Application of Augmented Reality Technology in the SDN 1 Sanur Building Recognition Application
on
p-ISSN: 2301-5373
e-ISSN: 2654-5101
Jurnal Elektronik Ilmu Komputer Udayana
Volume 10 No. 1, August 2021
Application of Augmented Reality Technology in the SDN 1 Sanur Building Recognition Application
I Made Satya Vyasaa1, I Gede Arta Wibawaa2
aInformatics Department, Udayana University
Jalan Raya Kampus Unud, Jimbaran, Bali, 80361, Indonesia 1satyavyasa77@email.com
Abstract
This study aims to build an application to introduce the Sumerta 1 public elementary school building. This research uses AR (Augmented Reality) technology, which with this technology makes it possible to display an object in virtual form in a real world view. The method used in this application is marker-based which identifies the pattern of a marker, in the application development itself the model used is the waterfall model. In the process of building this application, using the Vuforia software development kit (SDK) and Unity as the engine..
Keywords: Marker Based, Augmented Reality, Unity, Vuforia, School environmrnt
An educational institution such as a primary and secondary school, of course, provides various facilities to support teaching and learning activities. The facility is usually divided into rooms in the form of laboratory rooms, classrooms, or rooms for administration such as an administrative room. No exception Elementary school (SD) number 1 Sumerta as a public elementary school located in Denpasar, Bali. Which every year SD 1 Sanur will accept new students, which is before starting teaching and learning activities the school will first introduce the school environment to these new students.
An educational institution such as a primary and secondary school, of course, provides various facilities to support teaching and learning activities. The facility is usually divided into rooms in the form of laboratory rooms, classrooms, or rooms for administration such as an administrative room. No exception Elementary school (SD) number 1 Sumerta as a public elementary school located in Denpasar, Bali. Which every year SD 1 Sanur will accept new students, which is before starting teaching and learning activities the school will first introduce the school environment to these new students.
In several studies, to be able to provide new experiences and to increase students' interest in getting to know the school environment. Then the AR (Augmented Reality) technology was applied. This AR technology allows users to visualize an object in 3D[1].
Research on the introduction of the building was conducted in 2016 at Kanjuruhan University Malang, by Galih Laksono and Eko Fachtur Rohman. In this study, the application of AR technology with a markerless method was carried out. In this study, the AR application is made to run on an Android smartphone device. From the tests that have been carried out on this application, it is known that the application has not been able to display the location of the building accurately. Due to the lack of accuracy on the GPS on the smartphone.
In this research, the writer will use AR (Augmented Reality) technology with a marker-based method where Augmented Reality itself is a real-time display of information overlaid with virtual objects in the real world view. The use of AR technology itself is considered very suitable by the author if it is used as a medium for recognizing an object where the object to be used here is the building from SD 1 Sumerta. In this research, AR technology will be combined with the Vuforia SDK library with the Unity Tools.
-
1.1 Unity
Unity is a game engine based on cross-platform. This is where this application serves to create a 3D form of an object in video games, visual architecture, and 3D animation in real-time.
-
1.2 Vuforia
Vuforia is an Augmented Reality Software Development Kit (SDK) for mobile devices commonly used in AR-based application development.
-
1.3 Blender
A blender is a software that is used to do 3D designs, both in making games, films, and 3D animation..
2. Reseach Methods
In this research, the test method used is the SDLC method, with a waterfall model. The waterfall
model or so-called linear sequential model, where this model starts a systematic and sequential approach to software developers[5]. The process of making the SDLC waterfall model in this
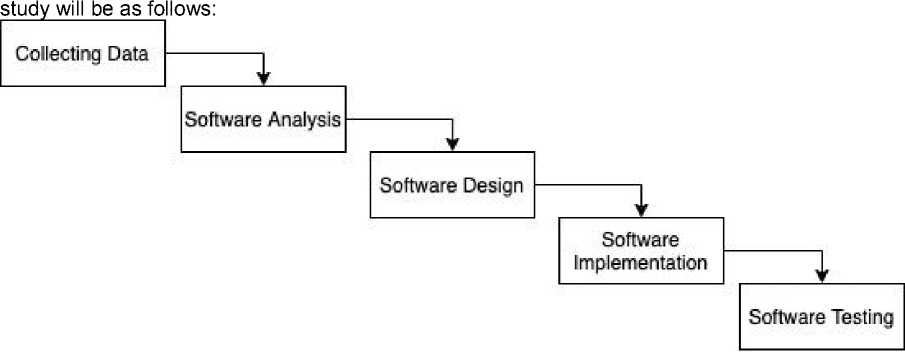
-
2.1 Collecting Data
The data collection process in this study was carried out by conducting interviews with the school to be able to find out information about the buildings and classes at the school. whereas for the shape of the 3D object to be made based on the shape and layout of the school, which is obtained through direct observation in the school environment[1].
-
2.2 Software Analysis
In this study, the analytical method used is the SDLC (System Development Life Cycle) method with the Waterfall model, which makes software development sequential and systematic[3]. In the development of the processing application, it starts from the requirements analysis stage, then the system design, then implementation, and testing. In this modeling, before entering the next stage, the previous stage must have been completed. Therefore, in this model, the results obtained will be strongly influenced by the previous process[2]. The software analysis will be described as follows:
-
a. Software Requirements
This application uses AR (Augmented Reality) technology with a marker-based AR method. This application runs if the markers used are appropriate and if the markers used are appropriate, the application will display a 3D model of the school building. in this application, users can see a 3D model of the school building along with the layout of the room. This application is made on the Android platform, and the software used in the development of this application is unity with the Vuforia library.
-
b. Software Input and Output
This application requires input in the form of a marker, which in this study uses a QR code, then the marker will be scanned using the camera on the smartphone, then the application will output a 3D model that can be seen through the smartphone layer.
-
c. Software Limitation
There are various versions of the Android operating system, therefore limitation analysis is needed to find out what specifications the application can run on. In this study, applications that are needed can run on the Android 4.1 or higher operating system.
-
2.3 Software Design
After going through the analysis stage, the next process will enter the software design section. In this section, the details of the design that will be made are based on several parameters, an example of which is processing time, budget constraints, and the technology to be used. The design model for this application is as follows.
-
a. Software Technology
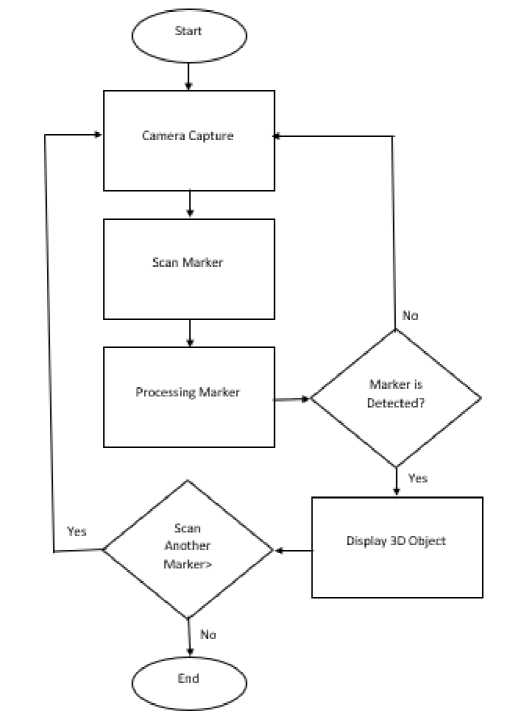
Figure 1. Flowchart Application proses
From the system design that has been previously made, the technology design that will be used in this application is AR (Augmented Realit) technology, where the method used is marker-based. Marker based is an AR technology that uses a marker in the form of a 2D object that has a certain pattern that will later be read using a camera or webcam.
Based on the flowchart above, it is known that the first process that is carried out when the application has been run is to prepare the camera to scan the markers that have been provided. Then the scan results of the marker will be identified whether the marker has been detected or not. If the marker has been detected, the application will display the 3D object.
-
b. Use Case Diagram
Use case diagrams are diagrams that state the visualization of interactions that occur between users (actors) and a system[4]. The following is a use case diagram in this application.
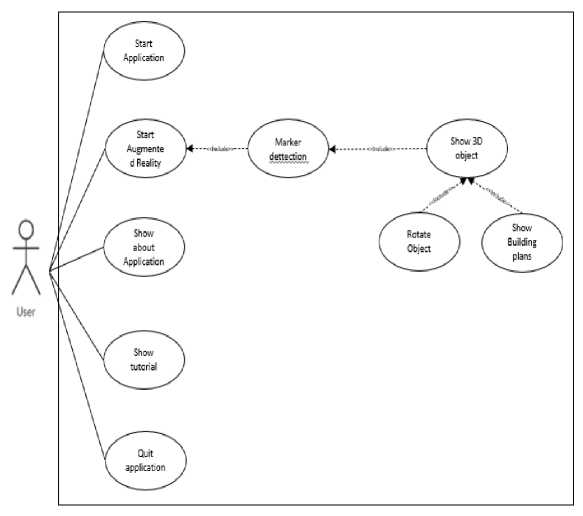
Figur 2. Use case diagram
-
3. Result and Discussion
This section displays the results and discussion of the implementation and testing of the software that has been made.Implementation
-
3.1. Implementation
(This section displays the results of the application implementation in the form of screenshots. The screenshots of the application are as follows:
-
a. Main menu
b.
c.


View Plan
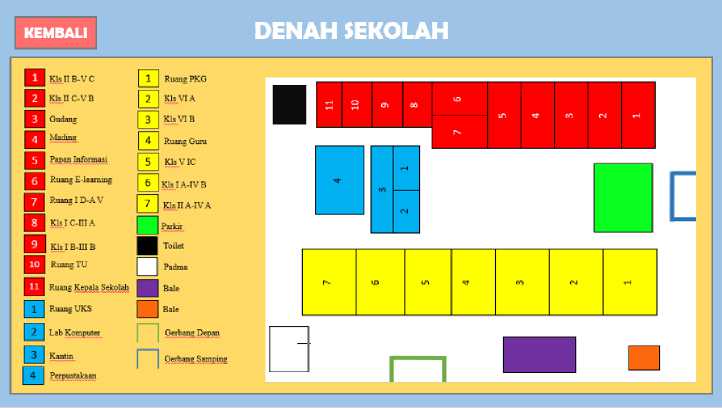
d. About Application

e. How to use

In this study, the testing method used was the BlackBox method. This method aims to determine the correctness and suitability of the process in the application and on several devices. This process is seen only in terms of the output generated from a given data for the functions contained in the software without seeing how the process is to get the output. In this test using several pieces of equipment including OPPO K1, Xiaomi Readmi Note 7, Xiaomi Readmi Y3, Samsung A6 Plus.
|
No |
Fungsional |
Hasil Tes |
Keterangan |
Perangkat Uji |
|
1 |
Start Application |
success |
Displays the Main Menu |
All test devices |
|
2 |
Augmented Reality Button |
success |
Displays the Camera |
All test devices |
|
3 |
How to use Button |
success |
Shows how to use |
All test devices |
|
4 |
About Application Button |
success |
Displays Information Regarding Applications |
All test devices |
|
5 |
Tracking markers |
success |
Displays 3D school building objects |
All test devices |
|
6 |
Rotate Button |
success |
Rotate 3D objects |
All test devices |
|
7 |
View Plan button |
success |
Show school plans |
All test devices |
|
8 |
Exit button |
success |
Exit of the application |
All test devices |
This study aims to create an application that can help students get to know the school environment in a way that is more fun and easier. This application uses AR (Augmented reality) technology with a marker-based method that can detect a marker in the form of a 2D image. The output of this application is a 3D model of the SDN 1 Sumerta school building. In the development process, this application uses the SDLC (Software Development Life Cycle) method with a waterfall model. Meanwhile, in making the application using the Unity software with the Vuforia library. For the testing process, this application uses the black-box testing method, wherein the testing process this application has been running well according to its function on different devices, all features have worked successfully, and can display 3D models using markers that have been prepared.
References
-
[1] I. G. P. B. N. W. Prayoga, I. K. R. Arthana, and I. G. M. Darmawiguna, “Pengembangan Aplikasi Augmented Reality Markerless Teknik Dasar Prenatal Yoga,” Kumpul. Artik. Mhs. Pendidik. Tek. Inform., vol. 6, no. 3, p. 247, 2017, doi: 10.23887/karmapati.v6i3.12058.
-
[2] I. G. A. Wicaksana, I. K. R. Arthana and I. M. A. Wirawan, "PENGEMBANGAN GAME BANTEN BERBASIS ANDROID," Kumpulan Artikel Mahasiswa Pendidikan Teknik Informatika , vol. 6, no. 1, pp. 142-149, 2017.
-
[3] N. L. M. D. A. Astita, A. F. Rochim, and K. T. Martono, “Aplikasi Augmented Reality Denah SMP Negeri 36 Purworejo Menggunakan Mobile Android,” J. Teknol. dan Sist. Komput., vol. 3, no. 4, p. 456, 2015, doi: 10.14710/jtsiskom.3.4.2015.456-460.
-
[4] A. K. O. SUDANA, K. S. WIBAWA e I. M. A. D. TIRTHA, “Learning Media Of Baliese Script Writing Based On Augmented Reality,” Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology, vol. 90, 2016.v
-
[5] S. Barjtya, A. Sharma e U. Rani, “A detailed study of Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) Models,” International Journal Of Engineering And Computer Science, vol. 6, 2017
This page is intentionally left blank
52
Discussion and feedback