THE MINERAL OXIDE CONTENTS OF THE TEGAL LENGA BEACH IRON SAND
on
Buletin Fisika Vol 20 No. 2 Agustus 2019: 31 – 34
Determination of The Oxide Mineral Contents of the Tegal Lenga Beach Iron Sand by Using XRD
P. Suardana1*, I B. Sujana. M2, Nyoman Wendri3
-
1, 2, 3 Department of Physics, Faculty of Mathematic and Natural Sciences, Udayana University Kampus Bukit Jimbaran, Badung, Bali, Indonesia (80361)
*suardanaputu@unud.ac.id, sujana_manuaba@unud.ac.id, wendri@unud.ac.id
Abstract – The research of determination of the oxide mineral contents of the Tegal Lenga Beach iron sand by using XRD has been done. Iron sand samples were taken from the top layer of the Tegal Lenga Beach sand. The three sand samples were taken from three different places which were separated at a distance of 15 m one another. The separation process is carried out using magnetic separation method. The characterization methods include mass fraction and X-ray diffraction (XRD). It obtained that the average mass fraction of the Tegal Lenga Beach iron sand is 54.71%. The minerals oxide contained are magnesium diiron (III) oxide (Mg Fe2 O4 and iron iron (III) titanium aluminum magnesium vanadium manganese silicon oxide (Fe4.42 Fe5.245 Ti4.72 Al0.7 Mg0.4 Cr0.3 V0.15) (Fe7.82 Mn0.114Si0.06) O32). The main oxide mineral compound is Magnesioferrite (MgFe2O4) oxide mineral of 51.34%.
Key words: Mineral oxide, Tegal Lenga Beach iron sand, X-ray diffraction (XRD)
Abstract – Penelitian penentuan kandungan mineral oksida pasir besi Pantai Tegal Lenga dengan menggunakan XRD telah dilakukan. Sampel pasir besi diambil dari lapisan atas pasir Pantai Tegal Lenga. Tiga sampel pasir diambil dari tiga tempat berbeda yang dipisahkan pada jarak 15 m satu sama lain. Proses pemisahan dilakukan dengan menggunakan metode pemisahan magnetik. Metode karakterisasi meliputi fraksi massa dan difraksi sinar-X (XRD). Diperoleh bahwa fraksi massa rata-rata pasir besi Pantai Tegal Lenga adalah 54,71%. Mineral oksida yang terkandung adalah magnesium diiron (III) oksida (Mg Fe2 O4) dan besi besi (III) titanium aluminium magnesium vanadium silikon oksida mangan (Fe4.42 Fe5.245 Ti4.72 Al0.7 Mg0.4 Cr0.3 V0.15) (Fe7.82 Mn0.114Si0.06) O32). Senyawa mineral oksida utama adalah mineral oksida Magnesioferrite (MgFe2O4) yaitu 51.34%.
Kata kunci: Mineral oxide, pasir besi Pantai Tegal Lenga, X-ray diffraction (XRD)
iron sand and the dried-cleaned iron sand are weighed. Finally, the dried-cleaned iron sand were characterized by XRD.
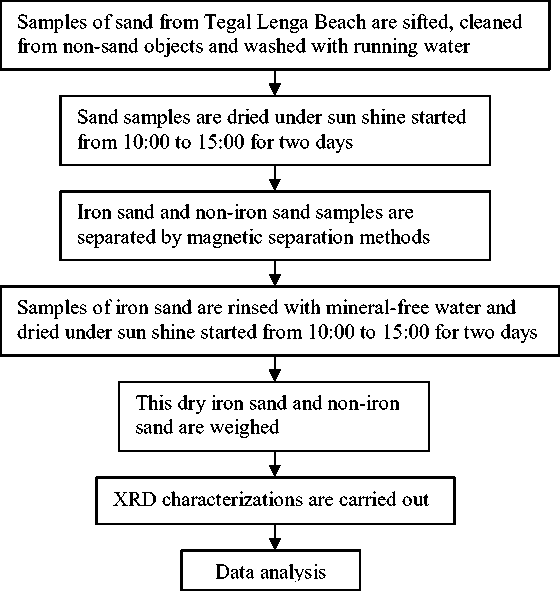
Fig. 1. The scheme of the experiment conducted.
-
3. Results and Discussion
Figure 2a shows the Tegal Lenga Beach sand before separated. Figure 2b shows the separation process of the Tegal Lenga Beach sand by using magnetic method and Figure 2c shows the Tegal Lenga Beach iron sand obtained from the magnetic separation method.

(a)

(b)

(c)
Fig. 2. (a) Tegal Lenga Beach sand before separation, (b) the separation process of the Tegal Lenga Beach sand by using magnetic method, and (c) the Tegal Lenga Beach iron sand obtained by using the magnetic separation method.
The data obtained from the separation process of iron sand and non-iron sand, which are parts of sand that stick to and not stick to the bar magnet are shown in Table 1. It shows that the percentage of the iron sand mass on each sample is almost the same. The average mass percentage of iron sand of Tegal Lenga Beach is 54.71%.
Table 1. The mass of the Tegal Lenga Beach iron sand samples.
|
No |
Mass of iron sand (g) |
Mass of noniron sand (g) |
Percentage of Iron Sand (%) |
Average Percentage of Iron Sand (%) |
|
1 |
81.06 |
67.88 |
54.43 | |
|
2 |
87.09 |
70.26 |
55.35 |
54.71 |
|
3 |
72.25 |
60.65 |
54.36 |
The X-ray diffractogram of the three iron sand samples are shown in Fig. 3. The analyzes are shown in Table 2.
From Fig. 3 and data on Table 2 shows that the mineral oxide compounds of Sample 1 are dominated by Magnesioferrite (MgFe2O4) oxide minerals with a volume fraction of 62.95%. The mineral oxide compounds of Sample 2 is iron iron(III) titanium aluminum magnesium chromium vanadium(III) manganese silicon oxide (Fe4.42 Fe5.245 Ti4.72 Al0.7 Mg0.4 Cr0.3 V0.15) (Fe7.82 Mn0.114Si0.06)O32) with a volume fraction of 39.78%. While the mineral oxide compounds of Sample 3 are also dominated by Magnesioferrite (MgFe2O4) oxide minerals with a smaller volume fraction than Sample 1 of 39.74%. Based on this results, it concluded that the oxide mineral content of the Tegal Lenga Beach sand is dominated by iron oxide mineral.
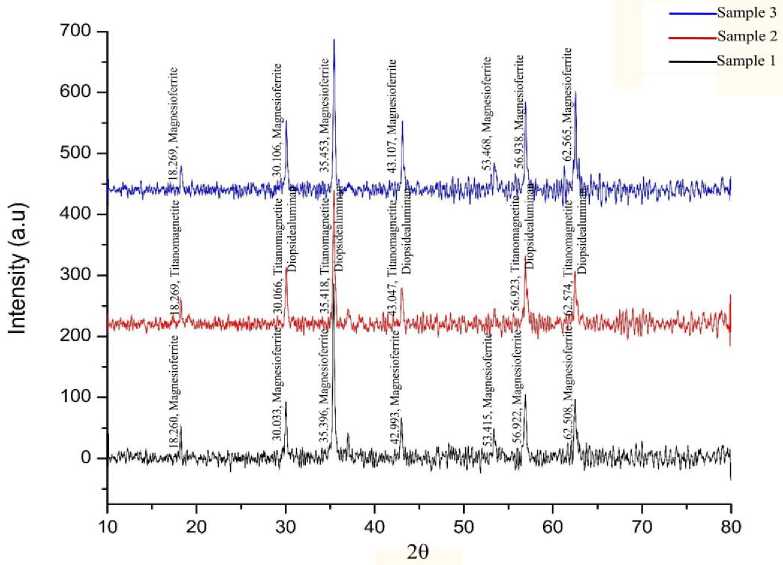
Fig. 3. The XRD pattern of the Tegal Lenga iron sand of Sample 1, 2 and 3.
Table 2. The mineral oxide compounds of Tegal Lenga iron sand.
|
No. |
Ref. Code Compound Name Chemical Formula Volume Fraction (%) |
|
1 |
01-088-1943 Magnesium diiron(III) oxide Mg Fe2 O4 62.95 |
|
2 |
01-074-2034 Iron iron(III) titanium (Fe4.42 Fe5.245 Ti4.72 Al0.7 39.78 aluminium magnesium Mg0.4 Cr0.3 V0.15) (Fe7.82 chromium vanadium(III) Mn0.114Si0.06) O32 manganese silicon oxide |
|
3 |
01-088-1938 Magnesium diiron(III) oxide Mg Fe2 O4 39.74 |
-
4. Conclusion
The determination of the oxide mineral contents of the Tegal Lenga beach iron sand by using XRD has been done. It obtained that the average mass fraction of the Tegal Lenga Beach iron sand is 54.71%. The minerals oxide contained are magnesium diiron (III) oxide (Mg Fe2 O4) and iron iron (III) titanium aluminum magnesium vanadium manganese silicon oxide (Fe4.42 Fe5.245 Ti4.72 Al0.7 Mg0.4 Cr0.3 V0.15) (Fe7.82 Mn0.114Si0.06) O32) with the volume fraction of each compound are 62.95%, 39.78% and 39.74%. The main oxide mineral compound is Magnesioferrite (MgFe2O4) oxide mineral of 51.34%.
Acknowledgement
We thank to Udayana University for the research budget, PUPS 2019 as well as the publication.
References
-
[1] Zulkarnain, 2000, Kemungkinan Pemanfaatan Pasir Besi Pesisir Pantai Aceh untuk Fabrikasi Magnet, Prosiding Seminar Nasional Bahan Magnet I, Serpong, 11 Oktober 2000, ISSN 1411 -7630, pp. 59-61
-
[2] Yulianto, A., Bijaksana, S. dan Loeksmanto, W, Karakterisasi Magnetik dari Pasir Besi Cilacap. Jurnal Fisika, Himpunan Fisika Indonesia, Suplemen Prosiding, Hal. A5-0527, 2002.
-
[3] Yulianto, A., Bijaksana, S. dan Loeksmanto, W, Comparative Study on Magnetic Characterization of Iron Sand from Several Locations in Central Java.Kontribusi Fisika Indonesia, Vol. 14, No. 2, Hal. 63-66, 2003.
-
[4] Kementrian Energi dan Sumber Daya Mineral, Badan Geologi, Pusat Daya Geologi, Pasir Besi di Indonesia, Geologi, Ekplorasi, dan Pemanfaatannya, 2014.
-
[5] Bilalodin, Kajian sifat Magnetik dari Pasir Besi Pantai Logending Kabupaten Kebumen, Molekul, Vol. 5, No. 2, 2010.
-
[6] Peters, C. dan Thompson, R, Magnetic Identification of Selected Natural Iron Oxides and Sulphides. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, Vol. 183, Hal. 365- 374, 1998
-
[7] Kementerian Riset dan Teknologi, Universitas Udayana, Rencana Induk Penelitian (RIP) Universitas Udayana 2017 – 2021, 2016.
34
Discussion and feedback