Derivational Noun in The Economist Magazine “The Trump Presidency So Far”
on
DOI: 10.24843/JH.2018.v22.i02.p24 ISSN: 2302-920X
Jurnal Humanis, Fakultas Ilmu Budaya Unud
Vol 22.2 Mei 2018: 447-452
Derivational Noun in The Economist Magazine “The Trump Presidency So Far”
*
I Putu Adi Manggala1
English Department, Faculty of Arts, Udayana University [adimanggala96@gmail.com]
Abstract
The title of this study is Derivational Noun in The Economist Magazine “The Trump Presidency So Far”. This study was conducted in order to explain the base form and the meaning of derived noun, and also to explain the tree diagram structure of derived noun in the magazine. The data in this study were taken from the articles in The Economist Magazine “The Trump Presidency So Far”.The data were collected by using documentation method and analyzed using qualitative method. The main theories used in analyzing the data are theory of derivational morpheme proposed by Katamba (1993:47), theory of fabricating word proposed by Katamba (1994:56) and the theory of nominalizing of derivational proposed by Randolf Quirk (1973:432). The analysis shows that there are two kinds of derivational process of noun, namely class maintaining and class changing derivation.The derived nouns can be formed by attaching prefix and suffix to base word noun, verb and adjective. The affixes of derived noun also have their own meanings and the tree diagram is used in order to show the constituent structure of the derived noun.
Keywords: derivation, affixes, lexemes, noun
Abstrak
Judul penelitian ini adalah Kata Benda Turunan di Majalah The Economist “The Trump Presidency So Far”. Penelitian ini bertujuan untuk menjelaskan bentuk dasar dan makna dari kata benda turunan dan juga untuk menjelaskan struktur diagram pohon dari kata benda turunan di majalah tersebut. Data dalam penelitian ini diambil dari sejumlah artikel di Majalah The Economist “The Trump Presidency So Far”. Data tersebut dikumpulkan menggunakan metode observasi dan dianalisis menggunakan metode kualitatif. Teori utama yang digunakan dalam menganalisis data adalah teori morfem turunan oleh Katamba (1993:47), teori pembentukan kata oleh Katamba (1994:56) dan teori nominalisasi turunan oleh Randolf Quirk (1973:432). Analsis menunjukkan bahwa terdapat dua jenis proses turunan dari kata benda, yaitu penurunan yang mempertahankan kelas kata dan penurunan yang merubah kelas kata. Kata benda dapat dibentuk dengan menambahkan awalan dan akhiran pada kata benda, kata kerjadan kata sifat dasar. Imbuhan juga memiliki makna tersendiri dan diagram pohon digunakan untuk menunjukkan struktur pokok dari kata benda turunan.
Kata Kunci: penurunan, imbuhan, lexem, kata benda
Word is the simplest unit of a language (Katamba 1993:17). How a language is developed is also influenced by the development of the word. Languages organize their parts of speech into classes according to their functions.
Each of them makes a basic distinction between a group of words that denote things called nouns and group of words that donate actions called verbs. Other common categories are adjectives, words that describe properties or qualities of nouns, for example, smooth or handsome.
An adverb is a word that adds information to a verb, adjective, or phrase. Some words are alive. They can grow, change and move from one class into another. The study about word formation is called morphology.
According to Bauer (1983:3), morphology is a sub-branch of linguistics dealing with the internal structure of word-forms.It is concerned with the categories and rules in word formation of a language. In other words, morphology is the branch of linguistics that studies patterns of word formation and across languages, and attempts to formulate rules that the knowledge of the speakers of those languages. Word formation is the creation of a new word, sometimes it changes the meaning of the word. Furthermore, the core unit morphology is called morpheme.
Morpheme is the smallest grammatical unit in a language. A lot of words are constructed by morphemes and they cause classes of the words to change. For instance, the word ability is made up fromthe adjective base able and added by a suffix /-ity/, the word class of able after it is added by the suffix /-ity/ changes into a noun. This process is called derivation through affixation. Affixation is the process of adding a morpheme to a word to create either a different form of that word or a new word. In English, there are two categories of affixation; they are derivational and inflectional affixes. Particularly in derivational affixes it alters the meaning or grammatical category of the base.
In order to understand English well, it is necessary to know the process of English word formation referred to as Morphology; the study which is concerned with the structure between words (Carstairs 2002:16)
This study focuses on the analysis of derivational noun in particular, the derived nouns to find out
which word classes can be changed into nouns. From those categories of words, a noun is chosen since it is the largest number in English word classes which have more than three hundred thousand members. The unconsciousness to the alteration in English words that change the word class of the word itself since the additional process of morpheme makes it interesting to analyze this topic. Moreover, there are still a small amount of studies which specifically discuss the derivational affixation of noun. The data were obtained from The Economist Magazine entitled “The Trump
Presidency so far”; edition April 1st – 7th 2017;this magazine has a lot of derivational nouns that can be analyzed in this study.
In order to understand the derivational affixation, mainly in derived nouns formation, the problems that appear in this study are as follows.
-
1) What forms and meanings of the derived nouns are found in The Economist Magazine?
-
2) How are the word structureof derived nouns found in The Economist Magazine?
In order to answer the previous problems, the aims of this study are:
-
1) To explainthe forms and meanings of derived nouns inThe Economist Magazine.
-
2) To analyze the word structures of derived nouns found in The Economist Magazine.
The research method consisting of three parts. including: data source, method, and technique of collecting data, and method and technique of analyzing data.
The Data source is the first element of research method. It deals with the source from which the data are taken. The data of this study were primary data. Primary data are the data that are previously unknown and which have been obtained directly by the researcher. The data were taken from The Economist Magazine entitled “The Trump Presidency so far” that edition April 1st – 7th 2017, which consist of 78 pages. It is a weekly English version
magazine newspaperformat owned by the Economist Group and edited at offices in London. It is interesting to analyze this magazine because The Economist Magazine is famous trusted magazine in the world and it is also bestselling consumer in England. The magazine was downloaded from http://magazinelib.com/all/the-economist-europe-april-17-2017/.
The data were collected from the articles in The Economist Magazine “The Trump Presidency So Far” through the Documentation method. Documentation method means analyzing the content of documentary materials. Some steps were applied.
The first step was downloading the magazine from
http://magazinelib.com/all/the-economist-europe-april-17-2017/. Second, the magazine was red carefully, here, the magazine was read starting from the first page up to the last page. During this step, derived nouns found from the magazine were underlined and written down. Then, the data were selected in order to avoid the occurrence of the same data. And last, the important point related to the data, such as the sentences in which the data occur and their pages were written down.
The collected data were analyzed by using Descriptivequalitative method.
The method was applied with some supporting techniques. First of all, the base from of the derived noun was identified. In this stage, each base form was classified based on their word class onto a table. Second, the data were explained based on the form of derived noun based on the theory of derivational morpheme proposed by Katamba (1993:47), Third the meaning of nominalizing was explained based onthe theory of nominalizing of derivational proposed by Randolf Quirk (1973:432) and oxford dictionary. Fourth step was analyzing the word structure of derived nouns by using tree diagram analysis based on the theory of fabricating word proposed by Katamba (1994:56). Through this technique, the structure of the derived noun can be more clearlyrepresented. Finally, this research would be descriptively described according to the theory that was concerned.
This study applied the formal and informal methods to present the analysis. Formal method is the method in which the findings are presented by using symbols, diagrams, figures, and tables, while informal method refers to the method of presenting the analyzed data using words (Sudaryanto 2015:241). It means that informal method can be described by using words. In presenting the data, several steps were taken. First, the data were classified based on their word classes onto a table. The following step was explaining the meaning of the nominalization. And last analyzing the word structure using tree diagram.
Derivational nouns may be subdivided into two types. They are class maintaining and class changing derivation. The explanation isfollowed by the analysis of meaningnominalizing. The derived nouns were also represented using the tree diagram structure. The analysis of derivational nouns is explained as follows:
-
(5-1) …..Malnutrition has fallen sharply. (The Economist,2017:38)
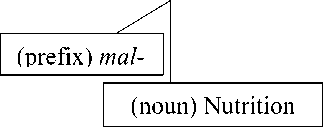
Based on the data above, the word in boldmalnutrition isformed through derivational process. It is new lexeme, which is derived from the noun base nutrition with the prefix {mal-}. The attachment to this prefix does not change the grammatical classof base.
Prefix {mal-} has function to form noun into noun, and means bad. The meaning of the derived noun malnutrition is lack of proper nutrition, caused by not having enough to eat.The process of derivational affixes is shown in the table and the derived noun can be seen from the tree diagram below:
The Formation of New Lexemes by the Prefix {mal-}
|
Base |
New Lexeme |
Class Mainta ing |
Meaning of nominali zing affixes |
|
nutriti |
malnutrit |
Noun |
bad |
|
into | |||
|
on |
ion |
noun |
The Structure of New Lexemes by Tree Diagram:
malnutrition (noun)
(5-2) As one historian put it: the Middle Kingdom has lost its middle. In a society without universal rules,… (The
Economist,2017:72)
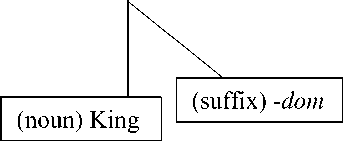
Based on the data above, the word in bold as Kingdom is formed through derivational process. It is the new lexeme, which is derived from the noun baseking that is attached by suffix {-dom}. The attachment to this suffix does not change the word class from the base.
The suffix {-dom} means domain or condition.Based on the data above, the meaning of the nominalizing affixes of the derived noun kingdom is domain that isruled by a king or queen. The derivational process and the constituent structure of those derived nouns are shown in the table and in the diagram below:
The Formation of New Lexeme by Suffix {-dom}
|
Bas e |
New Lexem e |
Class Maintai ng |
Meaning of nominaliz ing affixes |
|
kin |
Kingdo |
Noun | |
|
into |
domain | ||
|
g |
m |
noun |
The Structure of New Lexeme by Tree Diagram
Kingdom (noun)
(5-3) ….to recuse himself from his department’s investigation into allegations that Mr Trump’s team colluded (The
Economist,2017:20)
(5-4) Zegna, run by its fourth generation of family owners,… (The Economist,2017:51)
(5-5) Chart 1, below. In 1981 some 42% of the world’s population were extremely poor, (The Economist,2017:48)
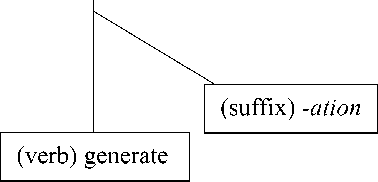
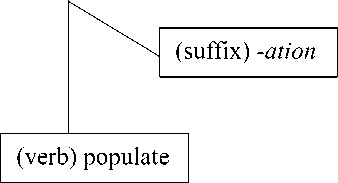
Based on the previous data, the words investigation, generation and populationare formed through derivational process. They are new lexemes, which are derived from verb base invest, generate and populate to which suffix {-ation} is added. The attachment to this suffix changes the grammatical class of the word from verbs into nouns.The attachment to suffix in derived noun investigation is through morphophonemic process.
The suffix {-ation} means state, action or institution. Based on the data, the meaning of nominalizing affixes of the
derived noun investigation means action of investigating something or someone, generation and population means state of beinggenerateand populate. The derivational process and the constituent structure of those derived nouns are shown in the table and in the tree diagram below:
The Formation of New Lexemes by the Suffix {-ation}
|
Base |
New Lexeme |
Class chang ing |
Meaning of nominali zing affixes |
|
investig ation |
verb | ||
|
invest |
into |
action | |
|
noun | |||
|
generati |
verb | ||
|
gener |
into |
state | |
|
ate |
on |
noun | |
|
popul |
populati |
verb into |
state |
|
ate |
on |
noun |
The Structure of New Lexeme by Tree Diagram
Investigation (noun)
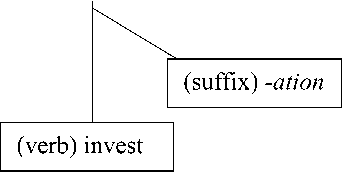
Generation (noun)
Population(noun)
Based on the previous analysis about the derivational process of noun, it can be concluded that the derived nouns can be formed by attaching prefix and suffix to noun base word (class maintaining with noun base), verb (deverbal noun) and adjective (deadjectival noun). But on the previous analysis, class changing prefix does not exist in the magazine.
The kinds of noun prefixes and suffixes are found in The Economist Magazine “The Trump Presidency so far”. The prefix {mal-} is used to form noun which is derived from the noun base. Suffixes {-dom}, {-ship}, {-ocrary}, {-ism}, {-y}, are used to formnouns which are derived from the noun base. Suffixes {-ation},{-al},{-er},{-ment},{-ants},{-on}, {-y}, {-age} are used to form nouns which are derived from the verb base. And the last are suffixes {-ness}, {-cy}, {-th}which are used to form noun which is derived from adjective base. Those affixes also have their own meaning.
The derivational process is creating new words by modifying the meaning of the base without changing the grammatical category of the base (class maintaining) or by modifying the meaning and the grammatical categories (class changing). The derived noun can also be represented by using tree diagram in order to distinguish which suffix is categorized as derivational affix.
Bauer, Laurie. (1983). English WordFormation. Cambridge: Pitman Press, Bath
Carstairs, McCharty Andrew. 2002. An introduction to English
Morphology: Edinburgh
University press
Creswell, Jhon W. (1994).Research
Design Instructor's Resource:
Qualitative, Quantitative, and Mixed Methods Approaches:
London, Sage Publication
Katamba, Francais. (1993). Morphology. Macmillan: Palgrave Macmillan
Matthews, P.H. (1969). Morphology. Cambridge: Cambridge
University Press
Quirk, R,Greenbaum, S. (1973). University Grammar of English. Sydney: Longman
Sudaryanto. (2015). Metodedan Aneka Tehnik Analisa Bahasa
(Pengantar Penelitian Wahana Kebudayaan secara Linguistik). Yogyakarta : Duta Wacana
Univesity Pers
The Economist Magazine, “The Trump Presidency So Far” April 1st – 7th 2017 Edition. downloaded from: http://magazinelib.com/all/the-economist-europe-april-17-2017/ (accessed 3 April 2017)
452
Discussion and feedback