Lexical and Structural Ambiguity Found in Articles in The Jakarta Post Daily Newspaper
on
DOI: 10.24843/JH.2019.v23.i01.p04
p-ISSN: 2528-5076, e-ISSN: 2302-920X
Jurnal Humanis, Fakultas Ilmu Budaya Unud
Vol 23.1 Pebruari 2019: 19-24
Lexical and Structural Ambiguity Found in Articles in The Jakarta Post Daily Newspaper
Julie Puspitasari1*, Ni Luh Sutjiati Beratha2, [123]English Department - Faculty of Arts - Udayana University 1[juliepusp@gmail.com] 2[sutjiati59@gmail.com]
*Corresponding Author
Abstract
This study aims at finding out lexical and structural ambiguity which occurs in the articles and explaining the causal factors in each ambiguity. The data in this study were taken from nineteen articles in The Jakarta Post daily newspaper from edition November 14 to November 25, 2017. Recording method and note taking technique were applied in this study for collecting the data. Meanwhile, the data were analyzed using qualitative method. Ulmannʼs theories that involved kinds of ambiguity and the causal factors of ambiguity, by using Macmillan Dictionary to find the definition of each word in lexical ambiguity and labeled and bracketed sentences/phrases proposed by Yule were used to analyze the data. The result of the analysis shows that there were 20 ambiguous words, phrases or/and sentences found in nineteen articles in The Jakarta Post. There were 8 cases of lexical ambiguities and 12 cases of structural ambiguities. The result of this study shows the causal factors of each ambiguity as well, there were 8 lexical ambiguities caused by polysemy and 12 structural ambiguities caused by equivocal phrasing.
Keywords: Lexical, Structural, Ambiguity, The Jakarta Post
Abstrak
Penelitian ini bertujuan untuk mengetahui ambiguitas leksikal dan struktural yang terjadi dalam artikel dan menjelaskan faktor-faktor penyebab dalam setiap ambiguitas. Data dalam penelitian ini diambil dari sembilan belas artikel di surat kabar harian The Jakarta Post dari edisi 14 November hingga 25 November 2017. Metode pencatatan dan teknik pencatatan digunakan dalam penelitian ini untuk mengumpulkan data. Sementara itu, analisis data menggunakan metode kualitatif. Teori-teori Ulmann yang melibatkan jenis-jenis ambiguitas dan faktor-faktor penyebab ambiguitas, dengan menggunakan Macmillan Dictionary untuk menemukan definisi dari setiap kata dalam ambiguitas leksikal dan kalimat-kalimat yang dilambangkan dan diberi tanda kurung / frase yang diusulkan oleh Yule digunakan untuk menganalisis data. Hasil analisis menunjukkan bahwa ada 20 kata ambigu, frasa atau / dan kalimat yang ditemukan dalam sembilan belas artikel di The Jakarta Post. Mereka adalah 8 kasus ambiguitas leksikal dan 12 kasus ambiguitas struktural. Hasil dari penelitian ini menemukan faktor penyebab dari setiap ambiguitas juga, ada 8 ambiguitas leksikal yang disebabkan oleh polisemi dan 12 ambiguitas struktural yang disebabkan oleh frase samar-samar.
Kata kunci: Leksikal, Struktural, Ambiguitas, Jakarta Post
Language is a communication instrument needed by people for interaction with one another. The language has a meaning whether it is a spoken language or written language. We can learn the meaning itself in semantics. Sometimes we do not state the meaning clearly; therefore, we make the listeners or the readers interpret our meaning into different meaning. This misunderstanding is known as ambiguity.
Ambiguity is a language phenomenon that usually happens in human daily communication. According to Fromkin Rodman (1983:169), “A word or a sentence is ambiguous if it can be understood or interpreted in more than one way.” It is a term which is against meaning properties of a language because it refers to an utterance (a word, a phrase, or a sentence) that has more than one meaning. As Leech (1981:30) says “An expression is said to be ambiguous when more than one interpretation can be assigned to it.” This ambiguous expression can happen in one word or one sentence/phrase. As we know as lexical and structural ambiguity.
Ullmann (1977:156) divides ambiguity into three kinds; phonetic, lexical and grammatical. However, this study focuses on the lexical and structural ambiguity. If lexical ambiguity is caused by a word with more than one meaning, structural ambiguity is caused by the structure of the words when they are combined even though those words exactly have only one meaning.
Ambiguity is not only found in daily conversation but also in media such as in newspaper. A newspaper is a media on which most of people update their knowledge of what is happening around
the world. The journalists sometimes use ambiguity in presenting
the news. This often creates different interpretation from people who read it. Therefore, studies or research on ambiguity are absolutely important.
Newspapers in Indonesia are divided into two, based on their scope: local newspapers and national newspapers. Local newspapers usually emphasize presenting the news about what has happened in a particular area. Meanwhile, national newspapers present the news in wider scope that is about what has happened in a country. One of national newspapers in Indonesia is The Jakarta Post. Besides presenting the news around this country, Indonesia, this newspaper also uses the English language in all sections of the newspaper. The use of English is expected to give opportunity for foreigners to participate in reading the news. Besides, this is also helpful for foreign learners to take the English data from the newspapers. This is the reasons why The Jakarta Post will be taken as a source of data in this study.
Based on the phenomenon and explanation above, the writer is interested to conduct the research related about ambiguity. This study would analyze the words, phrases or/and sentences which contain ambiguities found in articles of The Jakarta Post daily newspaper. Furthermore, the causal factors of each ambiguity was also explained in this study.
-
a. What lexical and structural ambiguities are found in articles in The Jakarta Post daily newspaper?
-
b. What are the causal factors of ambiguities found in articles in The Jakarta Post daily newspaper?
-
a. To find out lexical and structural ambiguities found in articles in The Jakarta Post daily newspaper.
-
b. To explain of the causal factors of each ambiguity found in articles of The Jakarta Post daily newspaper.
There are four points in the research method, they are: Data Source, Method and Technique of Collecting Data, Method and Technique of Analyzing Data, and the last is Method and Technique of Presenting Data Analysis.
The data in this study were taken from nineteen articles in The Jakarta Post Daily Newspaper from edition November 14 to November 25, 2017. Total of the newspapers is ten pieces, last two editions of newspapers in November 16 and 19, 2017. This newspaper was selected as a data source, because it is one of the famous daily English language newspapers in Indonesia.
The Jakarta Post is owned by PT Bina Media Tenggara and this paper has been in existence since April 1983. The Jakarta Post, like other newspapers, is composed of some parts or sections. This classification is made to ease the readers to find out which information they need to know.
The data were collected through recording method, because the source of this analysis was taken from articles in daily newspapers. The technique used in collecting data was note-taking technique, all of the words, phrases and/or sentences containing ambiguous in the articles were noted. Firstly, all the articles of selected in The Jakarta Post
daily newspaper were read intensively one by one to obtain the words, phrases and/or sentences which contains ambiguous. Secondly, note-taking the words, phrases and/or sentences which contain ambiguities. Thirdly, all data were grouped into each type of ambiguity. Then, finding out the causal factors of each ambiguities.
The collected data were analyzed using the qualitative method. This method was used to interpret the data descriptively. This study used several techniques to analyze the data. Firstly, all the data found in The Jakarta Post were grouped into the types of ambiguities whether the lexical or structural ambiguities based on the theory proposed by Ulmann (1972, in Pateda, 2001: 202). Secondly, analyzing the lexical ambiguities by interpreting them using Macmillan Dictionary. Thirdly, analyzing the structural ambiguities by labelling and bracketing based on the theory proposed by Yule (1985: 75). And the last step, analyzing the causal factors of each ambiguity which contribute to the lexical and structural ambiguities using Ulmann’s theory (1972, in Pateda, 2001: 203-206).
Formal and informal methods were applied in presenting data. Formal method refers to the method of presenting data analysis using diagrams, tables and symbols, while informal method means presenting the result of the data analysis using words and sentences.
In this study, formal method was used to see the sentence structure in the diagram, meanwhile, informal method was used to present the data
descriptively. The labeling and bracketing in sentence/phrase of structural ambiguities were presented by using diagrams. In addition, the meaning and the causal factors of each ambiguity was presented descriptively.
The data were collected from nineteen articles in The Jakarta Post daily newspaper from edition November 14 to November 25, 2017. The data were analyzed using Ulmann’s theory to find the lexical and structural ambiguities in the articles, using Macmillan Dictionary to find the definition of words and using Yule’s theory to label and bracket the sentences/phrases. Here are the words and sentences/phrases that possibly made the readers confused.
The campground is located on Paloh Beach in Sambas regency, where rare sea turtles lay eggs in the longest nesting area in the country stretching 63 meters along the coast.
The sentence above is considered as lexical ambiguity based on Ulmann’s theory. It is shown by the word ʻstretchingʼ which has more than one meaning.
Ambiguity Interpretations
The word ʻstretchingʼ has some meanings based on Macmillan Dictionary:
-
- to pull something to make it longer or wider
-
- to continue for a particular distance
Therefore, based on the definitions of the word ʻstretchingʼ above, the sentence may be interpreted as: a. First Interpretation
“The campground is located on Paloh Beach in Sambas regency, where rare sea turtles lay eggs in the longest nesting area in the country to pull the nest longer 63 meters along the coast.”
-
b. Second Interpretation
“The campground is located on Paloh Beach in Sambas regency, where rare sea turtles lay eggs in the longest nesting area in the country stretching 63 meters along the coast.”
In the case of ambiguity of the word ʻstretchingʼ, there is no word class inferring the interpretations. The interpretations come from the word ʻstretchingʼ as (only) the verb which has some meanings. To understand the exact meaning of the word ʻstretchingʼ the readers may read the paragraph below:
“Itʼs fantastic, drinking honey directly from a beehive, sweet and a bit sour,” said the ninth grader from Pontianak, West Kalimantan, who spent 12 hours on the road to reach the Belacan River campground.
The campground is located on Paloh Beach in Sambas regency, where rare sea turtles lay eggs in the longest nesting area in the country stretching 63 meters along the coast.”
Source: The Jakarta Post edition Nov 14, 2017
From the two paragraphs above, the readers know that what the writer intends to talk about is the word ʻstretchingʼ which refers to continue for a particular distance.
Proposing another approach, White suggested the regionʼs players should band together to think of “new models
for a new region”, one that would be less formal but more substantive.
By using Ulmann’s theory, there is structural ambiguity found in the sentence above. ʻShould band togetherʼ is considered as the ambiguous one which leads the readers to have the different interpretations.
Ambiguity Interpretations
a. First Interpretation
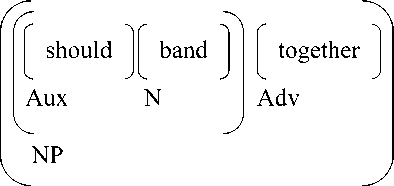
NP
b. Second Interpretation
should
Aux
together
Adv


NP
Based on Yule’s theory, in the diagram (a) the word should modifies only the word band. By the diagram shows that the sentence means “Proposing another approach, White suggested the region’s players should band of together to think of “new models for a new region”, one that would be less formal but more substantive.”
In diagram (b) the word should modifies the whole phrase band together; therefore, the sentence means “Proposing another approach, White suggested the region’s players should of band together to think of “new models for a new region”, one that would be less formal but more substantive.” In this case, the
phrase ʻband togetherʼ is a noun phrase in which those words have meaning, if those words are separated then the words have no meaning.
There are two types of the causal factors of ambiguity proposed by Ulmann’s theory, the causal factors of lexical ambiguity and the causal factors of structural ambiguity.
-
5.2.1 The Causal Factors of Lexical Ambiguity
01/LA/TUE/NOV/14
The campground is located on Paloh Beach in Sambas regency, where rare sea turtles lay eggs in the longest nesting area in the country stretching 63 meters along the coast.
It is lexical ambiguity in the case of polysemy. As polysemy, there are some meanings of the word ʻstretchingʼ: - to pull something to make it longer or wider
-
- to continue for a particular distance
-
5.2.2 The Causal Factors of Structural Ambiguity
09/SA/FRI/NOV/24
Proposing another approach, White suggested the regionʼs players should band together to think of “new models for a new region”, one that would be less formal but more substantive.
The phrase ʻband togetherʼ is considered as a structural ambiguity in the case of equivocal phrasing. In this case, the phrase ʻband togetherʼ is a verb phrase which means if the words are separated then those words have no meaning. Therefore, the words cannot stand alone and interrelated.
Based on the foregoing analysis and discussion, the following points can be drawn as conclusions:
There are two kinds of ambiguity found in nineteen articles in The Jakarta Post Daily Newspaper; lexical ambiguity and structural ambiguity. Lexical ambiguity arises when a single word has more than one meaning and structural ambiguity arises when phrase, clause or sentence creates ambiguity because their structure may be interpreted more than one way. There are 8 cases of lexical ambiguity and 12 cases of structural ambiguity.
The analysis also found the causal factors of each ambiguity, there are two causal factors of ambiguity; the causal factors of lexical ambiguity and the causal factors of structural ambiguity. There is only one causal factor of lexical ambiguity, it is polysemy. There are 8 lexical ambiguities caused by polysemy. And there is only one causal factor of structural ambiguity, it is equivocal phrasing. There are 12 structural ambiguities caused by equivocal phrasing.
References
Fromkin, Victoria., Rodman, Robert.,
Ityani, Nina. 2006. An Introduction to Language. Nelson.
Hurford, James and Brendan Heasley. 1983. Semantic: A Course Book. Cambridge:
Cambridge University Press.
Katz, Jerrold J. 1972. Semantic Theory.
New York Harper & Row Publisher.
Kempson, R. M. 1977. Semantic Theory.
Great Britain: Cambridge
University Press.
Leech, Geoffrey. 1981. Semantics: The
Study of Meaning. London: Penguin Books.
Lyons, J. 1981. Language and Linguistic An Introduction. Great Britain: Cambridge University Press.
Palmer, F. R. 1976. Semantics: A New Outline. London: Cambridge
University Press.
Pateda, M. (2001). Semantik Leksikal. Jakarta: PT Rineka Cipta.
Ullmann, Stephen. 1972. Semantics: An Introduction to the Science of
Meaning. Oxford: Basil
Blachwell.
Ullmann, Stephen. 1977. Semantics: An Introduction to the Science of Meaning.
Oxford: Basil Blachwell.
Yule, George. 1985. The Study of Language. Cambridge University Press.
Yule, George. 1996. The Study of
Language (Second Edition). Great Britain: Cambridge University
Press.
24
Discussion and feedback