Geographic Information System of Public Complaint Testing Based On Mobile Web (Public Complaint)
on
LONTAR KOMPUTER VOL. 9, NO. 2, AUGUST 2018
DOI : 10.24843/LKJITI.2018.v09.i02.p04
Accredited B by RISTEKDIKTI Decree No. 51/E/KPT/2017
p-ISSN 2088-1541
e-ISSN 2541-5832
Geographic Information System of Public Complaint Testing Based On Mobile Web (Public Complaint)
Made Yudha Putra Mahendraa1, I Nyoman Piarsaa2, Dwi Putra Githaa3
Information Technology, Universitas Udayana Bali, Indonesia 1yudhaputra77@gmail.com 2manpits@unud.ac.id 3dwiputragitha@gmail.com
Abstract
A public complaint is a reciprocal of the population against the government to convey opinions or problems encountered in certain areas. The complaint process using a suggestion box or counter complaint is less effective and efficient so that the complaint handling process is slow. The geographic information system of public complaints is an information system built as an intermediary for the public to make complaints against the government. This public complaint geographic information system is built by utilizing location-based services. Geographic information systems of public complaints that have been built require a test to ensure all functions contained on the system can run properly. This study discusses the testing of the geographic information system of public complaints that have been built by blackbox testing and test by involving respondents from the general public. The results of testing system usage by the user based on aspect of system interface display and conformity aspects of processes and features involving respondents from the general public. Tests conducted to get the average results of respondents gave very good value 28%, good 59.8, enough 10.2% and less by 2%. Comparison of systems conducted on two similar systems taken through a literature study showed that a mobile web-based public complaint geographic information system (Public Complaint) has more features in tracking the location of complaints.
Keywords: Geographic Information System, Location Based Service, Public Complaint, Testing.
Information and communication technology has long been used in the government environment, which now raises the term e-Government which shows the development toward improving public services by agencies that apply it. In general e-Government is an internet-based information management and service system. This service is provided by the government to the public in various fields. A public complaint is a reciprocal of the population to the government, and is a problem experienced by all cities in the world, both big cities and small towns. The public complaints geographic information system is a system built to accommodate information about problems in the field in terms of damaged public facilities, cleanliness and environmental issues sent by the public to the government containing location information, and real conditions on the ground as evidenced by the complaint photo. The public complaint information system that has been built needs to be tested to find out how far this system can work in accordance with what is needed by the society today. This public complaint information system test is also useful as a basis for developing a better public complaint information system. Here are the previous studies used as literature studies. Research Swapnil R. Rajput, Mohd Sohel Deshmukh, Karbhari V. Kale, PhD entitled "Cross-platform Smartphone Emergency Reporting Application in Urban Areas using GIS Location-based and Google Web Services" discusses emergency complaint applications utilizing Location Based Service (LBS ), where the user can use the application when in an emergency by sending a report in the form of photos, description of the report and equipped with the location of the complaint which is then sent to the rescue team to ask for help [1]. Research by Mohd Sohel Deshmukh and Swapnil R.Rajput, entitled
"Smartphone Based Citizen Complaint System for Urban Maintenance Using GIS" discusses the geographic information system of citizen complaints using android based smartphones for urban maintenance. This study provides a broad overview of the use of location-based services that exist in systems aimed at citizens to make complaints equipped with photos and coordinates the location of complaints of problems that occur in the vicinity of citizens [2]. The study, titled "GEO ALERT- A Location Based Alarm System Using GPS in Android" by Deepika Garg and Dr. Anupam Shukla discusses the use of location-based services to assist travelers in locating and storing the locations of tourist attractions visited. This research helps tourists to know the location of the object through the android smartphone, the application will provide a warning of the location if tourists are in a particular tourist attraction [3]. Research by Akshay Belan, Rohit Mudliar, Shantanu Muley, Chaitanya Darade and Mrs. R. A. Kudale entitled "Location Based Emergency Services" discusses the use of location-based services in an emergency. This study utilizes location-based services using an android smartphone if the user is in an emergency to deliver locations to ambulances, firefighters and police [4]. The above research shows that the role of location-based services in a system becomes very important to know the location of problems experienced by the user so that handling problems can be handled with reference to the location of problems sent by the user.
The framework of DSRM (Design Science Research Methodology) is a research method that has a workflow that is literature study, problem identification, determination of research objectives, design and manufacture of applications, testing, final analysis, and reporting research as shown in Figure 1.
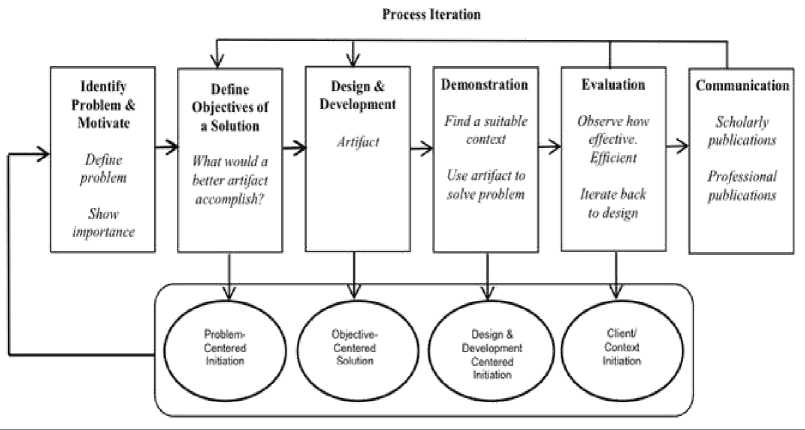
Figure 1. DSRM Methodology Workflow
Software testing is a test done to ensure software that is or is being made to run in accordance with the expected functionality. Software developers or testers should prepare a special session to test programs that have been created so that errors or deficiencies can be detected early and corrected as soon as possible. Testing or self-testing is a critical element of software quality assurance and is an integral part of the software development lifecycle as well as analysis, design, and coding [5].
Black box testing is one of the software testing techniques that focus on the function of a software to ensure all functional on the software has been running well. Black box testing is
done by testing the input and output on the software without looking at the program code in the software [6].
Geographic information system is a special information system that manages data that has spatial data information (spatial dimension). Geographic information system is one form of information systems used to present information in graphical form by using the map as an interface or interface. The main function of geographic information systems is to assist in improving the ability to analyze spatial data for planning and decision making. Geographic information systems provide information to decision makers to analyze and apply information equipped with spatial data[7].
Prototype is one of the software development methods that focuses on the approach of design aspect, function and user-interface. Developers focus on the user interface and together define the specifications, functions, design and how the software works. Developers and users meet and communicate and define common goals, known needs and descriptions of parts required. Developers gather details of needs and provide an overview with a blueprint (prototype). From the process will be known details that must be developed or added to the blueprint, or remove the details that are not required by the user [8].
Location Based Service is location-based information service that can be accessed through a mobile device by using the mobile network, equipped with the ability to take advantage of the location of the mobile device. LBS requires 2-way communication between the user and the service provider. The user gives a request to the service provider to provide the required information, with reference to the position of the user. Location Based Service (LBS) is a platform that facilitates information services based on geolocation, supported by a map platform or electronic framework. Geolocation information (long and longitude coordinates) of Smartphone users can be obtained through the mobile communication network or Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS). LBS can be described as a service that is at the meeting of 3 (three) technologies that are GIS, internet service and mobile device [9].
Global Positioning System is a satellite-based navigation system consisting of satellite networks placed into earth orbit. Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) is a geo-positioning system, using a special receiver, geo-position in space and time can be calculated based on satellite signal reception. Mobile devices now have a GPS receiver that can decode GPS signals. Assisted-GPS is a new technology for smartphones that boosts startup or time-to-firstfix (TTFF) performance from satellite-based GPS system positions, with this technology enabling smartphones to make mobile phone locations, much faster and with better accuracy. GPS is a global coordinate system that can determine the position of object coordinates anywhere on earth also it is longitude, latitude or altitude. GPS can be used as an efficient alternative to get spatial data automatically and in real time [10].
Results and discussion were done by performing comparisons and test systems such as, making account, login, manufacture and delivery of complaints by users through android applications. The next trial is done on the admin side as a manager of complaints data on the web where there is a data map of the spread of complaints.
System testing is performed to ensure the system is running properly, system testing is performed from the system display aspect and testing the conformity of the process and system features by using questionnaires distributed to respondents from the general public.
The system built on the android mobile platform has the appearance shown in Figure 1 below.


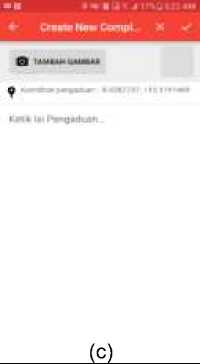
Figure 2. Main Menu Application
Figure 2 is the main menu view of the system on the android mobile platform after the user successfully login. The main menu view of the system consists of an entire data view of complaints equipped with a filter and searching features, but there are also buttons to make new complaints.
The results of web design trials on GIS public complaints include dashboard display. The admin dashboard has a main menu that is the master data menu of the complaint, the master data category, the master data admin, and the data master instance.

Figure 3. Main View Admin Dashboard
Figure 3 is an admin dashboard view after successfully login. The main display on the admin dashboard comprises a menu and spread map of all complaints marked with a blue cluster marker. Admin can view details of complaint by selecting blue cluster marker, then cluster marker will be broken down into new points of complaint location with detail information of complaint done by the user. Admin may respond to complaint data by changing the status of the complaint if the complaint is being handled or has been handled.
System testing is done to know that all the features on the system have been able to run properly. Feature test results are the results obtained to ensure all features and functionality of the system works well. The following is a test result of the system features can be seen in Table 1.
Table 1. Black Box Testing Result
|
No. |
Feature |
Scenario |
Result |
|
1 |
Register |
Biodata input, valid email, username is available. |
Registration Success |
|
2 |
Login |
Username and password are correct, account already in verification. |
Login success. |
|
3 |
Add Complaint |
Input complaint title, destination agency, complaint category, complaint photo, complete complaint description. |
Add complaints success. |
|
4 |
Add Comment |
Select a complaint, select the comment button, comment input, submit a comment. |
Add comment success. |
|
5 |
Close Complaint |
Select a complaint, select the complaint close button. |
close complaint success. |
|
6 |
Search |
Select the search button, input keyword. |
Search complaints are successful if the keywords match the complaint data. Search failed if the keyword does not match the complaint data. |
|
7 |
Filter Complaint |
Select the status of the complaint on the complaint status combo box. Select a complaint category in the complaint category combo box. |
Complaint filter is successful, complaints are displayed based on the status and categories that have been selected. |
|
8 |
Add Agency |
Select the agency menu, select the add complaint button in the list of agencies. Enter the name of the agency in the textbox. |
Add agency success. |
|
9 |
Add Admin |
Select the admin menu, select the admin plus button on the admin list. Select agency and position then input admin data in the form of the name, address, identity, email, username and password. |
Add admin success. |
|
10 |
Add Category |
Select the complaint category menu, select the add category complaint button and enter the category name of the complaint. |
Add category success. |
|
11 |
Tracking Complaint |
Select the red complaint location |
The route to the |
|
Location |
marker on the complaint spread map and select the text directions. |
location of the complaint is displayed on the google maps map. Tracking the location of the complaint was successful. | |
|
12 |
Verification Complaints |
Select the complaint data, select the complaint view menu and update the complaint status in the combo box. |
Complaint verification success. |
The test results that have been done on geographic information system of public complaints by using black box testing indicate that all functions contained in the system can run well.
Comparison of the system is a process done to compare the geographic information system based on mobile web society (Public Complaint) with some information systems that have the same role that is to process and collect information on complaints. The system used for comparison is taken from several literature studies Swapnil R. Rajput, Mohd Sohel Deshmukh, and Karbhari V. Kale, PhD, entitled Cross-platform Smartphone Emergency Reporting Application in Urban Areas using GIS Location and Google Web Services "[1] and research by Osman Nasr, Enayat Alkhider entitled “Smartphone Based Citizen Complaint System for Urban Maintenance Using GIS” [2]. Here is a comparison table of the three systems contained in the table below.
Table 2. System Comparison Table
|
No. |
System Name |
Features |
Platform | ||
|
1 |
Geographic Information System of Public Complaint Based On Mobile WEB (Public Complaint) |
a. b. c. d. e. |
Complaints are provided with location coordinates of longitude and latitude taken from GPS on a smartphone, then converted to address. Photo of the complaint Complaints are made in real-time. Cluster Marker mapping complaints on web admins. Tracking the location of the complaint using Google Maps API. |
Android Web |
and |
|
2 |
Cross-platform Smartphone Emergency Reporting Application in Urban Areas using GIS Location-based and Google Web Services [1]. |
a. b. c. d. e. |
Complaints are made only for emergency conditions with location features such as longitude and latitude taken through GPS on a smartphone. Complaints can be made via SMS which is equipped with the location link of the complaint. Complaint mapping using markers on the Google Maps map. Photo of the complaint Calculation of the distance of the complaint location from the admin location on the web. |
Android Web |
and |
|
3 |
Smartphone-Based Citizen Complaint System for Urban Maintenance Using GIS [2]. |
a. b. |
Complaints are provided with the coordinates of the location of the complaint which is then converted to an address. Photo of the complaint |
Android Web |
and |
Table 2 is a comparison table of the public complaints geographic information system compared with 2 systems from the literature study. The comparison of the system shows the three systems have a similarity that is using the same use of location-based services, the geographic information system of public complaints has advantages compared with 2 other system features that are with the feature of tracking the location of complaints and cluster marker complaint using google maps API.
Calculation and Presentation of Data is the calculation done to the survey through the spread of test questionnaires conducted by users by involving respondents from the general public.
Test variables are aspects of the application that can be qualitatively calculated by the user. The test variables are divided into two: the system interface testing variables and the suitability testing of variables and system features.
The results of testing the interface aspect of the system are done by calculating the questionnaire based on the variables and values obtained. The following is a result of testing the system interface.
Tabel 3. Interface Test Result
|
No |
Variable |
Value | ||||
|
Very Good |
Good |
Enough |
Less |
Very Less | ||
|
1 |
Interface design |
9 30% |
19 63.3% |
2 6.7% |
0 |
0 |
|
2 |
The colors used are comfortable to look at |
7 23.3% |
21 70% |
2 6.7% |
0 |
0 |
|
3 |
Fonts and letters read clearly |
4 13.3% |
22 73.4% |
4 13.3% |
0 |
0 |
|
4 |
Menu buttons and icons are easy to understand |
12 40% |
14 46.7% |
4 13.3% |
0 |
0 |
|
Total Results |
26.7% |
63.3% |
10% |
0 |
0 | |
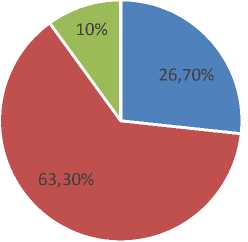
Table 3 is the result of the system test based on the aspect of the application interface display assessed by 30 respondents. The overall results of the test results obtained 26.7% of the total respondents gave a very good answer, 63.3% gave good answers and 10% of the total respondents gave enough answers. The following is the test result shown in the diagram form in Figure 4.
Interface Testing Results
-
■ Very Good ■ Good ■ Enough ■ Less ■ Very Less
Figure 4. Interface Testing Result Diagram
The results of testing the conformity aspects of the process and features done by performing calculations on the questionnaire based on the variables and values obtained. The following is a result of the testing of the conformity aspects of the process and system features.
|
Table 6. Process and Feature Testing Results | ||||||
|
No |
Variable |
Value | ||||
|
Very Good |
Good |
Enough |
Less |
Very Less | ||
|
1 |
The application runs well on Android smartphones |
12 40% |
16 53.3% |
2 6.7% |
0 |
0 |
|
2 |
Conformity of key functions |
6 20% |
21 70% |
3 10% |
0 |
0 |
|
3 |
Application is easy to operate |
15 50% |
15 50% |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
4 |
Can search for data and complaint information to be known |
11 36.7% |
15 50% |
4 13.3% |
0 |
0 |
|
5 |
Data and complaint information is displayed quickly |
11 36.7% |
11 36.7% |
3 10% |
5 16.6% |
0 |
|
6 |
The location of the complaint corresponds to the complaint photo |
12 40% |
15 50% |
3 10% |
0 |
0 |
|
7 |
Fast delivery time |
5 16.7% |
21 70% |
4 13.3% |
0 |
0 |
|
8 |
Ease of complaint |
3 10% |
21 70% |
6 20% |
0 |
0 |
|
Total Result |
31.25 % |
56.25 % |
10.5 % |
2 % |
0 | |
Table 6 is the result of application testing based on the conformity aspects of the process and application features assessed by 30 respondents. The overall results of the test resulted in 31.25% of the total respondents gave a very good answer, 56.25% gave a good answer, 10.5% gave enough answer and 2% gave less answer. The following is a test of the suitability of the process and system features shown in the diagram in Figure 4.
Process and Features Testing Results

-
■ Very Good ■ Good ■ Enough ■ Less ■ Very Less
Figure 4. Process and Features Testing Results Diagram
Public complaint information system test using location-based services conducted in this study resulted in a conclusion after direct test by user application from aspect display system interface and conformity of system features. Tests conducted to get the average results of respondents gave very good value 28%, good 59.8, enough 10.2% and less by 2%. The results of testing the system using black box testing indicate that the entire process and features on the system havebeen running well. Comparison of the system that has been done shows that on every complaint system all equipped with features of location-based services to facilitate the authorities to handle quickly and precisely. Comparison of the three complaint systems shows that the geographic information system of public complaints based on mobile web has more features in tracking the location of complaints.
Reference
-
[1] S. R. Rajput, M. S. Deshmukh, and P. Karbhari V. Kale, "Cross-platform Smartphone Emergency Reporting Application in Urban Areas using GIS Location based and Google Web Services," International Journal of Computer Applications, vol. 130, no. 12, pp. 27-33, 2015.
-
[2] M. S. Deshmukh and S. R. Rajput, "Smartphone Based Citizen Complaint System for Urban Maintenance Using GIS," International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, vol. 7, no. 5, pp. 1591-1599, 2016.
-
[3] D. Garg and D. A. Shukla, "GEO ALERT- A Location Based Alarm System Using GPS in Android," International Journal of Multidisciplinary in Cryptology and Information Security, vol. 2, no. 3, pp. 11-14, 2013.
-
[4] A. Belan, R. Mudliar, S. Muley, C. Darade, and M. R. A. Kudale, "Location Based Emergency Services," International Journal of Engineering Research and Technology (IJERT), vol. 3, no. 2, pp. 2517-2520, 2014.
-
[5] M. S. Mustaqbal, R. F. Firdaus, and H. Rahmadi, "Pengujian Aplikasi Menggunakan Black Box Testing Boundary Value Analysis (Studi Kasus: Aplikasi Prediksi Kelulusan Snmptn)," Jurnal Ilmiah Teknologi Informasi Terapan (JITTER), vol. 1 no.3, pp. 31-36, 2015.
-
[6] M. Kumar, S. K. Singh, and D. R. K. Dwivedi, "A Comparative Study of Black Box Testing and White Box Testing Techniques," International Journal of Advance Research in Computer Science and Management Studies, vol. 3, no. 10, pp. 32-44, 2015.
-
[7] S. Rahayu, I. N. Piarsa, and P. W. Buana, "Sistem Informasi Geografis Pemetaan Daerah
Aliran Sungai Berbasis Web," LONTAR KOMPUTER, vol. 7, no. 2, pp. 71-82, 2016.
-
[8] P. S. Saputra, I. M. Sukarsa, and I. P. A. Bayupati, "Sistem Informasi Monitoring
Perkembangan Anak di Sekolah Taman Kanak-kanak Berbasis Cloud " LONTAR KOMPUTER, vol. 8, no. 2, pp. 112-123, 2017.
-
[9] P. Doshi, P. Jain, and A. Shakwala, "Location Based Services and Integration of Google Maps in Android," International Journal of Engineering and Computer Science, vol. 3, no. 3, pp. 5072-5077, 2014.
-
[10] A. Damani, H. Shah, and K. Shah, "Global Positioning System for Object Tracking," International Journal of Computer Applications, vol. 109, no. 8, pp. 40-45, 2015.
103
Discussion and feedback