THE IMPACT OF SERVICE QUALITY, FACILITY, PRICE, EMOTIONAL FACTOR AND LOCATION ON CUSTOMER SATISFACTION AND LOYALTY AT THE 3-STAR HOTELS IN BEKASI
on
Suresh Kumar, The Impact of Service Quality, Facility... 51
THE IMPACT OF SERVICE QUALITY, FACILITY, PRICE, EMOTIONAL FACTOR AND LOCATION ON CUSTOMER SATISFACTION AND
LOYALTY AT THE 3-STAR HOTELS IN BEKASI
Suresh Kumar1 Budi Winarto*)2 Mariana Astuti*)3
-
1,2,3 Department of Business Administration, President University e-mail: sureshkumar@president.ac.id
Abstract : The Impact Of Service Quality, Facility, Price, Emotional Factor and Location On Customer Satisfaction And Loyalty At The 3-Star Hotels In Bekasi. Hospitality business is one of the industries that has the greatest impact at which foreign companies are entering, namely telecommunications, air transportations, bankings, hotels, etc. To stay in competition, customer satisfaction must be fulfilled by hoteliers. In order to do that, service quality can be one of the factors to determine satisfaction. Other than service quality, facility, location, emotions, price also play a significant influence on satisafaction which lead to loyalty. Construct validity is checked through correlation and found that the variables were loaded on its respected factor, and reliability result shows higher than 0.7. Service quality was rejected since the results showed negative sign. Factors like facility, location, price and emotions show significant influence on customer satisfaction and customer satisfaction influneces loyalty. Hotel managers can focus on these factors to stay in the competition.
Keywords : consumer satisfaction, loyalty, service quality, price, facility, emotional factor, location
Abstrak : Pengaruh Kualitas Pelayanan, Fasilitas, Harga, Faktor Emosional dan Lokasi Terhadap Kepuasan Konsumen Dan Loyalitas Konsumen Pada Hotel Bintang Tiga Di Bekasi. Bisnis perhotelan adalah salah satu industri yang memiliki dampak terbesar di mana perusahaan asing dapat ikut bersaing, yaitu telekomunikasi, transportasi udara, perbankan, hotel, dan sebagainya. Untuk bertahan dalam kompetisi, kepuasan pelanggan harus dipenuhi oleh pelaku bisnis perhotelan. Kualitas pelayanan menjadi salah satu faktor untuk menentukan kepuasan. Selain kualitas layanan, fasilitas, lokasi, dan factor emosional, harga juga memainkan pengaruh yang signifikan terhadap kepuasan yang menimbulkan loyalitas. Validitas konstruk diperiksa melalui korelasi dan menemukan bahwa variabel yang dimuat pada faktor yang digunakan, dan reliabilitas menunjukkan lebih tinggi dari 0,7. Kualitas layanan ditolak karena hasil menunjukkan tanda negatif. Faktor-faktor seperti fasilitas, lokasi, harga, dan factor emosional menunjukkan pengaruh yang signifikan terhadap kepuasan pelanggan dan loyalitas pelanggan. Para manajer hotel dapat fokus pada faktor-faktor ini untuk dapat bertahan dalam kompetisi.
Kata kunci : kepuasan pelanggan, loyalitas, kualitas pelayanan, harga, fasilitas, faktor emosional, lokasi
INTRODUCTION
It is very interesting to see the growing competition in Indonesia as a result of globalization especially in economics that lead not only national level but also foreign investors are digging their hope to be chosen by customers. Hospitality business is one of the industries has the greatest impact at which foreign companies are entering, namely telecommunications, air transportations, bankings, hotels, etc. Hence, it has forced the local companies to understand the
needs and wants of consumers to fit them in order to stand a chance in the tough competition.
At the same time, companies have to offer more and different services compare to other companies to survive in the competition. These differences will give more satisfaction to customers and make them tend to return back to the company. But the problem is there is no one standard to satisfy all customers, hence companies have to observe and research on the changing of customer behaviors to adjust their strategy either in marketing or service.
Table 1.
3-Star Hotels in Bekasi ( 2014 )
|
HOTEL |
CLASS |
LOCATION |
|
Grand Zuri Jababeka Hotel |
3-Star |
Jl. Niaga Raya Kav.AA-2, Kawasan Industri Jababeka II, Bekasi 17530, Indonesia |
|
Horison Hotel Bekasi |
3-Star |
Jl.KH. Noer Alie, Bekasi. 17148. Indonesia |
|
Hotel PEC |
3-Star |
Jl. Jababeka Raya Cikarang 333 Industrial State, Bekasi.17530. Indonesia |
|
Zuri Express Lippo Cikarang Hotel |
3-Star |
Jl. Kemang Raya.Kav.6.Commercial Park, Lippo Bekasi. Bekasi 17550, Indonesia |
|
Hotel Grand Cikarang Bekasi |
3-Star |
Jl. Jababeka Raya CIkarang Industrial Estate I, Bekasi, 17530. Indonesia |
Source :http://bekasikota.go.id/readotherskpd/128/526/data-hotel-di-kota-bekasi
To stay in competition, customer satisfaction must be fulfilled by hoteliers. In order to do that, service quality can be one of the factors to determine satisfaction. Service quality is basically fulfilling the needs of customers. But since it is difficult to fulfill each customer, usually hoteliers define their own definition of service which customers will perceive it during the delivery process. Services offer usually facilities fit to businesspeople, family, tourists, etc. Other than that, the employees are trained to be humble, quick response, trusted and hospitality.
While hotels give almost the same service, it is even difficult to gain loyal customers. Thus, price is also considered to be one of the tactics by hotels to attract more and more customers. On the other hand for cities with high traffic location becomes one of the main factors for customers to choose (Murti and Soeprihanto, 1999). It is futher strengthen by Heizer (2001) that location has the power to succeed companies strategy.
LITERATURE REVIEW
According to Kotler (2008) service is any behavior or act based on a contact between two parties: the provider and receiver, and the essence of this reciprocal process is intangible. Andreassen and Lindestad (1998) claim that “when service is given can exceed the customers’ expectation, thus customers will be satisfied. From these definitions we conclude that service quality is characteristic of
a product or service which has the ability to satisfy consumers need.
Service Quality influences customer satisfaction
In his research Factors Influencing Customer Satisfaction with Chain Budget Hotels in Bangkok, Cherdchamol and Sriboonjit (nd) found that physical facilities influence customer satisfaction. Also Ekinci et al. (2008) states that one of the factors to improve satisfaction is physical quality. In the study The Impact of Physical Environment Factors in Hotels on Arab Customers’ Loyalty by Alsaqre also reveals that physical factors like design of the hotels, the equipment and the ambient conditions influence customer loyalty.
Facility influences customer satisfaction
Though price plays a significane role in marketing mix, it won’t give any beneficial if hotels can figure out the impact of price on customer satisfaction. Tjiptono (2006) defines price is an amount of money or monetary and nonmonetary which is utilized to get a product of service.
Price influences customer satisfaction
Emotios play an important role on determining satisfaction with service as well (Liljander and Strandvik, 1997). Wong (2004) also finds that service quality is positively associated with emotional satisfaction. Yu and Dean (2001) find that emotions as the best predictor in satisfaction and loyalty. Van
Dolen, de Ruyter, and Lemmink (2002) reveals a significant influence of emotions on satisfaction. Hence, the customer’s emotions have been proved to be a key determinant to turn a satisfied customer into a repeated one (Chatzigeorgiou, 2009). Smith and Boloton (2002)suggest that customers’ emotional responses to service failures will influence their recovery effort evaluations and satisfaction judgments in some circumstances and that the effects of emotion vary across industry settings.
Emotional factor influences customer satisfaction
Unlike advertising, pricing or promotion programs that can easily be changed to suit the competitive environment, a decision of where to place a hotel needs to be taken seriously since it involves a huge investment. Not only a huge investment is considered but also it attracts hotel guests to choose which hotel to choose (Yang,Wong and Wang, 2012). A study by Mount also reveals that the location choice helps the hotel for its delivery speed performance, and firm’s flexibility to compete not to mention guests’ satisfaction (as cited in Adam, 2012). Even Conrad N. Hilton, the former operatir of Hilton hotels, claims that the first, second and third most important for the success of a hotel is location (as cited in Ju, Jang-Geon, 1999). Inline with Hilton, Lamb, Hair, Mc.Daniel (2001) also stress the importance of location. Swastha (2002) further reveals that to chooce a location it involves the location in the city where the hotel is located, how to reach and time consumed to reach the location.
Location influences customer satisfaction
All these factors lead to customer satisfaction. Kotler (2008) defines satisfaction as the level of a person’s perception of perceived and expected quality. Where Oliver states that satisfaction is consumers’ perceived of its need (as cited in Shukla and Gekara, 2011). Therefore, consumers perceive goods or services are based on their perception whether it fulfills or exceeds it. By having customer satisfaction it leads to loyalty. (Tjiptono, 2006).
Customers satisfaction influences loyalty
Gremler and Brown states that loyal customers are customers who are not only repeat buyers but also have positive image towards the company hence they are willing to say positive things about the company. Loyalty is about trust, willingness to act
by calculating the benefits may be got based on commitment, repeat buying and its proposition on repeat buying. (as cited in Kheng et al, 2010). Hence it can be concluded that customer loyalty to a company or to a certain product along with an action to repeat buying dan the willingness of the customers to extend the relationship again.
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
Respondents were the guests who stayed in 3-star hotels in Bekasi region ( Grand Zuri Jababeka Hotel, Horison Hotel Bekasi, Hotel PEC, Zuri Express Lippo Cikarang Hotel and Hotel Grand Cikarang Bekasi) with total 209 guests. For the questionnaires were divided into two sections, respondents’ profile and five independent variables: service quality, facility, price, emotional factor and location; 2 dependent variables: consumer satisfaction and loyalty.
Respondents’ Profile
Most respondents from 209 respondents were females (62%) and followed by males (38%). As for the employment, most respondents were private employees (58%), followed by self-employment (21%), civil servants (15%), army or police (6%) and there wasn’t any students participated in this survey.
RESULT AND DISCUSSION
Data Analysis
Validity and Reliability
As shown in Table 2 that item questions for service quality correlated highly on average service quality which means all questions converge to only one factor which is service quality and low correlation against other factors which means there is no divergent problem. The same results apply to other factors as well. And for reliability test, shown in Table 3, also higher than cutoff value 0.6, hence data used were reliable.
Multiple Regression
Before conducting Multiple Regression, it is required the data used not only valid and reliable but also it must pass classical assumptions namely normality, multicollinearity and heterocedasticity. Normality Test
From Figure 1, it shows that data were under bell curve and Figure 3, it shows that data were scatterd around the diagonal line, hence it can be concluded that data were normal. As also shown in Figure 2 and 4, the data were normal.
Table 2.
Validity Test
|
ASQ |
AFAC |
APRIC |
AEMOT |
ALOC | |
|
SQ4 |
.792 |
.782 |
.235 |
.202 |
.296 |
|
SQ5 |
.921 |
.289 |
.167 |
.253 |
.212 |
|
SQ6 |
.885 |
.694 |
.103 |
.260 |
.183 |
|
FAC1 |
.775 |
.758 |
.319 |
.175 |
.196 |
|
FAC2 |
.612 |
.810 |
.258 |
.297 |
.389 |
|
FAC3 |
.765 |
.908 |
.119 |
.351 |
.305 |
|
FAC4 |
.776 |
.881 |
.084 |
.252 |
.217 |
|
PRI1 |
0.87 |
.053 |
.710 |
-.394 |
-.013 |
|
PRI2 |
.127 |
.070 |
.681 |
-.410 |
-.070 |
|
PRI3 |
.237 |
.316 |
.826 |
.269 |
.215 |
|
PRI4 |
.103 |
.162 |
.821 |
-.049 |
.144 |
|
EMOT2 |
.257 |
.280 |
-.048 |
.932 |
-.031 |
|
EMOT3 |
.256 |
.323 |
-.156 |
.930 |
-0.24 |
|
LOC1 |
-.037 |
0.056 |
0.063 |
-.141 |
.717 |
|
LOC3 |
.307 |
.375 |
.096 |
-.074 |
.853 |
|
LOC4 |
.325 |
.349 |
.083 |
.116 |
.915 |
|
LOC5 |
.242 |
.263 |
.017 |
.018 |
.757 |
Source : Data processed (2014)
Table 3.
Reliability Test
|
Variables |
Cronbach Alpha |
|
Service Quality |
0.834 |
|
Facility |
0.862 |
|
Emotion |
0.847 |
|
Location |
0.821 |
|
Price |
0.748 |
Source : Data processed (2014)
Satisfaction
Histogram
Figure 3. P-Plot: Customer Satisfaction
Figure 4. P-Plot: Loyalty
Table 4.
Multicollinearity Test
|
Mcxiel |
C o 11 i π ei r ity St atistics | ||
|
Tcierarce |
VIF | ||
|
(GbnsAit) ASQ |
.241 |
4.157 | |
|
AFAC |
.206 |
4.854 | |
|
APRlC |
.855 |
-.169 | |
|
AEhIOT |
.809 |
-.Ξ36 | |
|
ALCC |
804 |
-.244 | |
|
ASAT |
JM9 |
1.®4 | |
Multicollinearity Test
-
a. DepencentVerabb: ALW
Source : Data processed (2014)
To make sure that there is no multicollinearity less than 10, hence there is no multicollinearity problem in the data before further analyze with problem.
Mulitple regression the VIF value has to be less than Heterocedasticity Test
-
10, and from Table 4 it shows that VIF value were
-
Figure 5. Scatterplot: Satisfaction
-
Figure 6. Scatterplot: Loyalty
Scatterplot
Dependent Variable: KepuasanKonsumen
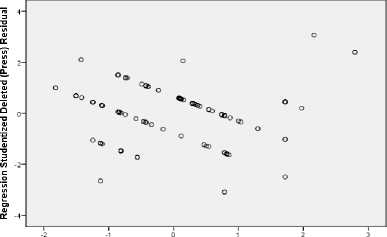
Regression Standardized Predicted Value
Scatterplot
Dependent Variable: LoyaIitasKonsumen
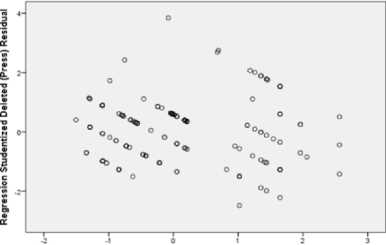
Regression Standardized Predicted Value
From Figure 5 and 6, all data were scattered above and below 0 wihtout forming any patterns, hence there were no heterocedasticity problems. Thus these data were eligible to be used to predict the influence of service quality, facility, price and location on satisfaction and loyalty of 3-star hotels’ guests in Bekasi.
Hypothesis Testing
From Table 5, it shows that service quality, facility, price, location and emotional factor influence
customer satisfaction (p<0.05). It is also seen that for service quality it has a negative influence on customer satisfaction, hence the first hypothesis is rejected. Based on beta coefficient it shows that Facility factor influences customer satisfaction the most (b=0.269), followed by Price (0.175), Location (0.125) and Emotions (.102). All the signs show positive sign; hence any improvement made on these factors will increase customer satisfaction.
Table 5.
Satisfaction Coefficient
|
Model |
Unstandardized Coefficients Standardized t Sig. Coefficients B Std. Error Beta |
|
(Constant) ASQ 1 AFAC APRIC AEMOT ALOC |
1.772 .249 7.107 .000 -.128 .069 -.216 -1.862 .064 .269 .073 .454 3.706 .000 .175 .048 .222 3.685 .000 .102 .036 .180 2.872 .005 .125 .031 .247 4.013 .000 |
Source : Data processed (2014)
From Table 6, it shows that customer satisfaction Though Emotion and Location influence loyalty influences customer loyalty (p<0.05) with positive as well but since beta coefficient shows negative sign. Hence the more customersare satisfiedthen the value, hence it is rejected, they have no direct effect more loyal they will be.Service Quality, Facility and towards loyalty.
Price also have direct effect on loyalty (p<0.05).
Table 6.
Loyalty Coefficient
|
Model |
Unstandardized Coefficients |
Standardized Coefficients |
t |
Sig. | |
|
B |
Std. Error |
Beta | |||
|
(Constant) |
-.190 |
.355 |
-.536 |
.593 | |
|
ASQ |
.212 |
.088 |
.212 |
2.402 |
.017 |
|
AFAC |
.497 |
.095 |
.496 |
5.209 |
.000 |
|
1 APRIC |
.215 |
.063 |
.161 |
3.440 |
.001 |
|
AEMOT |
-.198 |
.046 |
-.206 |
-4.285 |
.000 |
|
ALOC |
-.108 |
.041 |
-.127 |
-2.627 |
.009 |
|
ASAT |
.377 |
.089 |
.223 |
4.221 |
.000 |
Source : Data processed (2014)
All the variables (service quality, facility, price and customer satisfaction) contribute 61.1% to measure
customer loyalty (Table 7), hence there is still around 38,9% of other factors that influence loyalty.
Table 7.
Coefficient of Determination
|
Model |
R |
R Square |
Adjusted R Square |
Std. Error of the Estimate |
|
1 |
.789a |
.623 |
.611 |
.33529 |
Source : Data processed (2014)
CONCLUSION AND RECOMMENDATION
It is concluded that Service Quality, Facility, Price, Emotions and Location factors influence customer satisfaction. Since Service Quality shows negative influence hence it is rejected as the factor contribute to 3-star hotel’s guests satisfaction. It is mainly because people look for 3-star hotel and realize that they cannot expect much on the service. But it doesn’t mean that by not offering the best service is alright. Hotels need to give their unique service in order to compete with their competitors, since better service will impact to higher price as well.
Facilitiy as the most preferable factor for the guests mainly due to most of the respondents come from civil servant and employees from private companies. They really need facility to support their activity such as internet, fax, meeting room etc.Hence it is crutial to provide free wifii a separate business room to be used by guests and not to mention meeting rooms.
Though it is strange, the result shows that price has positive influence on satisfaction instead of negative, it has been confirmed by the respondents that in general all the prices offered by 3-star hotels are alike. To persuade customers, hotels management can try to give them something for free though the in general the price of 3-star hotels are alike.
Hence they prefer location to be the priority after facility. Location becomes crusial for them since the traffic condition in Bekasi region is really bad, they prefer hotels near the place where they want to visit. Due to location problem, it is advisable for hotels management to cooperate with public transportation to ease the customers. Beside that hotels can also provide free transportation to airport to increase their competitiveness.
The last factor is emotion, it is also proven as a significant determinant for customer satisfaction. This finding is inline with other researchers like Wong (2004), Yu and Dean (2001), Lemmink(2002) and (Chatzigeorgiou, 2009). In order to move people’s emotions it is advisable to decorate the room or lobby with color, music etc (Levy and Weitz, 2011)
REFERENCES
Adam, I. 2012. Hotel location decision-making in the Kumasi Metropolis of Ghana:
with whom and why?. African Journal of Hospitality, Tourism and Leisure Vol.2 (2)
Alsaqre, O.E. (nd) The Impact of Physical Environment Factors in Hotels on Arab Customers. Loyalty. University Sains Malaysia.\
Andreassen, T. W.; and Lindestad B. 1998. Customer loyalty and complex services: The impact ofcorporate image on quality, customer satisfaction and loyalty for customers with varying degrees of service expertise. International Journal of Service Industry Management,.Vol. 9, No.1, pp. 7 – 23.
Chatzigeorgiou, Chryssoula and Christou, Evangelos and Kassianidis, Panagiotis and Sigala, Marianna. 2009. Examining the Relationship between Emotions, Customer Satisfaction and Future Behavioral Intentions in Agrotourism. TOURISMOS: An International Multidisciplinary Journal of Tourism. Vol. 4, No. 4 (15. December 2009): pp. 145-161.
Cherdchamadol, P., Sriboonjit, J. (nd). The factors Influencing Customer Satisfaction With Chain Budget Hotels in Bangkok. Thamasat Business School, Thammasat University, Thailand.
Ekinci, Y., Dawes, P.L. And Massey, G. R. 2008. An extended model of the antecedents and consequences of consumer satisfaction for hospitality services. European Journal of Marketing, Vol. 42, No. 1/2, pp. 35-68.
Ghozali, I. 2006. Aplikasi Analisis Multivariate dengan Program SPSS. Badan Penerbit Universitas Diponegoro.
Goleman. D. 2002. Emotional Intelegention. PT. Gramedia Pustaka Utama: Jakarta
Irawan, H, 2008. Membedah Strategi Kepuasan Pelanggan. Cetakan pertama: PT. Gramedia: Jakarta
Khen, L.L., Mahamad, O., Ramayah, T., Mosahan, R. 2010. The Impact of Service Quality on Customer Loyalty: A Study of Banks in Penang, Malaysia. International Journal of Marketing Studies.Vol 2.No.2.
Kotler, P. 2000. Manajemen Pemasaran. Jakarta: Prenhallindo.
Lamb, C.W., Hair, J.F., McDaniel, C., Summers, J., Gardiner, M. 2009. Essentials of Marketing. Cengage Learning Australia Pty Limited
Lemmink, Jos G.A.M., Ravi S. Behara, and Warren W. Fisher, . 2002. Modelling and evaluating service quality measurement using neural networks. International Journal of Operations & Production Management, Vol. 22. Iss: 10, pp.1162 – 1185
Levy, M. and Weitz, B. A. 2011. Retailing Management (8th Edition). McGraw-Hill Irwin, Boston
Shukla, A., Gekara, M. G. 2011. Measurement of Consumer Satisfaction During Post Merger Period. International Journal Business
Management Economics Research.Vol 2(1), pg 140-151.
Smith, A.K., Bolton, R.N. 2002. The Effect of Customers’ Emotional Responses to Service Failures on Their Recovery Effeort Evaluations and Satisfaction Judgement. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science Vol 30.No.1 pg 5-23. Academy of Marketing Science.
Sulastiyono, A. 2006. Manajemen Penyelenggaraan Hotel, Edisi Ketiga. Bandung: Alfabeta.
Sugiyono. 2004. Metode Penelitian Bisnis, Cetakan Kedelapan. Bandung: Alfabeta.
Supranto, J. 1996. Pengukuran Tingkat Kepuasan Pelanggan. Usahawan, No.04,Th.XXV, April, p. 46-49.
Swastha, B. 2002. Manajemen Pemasaran. Edisi Kedua. Cetakan Kedelapan. Jakarta: Penerbit Liberty
Utami, C.W., 2006. Relationship Effort dan Kualitas Layanan sebagai Strategi Penguat Relationship Outcomes (Sebuah Tinjauan Konseptual dalam Bisnis Ritel Modern di Indonesia). Jurnal Manajemen Pemasaran, 1: 22–34.
Wong, A. 2004. The role of emotions in service encounters. Managing Service Quality, Vol. 14.No. 5, pp. 365-76.
Yang, Y., Wong, K. and Wang, T. 2012. How do hotels choose their location? Evidence from hotels in Beijing. International Journal of Hospitality Management, 31(3), 675-685
Yu, Y. T., & Dean, A. 2001. The contribution of emotional satisfaction to consumer Loyalty. International Journal of Service Industry Management.
Discussion and feedback