MYOGLOBIN CONTENT IN CARDIAC MUSCLE OF PHYSICAL EXERCISE INDUCED RAT (Rattus norvegicus)
on
JURNAL SIMBIOSIS IV (2): 39-41
Jurusan Biologi FMIPA Universitas Udayana
I SSN: 2337-7224
September 2016
http://ojs.unud.ac.id/index.php/simbiosis
Directoryof
OPEM ACCESS
Jourmals
MYOGLOBIN CONTENT IN CARDIAC MUSCLE OF PHYSICAL EXERCISE INDUCED RAT (Rattus norvegicus)
1* 2
Sri Rahayu, Rini Puspitaningrum1,Mohammad Sadikin
1 Department of Biology, Faculty of Mathematic and Natural Sciences, State University of Jakarta, Jakarta, Indonesia 2Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Faculty of Medicine, Universitas Indonesia, Jakarta, Indonesia Coorespondence author*: fi_a_ra@yahoo.com
ABSTRACT
The research was aimed to analyzing the impact of 7 days arobic exercise in elevating rat cardiac muscle myoglobin. Experimental in vivo study on 20 male Wistar rat induced by 20m/ min treadmill aerobic exercise for 1, 3 and 7 days. Research was done in Animal house and protein laboratory, Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Department, FK UI and laboratory of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Biology Department FMIPA UNJ for 10 months. Myoglobin concentration was analyzed by spectrofotometry techique based on myoglobin Soret absorbance in λ503nm. Myoglobin protein expression was assesed with Western blot technique. Standard curve measurement on myoglobin content with horse myoglobin shown that there was an increase on the absorbance value. The result showedanthat the standar curve was able to be used as standard curve to calculate myoglobin concentration on cardiac muscle within 503 nm. Spectrophotometry myoglobin concentration measurement on Soret absorbance has shown increasing concentration on myoglobin since the first treatment day. Mean myoglobin concentration value has increased on the 3rd and 7th day, with highest value on the 7th treatment day (0,0656 ± 0,0001). Western blot analysis showed ng on darker band on treatment group compared on to control. When aerobic exercise was given longer, the band shown darker means that myglobin content was higher. Myoglobin concentration can be measured by spectrophotometry on 503 nm. Aerobic physical exercise increased myoglobin on rat cardiac muscle since the first treatment day and still increase oduring the treatment day. Highest level was shown on the 7th treatment day.
Keywords : myoglobin, cardiac, muscle, exercise, rat
INTRODUCTION
Mammals will develop responses under hypoxic condition through some ways. There are erythropoesis, angiogenesis, increase glycolitic enzyme and globin protein concentration1,2. One of which i.e. myoglobin protein. Myoglobin is a globin class protein which has important rule as oxygen storage. Oxygen stored on myglobin will be released under hypoxic condition3,4. This rule made myoglobin as a target for treatment of some diseases related to hypoxia. One modulation known to increase myoglobin is physical exercise5. During physical exercise, muscle contraction will occur. This contraction is responsible for calcium release from sarcoplasm reticulum. The release will activate NFAT (Nuclear factor of activated T- Cells) gene. NFAT gene will translocate to nucleus and activate the transcription of myoglobin gene6. There are two kinds of physical exercise, the aerobic and anaerobic. Aerobic exercise is known to enhance aerobic metabolism capacity without fatigue and lactate pooling7. Based on the background, the study assessed erobic exercise in increasing myoglobin content on cardiac muscle. So that the modality might be used as therapeutic program ofhypoxia diseases or preventing hypoxia. The study also identified the impact of treatment day in increasing myoglobin content based on spectrophotometry and western blott method.
METHODS
Study design and sampling
Experimental in vivo study on 20 male Wistar rat induced by 20m/ min treadmill aerobic exercise within 1, 3 and 7 days. Research was done in Animal house and protein laboratory, Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Department FK UI and laboratory of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Biology Department FMIPA UNJ for 10 months. The procedure has been legalized under the committee of the medical research ethics, faculty of medicine, University of Indonesia number 79/PT.02.FK/ETIK/2011.
Physical exercise induction
Rats were given aerobic physical exercised on animal treadmill machine based on soya. Rats were run on treadmill machine of 20m/min for 30 minutes. Treatment was done on 1, 3 and 7 day of exercise.
Myoglobin analysis
Myoglobin concentration was analyzed by spectrophotometry method based on Myoglobin Soret absorbance in λ503 nm. Protein expression was assessed with Western blot. Cardiac muscle of the samples was homogenized and protein concentration was measured n myoglobin Soret absorbance (503 nm) with myoglobin standard curve equation. Horse myoglobin was used as positive control (sigma Aldrich, USA). Homogenized samples with buffer were heated on 95°C and inserted into SDS-PAGE well to separate the protein. Proteins that have been separated on SDS- PAGE gel were transferred into nitrocellulose membrane and incubated overnight. Blocking of the membrane was done by 1% gelatin overnight. First antibody reaction was diluted in 1:500 (rabbit polyclonal anti mouse myoglobin FL 154 by Santa cruz), then as incubate for 2 hours. second antibody was diluted in 1:1000 (Goat anti rabbit IgG hrp sc 2030 by santa cruz) for 2 hours. Detection was done by sinking the membrane into AEC solution (REF 00-1111 by invitrogen) for 10 minutes. After washing the AEC with aquadest, color seen on the membrane was documented.
Statistical analysis
Mean values are presented as mean ± standard error of mean (SEM). Comparison of the two means of myoglobin concentration was carried out by using two ways analysis of variance (Anova).
RESULTS
Myoglobin standard curve
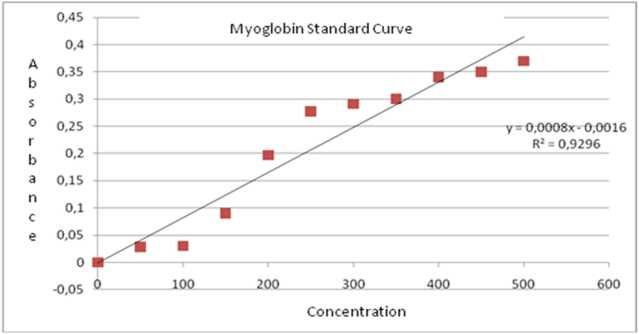
Figure 1. Myoglobin standard curve, concentration (x, μg/ml) and absorbance (y) of horse on λ503 nm
Directoryof OPEN ACCESS JOURNALS
Myoglobin concentration measurement
Table 1. Rat myoglobin on cardiac muscle (mg/mg tissue)
Sample Control Aerobic exercise
|
1 day |
3 day |
7 day | ||
|
1 |
0,0255 |
0,0580 |
0,0570 |
0,0630 |
|
2 |
0,0255 |
0,0575 |
0,0630 |
0,0630 |
|
3 |
0,0220 |
0,0615 |
0,0610 |
0,0680 |
|
4 |
0,0200 |
0,0610 |
0,0620 |
0,0660 |
|
5 |
0,0205 |
0,0620 |
0,0595 |
0,0680 |
|
Mean±sem |
0,0219± |
0,0600± |
0,0605± |
0,6565± |
|
0,0003 |
0,0009* |
0,001* |
0,0001* | |
Significance difference compare to control (p<0,005)
198 kda
98 kda
62 kda
49 kda
38 kda
28 kda
17 kda
14 kda
6 kda
3 kda
1 2 3 4
Myoglobin expression detection
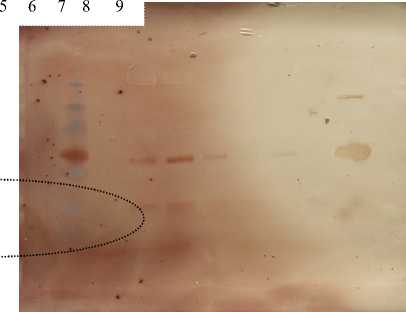
Figure 2. Western b o ana ys s of myoglobin on rat cardiac muscle. Expression was shown on 1,3, and 7 treatment day in 17 kda. Line 1(protein marker), line 2 (control), line 3 and 4( 7 treatment day), line 5 and 6( 3 treatment day), line 7 and 8 (1 treatment day), line 9 (horse myoglobin)
DISCUSSIONS
Myglobin content on cardiac muscle of rat was assessed with spectrophotometry method. This method has long been used as a tool for calculating protein concentration7. Colored protein is known to be able to give absorbance and fluorescence under specific wavelength of light. Globin protein, including myoglobin has porphyrin ring that can absorb light8. Myoglobin is four heterocyclic pirol protoporphyrin which tie zinc coplanary to form heme . Porphyrin on myoglobin make the protein colorful, and has absorbance and flouroscence characteristic when given a light on specific wavelength ( Soret Absorbance). Myoglobin has Soret absorbance at 503 nm 10.
Research result on myoglobin content with spectrophotometry method, it showed that aerobic physical exercise was able to enhance myoglobin concentration on rat cardiac muscle. Cardiac muscle myoglobin of treatment group was higher comparing to control.
Cardiac muscle is categorized into the red fibre muscle type. This type of muscle has higher myoglobin content compare to white muscle, which make it has darker color11. Cardiac muscle is type I of slow twitch muscle. 12. This type of muscle has aerobic capacity and many mitochondria to maintain permanent contraction. Anatomical structure of cardiac muscle has 40% of mitochondria11. This structure strongly indicates how the organ relies on oxygen and aerobic metabolism to produce energy for contraction. For its activity, cardiac muscle will oxidized fatty acid as energy source2,12,13,14. The process needs oxygen in adequate amount to maintain contraction in cardiac muscle. Adequate amount of oxygen reserve in myoglobin has play important role in handling high oxygen demand during aerobic physical exercise15. Under normal condition, without exercise, cardiac muscles will continues to contract and need huge amount of ATP as energy source. Aerobic exercise will create cardiac muscle to contract more than normal condition to fulfil oxygen need. This condition has created higher ATP demand. Aerobic metabolism is capable of producing 36-38 ATP on every oxidation of 1 mol of glucose. Whilst, Anaerobic metabolism will only produce 2 ATP from the breakdown of 1 mol of glucose to lactate11,16. Fatty acid has been the main substrate for cardiac muscle
contraction (60- 80%) by β oxidation. The process obviously needs oxygen and this explains why aerobic metabolism is the main source for cardiac contraction. That also explains why myoglobin as oxygen source or oxygen reserve is directly needed in this organ.
Seven day of aerobic exercise given in the treatment group was decided based on physiologic adaptation which might take place from the first day of aerobic exercise. This is supported by the fact that JNK gene will be 100% increased even on the first treatment day of aerobic exercise. The research result has indicated that aerobic exercise would increase myoglobin content on cardiac muscle from the first treatment day and kept on increase until the 7th day.
Western blott analysis was done under the basic of immunology reaction between antigen antibody17,18,19,20. The research result showed that myoglobin was expressed in cardiac muscle of rat induced by aerobic exercise in the higher expression compared to control. Cardiac muscle will contract continuously for the whole life time. Aerobic exercise has caused the muscle contract even harder and released more calcium form reticulum sarcoplasm21. This condition made higher amount of NFAT defosforilated by calcineurin and traslocatedto nucleus to activate myoglobin transcription.
This result showed that aerobic exercise would be able to increase myoglobin expression on cardiac muscle through the activation of gene transcription by NFAT6,21,22. Myoglobin expression is obviously regulated y transcription mechanism17. Increase expression of myoglobin protein lead to the increase of the protein content on cardiac muscle. Calcineurin pathways activation through aerobic exercise was the central key on this research. Muscle contraction will increase intracellular calcium and activate calcineurin22.
Based on the research, it showed that aerobic exercise was the modulation that can be used in increasing myoglobin content on cardiac muscle. Aerobic exercise benefits can be gained from the first day of exercise. Myoglobin expression modulation thrrough continuous aerobic exercise can be used as therapeutic regiment of diseases related to hypoxia or prevention of hypoxia. The result also explained the importance of doing aerobic exercise for oxygenation mainly on cardiac muscle as prevention effort of cardiac hypoxia.
FAO Λ I Directoryof
OPEN ACCESS
∖-J∖yrΛU JOURNALS
Acknowledgments
and Molecular Biology Faculty of Medicine University of Indonesia for providing laboratories facilities.
We would like to acknowledge the Hibah pasca sarjana RUUI 2011 for the research grant and Department of Biochemistry
REFERENCES
Fedele OA, Whitelaw ML, Peet DJ. Regulation of Gene Expression by Hipoxia Inducible Factor. J Mol Inter. 2002; 2: 229-40.
Storey BK, editor. Functional Metabolism: Regulation and Adaptation. New Jersey: John Wiley & Son; 2004.
Puspitaningrum R. Ekpresi dan karakterisasi molekul mioglobin tukik Chelonia mydas sebagai model protein pengikat dan penyimpan oksigen hewan toleran hipoksia. Disertasi. 2010.
Brebrink M. Myoglobin’s old and new clothes: from molecular structure to integrated function and evolution. J Exp Biol. 2010; 213: 2711-12.
Wittenberg BA. Both Hypoxia and Work are Required to Enhance Expression of Myoglobin in Skeletal Muscle. Focus on Hypoxia Reprograms Calcium Signaling and Regulates Mmyoglobin Expression. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2009; 296:390-2.
Kanatous SB, Mammen PA, Rosenberg P, Martin C, White M, Dimaio M et al. Hypoxia Reprogram Calcium Signaling and Regulates Myoglobin Expression. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2008; 296: C393- C402.
Boyer R. Biochemistry Laboratory: Modern Theory and Techniques. USA: Benjamin Cummings; 2009.
Reeder B, Svistunenko P, Wilson M. Lipid Binding to Cytoglobin Leads to a Change in Heme Coordination: A Role for Myoglobin in Lipid Signaling of Oxidative Stress. J Biochem. 2010; 434: 843- 92.
Brunori M, Antonini E. Hemoglobin and Myoglobin in Their Reaction with Ligands. North Holland: The Netherland; 1971. Bowen WJ. The Absorption Spectra and Extinction of Myoglobin. J Biol Chem. 1948; 179: 235- 245.
Voet D, Voet J. Biochemistry. Inter ed. USA: Wiley. 2004.
Mooren F, Volker K. Molecular and Cellular Exercise Physiology. New Zealand: Human Kinetics; 2005
Murray R K, Granner DK, Rodwell VW. Harper’s Biochemistry. 25th ed. America: Appleton & Lange; 2000 Mathews A, Holde M, Athern H. Biochemistry. 3rd ed. New York: Addison- Wesley; 2000.
Meyer AR,. Aerobik performance and the function of myoglobin in human skeletal muscle. Am J Physiol Integ. 2004; 287 : 1304-5.
Sherwood L. Human Physiology From Cells to Systems. USA: Thomson. 2004
Wiever R. Molecular Biology. USA: Mc Graw Hill; 2005
Jin H, Yang R, Li W, Lu H, Ryan A, Ogasawara AK et al. Effect of Exercise training on cardiac function, gene expression and apoptosis in rat. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2000; 279: 2994- 30002.
Cake L, Kaufman PB, Podila G, Tsai SJ. Handbook of Molecular and Cellular Methods in Biology and Medicine. New York: CRC Press; 2004.
Work T, Work E. Laboratory Technique in Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. London: NHC; 1969.
Kanatous SB, Mammen PA. Review: Regulation of Myoglobin Expression. J Exp Biol. 2010; 213: 2741- 47.
Ordway G, Garry D. Myoglobin: an essential hemoprotein in striated muscle. J Exp Biol. 2004; 207: 3441-6.
41
Discussion and feedback