The Application Of Augmented Reality in Introducing Temples in Denpasar
on
Jurnal Elektronik Ilmu Komputer Udayana
Volume 9, No 3. February 2021
p-ISSN: 2301-5373
e-ISSN: 2654-5101
The Application of Augmented Reality in Introducing Temples in Denpasar
Ida Bagus Mahendraa1, Agus Muliantaraa2
aDepartment of Informatics, Udayana University Bali, Indonesia 1ibmhndr@gmail.com 2muliantara@unud.ac.id
Abstract
Over time, the situation has changed the mindset of the Hindu community, especially in Bali in carrying out their worship. People no longer come to the temple just to pray and go home, but they wanted to know more about the temple itself. Due to the influence of the current era which quickly eroded historical existence, many were interested in knowing information about the temples they visited. However, this information does not just exist in a temple. The, specific information is stored in the literature and part of it is known by the temple administrators so that the public must look for it to find out. Due to lack of references and time constraints, people often give up their intention. This happened on people in Denpasar where there are many temples that are often visited by Hindu people from various regions. Denpasar is the capital of Bali, where all activities are generally carried out. Hindu community usually pray in temples in Denpasar if they do not have the time to pray in their village. This is the main reason why the information of temples in Denpasar is necessary to be told. By using augmented reality (AR) technology this problem can be overcome. AR technology is able to project virtual objects as if they look real to the human eye. In this case, AR is used to display the temple model and information with interactive illustrations to help the community recognize the temple. Users only need to install the application on their smartphone device and scan the QR code provided, then the temple as an object shows up and information can be displayed immediately. This application applies multi-target markerbased AR so that each temple information is stored and ran on different markers. Based on testing using the blackbox method, the results show that the application can run smoothly on several different devices both in terms of device resolution, memory speed and processor.
Keywords: Balinese Temple, Augmented Reality, Unity, Vuforia, Android .
People in their community recognizes the temple as a holy place for the Hindu in carrying out their worship. People nowadays, going to the temple, not only making offerings or pray and then go home. They want to know who is in a temple, even many of them ask about what and who [1]. This is very important, since in carrying out prayers a person is obliged to know about what, who and how the origin of the place where he performs the worship. Generally, by knowing this information, people can pray with a clear concentration and direction of their thoughts towards God Almighty [1].
Sometimes, complete information about temples can not be found in a temple. Specific information is stored in the literature and part of it is known by the temple administrators so that the community must look for it to find out. Due to lack of references and time constraints, people often give up their intention. This happened on people in Denpasar where there are many temples that are often visited by Hindu people from various regions. This is the main reason why the information of temples in Denpasar is necessary to be told.
Based on journal “Application of Basic Balinesse Dance Using Augmented Reality On Android” [2] an application was developed to display a variety of information up to 21 Balinese dance movements with illustrations and information. From the application that serves to preserve Balinese culture using Augmented Reality (AR) technology, it is found that the application is interesting and is able to provide information in learning Balinese dance with a proportion of 70% of the 30 testers. In addition, in the journal "Application Development of Augmented Reality
Balinese Story 'I Gede Basur'" [3] an application was developed that implements the folklore of I Gede Basur as a medium of introduction and education. From the results of the application test that involved a number of participants, the application was considered to meet an average percentage of content test results of 80%, the media expert test was 98.33% and the user response test was 91.27%. Based on these two results, it is concluded that, augmented reality technology is very useful for providing information and increasing public interest in the introduction of local culture through introduction of interactive media.
Based on the problem and literature, it is concluded that the Augmented Reality (AR) application can be used in solving problems, in providing information on temples in Denpasar with an interactive introduction model. It can also be determined that the purpose of this journal is to build an augmented reality application for the introduction of temples in Denpasar by using case studies of Pura Agung Jagatnatha and Pura Luhur Candi Narmada.
The data collection process in this study was obtained from direct interviews with temple administrators and data from literature in the form of books. For Pura Agung Jagatnatha, the data was obtained from interviews with a temple organizer named I Gusti Lanang Rai accompanied with additional literature books obtained at the Denpasar Kabagkesra Office entitled "Pura Agung Jagatnatha Ring Denpasar" [4]. Meanwhile, for Pura Luhur Candi Narmada, data was obtained from a book entitled "Pura Luhur Candi Narmada Tanah Kilap [1]" which was obtained at the temple.
After data, problem representations and solutions to problems are obtained, the next step is software analysis according to the SDLC (System Development Life Cycle) method with a waterfall model. The waterfall model is a sequential software development model that consists of requirements analysis, design, implementation and testing stages. This model is widely used because it is relatively easy to manage and easy to understand. In this model each stage must be completed before moving on to the next stage [5]. The analysis of the software is described as follows,
a Software Definitions and Requirements
Applications built are using Augmented Reality (AR) technology. The type of AR to be used is multitarget marker-based AR because each temple is defined by one marker. The application is presented by displaying a 3D model of the object from the temple and the information right above the AR marker. In addition, the application is made on a platform based on the android operating system. In this case, the software that will be used in its development is the unity engine game software along with the AR development library software, namely Vuforia which is easy to use and has multiplatform support.
b Software Input and Output
The input and output of software are needed to be able to define the work system of the software to be designed. The input required from this application is a fidusial marker or QR code marker. Where this QR code will be used in the form of a scan object for the camera in determining the position where the AR object will be displayed. While the output of this application is the result of rendering a visual object that displays an illustration of the shape of the temple building along with temple information such as temple name, location, historical origin, rahina pujawali pura (praying schedule of the temple) and a list of buildings in the temple.
c Software Limitation
In software development, limitations are important to assess the extent to which the software can be used. The limitations of this software design include the application made using 2 case studies of temples in Denpasar, namely Pura Agung Jagatnatha and Pura Luhur Candi Narmada. This application only runs on an android operating system at least version 4.4 Kitkat and above.
Software design is the stage where the developer starts the software design to be able to meet each of the requirements from the previous analysis. The technical details of the design are discussed according to interest with various parameters and then the best design approach is selected for the product [5]. The form and design model for this application are as follows,
a Software Technology
Based on the previous system analysis, it was determined that the software design used multi-target marker-based Augmented Reality (AR) technology. Multi target marker-based AR is a method of detecting multiple image targets for multiple target objects simultaneously. The geometric arrangement of each image target is defined within a target. This makes it possible for each virtual object to have at least one image target to display when the target image is detected [6]. The development with this technology is realized using the Unity game engine software which is an integrated tool for creating 3-dimensional, 2-dimensional, virtual reality, and augmented reality application. In addition, using Vuforia or a software development kit (SDK) for AR using computer vision sources. The system overview model and the flowchart model for multi-target marker-based AR technology are described as follows,
BACK-END FRONT-END GED
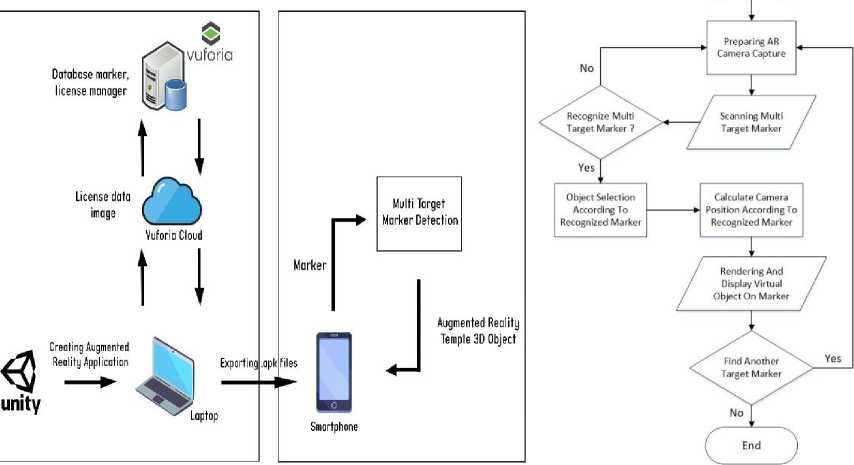
Figure 1. System Overview Model and Flowchart of Multi-Target Marker-Based AR Design
In this architecture, it is explained that the system is divided into 2 parts, namely the frontend and the back end. The back end defines the process of creating a system, the process starts with the creation of an augmented reality application on the unity engine game, which uses a target marker in the form of a QR code stored in the Vuforia marker database. The database is accessed via the cloud with a registered license manager. The result of this application is exported based on the .apk format which can be installed on the Android platform which leads directly to the front-end. On the front-end, users can use the application through the target marker scan which will display the AR temple object that has been designed.
While in the flowchart, multi target marker based AR described like a typical AR processing process. The initial step of the process begins with preparing the camera to track markers. After the marker is captured on the camera screen, the marker will be identified. If the marker is recognized, the process will continue to select the object according to the marker. For the selected object, its position will be adjusted from the location where the user points the camera towards the marker. If the position has been declared correct, then the object will be rendered and its position will be displayed right above the marker. The process will repeat as long as the user chooses to display other objects on different markers.
b Software Functional Model
The software functional model is used to determine the overall function of the application to be designed in the software development process. Use case diagrams are one of the modeling tools commonly used in describing the functionality of a system from the user's point of view (user) and is focused on the computerized process (automatic process) [6]. The use case diagram in developing this application is as follows,
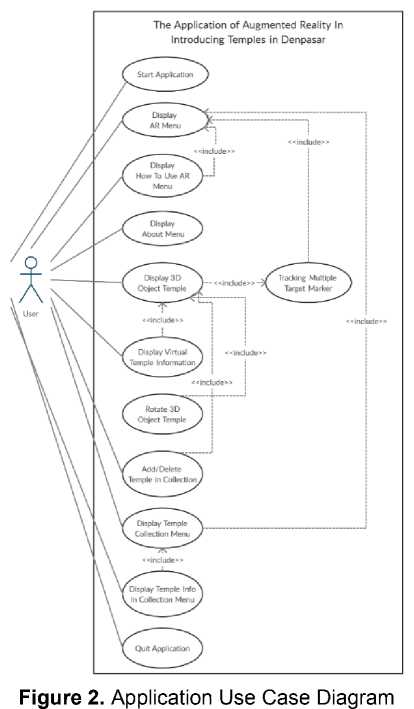
The use case diagram illustrates the process of each button or menu that can be accessed from the user. From all menus and buttons, there are a total of 11 different processes that can be accessed by users, including the process to start the application, display the AR menu, display the menu how to use AR, etc. From the use case diagram, the activity diagram can be determined. Activity diagrams describe the various activity flows in the system being designed, how each flow begins, the intersections that may occur, and how they end [6]. The activity diagram of this application is described as follows,
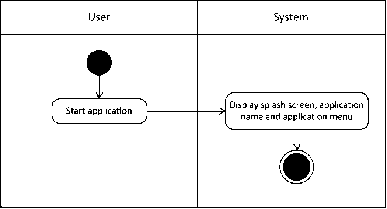
Figure 3. Activity Diagram Start Application Phase
The following activity diagram illustrates the process when the user accesses the application. In this case the system part will display the splash screen of the application, the name of the application as well as the main application menu which consists of the "Start AR", "About" and "Exit" buttons.
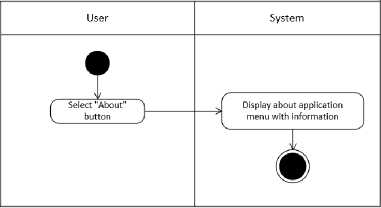
Figure 4. Activity Diagram About Menu Phase
This activity diagram describes the form of interaction when the user presses the "About" button. In this process the system / application will respond by displaying the "About" menu which contains information about the application and the developer of the application.
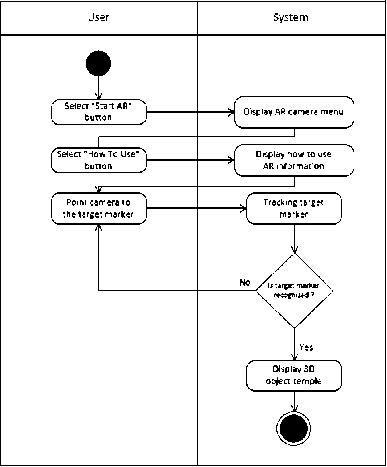
Figure 5. Activity Diagram Tracking AR Phase
The following activity diagram section contains the process when AR is used. When the AR starts, the application will display a camera containing a menu. The menu consists of buttons including "how to use" buttons, "collection" buttons and "exit" buttons. When the user presses the how to use button, the application will display a menu that says how to use the AR application. If the user points the camera at the marker, the application will immediately track the marker. According to the multi-target marker based algorithm, the 3D object will be displayed when the application recognizes the registered marker. Meanwhile, if not, there is no pretend 3D object displayed and the user must point the camera at another marker to start the redetection process.
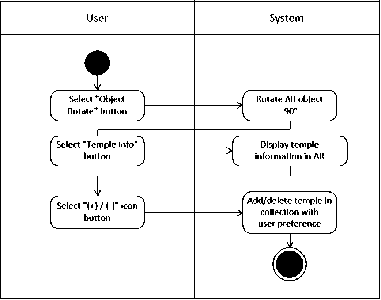
Figure 6. Activity Diagram On Display AR Phase
In Figure 6, the activity diagram explains the new button that is displayed when a marker is detected and a 3D object has been displayed. There are 3 buttons that can be used when the object has been detected which include the "Object Rotate" button to rotate object 90 degrees, the "Temple Info" button to display information about the temple such as the name of the temple, location, historical origin, rahina pujawali pura (praying schedule of the temple) also a list of buildings in the temple and the "(+)" / "(-)" or add/delete button icon to saved / deleted the name and temple information on the collection menu.
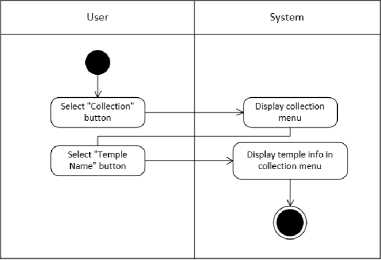
Figure 7. Activity Diagram Collection Menu Phase
Figure 7 is a process activity diagram that describes the collection menu. The collection menu contains information about list names of the temples that have been added previously. If one of the temple names is pressed, a new menu will appear containing information on the selected temple with its illustrations.
Figure 8. Activity Diagram Quit Application
Figure 8 shows the activity diagram when the user selects the "Exit" button which will direct the user to exit the application.
c Augmented Reality Marker Design
In developing a marker-based augmented reality application, a marker design is required to map the POI (point of interest) marker features that will be recognized by the application. In figure 9, there are 2 different markers used to identify each AR object, including the markers for Pura Agung Jagatnatha and Pura Luhur Candi Narmada. There are also dots in green depicting details of the marker target feature. The many details of each marker feature explains the accuracy of the marker to be able to render AR objects correctly. The accuracy of the points is rated with a 0-5 star rating which is processed through the computer vision algorithm of the vuforia library.

PURA AGUNG JAGATNATHA MARKER PURA LUHUR CANDI NARMADA MARKER
Figure 9. Augmented Reality Marker Design
The results and discussion section contains application implementation and testing of software that has been created. The sub-chapters that make up this section include,
This section explains the results of the implementation of the application in the form of a screenshot of the program. As for the menu and its parts,
-
a. Main Menu

Figure 10. Main Menu
-
b. About Menu

Figure 11. About Menu
-
c. How To Use Menu

Figure 12. How To Use Menu d. AR Object Temple Display

Figure 13. AR Object Temple Display
e. AR Object Info & Add/Delete Temple To Collection Display

Figure 14. AR Object Info & Add/Delete Temple To Collection Display
-
f. AR Object Rotate Display

Figure 15. AR Object Rotate Display
-
g. Collection Menu
h.

Figure 16. Collection Menu
Temple Collection Info

Figure 17. Temple Collection Info
Application testing is done using blackbox testing. Blackbox testing is a software testing method that only focuses on the functionality of the application without paying attention to how the process is carried out so that output is obtained. This test is done by trying to run the application on several different devices both in terms of device resolution, memory and processor. The test devices used include the Redmi Note 8 Pro, Redmi 9, Redmi 4X, MI A1 and MI A2. The tests are run by each different person. From the test process, the following data were obtained.
Table 1. Application Blackbox Testing
|
No |
Action |
Test Result |
Description |
Test Device |
|
1 |
Start the application |
Succeed |
Showing main menu of the application |
All test devices |
|
2 |
Press "About" button |
Succeed |
Showing “about” along with the information |
All test devices |
|
3 |
Press "Start AR" button |
Succeed |
Opening camera and AR menu |
All test devices |
|
4 |
Press "How to Use" button |
Succeed |
Showing menu about how to use |
All test devices |
|
5 |
Track the target marker |
Succeed |
Showing AR of the 3D temple object on the marker |
All test devices |
|
6 |
Press "Rotate Object" button |
Succeed |
Rotating AR of the 3D temple |
All test devices |
|
7 |
Press "Temple Information" button |
Succeed |
Showing AR information panel about the temple |
All test devices |
|
8 |
Press “+” or "-" button on temple information panel |
Succeed |
Adding/deleting the virtual temple in collection |
All test devices |
|
9 |
Press collection button |
Succeed |
Showing collection menu |
All test devices |
|
10 |
Press “temple” button on menu collection |
Succeed |
Showing temple information based on the selected temple button |
All test devices |
|
11 |
Press "Exit" button |
Succeed |
Running function to exit the application |
All test devices |
4. Conclusion
The Application of Augmented Reality in Introducing Temples in Denpasar was built with a purpose to solve the problem of lack of information on temples in Denpasar. The application used two case studies of temples in Denpasar, namely Pura Agung Jagatnatha and Pura Luhur Candi Narmada. This application technology applied multiple target markers based on augmented reality that receives input in the form of a QR code marker with an output in the form of AR 3D from several temples as objects. This software was created using the Unity game engine software along with the AR development library, namely Vuforia. The software design is designed using the SDLC (System Development Life Cycle) method with a waterfall model. From the application implementation, there are 11 functional process that can be interacted by the user. Based on testing using the blackbox method, the results show that the functional application can run smoothly on several different devices both in terms of device resolution, memory and processor.
References
-
[1] I. I. D. G. Mayadi, Pura Luhur Candi Narmada Tanah Kilap, Denpasar, 2007.
-
[2] N. P. S. Franza, A. O. Sudana and K. S. Wibawa, “Application of Basic Balinesse Dance Using Augmented Reality On Android,” Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology, vol. 90, 2016.
-
[3] I. G. G. R. Wiradarma, I. G. M. Darmawiguna and I. M. G. Sunarya, “Pengembangan Aplikasi Markerless Augmented Reality Balinese Story "I Gede Basur",” Jurnal Nasional Pendidikan Teknik Informatika (JANAPATI), vol. 6, 2017.
-
[4] I. N. Suprapta, Pura Agung Jagatnatha Ring Denpasar, Denpasar: Sanggar Sunari, 2010.
-
[5] S. Barjtya, A. Sharma and U. Rani, “A detailed study of Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) Models,” International Journal Of Engineering And Computer Science, vol. 6, 2017.
-
[6] A. K. O. Sudana, K. S. Wibawa and I. M. A. D. Tirtha, “Learning Media Of Baliese Script Writing Based On Augmented Reality,” Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology, vol. 90, 2016.
This page is intentionally left blank
324
Discussion and feedback