BRIEF EXPLANATION OF HOLISTIC POLITICAL COMPARISON METHOD (A METHODOLOGICAL REVIEW)
on
BRIEF EXPLANATION OF HOLISTIC POLITICAL COMPARISON METHOD
(A METHODOLOGICAL REVIEW)
Putri Hergianasari
International Relations Department Universitas Kristen Satya Wacana email : hergianasari.putri@staff.uksw.edu
ABSTRACT
In politics, comparative studies of politics have two roles at once namely, the first, comparative studies of politics as a theory, and the second name, the role of comparative studies of politics as a method. The study of political comparison as a theory is more directed to a collection of generalizations that are systematically linked, while the study of political comparison seen as a method is more directed to the process or procedure that involves the use of techniques and instruments. Method of comparing political system using one by one its structure descriptions are lame because people tend to unable create relation between organizational current issues and the positioning administration of political system appropriately. This paper is there for making us aware once more time about how doing the best comparison between one country and another. This study aims to create bridge to bring connection between political system’s work, issues that exist in the organization analyze structural cases using the method of political comparison cannot just compare different structures.
Keywords: political comparison, political science, international relations
ABSTRAK
Dalam politik, studi perbandingan politik memiliki dua peran sekaligus yaitu : yang pertama, studi perbandingan politik sebagai teori, dan kedua, peran studi banding politik sebagai metode. Studi perbandingan politik sebagai teori lebih mengarah pada sekumpulan generalisasi yang terkait secara sistematis, sedangkan studi perbandingan politik sebagai metode lebih mengarah pada proses atau prosedur yang melibatkan penggunaan teknik dan instrumen. Metode membandingkan sistem politik menggunakan satu per satu deskripsi memiliki struktur lemah karena orang cenderung tidak dapat menciptakan hubungan antara isu-isu organisasi saat ini dan administrasi posisi sistem politik secara tepat. Tulisan ini bermaksud membangun kesadaran sekali lagi tentang bagaimana melakukan perbandingan terbaik antara satu negara dan lainnya. Penelitian ini bertujuan untuk menciptakan jembatan untuk menghubungkan antara kerja sistem politik, masalah yang ada dalam organisasi menganalisis kasus struktural menggunakan metode perbandingan politik tidak bisa hanya membandingkan struktur yang berbeda.
Kata kunci: perbandingan politik, ilmu politik, hubungan internasional
INTRODUCTION
Politics investigation is focusing on understanding how related parties take control of every decision and then execute it for society. The principal element in the political system is government institutions as legislatures, bureaucracies, and courts. They are formulating and implementing the mutual goal of society. The goal is believed to be the best method for government maintaining order in their administration and at
the same time makes it possible for some organizations give consensus in the aspect of power division and its intersection. The entity governmental structures that surround and influenced groups of people with a same purpose is formulating a system. From this argument, construction of the political system will present the type of social system which involved in the making of authoritative public decision (G. Bingham Power, 2015).
All organization has politics on it because it has formed to fulfill shared likeminded goals of the members. We also understand that each member has a selfinterest, thus it may lead to a conflict of interest. The organization’s membership shall focus on common interest most than self-interest. Whether the interest gives advantages for many people or only part of it. A whole host of the institution, beginning with family and including public or private community, churches, school, corporation, and think tanks influence of political attitudes and public policy. The political system is referring to the whole collection of related, interacting institutions and agencies (G. Bingham Power, 2015).
In order to study how the political system work by collecting, identifying, interpreting, and decomposition of system’s element whether it works efficiently to accomplish the purpose, we should answer the fundamental questions in-country political system. It may lead to understanding who the actor that playing the role, what role that be played by actors, how actors play the role, which role be played by actors, why actor play the role and the result of action which is played by the actors. David Easton draws pragmatically the relationship of the political process (Easton, 1957).
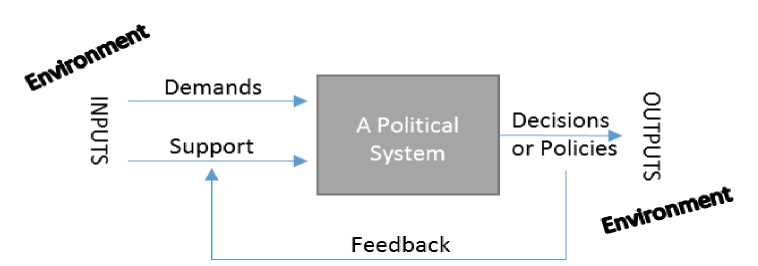
Figure 1. Easton’s Political Process Relationship
Easton argues that the boundary of the political system is formed by the actions of related element inside the systems that making of binding decision for society. Inside the decision-making elements need to obey the nature of environment, whether it
supporting the system or even obstruct it. It can be viewed as a living organismenvironment. Inputs and outputs in figure 1 can be said as, if we select political systems for special study and we believe that they have characteristics of important consequences for society, it be called an authoritative decision. Outputs are the consequences. Simply stated for an example, if we judge that the political system, that it did not have important outputs or we believe that the outputs are not meant to be, we can state that it is infeasible meaning because demand and support of the political system cannot be well implemented because it is not being supported by people. In the phase of inputs, we can see demands and support, while those can be explained as ingredients of a system for works. Demand sets triggers for making the political elements work creating a decision or policy (outputs) and demands are influenced by the need of organism who live in a certain environment. When elements are working, of course, they need to be firm by being supported by related parties. It happens because the inputs of demand alone are not enough to keep the political system operating (Easton, 1957). As energy in the form of actions, they will act to promote or resist the decision, to be put into the system, in order to keep the system running. The energy is also be called support. Supporting behavior may thus be of two kinds, it may consist of action promoting the goals, interest, and action of another person (Easton, 1957).
Since each environment, demands, support, and fundamental belief of every nation is different each other, then it can be resulted in different type of political system, see in exhibit 1 for more detailed information. Also, we can say that the relationship among them may be many different of a kind. For instance, in the field of international trade policy which Indonesia has different policy in each country, Indonesia has substantial trade relationship with some countries, some of them have more exports than imports and vise-versa. When NATO nations try to trade with Indonesia, the minister of foreign affairs need to settle different policy based on nation client characteristics.(Keman, 2002).
The government has specialized structures like parliaments, bureaucracies, administrative agencies, and courts. These structures perform a function which will be used for formulating, implement and enforce its policies. The assurance of how policies are being implemented effectively is the output or aim of the political system. The agencies or elements are being existed by means to achieve them. Figure 2 shown us six types of political structures political parties, interest groups, legislatures, executives, bureaucracies, and courts within the political system. These are formal organizations engaged in political activities. They exist in most contemporary political systems. This list is not exhaustive. Some structures, such as ruling military councils or governing royal families, are found in only a few countries. Some, such as Iran’s
Council of Guardians, are unique to one country’s political system (G. Bingham Power, 2015). Culture is the main factor in order to make related parties behave, in the culture lies ineffable rules are called the norm.
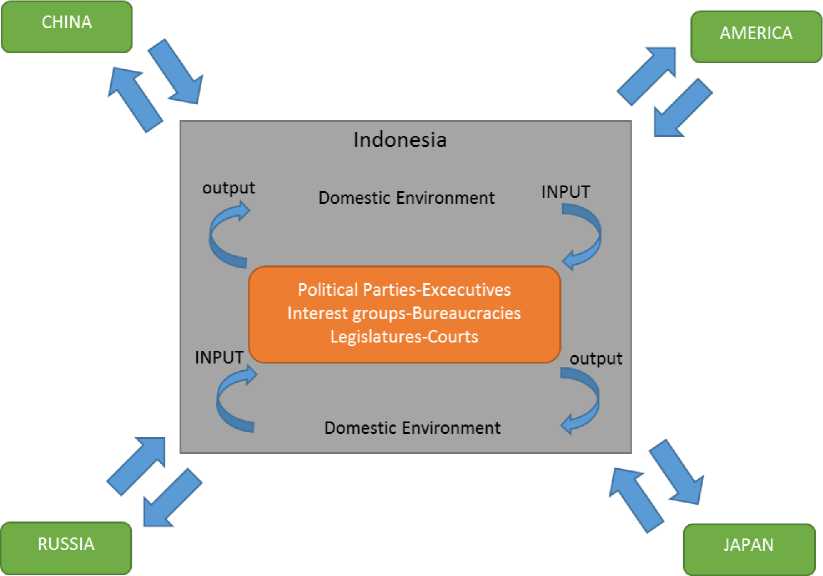
Figure 2. Indonesian Six political structures
FUNDAMENTAL THEORY
Some of comparative focus on analyze political institution or processes by looking at two or more cases that are selected to isolate their common and contrast features. Some of them bring out more to the government institution in different country such as legislature, executive, political party or court system and other compare specific process of making policy (Wadsworth, 2010). The view of Wadsworth it seems may same with what Easton David brought (Easton, 1957). Thematic features of comparative studies bring differences about richness of analysis, which always touch the causes and consequences of nationalist movement or revolution in different countries (Wadsworth, 2010).
Country is the basic building block for analyzing state per state comparative politics. Comparatist seek to understand about measure similarity or differences between one country and to another. One influential approach in comparative politics involves developing causal theories and hypotheses. Which is “If X is happen then Y will result”. (Kesselman et al., 2009) This relationship may be tested statistically by
searching correlation value between events. Another way to analyze causal relationship is by understanding the historical background, is there exist similar phenomenon within historical period and is there any causal explanation about it, second, we shall understand about the event that happen today is because of series of event that had happen in the past. Bingham 2015 said that there are three steps of frameworks that we need to do first before classify political system, those steps can be seen on the figure 3. By comparing between one political system and the other will provide information about possible outcome that will happen if one or many different experiments input of political system are running.
Method of comparisons divided by two categories first is level analysis and the second is causal theories. Level analysis is about how deep the analysis need to be done. For an instance, a state has institutional executive, cabinet, legislature, and judiciary. The next step is analyzing and doing comparison about the formation of those institution or group. Other key state of institution is the administrative bureaucracy, military, and the police. Level of analysis will be conducted until we found explanations about how deep our understanding about political legitimacy in certain country. After we found the factors then causal relationship between those factors need to be extracted.(O’Neil, 2009)
-
• Themes of Comparative Politics
In order to create the best comparative political result, we shall focus on the aim that we need to direct. Second approach to have deep understanding about political comparison is that choosing themes that today become issue in the world, and how we will address it. The four most common and arguable are world of states, governing the economy, democratic idea, and politics of collective identity which usually said politics of community such as gender, religion, etc.
-
• Classifying Political System
Finally, after all things are done, we shall take into notice that classification of our project shall meet two criteria such as meaning type of system and topology of political system. Doing the classifications are really matter because we can see where our subject is working from the subject taxonomy and when another researcher wants to do further research they easily connect and found important information.

Method Comparison

Themes of Comparative Politics
•World of states •Governing the Economy
•The Democratic Idea
•Politics of Collective Identity
Classifying Political
System
•Meaning type of system
•Topology of Political
System

Figure 3. Theory of Approaching Political Comparison

The logic of the comparative method is the same as the logic of the experimental method. The comparative method resembles the statistical method in all but one, namely that the number of cases handled is too small to allow systemic control by means of partial correlation. The comparative method is not equivalent to the experimental method but it is being used as substitute for imperfections, there is a case when theory unable explain the evidence, hence new theory may exist because of this occasion. The experimental method uses two equivalent groups, one of which is imposed on a stimulus while the other is not. Equivalence is achieved by an intentional randomization process. The experimental method is the most ideal method for scientific explanation, but this method is rarely used in political science because there are ethical and practical obstacles. An alternative to the experimental method is the statistical method. Statistical methods can be considered as estimates of experimental methods. Ernest Nage states that every branch of inquiry relating to empirical issues must use procedures that have the essential logic functions of experiments in inquiry. Statistical methods do not have this logical function because they cannot overcome the problem of control. Even experimental methods cannot perfectly solve the control problem. Statistical methods can also be referred to as experimental method estimates.(Wiles & Dartnall, 1999).
HOLISTIC PROCESS OF POLITICAL COMPARISON
Each of political system has heading on the process function which it has listed on the distinctive activities one country to another. Powel et. Al (2015) describe four roles of those process functions, such us
-
• Interest articulation, which it involves individual and group expressing needs
-
• Interest aggregation, which it combines different demand into policy proposal backed by significance resources
-
• Policy making, is deciding which policy proposal became authoritative rules
-
• And Policy implementation is carrying out and enforcing public policies, policy adjudication is setting disputes about their application.
The point is before policy has been decided all element shall agree with the decision. To be effective, however this demand must be combined into policy alternative. Thus, the arrow on the left the process moved from the interest of articulation into interest of aggregation. Then government need to consider alternative policy and choose between them. Any policy may affect several different aspects of society. These process functions are found by political structure as parties, legislature, political executives, bureaucracies, and courts. Since all of them are not immediately occur thus its analyzing process need to be extract from the beginning of its existence. There are several aspect of structural existence analyses, which are: historical background, leadership style, future aim and certain condition or environment that need to be faced. All of them can be explained as structural existence dimension that we shall consider when we do political comparison analysis. It is true that several countries have same type of political system, but inside the system which we before called as structural dimension need to be taken care of.(Hague & Harrop, 2005)
Function of all parts political process are:
-
• Political Socialization
It is involving family, school, communication media, churches, and all various political structures that develop and reinforce and transform the political the political culture and attitudes of political significance of the society.
-
• Political Recruitment
Refers to the selection of people for political activity and government. In democracy, competitive election plays major role in political recruitment. In authoritarianism may dominated by a single party as in China or by unelected religious leader as in Iran.
-
• Political Communication
Refers to flow of information through the society and the various structure that make up the political system. Gaining control over the information is the key goal of most authoritarian rules as shown in the elaborate effort of Chinese leaders to control content on the internet.
However comparative approach principally analyzes similarities and differences among country among countries by focusing on selected institution and processes. As we refer on previous statement, as researcher we cannot focus only on
one aspect. For example, when United States of America claim that it has the best health care system in the world then comparatists immediately wonder what kind of health care system exist in other country. In Figure 6 we can see about method of comparison which divided by two important aspect one is level of analysis and casual theories.(McCormick, 2009)
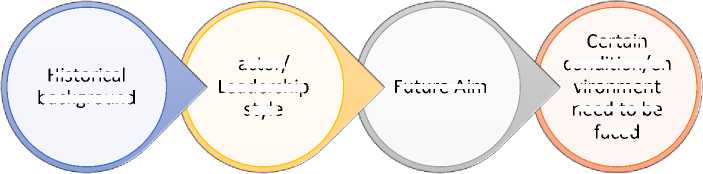
Future Aim
Historical
background
Certain
condition/en
vironment
need to be
faced
actor/
Leadership
style
Figure 4. Structural Existence Analysis
Level of analysis of comparison theory begin with how deep of political analysis which encompass political institution, culture, economic, ethnic, and other social identities. Although country often divided by internal conflict and peoples within boarders may have conflict with close country. A State claim that usually considerably success create rules notably law, administrative, until courts, for ensuring people stay, a state should remain and increase the power of legitimacy, which significant segment of citizen which believe that the state is entitled to command compliance from those who live under its jurisdiction (rule). Thus, level analysis of comparative politics looks closely at both state’s role in government and pressure excreted the state to develop and extent democratic participation. Next is causal theory being analyzed when we understand and have all independent and dependent variable from the research questions.
Making of Modern State
W
Political Economy Development
Governance and Policy Making
Representation and Participation
Politic and Transaction
Figure 5. Organizing issues as indicator of politics in certain country.
Next big thing is the theme for comparative analysis, which divided by four major themes like what (G. Bingham Power, 2015) did before. When the researchers classify large number of cases then we may cluster using feature which being held by object. Topology can facilitate comparison both Britain and U.S. We can also compare across cluster type. There are five main issues that need to be address when study political system (Wadsworth Cengage Learning, 2010) doing political were being formulated by Mark Kesselman et al (2010) are described above in figure 5. Those indicators are used to leveling how well political systems being implemented, and of course those indicators are backward analyzed in order to give us feedback about all implementation result, whether already desired or not.
Holistic approach of comparative politics is the result when the focus oriented inside political system and the method of analysis. Can be found at Figure 6. Author can say that using only model for analyzing political comparison is not suitable. Political comparison as a method can be used to conduct research. There are three processes or studies that use the participatory method. The first step is to explain the core subject of comparative inquiry. In other words, first formulate questions about what needs to be asked and how we need help and explain important systemic features. The second stage is developing a view of concepts that can be renewed well that we discuss that measures internal validity, while having a unifying capacity to explain political and social processes with generality or external validity. Then, use the third, namely, discuss the logic of the comparative method as a means to an end, rather than as an end in itself
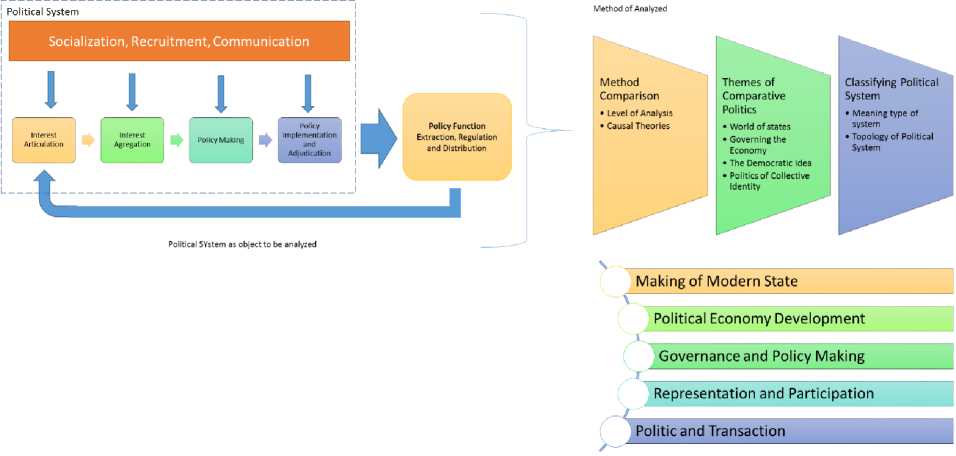
Figure 6. Holistic Approach of Analyzing Political System for comparison
CONCLUSION
Comparing political system only using single structure is not enough because structural existence analysis not being fulfilling. Holistic approach for creating political comparison analysis are the answer of single structure analysis. The need for systematic comparative political studies, so as to produce generalizations that help build theory. Thus, the political comparison of countries and the resulting generalizations enables fundamental predictions and lessons for other countries. In general, there are three fundamental reasons why a study of comparative politics is needed, namely classification, hypothesis testing, and prediction. By put the method of analyzing, five Indicators of organizing issues, and the political system as a standalone system will make the comprehensiveness research will be accounted.
References
Easton, D. (1957). An Approach to the Analysis of Political System. World of Politics, 9, No 3, 383-400.
G. Bingham Power, J. R. (2015). Comparative Politics Today: A World View. Pearson.
Hague, R., & Harrop, M. (2005). Comparative government and politics: An
Introduction (6. ed., fully rev. and updated, [Nachdr.]). Palgrave Macmillan.
Keman, H. (Ed.). (2002). Comparative democratic politics: A guide to contemporary theory and research. SAGE.
Kesselman, M., Krieger, J., & Joseph, W. A. (2009). Introduction to Comparative Politics (5th ed.). Wadsworth Publishing.
McCormick, J. (2009). Comparative Politics in Transition (6th ed.). Cengage Learning.
O’Neil, P. H. (2009). Essentials of Comparative Politics (third). W.W. Norton & Co.
Wiles, J., & Dartnall, T. (1999). Perspectives on Cognitive Science: Theories, Experiments, and Foundations. Greenwood Publishing Group.
Wadsworth. (2010). Introduction to Comparative Politics: Political Challanges and Changing Agendas. Boston: Warsworth Cengage Learning.
Wadsworth Cengage Learning. (2010). Introducing Comparative Politics: Political Changes and Changing Agenda. In J. K. Mark Kesselman, Introducing Comparative Politics (pp. 22-63). Wadsworth Cengage Learing
97
Discussion and feedback