structure. The source language must be transferred and held constant and the form of its translation may change. However, the translation activities do not only deal with transferring language from one language into another language, but also deal with the most important thing. Those are the process of transferring the message and the meaning from source language into target language. Catford (1965) stated that as a process, translation is always performed in a given direction from a source language into target language. There are some dificulties in translating an English text into Indonesian. Besides, there are also some external factors that contribute to such differences that is called as a culture. However, there are some strategies and procedures that can be done to the solutions to such difficulties. It is important for the translator to make assesment as needed in order to make the product of translation to be readable and understandable. As an object in this study, in translating an English text into Indonesian, the use of prepositions can be one of the things that make the process of
translation to be complicated. It can be seen from the illustration that the preposition ‘with’ is equivalent to ‘dengan’. The prepositions can contribute to the fact that it is difficult to translate prepositional phrase into target text. Therefore, this inspires the author of this study to discuss the prepositional phrase and its translation analysis. In analyzing the translation process, the author choose the novel entitled Budha, A Story of Englightenment. It is a novel that was written by Dheepak Chopra. The author tried to bring the Buddha back to life in this gripping account of the young prince who abandoned his inheritance to discover his true calling. This study analyzes the syntax structure of prepositional phrase and finds out about the form of prepositional phrase found in the novel. In analyzing the prepositional phrase in the translation process occured, this study used the theory proposed by Jackson (2000). According to the theory of prepositional phrase that is proposed by Jackson (2000), phrase is divided into noun phrase, verb phrase, adjective phrase, adverbial phrase and prepositional phrase. Prepositional phrase can be meant as a combination of two elements “preposition’ and ‘phrase’. In prepositional phrase, there are the relation between a noun and a verb. Moreover, Downing and Locke (2006) stated that preposition consists of two types. Those are simple preposition and complex preposition. In simple preposition, preposition has single prepositional particle. Part of single prepositional particle are: about, across, after, around, as, at, in, towards, etc. In complex preposition, preposition is formed by the combination of two prepositional particles. It is separated with a noun, an adjective, an adverb, and even phrases. The complex prepositional particles are as follows: as for, except, according to, by means, in return for, on the part of, etc. It is stated that simple prepositional phrase is a phrase consisting of a single prepositional word and followed by modifiers or complements. The complements consist of a noun, a noun group, a pronoun, an adverb, an adjective, a prepositional phrase, and a wh-clause. In complex prepositional phrase, phrase consists of two or three prepositions. It is modified with a noun, noun group, a pronoun, an adverb, an adjective.
In analyzing the translation process, this study uses the theory of prepositional phrase that is proposed by Downing and Locke (2006). There are two types of prepositional phrases. Those are simple prepositional phrase and complex prepositional phrase. The theory of prepositional phrase proposed by Downing and Locke (2006) stated that in simple prepositional phrase, a phrase consists of a single prepositional word and it is followed by modifiers or complements. The complements can be a noun, a noun group, a pronoun, an adverb, an adjective, a prepositional phrase. In complex prepositional phrase, it consists of two or three prepositions and mostly modified with noun, noun group, adverb, adjective, preposition, conjunction. The modifiers can be a noun, an adjective, an adverb, and preposition, or phrase.
This study also uses the theory of translation to analyze the translation shift found in the sentence containing English prepositional phrase. In analizing the translation process, this study also uses the theory proposed by Catford (1965) in order to analyze the translation process which occurred in the sentence containing prepositional phrase. In the translation of shift, Catford (1965) stated that, shift is the departure from formal correspondence in the process from the SL into the TL. The translation shift is applied to have the natural equivalent of the source text message into the target text. Moreover, Catford (1965) stated that the translation shift divides the shift in translation into two types, namely: level/rank shift and category shift. Catford (1965) considers that there are two types of shift, namely: (1) Shift of level and (2) shift of category. The translation process in this study is applied using the theory proposed by Catford (1965). The form
of prepositional phrase is analyzed using the theory that is proposed by Downing and Locke (2006).
In the category of shift, it is stated as the departures from formal correspondence in translation. It is stated that formal correspondence is any grammatical category in the target language which can be said to occupy the same position in the system of the target language as the given source language category in the source language system. The category of shift can be divided again into structure shifts, class shifts, unit shift, and intra-system shifts. Structure shift is the changing of words sequence in a sentence. In the intra-system shift, it refers to the shifts that occurs internally, within the system; that is for those cases where the source and the target language possess systems which approximately correspond formally as to their constitution, but when translation gets selection of a non-corresponding term in the target language system. Intrasystem shifts can happen when a term is singular in the source language and its textual equivalent is plural. Moreover, Halliday stated that a class as that grouping of members of a given unit that is defined by operation in the structure of the unit next above. It is stated that class-shift occurs when the translation equivalent of a SL item is a member of a different class from the original item.
Translation-shift is used as the focus of analysis because the translator has shifted the forms to keep the meaning constant so that the messages can be communicative and natural. This study tries to find out the shifts in form and meaning of prepositional phrase from English into Indonesian Language. This is conducted because the core of equivalence and shifts are in the form and meaning. As we can see that an equivalence and shifts, the meaning is more important than the form. The data used in this study is the novel entitled “Budha, A Story of Englightenment”. The data source is written in English. The reason of using this novel as the data source is because there are some English prepositional phrases found in this novel. The novel that is used is one of popular novels with the best author. This study used the technique called teknik pilah that is proposed by (Sudaryanto, 2015). The data source is written in two languages, namely: English and Indonesian language. The data source is analyzed in English.
Moreover, Downing and Locke (2006) stated that preposition consists of two types. Those are simple preposition and complex preposition. It can be seen that in simple preposition, preposition has single prepositional particle. Part of single prepositional particles are: about, across, after, around, as, at, in, towards, etc. In complex preposition, the preposition can be formed by the combination of two prepositional particles. It can be separated with a noun, an adjective, an adverb, and even phrases. The complex prepositional particles are as follows: as for, except, according to, by means, in return for, on the part of, etc. It is stated that simple prepositional phrase is a phrase consisting of a single prepositional word and followed by modifiers or complements. The complements are consisting of a noun, a noun group, a pronoun, an adverb, an adjective, a prepositional phrase, and a wh-clause. In complex prepositional phrase, phrase consists of two or three prepositions. It can be modified with a noun, noun group, a pronoun, an adverb, an adjective.
This study also uses Intra-system shift that is proposed by Catford which refers to the shifts that occurs internally, within the system; that is for those cases where the source and the target language possess systems which approximately correspond formally as to their constitution, but when translation involves selection of a non-corresponding term in the target language system. It is stated that Intra-system shifts occurs when a term is singular in the source language and its textual equivalent is plural.
Text I
He needed a weakness to exploit, and he was confident the enemy had left one for him . (12)
Ia ingin mengetahui kelemahan musuh dan sangat yakin pasti musuhnya sudah menunjukkan kekurangan. (9)
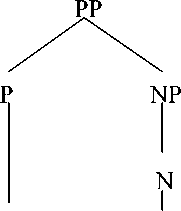
We can see from the prepositional phrase that is available in text I stating that prepositional phrase for him is formed by using preposition (for) +pronoun (him). Pronoun is used to complete the form of prepositional phrase. It is called as simple preposition. We can see the syntactix structure of prepositional phrase for him, as follows:
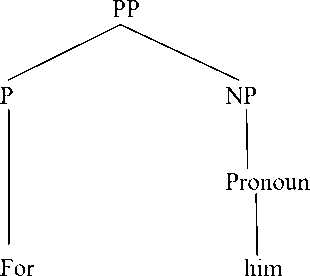
The prepositional phrase that is available in text I can be categorized as a simple prepositional phrase because it only has one preposition. As we can see from the sentence in text I that the prepositional phrase for him is not translated. Meanwhile, a word confident is translated into a phrase sangat yakin. The theory used in translating this is the theory proposed by Catford, stating that this type of translation shift is called a unit shift involving a change in rank. The unit shift occurs when the translation equivalent of a source text unit at one rank. It is stated that unit shift can be meant as the change in rank, that is, the departure from formal correspondence in which the translation equivalent of a unit at one rank in the source language. This shift is called as unit shift, that is, a change in higher rank that translates confident into sangat yakin.
Text II
Along with his army, the king would kneel in the temple and pray before he went to war, but he put no trust in divine help. (12)
Bersama tentaranya, sang raja berlutut di kuil dan berdoa sebelum berangkat perang. (10)
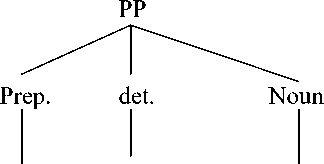
It can be seen from English prepositional phrase in text II, that preposition with his army is formed by using preposition (with) + possesive (his) + noun (army). It is categorized as a simple prepositional phrase because it only has one preposition with. We can see the syntactic structure of English prepositional phrase, as follows:
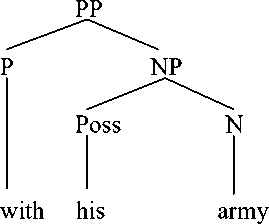
The prepositional phrase that is available in text II can be categorized as a simple prepositional phrase because it only has one preposition. As we can see from the sentence in text II that the prepositional phrase with his army is translated into tentaranya. The theory that is used in translating this preposition is proposed by Catford, stating that this type of translation shift is called a unit shift involving a change in rank. The unit shift occurs when the translation equivalent of a source text unit at one rank. It is stated that unit shift can be meant as the change in rank, that is, the departure from formal correspondence in which the translation equivalent of a unit at one rank in the source language. This shift is called unit shift, that is, a change in lower rank that is translating with his army into tentaranya.
Text III
Suddhodana was a warrior king, and the first thing to know about him is this, he mistook himself for a god. (12)
Suddhodana adalah raja perang, satu hal yang perlu diketahui tentangnya adalah ia mengira dirinya dewa. (10)
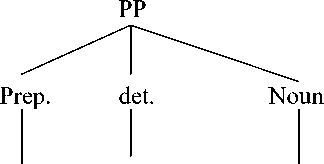
We can see from the English prepositional phrase for a god, the preposition consists of preposition for + determiner a + noun god. This kind of preposition is categorized as a simple prepositional phrase as it consists of preposition, determiner, and a noun. Here is the syntactic structure of English prepositional phrase for a god.
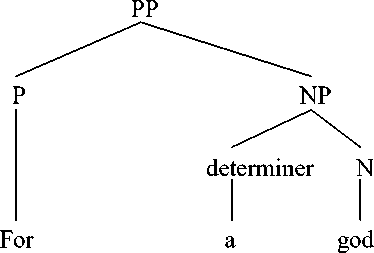
We can see from prepositional phrase that is available in text III that it is categorized as a simple prepositional phrase because it only has one preposition. It can be seen from prepositional phrase in text III that the prepositional phrase for a god is translated into dewa. The theory used in translating this preposition is proposed by Catford, stating that this type of translation shift is called a unit shift involving a change in rank. The unit shift can occur when the translation equivalent of a source text unit at one rank. It is stated that unit shift can be meant as the change in rank, that is, the departure from formal correspondence in which the translation
equivalent of a unit at one rank in the source language. This shift is called unit shift, that is, a change in lower rank that is translating for a god into dewa.
Text IV
By the time he came to the battlefield, its roiling activity and the smells that assaulted his nostrils. (13)
Begitu ia tiba di medan perang, gemuruh dan bau busuk yang tercium, hidungnya –
bau jerami dan darah. (13)
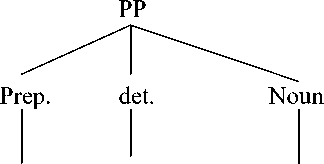
It can be seen from the English prepositional phrase in text IV, by the time, the prepositional phrase consists of preposition by + determiner the + noun time. It is categorized as a simple prepositional phrase as it consists of preposition, determiner, and a noun. Here is the syntactic structure of english prepositional phrase by the time.
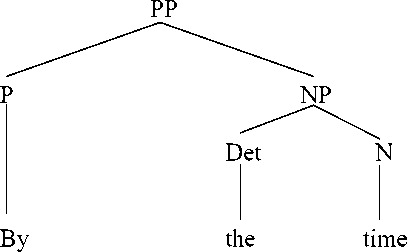
It can be seen from prepositional phrase in text IV that it is categorized as a simple prepositional phrase because it only has one preposition. As we can see from prepositional phrase in text IV that the prepositional phrase by the time is translated into begitu. The theory that is used in translating this preposition is proposed by Catford, stating that this type of translation shift is called a unit shift involving a change in rank. The unit shift can occur when the translation equivalent of a source text unit at one rank. It is stated that unit shift can be meant as the change in rank, that is, the departure from formal correspondence in which the translation equivalent of a unit at one rank in the source language. This shift is called unit shift, that is, a change in lower rank that is translating by the time into sehingga.
Text V
His sword whirled as he split a man’s head with a single blow. (14)
Pedangnya berputar-putar saat ia memenggal kepala seorang pria dengan sekali tebas.
(11)
Prepositional phrase with a single blow is formed by using preposition with + determiner a + adjective single + noun blow. Here is the syntactic structure of english prepositional phrase with a single blow.
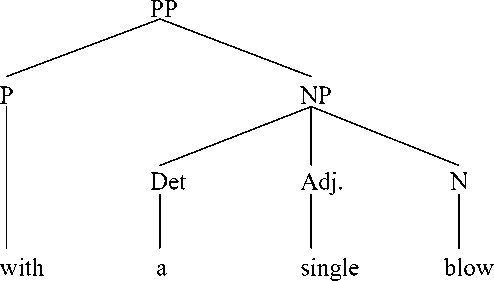
We can see from prepositional phrase in text V that it is categorized as a simple prepositional phrase because it only has one preposition. It can be seen from prepositional phrase in text V that the prepositional phrase with a single blow is translated into dengan sekali tebas. Unit shift in lower rank occured in translating his word into pedangnya.
Text VI
It was a meager company, consisting of six soldiers too old to serve in the war astride
six nags too weak to charge the enemy. (15)
Kelompok yang menyertai Maya lumayan kecil, terdiri atas enam serdadu yang terlalu tua untuk berperang, di atas enam kuda tua yang terlalu lemah untuk menyerang musuh. (13)
As we can see from English prepositional phrase in the war, it is formed by using preposition in + determiner the + a noun war. It can be categorized as a simple prepositional phrase as it consists of preposition, determiner, and a noun. We can see the syntactic structure of english prepositional phrase in the war, as follows:
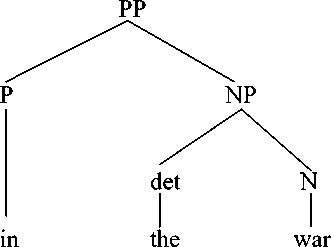
English prepositional phrase in text VI is categorized as a simple prepositional phrase because it only has one preposition. It can be seen from prepositional phrase in text VI that the prepositional phrase in the war is translated into untuk berperang. The theory that was used in translating this preposition is the theory proposed by Catford, stating that this type of translation shift is called a unit shift involving a change in rank. The unit shift occurs when the translation equivalent of a source text unit at one rank. It is stated that unit shift can be meant as the change in rank, that is, the departure from formal correspondence in which the translation equivalent of a unit at one rank in the source language. This shift is called unit shift, that is, a change in lower rank that is translating the phrase the war into berperang.
Text VII
Maya made no sound hidden behind the swaying silk drapes, except for a stifled moan whenever a bearer stumbled and the litter took a sharp jolt. (15)
Maya tak mengucapkan sepatah kata pun, hanya erangan kecil setiap kali salah satu penandu tersandung dan menyebabkan tandu tersebut tiba-tiba terguncang. (13)
English prepositional phrase for a stifled moan has been formed by using preposition for + determiner a + adjective stifled + noun moan. It is categorized as a simple prepositional phrase as it consists of preposition, determiner, adjective and a noun. We can see the syntactic structure of english prepositional phrase in the war, as follows:
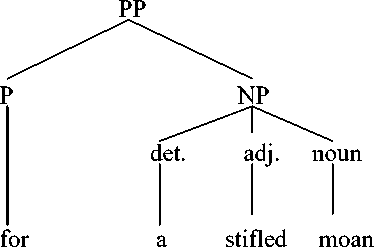
English prepositional phrase for a stifled moan in text VII is categorized as a simple prepositional phrase because it only has one preposition. We can see from English prepositional phrase in text VII that the prepositional phrase for a stifled moan is translated into hanya erangan kecil.
Text VIII
Three young ladies-in-waiting, who grumbled in low voices about having to walk, brought up the rear. (15)
Tiga dayang-dayang, yang diam-diam menggerutu karena harus berjalan kaki, berjalan di belakang. (13)
We can see from English prepositional phrase in low voices, that the preposition is formed by preposition in + adjective low + noun voices. It can be meant to be categorized as a simple prepositional phrase as it consists of preposition, adjective, and a noun. We can see the syntactic structure of english prepositional phrase in low voices, as follows:
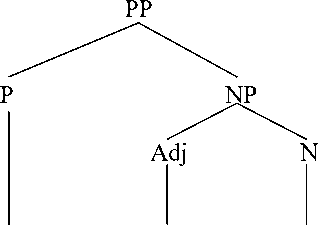
in low voices
English prepositional phrase in text VIII is categorized as a simple prepositional phrase because it only has one preposition. It can be seen from prepositional phrase in text VIII that the prepositional phrase in low voices is translated into menggerutu. The theory used in translating this preposition is the theory proposed by Catford, stating that this type of translation shift is called a unit shift involving a change in rank. The unit shift occurs when the translation equivalent of a source text unit at one rank. Unit shift can be meant as the change in rank, that is, the departure from formal correspondence in which the translation equivalent of a unit at one rank in the source language. This shift is called unit shift, that is, a change in lower rank that is translating the phrase in low voices into menggerutu.
Text IX
Tigers were known to snatch their prey from terrified bands of travelers in this area,
even in the brightest hour of the day. (15)
Konon kabarnya juga ada banyak harimau yang memangsa kelompok pengelana penakut yang melewati wilayah ini, bahkan pada siang hari bolong . (14)
As we can see from English prepositional phrase from terrified bands, it is formed by using preposition from + adjective terrified + a noun bands. It can be categorized as a simple prepositional phrase as it consists of preposition, adjective, and a noun. We can see the syntactic structure of English prepositional phrase from terrified bands, as follows:

It can be seen that English prepositional phrase in text IX can be categorized as a simple prepositional phrase because it has one preposition. It is seen from prepositional phrase in text IX that the prepositional phrase from terrified bands is translated into kelompok pengelana penakut. The theory that is used in translating this preposition is the theory proposed by Catford, stating that this type of translation shift is called a unit shift involving a change in rank. The unit shift can occur when the translation equivalent of a source text unit at one rank. Unit shift can be meant as the change in rank, that is, the departure from formal correspondence in which the translation equivalent of a unit at one rank in the source language. This shift is called unit shift, that is, a change in higher rank when translating the word bands into the phrase kelompok pengelana.
Text X
With the slightest bow from the shoulders that etiquette permitted, the guard said, “I’ll scout up ahead for camp. (15)
Dengan sedikit membungkuk demi sopan santun, pengawal itu berkata, “Aku akan berkuda duluan mencari tempat berkemah”. (14)
We can see from English prepositional phrase for camp, that the prepositional phrase is formed by (preposition) for + (noun) camp. It is categorized as a simple prepositional phrase as it consists of preposition, and a noun. We can see the syntactic structure of english prepositional phrase for camp, as follows:
for
camp
It can be seen that English prepositional phrase in text X that it is categorized as a simple prepositional phrase because it only has one preposition for. It can be seen from prepositional phrase in text X that the prepositional phrase for camp is translated into mencari tempat berkemah. The theory used in translating this preposition is the theory proposed by Catford, stating that this type of translation shift is called a unit shift involving a change in rank. The unit shift occurs when the translation equivalent of a source text unit at one rank. Unit shift is the change in rank, that is, the departure from formal correspondence in which the translation equivalent of a unit at one rank in the source language. This shift is called unit shift, that is, a change in higher rank that is translating the word camp into tempat berkemah. In analizing the translation process, this data also uses the theory that is proposed by Catford (1965) in order to analyze the translation process occurred in the sentence containing prepositional phrase. In the translation of shift, according to Catford (1965), shift is the departure from formal correspondence in the process from the SL into the TL.
Text XI
Funeral Smoke, oily and thick, twisted through the air and tainted the sky as Maya’s body burned atop the huge pile of sandalwood logs that had been chopped from the forest. (19)
Asap tebal api kremasi yang pekat dan berbau minyak bergulung-gulung di udara dan mewarnai langit saat jenazah Maya dibakar di atas tumpukan tinggi potongan-potongan kayu cendana hutan. (34)
It can be seen from the translation of English prepositional phrase from the forest, that the preposition is formed by (preposition) from + (determiner) the + (noun) forest. It is categorized as a simple prepositional phrase as it consists of preposition, determiner and a noun. We can see the syntactic structure of English prepositional phrase from the forest, as follows:
From the forest
It can be seen that English prepositional phrase in text XI can be categorized as a simple prepositional phrase because it has one preposition. It is seen from prepositional phrase in text XI that the prepositional phrase from the forest is translated into kayu cendana hutan. The theory that is used in translating this preposition is the theory proposed by Catford, stating that this type of translation shift is called a unit shift involving a change in rank. The unit shift can occur when the translation equivalent of a source text unit at one rank. Unit shift can be meant as the change in rank, that is, the departure from formal correspondence in which the translation equivalent of a unit at one rank in the source language. This shift is called unit shift, that is, a change in higher rank when translating the word foret into the phrase kayu cendana hutan.
Text XII
His face reddened as he shouted orders for more wood, a higher flame, more
melted ghee to pour over the body. (20)
Wajahnya memerah saat ia berteriak memberi perintah supaya orang-orang
suruhannya menambah kayu, memperbesar api, dan menuang lebih banyak dadih ke atas mayat itu. (34)
It can be seen from the translation of English prepositional phrase from more wood, that the preposition is formed by (preposition) for + (determiner) more + (noun) wood. It can be categorized as a simple prepositional phrase as it consists of preposition, determiner and a noun. We can see the syntactic structure of English prepositional phrase for more wood, as follows:
For more wood
It can be seen that English prepositional phrase in text XII can be categorized as a simple prepositional phrase because it has one preposition. It is seen from prepositional phrase in text XII that the prepositional phrase for more wood is translated into menambah kayu, stating that this type of translation shift is called a unit shift involving as a change in rank. The unit shift can occur when the translation equivalent of a source text unit at one rank. Unit shift can be meant as the change in rank, that is, the departure from formal correspondence in which the translation
equivalent of a unit at one rank in the source language. This shift is called unit shift, that is, a change in lower rank when translating for more wood into the phrase menambah kayu. It can be seen from the translation process occured above, that her face is translated into wajahnya. Unit shift in lower rank occured in translating the phrase her face into a word wajahnya. This translation process also uses the theory of translation to analyze the translation shift found in the sentence containing English phrase her face translated into wajahnya. In analizing the translation process, this study also uses the theory proposed by Catford (1965) in order to analyze the translation proses occurred in the sentence containing prepositional phrase. In the translation of shift, Catford (1965) stated that, shift is the departure from formal correspondence in the process from the SL into the TL. It can be seen from the text above that orders is translated into memberi perintah supaya orang-orang suruhannya. A shift occured in the translation process as a change in higher rank that is translating a word orders into phrase perintah supaya orang-orang suruhannya.
Text XIII
The ghee had been churned from the milk of sacred cows (20)
Dadih tersebut dihasilkan dari susu sapi suci. (34)
It can be seen from English prepositional phrase from the milk, that the preposition can be formed by (preposition) from + (determiner) the + (noun) milk. It can be categorized as a simple prepositional phrase as it consists of preposition, determiner and a noun. It can bee seen from the syntactic structure of english prepositional phrase from the milk, as follows:
From the milk
It can be seen from the text XIII that English prepositional phrase above can be categorized as a simple prepositional phrase because it only has one preposition. It is seen from prepositional phrase in text XIII that the prepositional phrase from the milk is translated into susu sapi, stating that this type of translation shift is called a unit shift involving a change in rank. The unit shift can occur when the translation equivalent of a source text unit at one rank. Unit shift can be meant as the change in rank, that is, the departure from formal correspondence in which the translation equivalent of a unit at one rank in the source language. This shift is called unit shift, that is, a change in lower rank when translating for the milk into the phrase menambah susu sapi. It can be seen from the translation process occured above, that for the milk had been translated into susu sapi. Unit shift in lower rank occured in translating the phrase her face into a word wajahnya. This translation process also uses the theory of translation to analyze the translation shift found in the sentence containing English phrase for the milk that is translated into susu sapi. In analyzing the translation process occured in the text, this data above also uses the theory proposed by Catford (1965) in order to analyze the translation process occurred in the sentence containing prepositional phrase. In the translation of shift Catford (1965) stated that, shift is the departure from formal correspondence in the process from the SL into the TL. It can
also be seen from the text that had been churned had been translated into dihasilkan. Therefore, translation shift occured in the translation process that changes in lower rank.
Text XIV
Maya had remembered playing there as a child, when noble girls from the region were brought to court on the chance that any might please young Suddhodana. (20) Waktu masih kecil, maya ingat pernah bermain-main di tempat itu, saat gadis-gadis berdarah biru dari daerah sekitar dibawa ke istana kalau-kalau salah satu dari mereka bisa menarik perhatian Suddhodana. (44)
It can be seen in text XIVfrom English prepositional phrase from the region, that the preposition can be formed by (preposition) from + (determiner) the + (noun) region. It can be categorized as a simple prepositional phrase as it consists of preposition, determiner and a noun. It can bee seen from the syntactic structure of english prepositional phrase from the region, as follows:
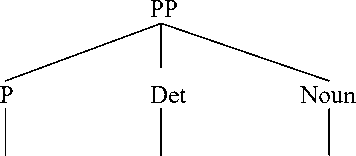
from the region
It can be seen from the text XIV that English prepositional phrase above can be categorized as a simple prepositional phrase because it only has one preposition. It is seen from prepositional phrase in text XIV that the prepositional phrase from the region is translated into dari daerah sekitar, stating that this type of translation shift is called a unit shift involving a change in rank. The unit shift can occur when the translation equivalent of a source text unit at one rank. Unit shift can be meant as the change in rank, that is, the departure from formal correspondence in which the translation equivalent of a unit at one rank in the source language. This shift is stated as unit shift, that is, a change in higher rank when translating a word region into the phrase daerah sekitar. It can be seen from the translation process occured above, that a word region had been translated into phrase daerah sekitar. The theory used in translating is called as unit shift. Unit shift in higher rank also occured in translating a word region into a phrase daerah sekitarnya. This translation process also uses the theory of translation to analyze the translation shift found in the sentence containing English word region that is translated into phrase daerah sekitar.
In analyzing the translation process occured in the text, this data above also uses the theory that is proposed by Catford (1965) in order to analyze the translation process which occurred in the sentence containing prepositional phrase. In the translation of shift Catford (1965) stated that, shift is the departure from formal correspondence in the process from the SL into the TL. It can also be seen from the text that region had been translated into phrase daerah sekitar. Therefore, translation shift occured in the translation process that changes in higher rank.
In analyzing the translation process, this study uses the theory of prepositional phrase proposed by Downing and Locke (2006). There are two types of prepositional phrases. Those are simple prepositional phrase and complex prepositional phrase. The theory of prepositional phrase proposed by Downing and Locke (2006) stated that in simple prepositional phrase, a phrase consists of a single prepositional word and it is followed by modifiers or complements. The complements can be a noun, a noun group, a pronoun, an adverb, an adjective, a prepositional phrase. In complex prepositional phrase, it consists of two or three prepositions and mostly modified with noun, noun group, adverb, adjective, preposition, conjunction. The modifiers can be a noun, an adjective, an adverb, and preposition, or phrase.
This study also uses the theory of translation to analyze the translation shift found in the sentence containing English prepositional phrase. Translation-shift can be used as the focus of analysis because the translator has shifted the forms to keep the meaning constant, therefore the messages can be communicative and natural. This study found out the shifts in forms and meaning of prepositional phrase in translating from English into Indonesian Language. This study is conducted because the core of equivalence and shifts are in the form and meaning. As we can see that in an equivalence and shifts, the meaning is more important than the form. The data that is used in this study is the novel entitled “Budha, A Story of Englightenment”. The data source is written in English. The reason of using this novel as the data source is because there are some English prepositional phrases found in this novel. Moreover, it is one of popular novels with the best author. This study used the technique that is called teknik pilah that is proposed by (Sudaryanto, 2015). The data source is written in two languages, namely: English and Indonesian language. The data source had been analyzed in English.
Brown K and Miller J. 1991. A Linguistic Introduction to Sentence Structure. London:
Routledge.
Broccias C. 2011. Motivating the Flexibility of Oriented –ly Adverbs”. Dis. (serial online), Jan-Mar, (cited 2011 Jun. 56. Available from URL:
http:/www.benjamins.com/gov/ncidod/EID/eid.htm
Downing and Locke. 2006. English Grammar A University Course. 2nd Edition. New York: Routledge.
Halliday, M.A.K., 1985. An Introduction to Functional Grammar. London: Edward.
Huddleston, Rodney and Pullum, Geoffrey K. 2005. A Student’s Introduction to English
Grammar. Canbridge: Cambridge University Press
Mukti, Hilman Fariz. 2002. Complete English Grammar. Yogyakarta: Ansolut.
Nuryanti. 2007. Adverbs and its Syntactic Function with Special reference to
Danielle Steel’s Daddy. Denpasar: Udayana University.
Petrus. 2005. The Morphosyntactic Analysis of –ize, -ify, and –en in English. Denpasar: Udayana University.
Quirk R and Greenbaum. 1973. A University Grammar of English. Hongkong:
Commonwealth Printing Press.
Rathadi. 2009. The Analysis of Adverb of Degree in Charlotte’s Web Novel. Denpasar: Udayana University.
Thomson, A.J. 1986. A Practical English Grammar. London: Oxford University Press.
Biography of Author

I Made Juliarta,S.S.,M.Hum. was born in Denpasar on July 9th 1990. He is a lecturer in Bali Dwipa University, English Department, Denpasar, Bali, Indonesia, Ph. +6283115041037. He finished his master degree in the postgraduate program, magister program, Linguistics Program, Udayana University in 2016.
Email: Madejuliarta330@gmail.com
Discussion and feedback