Influence Of Organizational Citizenship Behavior To Employee Performance With Employee Competences And Job Satisfaction As Predictors
on
Andhi Supriyadi, Influence Of Organizational... 271
MATRIK: JURNAL MANAJEMEN, STRATEGI BISNIS DAN KEWIRAUSAHAAN
Homepage: https://ojs.unud.ac.id/index.php/jmbk/index
Vol. 16 No. 2, Agustus (2022), 271-280
Influence Of Organizational Citizenship Behavior To Employee Performance With Employee Competences And Job Satisfaction As Predictors


SINTA 2
Andhi Supriyadi1), Aurilia Triani Aryaningtyas2)*
1,2 SekolahTinggi Ekonomi Pariwisata Indonesia (STIEPARI) Semarang email: aurilia.ta@gmail.com
DOI : https://doi.org/10.24843/MATRIK:JMBK.2022.v16.i02.p07
ABSTRACT
In the age of globalization where the midst of increasingly fierce competition, human ability as a resource for mastery of technology, adaptation and responsiveness to change is needed. This research is done to explore and analyze the impact of job satisfaction and competency on employee performance. Besides that organizational citizenship behavior is a mediating variable. Respondents used in this study were employees of the Garment Company factory in Semarang Regency as many as 105 people. The questionnaire method is used to collect the primary data needed. The AMOS SEM program is used for analytical tools. The results of the study found that: 1). Employee competency variables and job satisfaction variables have a positive influence on OCB. 2). Employee competency variables and job satisfaction variables have a positive influence on employee performance. 3). OCB has a positive influence on employee performance. 4). Employee competency variables and job satisfaction variables have a positive influence through OCB on employee performance.
Keywords: organizational citizenship behavior, employee performance, job satisfaction, employee competence
Pengaruh Dari Organizational Citizenship Behavior Pada Kinerja Karyawan Dengan Kompetensi Karyawan Dan Kepuasan Kerja Sebagai Prediksinya
ABSTRAK
Pada era globalisasi saat ini dimana persaingan yang semakin ketat, kemampuan manusia sebagai sumber daya atas penguasaan teknologi, adaptasi dan responsif terhadap perubahan sangat dibutuhkan. Penelitian ini dikerjakan untuk mendalami dan melakukan analisa adanya pengaruh kepuasan kerja dan kompetensi pada kinerja karyawan. Disamping itu variabel organizational citizenship behavior adalah sebagai sebuah variabel mediasi. Responden yang digunakan dalam penelitian yang dilakukan ini adalah karyawan pabrik Perusahaan Garmen di Kabupaten Semarang sejumlah 105 orang. Metode kuesioner dipergunakan untuk mengumpulkan data primer yang dibutuhkan. Program SEM AMOS dipergunakan untuk alat analisis. Hasil dari penelitian mendapatkan bahwa: 1). Variabel kompetensi karyawan dan variabel kepuasan kerja mempunyai pengaruh positif pada OCB. 2). Variabel kompetensi karyawan dan variabel kepuasan kerja mempunyai pengaruh positif pada kinerja karyawan. 3). OCB mempunyai pengaruh positif pada kinerja karyawan. 4). Variabel kompetensi karyawan dan variabel kepuasan kerja mempunyai pengaruh positif melalui OCB pada kinerja karyawan
Kata Kunci: organizational citizenship behavior, kinerja karyawan, kepuasan kerja, kompetensi karyawan
INTRODUCTION
In the age of globalization, where competition is increasingly tight, the ability of human resources who have the ability to master technology, adapt and be responsive to change is needed. Under these circumstances, in winning the competition a personal integrity becomes increasingly important (Sutrisno, 2012) The result of work that employees can do in performing tasks and jobs given in accordance with their responsibilities and responsibilities that what we can call employee performance is. Behavior that which known as OCB is a vital
thing since it can be “the organization's social engine lubrication” (Smith et al., 1983). Actions of an Individual discretionary of employees which outside of their official job description that what we said as OCB.
Managers need to be aware of the approval and rejection of OCBs in order to improve employee consistency in the best possible way for the company and prevent burnout, by linking organizational effectiveness with the characteristic and human behavior in their performing (Hansen, 2016). According to him, not only in roles, but also in extra-role behavior of the employee can affect the effectiveness of the organization. The nature of resources and also a type of behavior that can be seen when there are relationships between them that can affect performance in the organization (Tefera & Hunsaker, 2020).
Many factors that can affect to OCB, such as Job Satisfaction and Competence can affect to OCB which ultimately affects employee performance. Job satisfaction is an emotional condition that pleases employees in seeing the work individually. Employee competencies also will definitely needed by organization, since will certainly be easy to carry out all work responsibilities, able to read the situations and problems that occur in the work and can provide the right response and have a good adjustment to the work environment. Research on impact of Job Satisfaction and Competence to OCB and also to employee performance has been conducted by several other researchers, such as (Darsana, 2013), Supriyadi et al. (2017), Adianita et al. (2017), Sulistyawan (2017), Saragih et al. (2017), and Aryaningtyas & Th (2019). Generally, that employees who have high OCB, will have impact to the performance of the employee concerned.
Employee performance is the level of completion of a task that is in the employee's work (Byars, 1998). A company's success in achieving its goals depends on the performance of its employees. In order for employees to be able to show maximum performance, one of the ways it does is to improving OCB implementation. Individual discretionary bahaviors, which not known by the formal reward system directly or openly but develop an effectiveness function in the organization (Organ, 1998). OCB based on fundamental motives or values, voluntary form their behavior does’n necessarily indicate a true willingness. Hasibuan (2007) define "Job satisfaction is an emotionally happy attitude and loving of his work, this is an attitude that shown from discipline, work morale and work performance. The satisfaction of work can be enjoyed within his work, outside of his work, and the combination of the both". Bozkurt (2011) defining competencies is a behavior that determines the level of performance in a particular work context.
Based on the explanation above, this research proposes the following hypothesis:
-
1. Job satisfaction has an effect on OCB
-
2. Competence has an effect on OCB
-
3. Job satisfaction has an effect on employee performance
-
4. Competence has an effect on employee performance
-
5. OCB has an effect on employee performance
-
6. Competence and Job Satisfaction affect employee performance with OCB as a mediating variable.
Based on data of APO (Asian Productivity Organization) which published in Asian Productivity Organization Data Book on 2019, Indonesia's worker productivity position is ranked 5 out of 10 ASEAN countries. Indonesia's worker productivity hovers around 26,000 USD, which is only one-fifth of Singapore's. Singapore itself is ranked first with productivity per worker of 142,300 USD. While Malaysia with worker productivity of 60,000 USD. Lower productivity compared to other ASEAN countries has an impact on the competitiveness of labor in ASEAN and internationally. Generally companies or managers
will not look for a workforce that has a low level of productivity, because this can affect productivity and company targets in general (Supriyadi et al., 2017).
Therefore, this research intends to examine garment companies in Semarang Regency (Central Java). This research contributes to an empirical study of organizational citizenship behavior in the management of companies, especially garment companies. This study also wants to show the effect of organizational citizenship behavior on employee performance where employee competence and job satisfaction are predictors. Research on organizational citizenship behavior in garment companies is still very limited. This study also provides important empirical evidence to be considered for the leaders of various companies in order to make the right decisions in HR management.
METHOD
Bernadin and Russell giving limits on employee performance as record the results form function of a job or activity over a certain period of time (Gomes, 2003). Bernadin et al. (1993), formulate performance criteria of indicators to measure, namely: 1. Quality, 2. Quantity, 3. Timeliness, 4. Cost Effectiveness, 5. Need for supervision, 6. Interpersonal Impact.
On 1988 OCB’s formal definition of began to appear and formally known and used definition, namely “Behaviors of individual discretionary, which not known by the formal reward system directly or openly but develop an effectiveness function in the organization” (Organ, 1998). Using the Likert scale for five dimensions/indicators are Altruism, Conscientiousness, Sportmanship, Courtesy, Civic virtue, Organ defines discretionary as behavior that is not driven by the contractual terms of the employee but rather the issue of personal preference where it is generally understood that it is not done then will not be sanctioned.
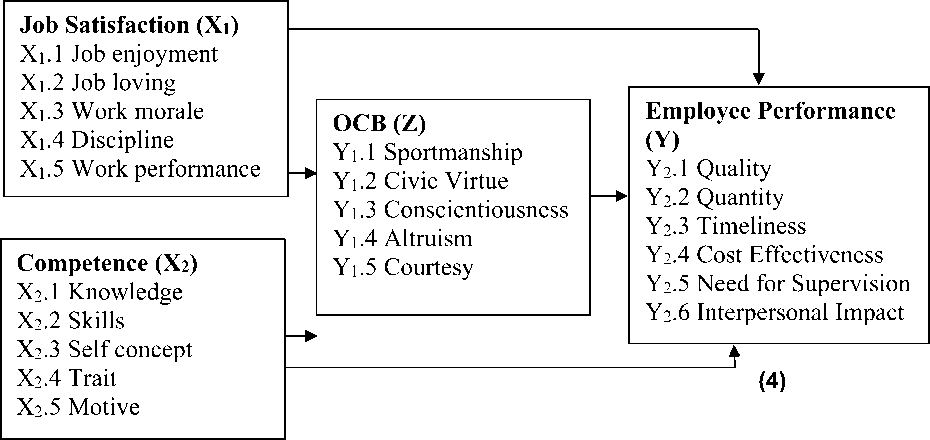
Figure 1. Frame of mind
Hasibuan (2007) define "Job satisfaction is an emotionally happy attitude and his work loving, this is an attitude that shown from discipline, work morale and work performance. The satisfaction of work can be enjoyed within his work, outside of his work and the combination of the both" (Luthans, 2008). “Job satisfaction is perception of employees about how good their job is and provide something important. In organizational behavior, job satisfaction is an important and often learned attitude” (Hasibuan, 2007). He
stated indicators of job satisfaction are: Job enjoyment, jobs loving, work morale, discipline, work performance.
The research which conducted is a quantitative research type by looking for causal relationships. The study og this research is study is a causal associative study, where the relationship studied is causal (Sugiyono, 2018). This research design is explanatory research that explains the relationship between one variable and another variable (Umar, 2008).
To predict the magnitude of variables, form relationships and determine the number and magnitude of influences of exogenous and endogenous variables using SEM (Structural Equation Modelling) analysis techniques operated through the AMOS Program. Respondents used in this study were employees of the Garment Company factory in Semarang Regency as many as 105 people. Based on (Agusty, 2002) when SEM analysis techniques were used, the number of samples as respondents was between 100 and 200. Used 5 x number of indicators = 5 x 21 = 105, so that a sample of 105 already meets the criteria of 100 - 200. Sampling techniques in this study were performed by purposive and stratified random sampling.
Variables are constructs that are given a value (Sanusi,2014). This study used exogenous variables (X), intervening variable (Z) and endogenous variable (Y).
Job satisfaction is an emotionally happy attitude and loving of his work, this is an attitude that shown from discipline, work morale and work performance. The satisfaction of work can be enjoyed within his work, outside of his work and the combination of the both (Hasibuan, 2007).Competencies is a behavior that determines the level of performance in a particular work context (Bozkurt, 2011). OCB is an Individual discretionary bahaviors, which not known by the formal reward system directly or openly but develop an effectiveness function in the organization (Organ, 1998). Employee performance as record the results form function of a job or activity over a certain period of time (Bernadin, 1993).
Validity tests are used to obtain the ability of instruments or tools used as data collectors in uncovering targets on the subject of measurement. Reliability tests are needed to determine the durability of the measuring instrument used. Measuring instruments can be said to be reliable.
Descriptive analysis with the help of SPSS. Descriptive analysis is carried out to find out an overview of respondents' responses about clarity of variable job satisfaction, variable competence, variable OCB and variable employee performance. Descriptive analysis is also carried out by testing the loading factor hypothesis which is identical to confirmatory factor analysis to determine the contribution of factor dimensions to their construct or latent variables.
Analysis to answer hypotheses in the ressearch using SEM ( Structural Equation Model) analysis with help of AMOS and SPSS program packages. The test on the hypothesis is carried out due to value of critical ratio and level of prob in regression weight, if cr value ≥ 2.00 and prob. ≤ 0.05 are the condition to accept a hypothesis.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Results test of validity shown, value of r calculates of each question item higher than value of r Table, with this result, question items of job satisfaction, competence, OCB, and employee performance are declared valid for use as variable measuring instruments. Cronbach's alpha value results of variables of job satisfaction, competence, OCB, and employee performance higher than 0.60 so that the question items of each variable are declared reliable.
The CFA result (Figure 2) shows the loading factor of every indicatorsover to the value of cut-off (0.5). The test shows if all indicators of job enjoyment (X1.1), job loving (X1.2), work morale (X1.3), discipline (X1.4) and job performance (X1.5) reflect job
satisfaction. his test shows that all indicators of knowledge (X2.1), skills (X2.2), self-concept (X2.3), self-characteristics (X2.4) and motives (X2.5) reflect competence. This evaluation shows that indicators: sportsmanship (Z1.1), civic Virtue (Z1.2), conscientiousness (Z1.3), altruistic (Z1.4) and courtesy (Z1.5) reflect OCB. This evaluation shows that indicators: quality (Y1.1), quantity (Y1.2), timeliness (Y1.3), cost effectiveness (Y1.4), need for supervision (Y1.5) and interpersonal impact (Y1.6).
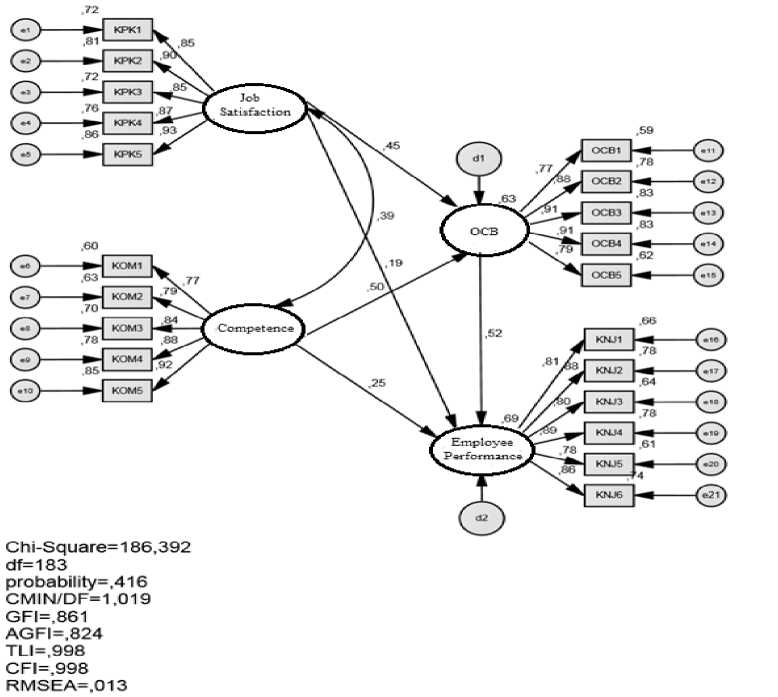
Figure 2. Path Analysis
The fit model test result showed that value of chi square is 186,39 less then value of chi square from Tables is 215,56 with a prob 0.416 higher than 0.05 that means, the matrix of covariance between prediction and observation is same. The other results are values of CMIN/ DF, TLI, CFI, and RMSEA in accordance to the specified value of cut of. Meanwhile, GFI and AGFI values are marginal since they are smaller than the specified standard of values. In general, can be concluded if this SEM model able to be categorized well in describing a causality relationship on the factors used.
From the results in the Table 1, it can be proven as follows:
-
a. The cr value of job satisfaction against OCB of 5,089 is higher from 2.00 and prob.*** lower from 0.05. This value of cr competence against OCB is 5,294 is higher from 2.00 and prob.*** lower from 0.05, So accept the hypothesis that states job satisfaction and competence affect OCB
-
b. This value of cr job satisfaction to employee performance of 2,105 is higher from 2.00 and prob. 0.035 is lower fromn 0.05. This cr value of competence towards employee performance of 2,564 is higher from 2.00 and prob. 0.010 is lower from 0.05. So accept the hypothesis that states job satisfaction and competence affect employee performance.
-
c. OCB's cr value for employee performance of 4,109 is greater than 2.00 with prob.*** smaller than 0.05, then accept the hypothesis that OCB behavior affects employee performance.
Table 1 Result Test of Hypothesis
|
Estimate |
S.E. |
C.R. |
P | |||
|
OCB |
<--- |
Job satisfaction |
,392 |
,077 |
5,089 |
*** |
|
OCB |
<--- |
Competence |
,562 |
,106 |
5,294 |
*** |
|
Employee -Performance |
<--- |
OCB |
,612 |
,149 |
4,109 |
*** |
|
Employee - Performance |
<--- |
Job satisfaction |
,193 |
,092 |
2,105 |
,035 |
|
Employee -Performance |
<--- |
Competence |
,324 |
,126 |
2,564 |
,010 |
Source: Processed data result
|
Table 2 Intervening Test Results | ||||
|
Variables |
Direct Influence OCB |
Direct Influence Employee Performance |
Indirect Influence Through OCB Employee Performance |
Total Influence |
|
Job |
0,448 |
0,186 |
0,232 |
0,418 |
|
satisfaction | ||||
|
Competence |
0,504 |
0,246 |
0,261 |
0,507 |
|
OCB |
0,517 | |||
Source: Processed data result
From the results in the Table 2, it can be proven as follows:
-
d. The indirect influence of job satisfaction through OCB to employee performance amounted to 0.232 and higher than direct impact variable of job satisfaction to variable employee performance, which is 0.186, and total influence of 0.418. Indirect influence of competence through OCB to employee performance amounted to 0.261 this higer than the direct impact variable of competence to variable of employee performance, which was 0.246, with a total influence of 0.507. So job satisfaction and competence influence through OCB as a mediation variable to employee performance.
Data analysis results show that six indicators of employee performance are able to reflect variable of employee performance, Results of the study is in accordance with the theory of Bernadin (1993). By looking at the amount of loading factor obtained from the endogenous variable confirmatory test obtained quantity as the largest reflection then successive cost effectiveness, need for supervision, quality, timeliness and the smallest interpersonal impact.
Data analysis results that five indicators of OCB were able to reflect OCB, this is in accordance with the theory of Organ (1998). By looking at the amount of factor loading obtained from the confirmatory test intervining variables obtained conscientiousness as the largest reflection then successive altruism, civic virtue, sportsmanship and the smallest courtesy.
The results of data analysis show that knowledge, skills, self-concepts, selfcharacteristics and motives are able to reflect competence, this is in accordance with the theory of Bozkurt (2011). By looking at the amount of factor loading obtained from the confirmatory test of exogenous variables obtained motifs as the largest reflection then successive self-characteristics, self-concept, skills, and the smallest knowledge.
The results of data analysis show that liking work, loving work, work morals, discipline and work achievement are able to reflect competence, this is in accordance with the theory of Hasibuan (2007). By looking at the amount of factor loading obtained from the confirmatory test of exogenous variables obtained work performance as the largest reflection then successively love work, discipline, pleasure work, and the smallest morale work.
Hypothesis tests prove that job satisfaction and competence have been shown to have an effect on OCB. Happy employees will show a positive attitude towards their work so that they are ready to work harder or work more than usual because they already feel good about what is gained from the company. Employees who have competence will master one or even more than one task area so that with this ability they will be asked to carry out several tasks other than the main tasks carried out.
The results of the description analysis show that for knowledge indicators get the highest average value. This is because employees have sufficient knowledge and get orientation and explanation from the company before doing the work. With the provision of knowledge possessed, employees will be given responsibilities according to the field of knowledge mastered as a whole means that the results of the task of the working group become a joint responsibility so that when there are obstacles faced by one member of the working group then other members must help because they have supporting knowledge. This condition creates OCB.
The satisfaction factor that affects OCB as a whole is also influenced by indicators of loving work, namely love makes employees loyal and loyal so that they are willing to sacrifice more to achieve the goals they want to get, then also work morale is always excited and in working and helping each other with colleagues so as to show high attention to work, in addition to discipline, namely employees who are disciplined by arriving on time and not skipping ditching means that there is a desire to sacrifice more every day to always come to work and leave early so as not to be late.
Research by Martini (2022) conducted with respondents of civil servants in Banyuwangi obtained the result that competence and job satisfaction affect OCB . The same is obtained from research Dewanti & Moko (2020) with honorary teacher respondents in Kediri. Likewise, research conducted by Anindita & Bachtiar (2021) with respondents to online media works. Other research was conducted by Widodo et al. (2021) where with respondents PLN Employees Mahakam Plant get results that are not much different.
Hypothesis tests prove that Job Satisfaction and Competence have been shown to affect Employee Performance. Satisfied employees will show better performance because they will run the job with positive actions. While employees who have competence, namely having expertise in the field of duty undertaken, can run it appropriately and can achieve results according to the goals they want to get so that employees who have competence will be able to produce good performance.
Competency factors that affect employee performance are also supported by skill indicators, namely by having experience and getting training, technically employees master their fields of duty and can overcome various problems that arise during the implementation of tasks, then have a self-concept, namely with demands to work according to regulations and the punishment for violating then the employees must work according to SOP (standard operating procedures) so that employees Employees work within their authority. Another
supporting indicator is self-characteristics, namely by conducting psychological tests and hiring employees as needed, it can be obtained employees who are assessed accordingly, both in terms of insight, behavior and mentality to carry out a task so that by giving the right task it is expected to show good performance.
Based on the respondent's statement, the indicator of liking work gets the highest rating. This means that with a sense of pleasure towards work that is reflected in employees devoting their abilities which means that they will release all the skills they have to carry out tasks, the results of work obtained will be better where skilled employees tend to be faster in carrying out tasks and the mistakes produced are also less. The sense of pleasure is also based on because employees know what the goals and importance of work are so they are ready to work hard by trying to achieve work targets because this is an important factor to continue to maintain their work position in the company and achieve higher goals such as career improvement.
Research by Martini (2022) onducted with respondents of civil servants in Banyuwangi obtained the result that competence and job satisfaction affect employee performance. The same is obtained from research Dewanti & Moko (2020) with honorary teacher respondents in Kediri. Other research was conducted by Widodo et al. (2021) where with respondents PLN Employees Mahakam Plant get results that are not much different.
Hypothesis tests prove that OCB is proven to affect employee performance, employees who have OCB will be more effort to work can be carried out or completed to the maximum without thinking about the greater sacrifices that must be made and not considering the additional value obtained such as from compensation.
Based on the results of the description analysis shows that for the indicator that gets the highest assessment, namely sportsmanship, it means that for OCB it is shown to be able to spend a lot of time achieving the organization's goal of utilizing working hours only to carry out tasks so that the goals achieved such as production and sales targets increase even though for that it must work to exceed working hours. In addition, it is also shown by focusing on what is right in the work not on the negative side, which means trying to do the work correctly even though sometimes you have to take the time to repeat the work or improve the results of the work again to produce a perfect or correct work output as set by the company. This kind of behavior will certainly improve the good performance of employees.
Also supports to research from Hanafi et al. (2018) where OCB has role which important to improve performance. In additional is a research did by (Supriyadi et al., 2017), obtained the result that improving OCB with readiness factors in providing assistance to those who need will be improved employee performance in the garment industry. Other research was conducted by Widodo et al. (2021) where with respondents PLN employees Mahakam Plant get results that are not much different.
Competence and Job Satisfaction have been shown to affect employee performance through OCB as a mediation variable. Satisfied employees mean that the value obtained in accordance with expectations or felt enough can be received such as from compensation and the burden of responsibility carried out. Employees who have competence means having knowledge or skills that can be applied to carry out tasks and also have the appropriate thought patterns to carry out these tasks.
Research conducted by Martini (2022) conducted with civil servant respondents in Banyuwangi obtained the result that variable competence and variable job satisfaction influence through OCB to employee performance. According to Dewanti & Moko (2020) OCB can improve performance of state junior high school honore teachers in Kediri City. Sulistyawan (2017) which shows that competence affects employee performance through
OCB as a intervining variable as well as Kasemsap (2013) which shows that job satisfaction impacts to employee performance through OCB be a mediation variable.
CONCLUSION
Some of the conclusions which can be drawn are: Hypothesis tests prove that job satisfaction and competence impacts to OCB. Hypothesis tests prove that job satisfaction and competence impacts to employee performance. Hypothesis tests prove that OCB impacts to employee performance. Job satisfaction and competence impacts to employee performance with OCB as a mediation variable.
Suggestions which can be conveyed of research obtained, are as follows: Employee job satisfaction should be further improved, especially in terms of achievement. Employee competence must be further improved, especially in terms of motives because they get the lowest average score. OCB improvement efforts can be done in terms of altruism because it gets the lowest average value
Further research can be change in the predictor variable so that a more comprehensive conclusion. Conducted research with a different work environment where in this research is only done in the garment industry as a light manufactur industry, can be done with other industries such as the chemical industry and so on
REFERENCE
Adianita, A. S., Mujanah, S., & Candraningrat, C. (2017). Kompetensi Karyawan, Emotional Quotient Dan Self Efficacy Pengaruhnya Terhadap Organizational Citizenship Behavior Dan Kinerja Karyawan Pada Indomobil Grup Di Surabaya. Jurnal Riset Ekonomi Dan Manajemen, 17(1), 199. https://doi.org/10.17970/jrem.17.170114.id
Agusty Ferdinand. (2002). Structural Equation Modeling Dalam Penelitian Manajemen (2nd ed.). Badan Penerbit UNDIP.
Anindita, R., & Bachtiar, N. P. (2021). The Impact of Organizational Culture Towards Organizational Citizenship Behavior Through Job Satisfaction and Competency Among Online Media Employees. Business and Entrepreneurial Review, 21(1), 193–216.
https://doi.org/10.25105/ber.v21i1.9279
Bernadin, John H., dan J. E. A. R. (1993). Human Resources Management an Experiental Approach. McGraw-Hill Inc.
Bozkurt Tülay. (2011). Management by Competencies.
Byars, Lloyd, L. dan L. W. R. (1998). Management: Theory and Application. Ricard D. Irwin Inc.
Darsana, M. (2013). The influence of personality and organizational culture on employee performance through organizational citizenship behavior. The International Journal Of Management, 35(4), 35–42. www.theijm.com
Dewanti, M. C., & Moko, W. (2020). The Role of Organizational Citizenship Behavior ( OCB ) and Organizational Commitments in Media- tion between Competence with Honorer Teacher Performance ( Study at State Middle School in Kediri City ). International Journal of Business, Economics and Law, 9(5), 1582–1588.
Fred Luthans. (2008). Organizational Behavior. (Tenth Edit). McGraw Hill.
Gomes, F. C. (2003). Manajemen Sumber Daya Manusia. Andi Offset.
Hanafi, A., Bemby Soebyakto, B., & Afriyanti, M. (2018). The Effect of Organizational Citizenship Behavior (OCB) and Quality of Work Life (QWL) on The Employee Work Performance with Motivation As An Intervening Variables at Industrial affairs Of South Sumatera Province. International Journal of Scientific Research and Management, 6(09), 676–685. https://doi.org/10.18535/ijsrm/v6i9.em03
Hansen, M. (2016). Organizational citizenship behaviours definitions and dimensions: Mutuality in business. Saïd Business School, 1, 1–16. www.sbs.oxford.edu/mutuality
Hasibuan, SP, M. (2007). Manajemen Sumber Daya Manusia (Edisi Revi). Bumi Aksara.
Kijpokin Kasemsap. (2013). Innovative Human Resource Practise: A Unified Framework and Causal Model of Psychological Empowerment, Job Satisfaction, Organizational Citizenship Behavior, and Organizational Performance. Suan Sunandha Rajabhat University, 11(11). https://doi.org/7763/IPEDR
Organ Dennis W. (1998). Organizational Citizenship Behavior: The Good Soldier Syndrome. Lexington Books.
Parulian Hutapea and Nuriana Thoha. (2008). Kompetensi Plus. PT. Gramedia Pustaka Utama.
Putu Ayu Rusmayanti, Ni Nyoman Putu Martini, N. Q. (2022). The Effect of Competence and Job Satisfaction on Organizational Citizenship Behavior and Employee Performance. International Journal of Business and Management Invention (IJBMI), 11(1). https://doi.org/DOI: 10.35629/8028-1101012129
Saragih, B., Sanusi, A., & Manan, A. (2017). The Influence of Job Satisfaction towards Employee Performance on the Antecedent of Competencies and Organizational Citizenship Behavior. IOSR Journal of Business and Management, 19(01), 21–27. https://doi.org/10.9790/487x-1901072127
Smith, C. A., Organ, D. W., & Near, J. P. (1983). Organizational citizenship behavior: Its nature and antecedents. Journal of Applied Psychology, 68(4), 653–663.
https://doi.org/10.1037/0021-9010.68.4.653
Sugiyono. (2018). Metode penelitian kuantitatif (Setiyawami (ed.); 1st ed.). CV. Alfabeta.
Sulistyawan, P. (2017). Organizational Citizenship Behavior (OCB) sebagai Pemediasi pada Pengaruh Kompetensi dan Modal Psikologi (Psychological Capital) terhadap Kinerja (Studi Pada Badan Pusat Statistik Provinsi Jawa Tengah). Aset, 19(2), 151–160.
Supriyadi, A., Sanusi, A., & Manan, A. (2017). A Study on the performance of
manufacturing employees: Organizational culture, compensation, organizational commitment, and organizational citizenship behavior. European Journal of Business and Management, 9(6), 32–43.
Sutrisno. (2012). Manajemen Sumber Daya Manusia (1st ed.). Prenada Media Group.
Tefera, C. A., & Hunsaker, W. D. (2020). Intangible assets and organizational citizenship behavior: A conceptual model. Heliyon, 6(7), e04497.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e04497
Widodo, U. B., Hidayati, T., & Setiawati, L. (2021). Influence Of Organizational Culture And Competence On Job Satisfaction And Organizational Citizenship Behavior And Employee Performance PT PLN ( Persero ) Parent Unit of Kalimantan Mahakam Plant Control Management Unit. 10(5), 20–35. https://doi.org/10.35629/8028-1005022035

Discussion and feedback