THE EFFECTIVENESS TEST OF INFUSION CELERY ROOT (Apium graveolens L.) AS A DIURETIC IN WISTAR MALE WHITE RATS (Rattus Norvegicus)
on

Journal of Pharmaceutical Science and Application Volume 4, Issue 1, Page 19-25, June 2022 E-ISSN: 2301-7708
THE EFFECTIVENESS TEST OF INFUSION CELERY ROOT (Apium graveolens L.) AS A DIURETIC IN WISTAR MALE WHITE RATS (Rattus Norvegicus): A LITERATURE STUDY
Ida Ayu Dhea Rahnia1*, Made Krisna Adi Jaya 1
1Department of Pharmacy, Faculty of Math and Science, Udayana University, Bali, Indonesia
Corresponding author email: idaayudhearahnia12@gmail.com
ABSTRACT
Background: Hypertension is defined by persistently elevated arterial blood pressure. The increase in systolic blood pressure is generally>140mmHg or diastolic blood pressure> 90mmHg. The prevalence of hypertension increases with lifestyle changes. Objective: To determine the diuretic effect of celery (Apium graveolens L.) on male wistar rats (Rattus norvegicus). Methods: This research uses a literature study method, the type of the research is descriptive qualitative with literature research (library research) systematic. Results: Based on research data, there were 5 groups of mice that received different treatments. Among the five treatment groups, 0.5 % CMC suspension (KP-) showed the least mean cumulative urine volume, and furosemide suspension (KP+) showed a large mean cumulative urine volume when compared to negative controls. Conclusion: Celery root infusion can increase urine volume, because it contains flavonoids that play a role in increasing urine volume (diuresis).
Keywords: Diuretic, Celery (Apium graveolens
INTRODUCTION
A persistent increase in arterial blood pressure is known as hypertension. Systolic blood pressure is generally >140 mmHg and diastolic blood pressure >90 mmHg. Smoking, food, obesity,
hypercholesterolemia, physical inactivity, and psychological stress all contribute to the development of hypertension [6]. Diuretics have something to do with this hypertension. Diuretics are drugs that stimulate urine output (diuresis) by acting directly on the kidneys [1]. The primary goal is to mobilize edema fluid, which entails resetting the fluid balance so that the extracellular fluid volume returns to normal (Katzung, 2007). Congestive heart failure, chronic nephritis, cirrhosis, kidney failure, hypertension, edema, diabetes insipidus, kidney stones, and hypercalcemia can all be treated with diuretics [1]. As a laxative, antispasmodic, and diuretic, it has been
L.), Furosemide, Hypertension, Wistar rats empirically used to overcome hypertension, launch breast milk, and as a laxative, antispasmodic, and diuretic [2].
One of the medicinal plants that is often people used as a laxative urine or diuretic is celery. Celery with the Latin name Apium graveolens L. is one of the natural ingredients that has people been used for a long time as food ingredients and empirically used as traditional medicine [1]. Celery contains among others flavonoids, saponins, 1% tannins, oil volatile 0.033%, flavo-glucoside (apiin), apigenin,
phytosterols, choline, lipase, pthalides, asparagine, bitter substances, vitamins (A, B and C), apiin, volatile oil, apigenin and alkaloids. Two compounds which is mannitol and apiin, are diuretics that help the kidneys remove excess fluid and salt from the body [1]. Apiin which functions as a diuretic substance is useful in increasing urine output. Apiin when given orally will
be hydrolyzed into apigenin and glucose in the gastrointestinal tract. Apigenin and apiol are known as compounds that function in diuretics[2].
METHODS
This research uses a literature study method type of the research is descriptive qualitative with literature research (library research) systematic. This literature uses primary data sources and secondary which is the result of research that has been published in national and international journals. Selection of journals used as a library is done in the database 1). Google Scholar, 2). pubmed which are journals that have been selected based on the criteria certain. Then the articles obtained are collected collectively in a storage device which is then distributed to members groups so that they can be accessed later. This research aims to knowing the effectiveness test of celery root infusion (Apium graveolens L.) as a diuretic in male white rat Wistar strain (Rattus norvegicus).
RESULTS
Indonesia is a country that has the biodiversity largest in the world with more than 30 thousand species of plants that are efficacious treatment Based on empirical experience in the community, there are several medicinal plants that have diuretic activity. One of the medicinal plants that use as laxative urine or diuretic is celery [1].
-
1. Utilization of Celery (Apium graveolens L.)
Plants have long been investigated for their impact on human health. Herbal medication is becoming more popular as a result of its low side effects and gradual mode of action. Celery is a plant that is frequently used in herbal medicine, either as a vegetable or as an extract from the plant Apium graveolens L. Apart from having few adverse effects, herbal medications are expected to have a substantial effect on research breakthroughs due to their high availability in nature, therefore they have the potential to be developed as a safer and
Volume 4, Issue 1, Page 19-25, June 2022 more inexpensive alternative to synthetic drugs [7].
Celery leaves are claimed to contain Apigenin, which prevents blood vessel constriction, and Phthalides, which relaxes the muscles of the arteries and blood vessels. The chemical in the body that controls blood flow. This permits blood arteries to dilate, lowering blood pressure. Flavonoids, saponins, 1% tannins, 0.033 percent essential oils, flavo-glucoside (apiin), apigenin, phytosterols, choline, lipase, pthalides, asparagine, bitter compounds, vitamins (A, B, and C), apiin, volatile oil, apigenin, and alkaloids can all be found in celery. Apigenin is a hypotensive agent [6].
Apiin is a flavonoid glycoside molecule that has been shown to have two sugar groups connected to its seven carbon chain, glucose and pyranose. Celery (Apium graveolens L.) has an identification chemical called apiin. Apiin compounds will be hydrolyzed in the body into sugars and aglycones apigenin with the help of gastric acid. Apigenin is the major flavonoid component in celery plants, and it belongs to the flavone family. Apigenin has vasodilator properties or widens blood vessels, a mechanism of action by inhibiting contractions caused by calcium release. Calcium antagonists work in a similar way, lowering blood pressure by preventing calcium from entering the bloodstream.
The muscle cell c contracts when calcium enters it. Blood vessels widen when the circular muscles in the blood vessels are inhibited from contracting, allowing blood to circulate freely and lowering blood pressure. Celery potassium will be helpful in increasing intracellular fluid by attracting extracellular fluid, resulting in alterations in the sodiumpotassium pump balance, resulting in a drop in blood pressure. One strategy in the management of hypertension is to change the Na+ to balance.
The change in Na+ balance is carried out by the administration of diuretics orally [5].
The study conducted by Jayadi et al (2015), weighed samples are placed in the infusion pan and aquades are added according to volume. The sample was heated to 90°C for 15 minutes, then filtered and scattered before being retrieved from the celery root infusion. And then the age group of rats consisted of five rats each taken at random. Wistar rats male and female in different age groups have different hematologic profiles and body masses. Treatment on test animals was given orally according to the dose. Amount 15 rats used were then divided into 5 groups, the data obtained in the form of rat urine volume and analyzed by one-way ANOVA followed by LSD (Least Significant Difference). To see any changes in the overall urine volume during the observation time can be seen in the Cumulative urine volume mean data are in Table 1.
Table 1. Cumulative average urine
volume data for each observation time
|
Treatme nt Groups |
Hourly Urine Volume (mL) | |||||
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 | |
|
Control |
1.1 |
2.6 |
1.6 |
1.6 |
1.7 |
1,9 |
|
(-) |
5 |
5 |
5 |
5 |
5 |
7 |
|
Control |
0.9 |
2.9 |
4.1 |
5.1 |
5.3 |
5.3 |
|
(+) |
2 |
7 |
1 |
2 |
2 | |
|
Group 1 |
2.1 |
3.5 |
4.7 |
5.0 |
6.8 |
6.9 |
|
5 |
5 |
8 |
3 |
2 | ||
|
Group 2 |
1.4 |
3.0 |
4.4 |
5.3 |
5.8 |
6.2 |
|
4 |
4 |
3 |
3 |
6 | ||
|
Group 3 |
1.5 |
2.1 |
3.9 |
4.3 |
5.6 |
6.0 |
|
5 |
7 |
2 |
1 |
7 | ||
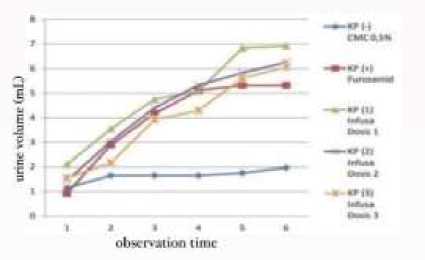
Figure 1. Graph of the average cumulative urine volume for each observation time
According to Santoso's research (2019), this study employs up to 1 kg of fresh celery leaves. Then it's put in the dryer to dry. This 127 g dry of Simplicia was subsequently extracted using the infusion technique. Extraction is a thick preparation made by extracting the active ingredient from plant and animal simplicia. Use a suitable solvent, then evaporate all of the solvents, leaving the bulk or powder in a condition that meets the stated specifications. Process control is not required for product quality criteria to be met, implying that standardized processes may guarantee standardized goods. The extraction method infusion was used in this investigation, where infundasi is the extraction process with water solvent at water bath temperature (96o – 98o C) for 1520 minutes. This method is commonly used to determine the amount of water-soluble active compounds present. This infusion method has the advantage of requiring less equipment and having reduced operational expenses.
There are 2 control groups and 3 experimental groups, each of which will be given treatment was then observed. The test animals used were male white mice BALB/C as many as 25 individuals were divided into 5 groups. The mice used had a weight of 20-30gram with ages 3-4 months. It aims to obtain a response that is relative to the research stimulus. Group 1 is given celery extract 280 mg, group 2 was given celery extract 420 mg, group 3 was given celery extract 560 mg, group 4 was given furosemide, and group V was given aquadest.
Table 2. Urine Volume Rats
|
Groups |
Volume Urine |
Mean |
Diuretic s action (%) | ||
|
30 |
90 |
120 | |||
|
1 |
0.2 |
3.5 |
3.14 |
2.28 |
34.65 |
|
2 |
0.6 |
4.3 |
3.04 |
2.65 |
29.81 |
|
3 |
1.1 |
5.1 |
2.48 |
2.89 |
27.33 |
|
4 |
1.8 |
5.1 |
1.78 |
2.89 |
27.33 |
|
5 |
0.1 |
0.5 |
1.78 |
0.79 |
0 |
According to a study conducted by Rahmi et al (2017), processing Celery herb simpliasia entails cleansing celery herbs from connected dirt (wet sorting), then washing with running water until clean, and then draining to eliminate any water left over after washing. Herbs that have been cleansed and free of washing water are dried in a 500°C oven, then cleaned again to remove any dirt that may have remained after dry sorting. The dried Simplicia is ground into powdered simplicia and sieved using a 60mesh sieve. Preparation of celery herb extract, namely by extracting the simplicia using the maceration process, which involves placing the sample in a tightly sealed container and keeping it away from light. Pour in 70 percent ethanol until the mixture is completely submerged. This experiment used a 9-day lengthy maceration period. A rotary evaporator will be used to concentrate the liquid extract after it has been obtained.
The experiment used 25 rats, then randomly divided into 5 groups with different treatments, namely group 1 by giving Na. CMC 0.5%, group 2 with furosemide, groups 3,4, and 5 using celery with different doses.
Fresh celery root is sliced into bits and dried at room temperature, according to Rehman et al (2016). An electric mill is subsequently used to grind the sample into a fine powder. The extract is prepared using the soxhletation process with 100% ethanol (Merck).
Table 3. Result Data Average Cumulative Urine Volume
|
Test |
Urine Volume (mL) | |||||
|
Time 1 |
Time 2 |
Time 3 |
Time 4 |
Time 5 |
Time 6 | |
|
Control (+) |
0.15 |
0.15 |
0.23 |
0.19 |
0.13 |
0.1 |
|
Control (-) |
0.17 |
0.43 |
0.96 |
0.59 |
0.51 |
0.45 |
|
Group 1 |
0.13 |
0.26 |
0.55 |
0.54 |
0.42 |
0.28 |
|
Group 2 |
0.12 |
0.27 |
0.18 |
0.44 |
0.30 |
0.20 |
|
Group 3 |
0.11 |
0.21 |
0.35 |
0.30 |
0.29 |
0.16 |
Dried celery extract (up to 10 grams) was made and cooked in 50 mL of water for 5 minutes, after which the extracted water was filtered using filter paper and supplied orally to rats according to their weight. The study used 20 rats which were divided into 4 groups each group consisted of 5 rats, with the distribution: Groups 1 (Normal control mice with only added salt), groups 2 (control mice e with an additional injection of i.p. gentamycin. 40mg/kg which for 14 days induced by AKI), groups 3 (development group with addition of Apium graveolens L., Extra ethanolic from Apium 50mg/kg oral dose, Ethanolic extract from Apium 50mg/kg oral dose after being added gentamicin i.p. 40mg/kg which has been induced by AKI for 14 days, Aqueous extract of Apium 10mg/kg orally, Aqueous extract of Apium 10 mg/kg orally after being added gentamicin i.p. 40mg/kg which has been induced by AKI for 14 days), groups 4 (Development group with added Furosemide, Furosemide 40mg/kg orally, Furosemide 40mg/kg orally after added gentamycin i.p. 40mg/kg which has been induced by AKI for 14 days) added gent 40mg/kg.
Fresh Apium graveolens L. leaves are washed separately and gently with water, then dried at room temperature for 14 days and powdered, according to Faris et al (2018). The extract was extracted with 70% ethanol using a magnetic stirrer for 72 hours at 50°C, then filtered and evaporated. A rotary evaporator is used to dry the product at 45°C under reduced pressure.
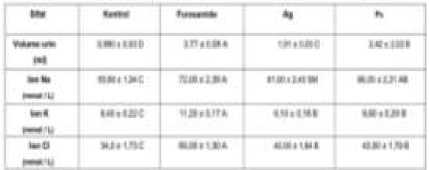
The study used twelve male rats divided into (4) groups of (3) each and are prohibited from being fed and drink for (18) hours. All mice received a normal initial dose of saline (25ml/kg) orally. Both the extracts of Apium graveolens L. (Ag) and Petroselinum crispum (Pc) and Furosemide as standard dissolved in normal saline.
Group (I) serves as a control in which only normal (25) ml/kg saline is administered by the intraperitoneal (i/p) route. Group (II) is presented as the
receiving standard Furosemide (20) mg/kg. Group III and Group IV each received (200) mg/Kg of leaf ethanol extract (Ag) and (Pc). Immediately after administration, rat (one in each cage) are housed in specially designed metabolic cages to separate urine and feces. Stored at room temperature (2425) °C, urine was collected in a measuring tube for up to (6) hours.
Table 4. Diuretic Activity of Ethanolic and Aqueous extract of Apium graveolens L.
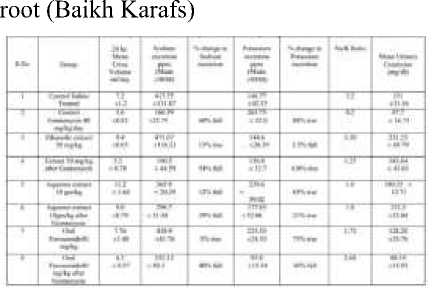
Table 5. Effect of oral administration of ethanolic extract from Apium graveolens L., Petroselinum crispum on urine volume and electrolyte extraction in male rats
DISCUSSION
According to research by Jayadi et al., (2015) cumulative urine volume data describes the increase in overall urine volume over time observation. From the average cumulative urine volume for 6 hours, it can be seen in the 0.5% CMC suspension (KP-) treatment group obtained 1.97 mL, furosemide suspension (KP+) 5.32, celery root infusion dose 1 (KP1) 6.92 mL, celery root infusion dose 2 (KP2) is 6.26 mL, and 6.07 mL of celery root infusion (KP3). The 0.5 percent CMC suspension (KP-) demonstrated the least
cumulative mean urine volume among the five treatment groups. The presence of flavonoids in celery root infusion can produce an increase in urine volume (diuresis), with the mechanism of action being that it slows the reabsorption of Na+, K+, and Cl-, resulting in an increase in electrolytes in the tubules, resulting in diuresis.
According to Santosa's research (2019), the results of this study obtained the number of frequency urination in rats of group I (celery leaf extract) dose of 280 mg) 22 times for 120 minutes and has a diuretic action of 40.93 percent, implying that group I has activity as a diabetes drug but minimal diuretic effect because it has the highest diuretic action. Diuretic action is one of the calculations other than calculating the percent power (potency) of diuretics in the diuretic test method. This method is thought to be effective in determining the diuretic condition value. The diuretic activity was determined by comparing the amount of urine voided in the test group to the amount excreted in the control group's urine. Group IV (celery leaf extract dose 560 mg) shows antihypertensive action but has a high frequency of urination. High diuretic action, comparable to group IV (furosemide), used as a positive control in chemical comparisons.
According to Rahmi et al., (2017), the Normal controls have the smallest mean urine volume of the five treatments. This is significant because the standard control Na.CMC 0.5 percent has no diuretic effect in order for the rats to have a typical diuresis impact. Control treatment group test 1, test 2, and test 3 had an increase in urine volume compared to the normal control treatment group was 0.5% Na.CMC suspension. This study found that a 70 percent ethanol extract of celery herbs could increase urine volume due to the presence of flavonoids, which play a role in increasing urine volume (diuresis) by inhibiting the reabsorption of Na+, K+, and Cl-, causing an increase in electrolytes in
the tubules and causing diuresis. Celery includes apiin, which is the identification compound of celery and is effective as a diuretic, in addition to flavonoids. Celery apiol chemicals have diuretic effects. The diuretic action of the putative 3-n-butylphtalide substance is similar.
Rehman et al. (2016) found that a decoction of Apium graveolens L. avoided a 31 percent fall in creatinine levels (a decrease of -28 percent). The result much better than furosemide in that it only prevents 9% (-46%) in gentamicin-induced kidney damage. Apium prevented the excretion of potassium significantly both when administered to normal animals (decreased 1.5%, p = 0.005) and gentamicin-induced animals (6.8% increased, p =0.016) when compared with the gentamicin control group. Furosemide also reduced potassium excretion by 36%; however, the results were substantially different from the gentamicin control (p<0.001). The herb and extract of Apium graveolens L. clearly have a helpful role in the treatment and prevention of kidney damage, as evidenced by the reversal of gentamicin's negative effects. In comparison to the common diuretic furosemide, ethanol and aqueous extracts of Apium graveolens L. (root) have significant diuretic efficacy.
Faris et al. did research (2018) The ethanolic extracts of Apium graveolens L. (Ag) and Petroselinum crispum (Pc) showed diuretic activity and significantly increased urinary electrolyte excretion. This is likely due to the presence of many compounds that can be responsible for the diuretic effect of plants, such as (flavonoids, Phthalide compounds, or organic acids), or can be acts by inhibiting vasopressin secretion and may act by causes dilation of the glomerular arterioles, thereby increasing the filtration rate glomerulus. Diuretic activity is considered good if the value of the diuretic index is greater of (1.50). In this study, the diuretic index value of the treatment group (Ag) and (Pc) are (2.17) and (2.75) respectively, this
indicates more than 2-fold increase in urine volume.
CONCLUSION
Based on the five journals used, the research results revealed that the apigenin content in Apium graveolens L. is able to increase the diuretic effect compared to furosemide, so hopefully, in the future, the development of Apium graveolens L. can be even better in order to produce products that can work faster, with side effects less, right on target, and at an affordable price.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
This paper was written independently. All authors disclose no financial or personal relationships with other people or organizations that could inappropriately influence the work.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We thank lecturers and staff in the Department of Pharmacy, Faculty of Math and Science, Udayana University, Bali Indonesia, for the support in the implementation of research.
REFERENCES
-
1. Faris, J. K., Ali, Al-ameedi, Rawaa S., and Shatha, M. A. Comparative Evalution of Diuretic Activity of Ethanolic Extracts of (Celery) Apium graveolens and (Parsley) Petroselinum crispum in Male Rats. Indian Journal of Natural Science.2018. 9(50):14835-14840
-
2. Jayadi, A. C., Widdhi, B., and Nancy, P. Uji Efektivitas Infusa Akar Seledri (Apium graveolens L.) Sebagai Diuretik Pada Tikus Putih Jantan Galur. Pharmacon Jurnal Imiah Farmasi. 2015. 4(4): 189-195.
-
3. Rahmi, I. K., Fajrin, N. and Dina, P. Uji Efektivitas Ekstrak Etanol 70% Herba Seledri (Apium Graveolens, L.) Sebagai Diuretik Pada Tikus Putih Jantan Galur Sparague Dawley. Farmagazine. 2017. 4(1): 42-49
-
4. Rehman, A. U., Humera I., Mohammad F., Dilnawaz S., Muhammad L. R., Baqar, S. N. et al. Comparative Study of Ethanolic and Aqueous Extraxts of Apium Graveolens L. Root with Furosemide for Its Diuretic Activity and Excretion of Urinary Metabolites in Wistar Rats. Sci. Int. (Lahore). 2016. 28(3): 2503-2507
-
5. Santoso Joko. Efektivitas Ekstrak Daun Seledri (Apium graveolens Linn.) terhadap Diuretic Action pada Mencit (Mus musculus) sebagai Obat Hipertensi. Jurnal Permata Indonesia. 2019. 10(1): 1-5
-
6. Saputra, O. and Fitria. Khasiat Daun Seledri (Apium graveolens) Terhadap Tekanan Darah Pada Pasien Hiperkolestrolemia. Majority. 2016. 5(2): 120-125
-
7. Syahid ah, F. M, and Sulistyaningsih. Potensi Seledri (Apium graveolens) untuk Pengobatan: Review Article. Farmaka. 2018. 16(1): 56-62
25
Discussion and feedback