LITERATURE REVIEW: SEXUAL DYSFUNCTION IN PATIENTS WITH SCHIZOPHRENIA
on
Community of Publishing In Nursing (COPING), p-ISSN 2303-1298, e-ISSN 2715-1980
LITERATURE REVIEW: SEXUAL DYSFUNCTION IN PATIENTS WITH SCHIZOPHRENIA
Sitti Rahma Soleman1, Warih Andan Puspitosari2
1Dosen Program Studi Keperawatan, Institut Kesehatan dan Teknologi Graha Medika Kotamobagu 2
Dosen Program Studi Kedokteran, Universitas Muhammadiyah Yogyakarta
Alamat Korespondensi: sittirahma.nursing@gmail.com
ABSTRAK
Terapi antipsikotik pada pasien skizofrenia dilaporkan menjadi faktor utama penyebab terjadinya gangguan seksualitas pada pasien skizofrenia. Sebagai manusia yang mempunyai kebutuhan biologis, fungsi seksualitas pada orang dengan skizofrenia harus diperhatikan. Pengkajian fungsi seksualitas sering mengalami kesulitan karena masih dianggap hal tabu dan terabaikan. Studi ini bertujuan untuk mereview penelitian tentang faktor-faktor yang mempengaruhi disfungsi seksualitas pada pasien skizofrenia. Studi ini menggunakan pendekatan studi literature review yang mereview beberapa hasil penelitian tentang seksualitas pada orang pasien skizofrenia. Pencarian literature melalui search engine EBSCO, Proquest, Science Direct, Pubmed, and Google Scholar. Dari hasil pencarian didapatkan 398 studi kemudian di telaah sehingga mendapatkan 19 studi yang relevan. Kata kunci yang digunakan adalah schizophrenia, sexuality, sexual function, sexual dysfunction. Dari 19 literature yang ditemukan ada beberapa faktor yang menyebakan terjadinya masalah seksualitas pada pada pasien skizofrenia. Faktor- faktor tersebut adalah penggunaan antipsikotik, stigma, diskriminasi, budaya, kepercayaan, dan spiritual. Disfungsi seksual apabila tidak ditangani dapat memberikan dampak buruk seperti menurunkan harga diri, memperburuk isolasi sosial, dan menurunkan kemampuan membangun hubungan seksual dengan pasangan. Selain itu disfungsi seksual juga dapat mempengaruhi kualitas pernikahan sehingga dapat menyebabkan perselisihan permanen dan bahkan perceraian. Dampak lain dari disfungsi seksual dapat mempengaruhi kualitas hidup, harga diri rendah, mood pasien, kepatuhan minum obat, dan kepatuhan mengikuti terapi. Faktor penggunaan antipsikotik masih menjadi penyebab tertinggi terjadinya disfungsi seksual pada pasien skizofrenia. Disfungsi seksual apabila tidak ditangani akan berpengaruh terhadap kualitas hidup pasien. Oleh karena itu diharapakan kepada tim profesional dalam hal ini dokter maupun perawat agar bisa meningkatkan perawatan dan dan evaluasi terkait kejaidan disfungsi seksual pada pasien skizofrenia.
Keywords: Schizophrenia, seksualitas, fungsi seksual, seksual disfungsi
ABSTRACT
Schizophrenia is a serious mental disorder characterized by incoherent thoughts, delusions, hallucinations, and impaired concentration. Antipsychotic therapy in schizophrenic patients is reported to be the main factor causing sexual function problems in schizophrenic patients. As humans who have biological needs, the function of sexuality in people with schizophrenia must be considered. The assessment of the function of sexuality often experiences difficulties because it is still considered taboo and neglected. The aim of the study was to review research on the factors that influence sexual functioning in schizophrenic patients. a literature review study approach was used to reviewed several research on sexuality in schizophrenia patients. Article search through EBSCO, Proquest, Science Direct, Pubmed, and Google Scholar. Search results, founds that 398 articles, then analyzed so that 19 relevant studies were obtained. The key words used were schizophrenia, sexuality, sexual function, sexual dysfunction. From 19 literature found that there are several factors that cause sexuality problems in schizophrenia patients. These factors are the use of antipsychotics, stigma, discrimination, culture, beliefs, and spirituality. Untreated sexual dysfunction can have negative effects such as lowering self-esteem, worsening social isolation, and the ability to build sexual relationships with partners. In addition, sexual dysfunction can also affect the quality of the marriage, which can lead to permanent disputes and even divorce. Other effects of sexual dysfunction can affect quality of life, low self-esteem, patient mood, medication adherence, and adherence to therapy. The use of antipsychotics is still the biggest cause of sexual dysfunction in schizophrenic patients. Untreated, sexual dysfunction will affect patient's quality of life. Therefore, it is hoped that the professional team in this case doctors and nurses can improve the care and evaluation of sexual dysfunction related events in schizophrenia patients.
Keywords: schizophrenia, sexuality, sexual function, sexual dysfunction
INTRODUCTION
Serious mental disorders such as schizophrenia are still one of the significant health problems in the world, including Indonesia. According to WHO data (2014) there are about 21 million people affected by schizophrenia. One in two people diagnosed with schizophrenia does not receive schizophrenia-specific treatment. In Indonesia, with a variety of biological, psychological, and social factors with a diverse population, the number of cases of mental disorders continues to increase which has an impact on increasing the burden on the country and decreasing human productivity in the long term (Ministry of Health, 2013). Riskesdas 2013 data on the prevalence of serious mental disorders such as schizophrenia in Indonesia reached around 400,000 people or as much as 1.7 per 1000 population (Ministry of Health RI, 2013).
Schizophrenia is a serious mental disorder characterized by symptoms such as incoherent or unreasonable thoughts, delusions, hallucinations, and impaired concentration (APA, 2017). Schizophrenia usually appears in late adolescence or early adulthood. The etiology of schizophrenia is not clear, but it is known that there are several factors that influence the occurrence of schizophrenia, namely heredity and the main trigger factors such as psychological stress (Just, 2015).
The symptoms of schizophrenic that appears in patients is decrease in several functions both in their life and in their environment. These symptoms include speech disturbances, disturbed affect, behavioral disturbances, neglected appearance and personal hygiene, perceptual disturbances (hallucinations) and disorders of the mind (delusions). One of the consequences of these symptoms is productivity and disturbed relationships (WHO, 2014). This symptom can be relieved
by treatment. Schizophrenia is treated by anti-psychotic drugs. The use of antipsychotics causes various side effects, from mild to permanent movement disorders. One of the side effects of using antipsychotics in schizophrenic patients is sexual dysfunction (Just, 2015).
As humans who have biological needs, sexuality is a need that must be considered (Kaplan et al, 1997 & Hamid, 1999). Assessment of sexual function often experiences difficulties because it’s considered intimate and clients are sometimes reluctant to discuss (Tharoor et al, 2015). In addition, doctors or professional teams often ignore problems of sexual function or sexual dysfunction in schizophrenic patients. There are almost no studies of sexual function in schizophrenic patients.
Untreated, sexual dysfunction will have a negative impact, such as lowering selfesteem, worsening social isolation, and reducing the ability to build sexual relationships. In addition, sexual dysfunction can also affect the quality of marriage and may lead to permanent disputes and even divorce (Hou et al., 2015). From some of the explanations above, the authors are interested in reviewing articles on the function of sexuality in schizophrenic patients.
METHODS
This study used a literature review study approach that reviewed several research related to the function of sexuality in schizophrenic patients. Based on the explanation above, the writer intends to review the article, identify, find out, and seek an understanding of how sexuality functions in schizophrenic patients. Search relevant literature on the relevant database, namely EBSCO, Proquest, Science Direct, Pubmed, and Google Scholar. The database search
used key words: schizophrenia, sexuality, sexual function, sexual dysfunction.
This review aims to provide an overview and explanation of the factors that influence sexual function problems in schizophrenic patients. Search
comprehensively and thoroughly in order to
Literature Review Process
get a systematic search. Search period from 2012-2017. The author limits the search to articles in English. Each article was identified by reading the full text and examining the factors of sexual dysfunction and the effects of sexual dysfunction in schizophrenic patients.
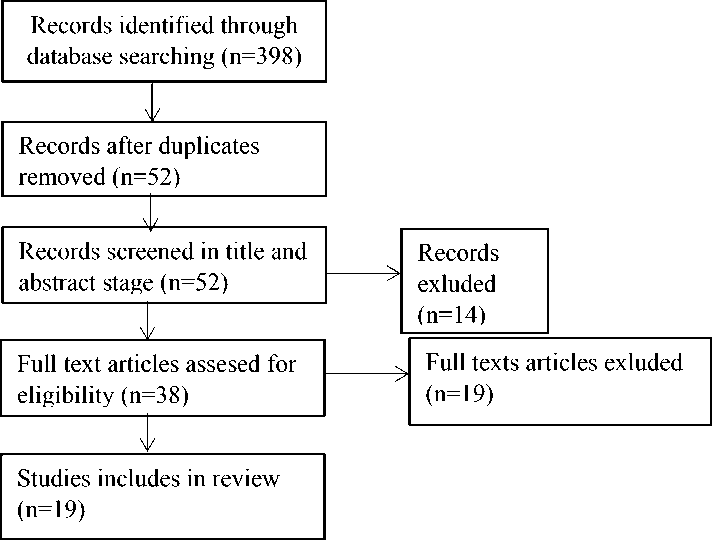
RESULT
Searching and determining process of the articles was done by filtering articles from 398 into 19 articles. The search process was carried out through electronic databases such as EBSCO, Proquest, Science Direct, and Google Scholar. Nineteen articles that had been reviewed, found several factors that cause sexual dysfunction and the impact of sexual dysfunction on schizophrenic patients. These factors include the use of antipsychotics (Lee et al., 2015), (Olisah, Sheikh, Abah, & Ajeigbe, 2016), (Hocaoglu, Celik, Kandemir, Guveli, & Bahceci, 2015), (Boer, Castelein, Wiersma, Schoevers, & Knegtering, 2017), (Bram et al., 2014),
(Shetageri, Bhogale, Patil, Nayak, & Chate, 2016), (Yee, Psychiatry, Rahaiza, Ramli, & Psychiatry, 2014), ( Vargas, Nunes, & Moreira, 2012), (Terevnikov, Stenberg, Tiihonen, & Burkin, 2016), (Kikuchi, Iwamoto, Sasada, & Aleksic, 2012) & (Paper, 2016), stigmatization and self-discrimination (Boer et al. ., 2017) (Sánchez-fuentes, Santos-iglesias, & Sierra, 2014) (Huguelet et al., 2014) (Laxhman, Greenberg, & Priebe, 2017). In addition, other factors that affect sexual dysfunction are a lack of interest in sexual intercourse, marital status, spirituality (Tharoor, Kaliappan, & Gopal, 2017), and cultural factors (Shetageri et al., 2016).
Table 1 Journals Summaries
|
No |
Title |
Author (Years) |
Aims |
Design |
Important Findings |
|
1. |
The influence of atypical antipsychotic drugs on sexual function |
Just (2015) |
To review the effect of atypical antipsychotics on sexual function. |
Review |
The use of antipsychotic drugs will affect sexual function. This is related to the activation of neurotransmitters such as dopamine and serotonin in the central nervous system. Antipsychotics affect sexual function in the following ways:
receptors in the hypothalamus, causing hyperprolactinemia, galactorrhea, menstruation, erectile disorders, and reduced libido.
activity. |
|
2. |
Sociodemographic and clinical correlates of sexual dysfunction among psychiatric outpatients receiving common psychotropics medications in a Neuropsychiatric Hospital in Northern Nigeria |
Olisah et al (2016) |
To describe the various types of sexual dysfunction in outpatient psychiatric patients receiving psychotropic drugs and the sociodemographic correlations associated with them. |
Descriptive research with cross-sectional design. |
causes of sexual dysfunction. Libido is regulated by dopamine, sexual arousal is regulated by acetylcholine and nitric oxide, and orgasm is regulated by serotonin and noradrenaline.
with erectile dysfunction. Whereas in women it is associated with the occurrence of orgasmic dysfunction.
the occurrence of orgasmic dysfunction in both men and women |
|
3. |
Sexual dysfunction in outpatients with schizophrenia in Turkey: a cross-sectional study. |
Hocaoglu et al (2014) |
Compared the self-reported sexual function of stable schizophrenic patients receiving antipsychotic therapy using the Arizona Sexual Experience Scale (ASEX). |
The crosssectional study uses 5 items in the Arizona Sexual Experience Scale (ASEX) to assess 5 |
sexual dysfunction than men.
function between patients taking first-generation antipsychotic drugs and second-generation antipsychotics. |
|
components of | ||||||
|
sexual function, namely: sex urge, sexual arousal, vaginal lubrication / penile erection, ability to achieve orgasm, and satisfaction with orgasm. | ||||||
|
4. |
The facts about sexual (dys)function in schizophrenia: An overview of clinically relevant findings. |
De Boer et al (2015) |
To describe the relationship between schizophrenia and sexual dysfunction |
A balanced clinical review of articles |
- - - |
Factors that affect sexual function in schizophrenic patients, namely primary disease, antipsychotic medication, comorbid somatic disorders, relationship factors, social competence, previous sexual experiences (positive or negative), or stigmatization and self-discrimination. Strategies for psychosocial problems, namely sex education, special interventions, relationship counseling, education about risky sexual behavior, prevention of unwanted pregnancy, abortion, and unwanted sexual relations. Strategies for treating sexual dysfunction due to antipsychotics include lowering the dose, switching to prolactin with an antipsychotic, and adding dopamine agonists, aripiprazole, or a PDE-5-inhibitor. |
|
5. |
Sexual dysfunctions in schizophrenia: Professionals and patients perspectives |
Tharoor et al (2015) |
to assess sexual dysfunction in schizophrenia and the attitude of a professional team in assesing symptoms of sexual dysfunction during clinical practice. |
Cross-sectional study |
- - |
Psychiatrists rarely asses sexual dysfunction in schizophrenic patients even though they were aware that good sexual function is important for the patient. Professional team caring for patients has an important role in managing sexual problems in schizophrenic patients. |
|
- Factors that affect sexual function, such aslack of interest in sexual relations, single status, physical illness, and spiritual involvement | |||||
|
6. |
Sexual dysfunction in Tunisian patients with schizophrenia |
Bram et al (2014) |
This study aims to assess and assess sexual dysfunction in schizophrenic patients |
Cross-sectional descriptive study |
sexual satisfaction.
antipsychotics.
negative symptoms and long-term use of antipsychotics |
|
7. |
Sexual dysfunction among females receiving psychotropics medication: A hospital-based crosssectional study. |
Shetageri et al (2016) |
To determine the prevalence and nature of sexual dysfunction in women receiving antipsychotics and to compare sexual dysfunction between female patients receiving antipsychotics and antidepressants. |
Cross-sectional |
of women who use psychotropic drugs
include the following:
- Cultural factors influence the patient in expressing sexuality problems experienced. |
|
8. |
Antipsychotic and sexual dysfunction: Epidemiology, mechanisms, and management |
Chiesa et al (2013) |
Review recent evidence on sexual dysfunction associated with antipsychotics and describe management strategies for antipsychotics associated with sexual dysfunction |
Review |
associated with sexual dysfunction are olanzapine, risperidone, haloperidol, clozapine, and thiorizadine.
quetiapine, and aripiprazole cause low-grade sexual dysfunction.
antipsychotics to increase prolactin levels and to bind to cholinergic, a-adregenic, histaminergic, and dopaminergic receptors.
dysfunction is to reduce the dose of antipsychotics and switch to anti-cycline, prolactin antipsychotics such as aripiprazole, |
|
9. |
Sexual dysfunctions and its impact on quality of life in Chinese patients with |
Hou et al (2015) |
The aim of this study was to describe the prevalence and correlation of sexual |
Cross-sectional survey |
- The prevalence of sexual dysfunction in primary care is high. The negative impacts that |
|
schizophrenia treated in |
dysfunction and its impact |
arise are social adaptation, quality of life, and |
|
primary care |
on the quality of life of schizophrenic patients - - - - - |
medication adherence. sexual dysfunction assessment makes patients embarrassed and even afraid of discrimination and gets negative responses. Sexual dysfunction is more common in male patients than female. Old age is a risk factor for sexual dysfunction. Sexual dysfunction can lower self-esteem, worsen social isolation, and the ability to build sexual relationships. Sexual dysfunction can also affect the quality of the marriage, which can lead to permanent strife and even divorce. |
|
10 Remitted male schizophrenia patients with sexual dysfunction |
Kheng Yee et al To know the prevalence of Cross-sectional - (2013) sexual dysfunction and the relationship between male - schizophrenic patients and sociodemography, - medication, depression, anxiety, pain psychopathology, BMI, and waist circumference. - - |
Orgasmic dysfunction in Malay patients is higher than Chinese patients because of the influence of religious education or culture of Malay patients Patients who have a higher level of education have a higher risk for orgasmic dysfunction Unmarried patients have a high rate of orgasmic dysfunction. |
|
11 Strategies for the treatment of antipsychotic-induced sexual dysfunction and/or hyperprolactinemia among patients of the schizophrenia spectrum: A review. |
Nunes et al Reviewing research on Review - (2012) strategies for the treatment of sexual dysfunction in schizophrenic patients |
The use of different antipsychotics will cause different risks of sexual dysfunction. |
|
12 Add-on mirtazapine improves orgasmic functioning in patients with schizophrenia treated with first-generation antipsychotics. |
Terevnikov et al Determine whether RCT - (2016) mirtazapine use can improve sexual dysfunction - associated with FGA use in schizophrenic patients |
The addition of mirtazapine to FGA did not worsen sexual dysfunction Mirtazapine improves orgasmic function |
|
13 |
Sexual dysfunction and hyperprolactinemia in japanese schizophrenia patients taking antipsychotics |
Kikuchi et al (2012) |
To know the prevalence of sexual dysfunction as evaluated by the Nagoya Sexual Function Questionnaire (NSFQ), hyperprolactinemia and the relationship between sexual dysfunction and serum prolactin levels. |
Cross-sectional - - |
The prevalence of sexual dysfunction in schizophrenic patients is high (male 66.7% and female 79.5%) There was no association between sexual dysfunction and serum prolactin levels. |
|
14 |
Effect of adjunctive aripiprazole on sexual dysfunction in schizophrenia: A preliminary open-label study. |
Fujioi et al (2016) |
To assess the effects of using aripiprazole for schizophrenia with sexual dysfunction |
quantitative - - |
Erectile dysfunction in men was significantly reduced at week 24 measured using the Nagoya Sexual Function Questionnaire (NSFQ) In women, irregular menstruation and galactorrhea was significantly reduced at week 24 measured using the Nagoya Sexual Function Questionnaire (NSFQ). |
|
15 |
Factors associated with self-rated sexual function in korean patients with schizophrenia receiving risperidone monotherapy |
Lee et al (2015) |
To know the factors related to sexual function in schizophrenic patients |
Cross-sectional - - - |
Sexual function is negatively related to age, duration of illness, sex, marital status, presence of tardive dyskinesia, Beck Depression Inventory Score. Sexual function was positively associated with the Subjective Well-Being scale under Neuroleptic Treatment Form (SWN-K) and the Drug Attitude Inventory (DAI). The analysis showed that male sex and married status had a significant positive relationship with sexual arousal and the presence of tardive dyskinesia and that disease duration was associated with bad sexual arousal. |
|
16 |
Sexual life and associated factors in psychiatrics patients |
Incedere et al (2017) |
Evaluate the specific factors that influence the sexual life of psychiatric patients. |
Cross-sectional - - - |
The incidence of sexual dysfunction in patients diagnosed with schizophrenia is much higher than in patients diagnosed with other diseases. More than 50% of patients report that they have a reduced sex urge 39% of patients claimed that their medication caused reduced sex urge. |
|
17 |
An exploration of sexual desire and sexual activities of women with psychosis. |
Huguelet et al (2014) |
To know the sexual desire and activity of women with schizophrenia |
quantitative - - |
Women with schizophrenia have the same sexual desires as healthy women Women with schizophrenia are less satisfied with their sexual activity. |
|
18 A systematic review of Sanchez-Fuentes To classify the variables sexual satisfaction et al (2013) related to sexual satisfaction and develop models of sexual satisfaction. |
Systematic Variables or factors related to sexual satisfaction: review - Individuals such as socio-demographic and psychological characteristics as well as physical and psychological health status
|
|
19 Satisfaction with sex life Laxhman et al Assessing the sex life among patients with (2017) satisfaction level of schizophrenia schizophrenic patients |
quantitative - Patients with schizophrenia were not satisfied with their sex life |
DISCUSSION
The results showed that sexual dysfunction in schizophrenic patients was influenced by several factors, namely the use of antipsychotics, gender, primary disease, age, marital status, beliefs and cultural values.
Use of Antipsychotics
The use of antipsychotics is a component of the mental disorders treatment that recommended by the National Institute of Health and Clinical Excellence, the American Psychiatric Association, and the British Society for Psychopharmacology (Just, 2015). The mechanism of antipsychotic drugs is considered as a cause of sexual dysfunction in schizophrenic patients (Just, 2015; Olisah et al, 2016; Hocauglu et al, 2014; Boer et al, 2015; Bram et al, 2014; Shetageri et al, 2016 & Chiesa et al. 2013). In a study conducted by Incedere et al (2017) states that 39% of patients claim that the antipsychotic treatment they were taking causes their sexual desire or desire to decrease (İncedere & Küçük, 2017). The use of different types of antipsychotics will lead to different risks of sexual dysfunction (Vargas et al, 2012). The antipsychotic drugs most commonly associated with sexual dysfunction are olanzapine, risperidone, haloperidol, clozapine, and thiriozadine. Antipsychotics of ziprasidone, perphenazine, quetiapine, and aripiprazole types cause low-grade sexual dysfunction (Chiesa et al, 2013).
Antipsychotic drugs will affect a person's sexual function. This is related to the activation of neurotransmitters such as dopamine and serotonin in the central nervous system. Antipsychotics cause sexual dysfunction by providing a central effect by blocking dopaminergic receptors in the hypothalamus, resulting in hyperprolactinemia, galactorrhea, menstruation, erectile disorders, and decreased libido. Peripheral effects by
blocking α-adrenergic receptors that serve to dilate arteries in the penis. Sedative effects cause decreased sexual desire, activity, and satisfaction (Just, 2015; Chiesa et al, 2013; Kikuchi et al, 2016 & Olisah et al 2016).
Based on a study conducted by Terevnikov et al (2016), the use of mirtazapine antipsychotics will improve orgasmic function (Terevnikov, Stenberg, Tiihonen, Burkin, & Joffe, 2017). In addition, in another study stated that the use of aripiprazole can significantly reduce erectile dysfunction in male patients with schizophrenia. Whereas in women the effect of using aripiprazole has the effect of menstrual periods becoming regular and galactorrhea is significantly reduced (Fujioi et al, 2016).
Stigma
Huguelet et al 2014 in their research stated that women with schizophrenia and healthy women have the same sexual desire. However, there are differences in the level of sexual satisfaction. Women with schizophrenia are less satisfied with their sexual activity (Huguelet et al, 2014 & Laxhman et al, 2017). This is influenced by the stigmatization and discrimination experienced by schizophrenic patients. The patient feels embarrassed and insecure. So that sexual function, sexual response, and sexual self-esteem will be disrupted (Sánchez-Fuentes et al., 2014) (Huguelet et al., 2014) (Laxhman et al., 2017). The professional team responsible for all aspects of the patient's needs avoids assessing sexual needs. So that stigmatization and neglect can hinder the handling and improvement of sexual function in schizophrenic patients (Huguelet et al & Boer et al, 2014).
Cultural, Belief, and Spiritual Factors
Cultural factors affect patient’s sexual function. In Hindi, expressing things about sexuality is not easy (Shetageri et al, 2016 &
Tharoor et al, 2015). This can prevent the doctor or nurse from knowing the patient’s sexuality problems. In addition, Chinese people apply a culture of shame in expressing sexual dysfunction they experienced. They believe that by expressing it, will make them embarrassed, afraid of being discriminated and receiving negative responses from others (Hou et al., 2016). The culture and spirituality of Malay people influence the high risk of orgasmic dysfunction, this will affect their behavior and emotions related to masturbation (Yee et al, 2013).
Impact of Sexual Dysfunction in Schizophrenic Patients
Untreated sexual dysfunction can have a negative impact on schizophrenic patients. Sexual dysfunction can lower selfesteem, worsen social isolation, and the ability to build sexual relationships with partners. In addition, sexual dysfunction can also affect the quality of marriage so that it can lead to permanent disputes and even divorce (Hou et al, 2015). Another impact of sexual dysfunction can affect quality of life, low self-esteem, patient mood, medication adherence, and adherence to therapy (Just, 2015).
CONCLUSION
The use of antipsychotics is still the biggest cause of sexual dysfunction in schizophrenic patients. If left untreated, sexual dysfunction will affect the patient's quality of life. Therefore, it is hoped that the professional team in this case doctors and nurses can improve the care and evaluation related to sexual dysfunction events in schizophrenia patients.
Limitations of The Study
The limitation of the study was the search for specific literature. There were not many studies related to sexual dysfunction in schizophrenic patients. More research on the
use of antipsychotics that affect sexual function. Therefore, the authors found only a few factors that influence the incidence of sexual dysfunction in schizophrenic patients. Then the limited time also becomes an obstacle in completing this study.
Acknowledgments
I thank my mentors and friends for their support, guidance, and motivation so that I can complete this literature review.
REFERENCES
American Psychiatric Association. (2017).
Schizophrenia Guidelines. Diakses pada 10 Desember 2017 Retrieved from https://psychiatryonline.org/guidelines.
Boer, M. K. De, Castelein, S., Wiersma, D.,
Schoevers, R. A., & Knegtering, H. (2017). The Facts About Sexual ( Dys ) function in Schizophrenia : An Overview of Clinically Relevant Findings, 41(3), 674–686.
https://doi.org/10.1093/schbul/sbv001
Bram, N., Rafrafi, R., Abdelghaffar, W., Lakhal, M. H., Ouanes, S., & Hechmi, Z. El. (2014).
Sexual dysfunctions in Tunisian patients with schizophrenia. Sexologies, 23(3), e65–e70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sexol.2014.05.004
Chiesa, A., Leucci, V., Serreti, A., De Ronchi, D.
(2013). Antipsychotics and sexual dysfunction: epidemiology, mechanisms, and management. Clinical Neuropsychiatry.
Fujioi, J., Iwamoto, K., Banno, M., Kikuchi, T., Aleksic, B., Ozaki, N. (2016). Effect of Adjunctive Aripiprazole on Sexual Dysfunction in Schizophrenia : A Preliminary Open- Label Study.
Hamid, Achir Yani. (1999). Buku Ajar Aspek Psikoseksual Dalam Keperawatan. Jakarta: Widya Medika.
Hocaoglu, C., Celik, F. H., Kandemir, G., Guveli, H., & Bahceci, B. (2015). Sexual dysfunction in outpatients with schizophrenia in Turkey : a cross-sectional study, 26(6), 347–356.
Hou, C.-L., Zang, Y., Rosen, R. C., Cai, M.-Y., Li, Y., Jia, F.-J., … Xiang, Y.-T. (2016). Sexual dysfunction and its impact on quality of life in Chinese patients with schizophrenia treated in primary care. Comprehensive Psychiatry, 65, 116–121.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.comppsych.2015.11.0 02
Huguelet, P., Mohr, S., Miserez, C., Castellano, P., Lutz, C., Boucherie, M., … Bianchi Demicheli, F. (2014). An Exploration of Sexual Desire and Sexual Activities of Women with Psychosis. Community Mental Health Journal, 51(2), 229– 238. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10597-014-9768-x
İncedere, A., & Küçük, L. (2017). Sexual Life and Associated Factors in Psychiatric Patients. Sexuality and Disability, 35(1), 89–106. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11195-017-9475-y
Just, M. J. (2015). The influence of atypical antipsychotic drugs on sexual function, 1655– 1661. https://doi.org/10.2147/NDT.S84528
Kaplan, H.I; Sadock, B.J & Grebb, J.A. (1997). Sinopsis Psikiatri: Ilmu Pengetahuan Perilaku Psikiatri Klinis. Jakarta: Binarupa Aksara.
Kementerian Kesehatan RI. (2013). Laporan Nasional Riset Kesehatan Dasar Tahun 2013 Jakarta: Badan Penelitian dan Pengembangan Kesehatan.
Kikuchi, T., Iwamoto, K., Sasada, K., & Aleksic, B. (2012). Progress in NeuroPsychopharmacology & Biological Psychiatry Sexual dysfunction and hyperprolactinemia in Japanese schizophrenic patients taking antipsychotics. Progress in Neuropsychopharmacology & Biological Psychiatry, 37(1), 26–32.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnpbp.2011.11.016
Laxhman, N., Greenberg, L., & Priebe, S. (2017). Satisfaction with sex life among patients with schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Research, 5–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.schres.2017.03.005
Lee, J., Kim, S., Lee, Y., Kang, H., Kim, S., Bae, K., … Yoon, J. (2015). Factors associated with self-rated sexual function in Korean patients with schizophrenia receiving risperidone monotherapy, (August 2014), 416–424. https://doi.org/10.1002/hup
Olisah, V. O., Sheikh, T. L., Abah, E. R., & Ajeigbe, A. F. M. (2016). Sociodemographic and clinical correlates of sexual dysfunction among psychiatric outpatients receiving common psychotropic medications in a Neuropsychiatric Hospital in Northern Nigeria, 799–806.
Sánchez-fuentes, M., Santos-iglesias, P., & Sierra, J. C. (2014). A systematic review of sexual satisfaction. International Journal of Clinical and Health Psychology, 14, 67–75.
https://doi.org/10.1016/S1697-2600(14)70038-9
Shetageri, V. N., Bhogale, G. S., Patil, N. M., Nayak, R. B., & Chate, S. S. (2016). Original Article Sexual Dysfunction among Females Receiving Psychotropic Medication : A Hospital - based
Cross ‑ sectional Study.
https://doi.org/10.4103/0253-7176.191379 Terevnikov, V., Stenberg, J. H., Tiihonen, J., Burkin,
M., & Joffe, G. (2017). Add-on mirtazapine improves orgasmic functioning in patients with schizophrenia treated with first-generation antipsychotics. Nordic Journal of Psychiatry, 71(1), 77–80.
https://doi.org/10.1080/08039488.2016.123399 6
Terevnikov, V., Stenberg, J., Tiihonen, J., & Burkin, M. (2016). Add-on mirtazapine improves orgasmic functioning in patients with schizophrenia treated with first-generation antipsychotics. Nordic Journal of Psychiatry, 0(0), 000.
https://doi.org/10.1080/08039488.2016.123399 6
Tharoor, H., Kaliappan, A., & Gopal, S. (2017). Sexual dysfunctions in schizophrenia : Professionals and patients perspectives, 57(1), 2015–2017. https://doi.org/10.4103/0019-5545.148532
Vargas, L., Nunes, A., & Moreira, H. C. (2012). Strategies for the Treatment of Antipsychotic-Induced Sexual Dysfunction and / or Hyperprolactinemia Among Patients of the Schizophrenia Spectrum : A Review Strategies for the Treatment of Antipsychotic-Induced Sexual Dysfunction and / or Hyperprolactinem, (September), 37–41.
https://doi.org/10.1080/0092623X.2011.606883
World Health Organization. (2014). Schizophrenia. Diakses pada tanggal 04 Desember 2017 Retrieved from http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/ fs397/en/.
Yee, O. K., Psychiatry, M., Rahaiza, E., Ramli, M., & Psychiatry, M. (2014). Remitted Male Schizophrenia Patients with Sexual Dysfunction, 956–965.
https://doi.org/10.1111/jsm.12246
711
Volume 9, Nomor 6, Desember 2021
Discussion and feedback