The Influence of Social Responsibility in Employee Satisfaction Mediated by Corporate Image and Organizational Commitment
on
Jurnal Ilmiah Akuntansi dan Bisnis
Vol. 15 No. 2, July 2020

AFFILIATION:
1,2Sekolah Tinggi Ilmu Ekonomi Indonesia Surabaya, Indonesia
*CORRESPONDENCE: wahidahwati@stiesia.ac.id
THIS ARTICLE IS AVAILABLE IN: https://ojs.unud.ac.id/index.php/jiab
DOI:
10.24843/JIAB.2020.v15.i02.p07
CITATION:
Wahidahwati, & Fauzi, A. N. C. (2020). the influence of social Responsibility in Employee Satisfaction Mediated by Corporate Image and Organizational Commitment. Jurnal Ilmiah Akuntansi dan Bisnis, 15(2), 234251.
ARTICLE HISTORY Received:
04 January 2020
Revised:
15 June 2020
Accepted:
27 June 2020
The Influence of Social Responsibility in Employee Satisfaction Mediated by Corporate Image and Organizational Commitment
Wahidahwati1*, Adilla Nanda Citra Fauzi2
Abstract
This study aimed to examine the effect of corporate social responsibility on employee satisfaction that was mediated by corporate image and organizational commitment. Type of research was quantitative research with survey methods conducted by distributing questionnaires. The sample in this study was obtained using a convenience sampling method, which was based on the availability of elements and the ease of obtaining them. The object of this research was employees of PT PJB UP Gresik, with a total of 170 respondents. The results of this study indicated that corporate social responsibility had a positive effect on employee satisfaction, corporate image, and organizational commitment. Other results found that corporate image and organizational commitment had a positive effect on employee satisfaction. The final result found that corporate image and organizational commitment succeeded in mediating the effect of corporate social responsibility on employee satisfaction.
Keywords: Corporate social responsibility, employee satisfaction, corporate image, organizational commitment.
Introduction
Companies must be able to run in a balanced manner of all aspects that can support the survival of the company, both in terms of companies’ finance, the interests of shareholders, as well as the interests of the general public (Ferreira & de Oliveira, 2014). One of the important aspects of companies that run the business today is corporate social responsibility for the community, especially for the community around the company.
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) is the company's ongoing commitment to behave ethically and contribute to economic development while still improving the quality of life of workers and their families, as well as the communities surrounding the company and society as a whole. CSR is not only an effort to show an organization's concern on social and environmental issues, but also can be a supporter of the realization of sustainable development by balancing economic aspects and social development supported by environmental protection (Marnelly, 2012). The Triple Bottom Line theory explains three
components known as 3P that companies must pay attention to implementing the concept of CSR, namely profit, people, planet (Purwanto, 2011). The Triple Bottom Line Theory concept implies that companies must prioritize stakeholder interests.
Pearce, John A. & Robinson, (2009) divide stakeholders into 2 parts: internal stakeholders, namely shareholders and employees of the company and external stakeholders, namely individuals or groups of people who have an impact on the activities of the company or the corporate social responsibility towards them. The most important internal stakeholders in implementing CSR are employees. Employees as those who carry out orders from company management, it is very possible that company employees will also enjoy the company's CSR programs.
Employees' perceptions arising from the company's CSR practices, one of which is employee satisfaction. In other words, job satisfaction is the result of employees' perceptions of how well their work provides elements that are considered important Low et al. (2017). CSR requires activities that are directly related to the physical and psychological work environment of employees, because this can be an element expected by employees. If CSR practices are included in the company, it results in employee job satisfaction Low et al. (2017). Employee transparency by involving them in the company's strategy makes them satisfied (Walton, 2010). Employees will continue to make achievements that will benefit the company, so that the company will always provide feedback in accordance with what has been done by their employees. Rupp et al. (2013), states that employees are morally concerned with corporate social responsibility and fairness, this is one mechanism that explains employee attitudes and behavior. Aguilera et al. (2007) also states that employees care about socially responsible actions because they feel they can share the same social values with the company.
The phenomenon occurs that PT PJB which is the object of this study managed to get a Gold PROPER award from the Ministry of Environment in 2017. In the same year through the 2017 Indonesia GCG Award PT PJB won platinum. 2017 and achieved TOP CSR in 2018. The phenomenon that shows the success of PT PJB certainly shows the company's commitment and good corporate image. The above phenomenon encourages this research.
This research was motivated by the research of Barakat et al. (2016b) in Brazil, with the object of employee research in 381 companies in Brazil entitled "The Influence of Corporate Social Responsibility on Employee Satisfaction". In addition, this study was also motivated by the research of Hamdani & Awatara (2016), with the object of employees in companies in the city of Surakarta. This study has differences with previous research, because in this study using two mediating variables, namely corporate image and organizational commitment.
The purpose of this study is to obtain empirical evidence that corporate social responsibility influences employee satisfaction mediated by corporate image and organizational commitment. The expected contribution of this research is to develop and confirm stakeholder theory, especially regarding the importance of employee perceptions of CSR practices carried out by the company. The results of this study are also expected to provide input to the company to prioritize concern for the interests of the company's stakeholders in order to ensure the survival of the company.
Stakeholder Theory states that the main essence of business lies in building relationships and creating value for all its stakeholders Freeman & Dmytriyev (2017)
even though industry has different compositions depending on the business model being run. Stakeholder theory provides something new in defining companies in a social and more human form, and of course also gives companies awareness about ethical social responsibility.
CSR can be a corporate strategy that will help meet the interests of stakeholders in the context of non-financial information. The formulation of key stakeholders along with relevant issues will greatly assist the company in formulating corporate social responsibility programs, or in other words stakeholder theory can be a guide for companies to formulate CSR strategies, policies and programs. It also can bring a positive influence in the company's foundation internally, namely the participation of employees in the implementation of CSR that can increase employee organizational commitment. From two positive sides that can be taken from the implementation of CSR can increase employee job satisfaction, so that it can be evidence that stakeholder theory can be a binding of all elements that strengthen the foundation of a company.
The legitimacy Theory comes from the concept of legitimacy expressed by Dowling & Pfeffer (1975), which states that legitimacy is important for an organization, boundaries emphasized by social norms and values, and reactions to those limits. According to Purwanto, (2011) the theory of legitimacy states that companies must continuously provide confidence that the activities or activities carried out in accordance with the restrictions and norms that apply in the society in which the company stands.
Legitimacy is as an appropriate strategy to build positive community perceptions and position yourself in the community environment in accordance with the norms prevailing in society (Purwanto, 2011). Legitimacy theory is used as the foundation of a company's relationship with the community, O’Donovan, (2002) argues that legitimacy can be seen as something given by the community to the company and something that companies want or look for from the community. Thus, legitimacy has benefits in supporting the survival of a company, so that it can run without conflict in the community or in the corporate environment. The development of the Corporate Social Responsibility program is a way that can be taken to provide a positive contribution to the community, so that the community and the environment around which the company operates can accept and not blame the existence of the company.
This study develops seven hypotheses to test the effect of CSR on employee satisfaction through corporate image and organizational commitment. The first hypothesis examines the effect of CSR on employee satisfaction. Rahman et al. (2016), states that when employees have a positive attitude towards CSR, they tend to be more satisfied with the company where they work and can lead to a sense of pride in their company. Kartini (2009) which states that CSR activities one of which is voluntary workers (Community Volunteering) can increase employee satisfaction. This can happen if the company can make CSR as an ethical commitment in meeting the needs of employees so that it will give satisfaction to employees. Barakat et al. (2016), Raihan & Al Karim (2017), Agler (2013) also stated that, corporate CSR has a positive and significant relationship to employee satisfaction
H1 : Social responsibility has a positive effect on employee satisfaction
The second hypothesis predicts that social responsibility (CSR) affects the corporate image. Yenti (2013), conducted a research on the effect of the implementation of corporate social responsibility on corporate image. The results of this study note that social dimensions and environmental dimensions have a positive and
significant effect on corporate image. This is also supported by research conducted by Kartikasari et al. (2017) which also states that the three dimensions of CSR namely economic, environmental, and social have a positive and significant influence on the corporate image. A research by Al Mubarak et al. (2018), argues that the four components of CSR, namely economics, law, ethics, and philanthropy have a significant influence on the corporate image. Kartikasari et al. (2017), Maruf (2013) and Prasiska et al. (2017), Famiyeh et al. (2016) also confirms that there is a positive and significant influence between CSR and company reputation in terms of product and service quality, management performance and company attractiveness. This study also provides information to managers not to see CSR activities as a waste or just a cost to the company, but as a potential that can enhance the reputation of the company and the overall company.
H2 : Social responsibility has a positive effect on the corporate image
The third hypothesis predicts the effect of social responsibility on organizational commitment. Employees are committed to their organization if they recognize that their company implements CSR activities. As a result, it can improve the performance of employees (Arslan & Roudaki 2017). Nejati & Ghasemi (2013), Hamdani & Awatara (2016), Prutina (2016), Huang (2016) also emphasized that employees showed higher commitment when working in socially responsible companies
H3 : Social responsibility has a positive effect on organizational commitment.
The fourth hypothesis predicts the influence of corporate image on employee satisfaction. Corporate image is formed prior to the company's reputation, or it can be said the corporate image as the foundation for the formation of a positive corporate reputation. If the positive reputation of the company has been formed, it is very certain that a good corporate image has existed before the establishment of that reputation. Therefore, the effect of company reputation on employee satisfaction can help in formulating hypotheses the influence of corporate image on employee satisfaction can be proven through research Alniacik et al. (2011) which states that company reputation has a positive and significant effect on employee satisfaction directly. Agree with Alniacik et al. (2011), Tanwar & Prasad (2016) the results of the study also showed that organizational reputation influences job satisfaction and is the second most significant factor of the company reputation factors in the study.
H4 : Corporate image has a positive effect on employee satisfaction.
The fifth hypothesis predicts the effect of organizational commitment on employee satisfaction. Hartono & Setiawan (2013) and Parimita et al. (2017) find evidence of a positive and significant influence on organizational commitment to employee job satisfaction. In addition, the research of Taufik et al. (2018), Parimita et al. (2014), Arifah & Romadhon (2015), also find a positive influence on organizational commitment to employee job satisfaction caused by employee normative commitment where employees work with all their abilities and the belief that what has been done is in accordance with the provisions so to move to another company is unethical for that employee.
H5 : Organizational commitment has a positive effect on employee satisfaction.
The sixth hypothesis predicts the effect of social responsibility (CSR) on employee satisfaction mediated by the corporate image. Barakat et al. (2016b) also reveal that CSR-oriented actions taken by companies will lead to a better organizational image, so that it will lead to greater employee satisfaction. Barakat et al. (2016b) also
show a positive and significant influence of CSR on job satisfaction when mediated by corporate image. Therefore, with some of the findings above can be used as a benchmark for the relationship between CSR and employee satisfaction mediated by the corporate image.
H6 : Social responsibility has a positive effect on employee satisfaction mediated by the corporate image.
The relationship of corporate social responsibility, job satisfaction, and organizational commitment is shown in research of Tuzcu (2014), in this study it is explained that the company can meet the emotional and social expectations of employees, can increase organizational commitment and job satisfaction, although in this context organizational commitment has not been explained as mediating the relationship of CSR with job satisfaction. But it can help in the formulation of the hypothesis this time.
The influence of CSR on employee satisfaction mediated by organizational commitment cannot be found at prior research, but the researcher tries to strengthen the formulation of this hypothesis by showing the relationship between CSR with organizational commitment and then the relationship between employee satisfaction with organizational commitment. In the formulation of the previous hypothesis it has been shown that among previous studies it has been found that CSR has a positive and significant influence on employee satisfaction directly, as well as organizational commitment also has a positive and significant direct effect on employee satisfaction. This can be used as a reference that organizational commitment can be used as a mediator of the relationship between CSR and employee satisfaction.
H7: Social responsibility has a positive effect on employee satisfaction mediated by organizational commitment.
Research Method
This research was conducted at one of the companies that won the 2017 TOP CSR, namely PT Pembangkit Jawa-Bali (PJB). The TOP CSR 2017 is an assessment and awarding activity for companies operating in Indonesia, which are considered to have run the best CSR / PKBL / Community Development programs. A total of 117 leading companies in Indonesia from various industrial sectors took part in the 2017 TOP CSR activity with the theme "Aligning CSR to Business Strategy" in Jakarta on April 5, 2017. This study only took 1 (one) best company as the winner of the 2017 TOP CSR in the category of Local People Development through Community Academy, namely PT. Pembangkit Jawa-Bali as a place of observation.
The data used in this study were primary data obtained directly from the original source. The primary data were collected through a survey method by distributing 200 questionnaires distributed directly to employee PT PJB Gresik Generating Unit as research objects. Of the 200 questionnaires, only 170 questionnaires could be processed in this study, as many as 17 questionnaires were declared not returned and 13 questionnaires were declared as damaged data due to incomplete questionnaire filling. The variables used in this study were Corporate Social Responsibility, Employee Satisfaction, Corporate Image and Organizational Commitment. This research was measured using indicators outlined in the questions in the questionnaire adopted from several studies as shown in Table 1.
The data were processed by using Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) analysis. SEM is a multivariate analysis that can analyze relationships between variables in a more complex way. This technique allows researchers to examine the relationship between latent variables with manifest variables (measurement equations), relationships between one latent variable with other latent variables (structural equations), as well as describing research errors (Sarjono & Julianita, 2015). This study used SEMPLS-based variants which are assisted by the SmartPLS 3.0 application.
Result and Discussion
Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) analysis in this study was conducted in two stages, namely the measurement model analysis (outer model) and structural model analysis (inner model).
Measurement Model (Outer Model), in this analysis, measurement analysis was carried out on indicators that build the construct of corporate social responsibility, employee satisfaction, corporate image, organizational commitment. Assessing the outer model with PLS, there were three criteria that must be met, namely convergent validity, discriminant validity (in the form of AVE), and composite reliability. Figure 1 shows the overall correlation of each variable:
In Figure 1. which presents a structural model, all construct correlations have a value of more than 0.700, but not the correlation value between the indicators OC7 and OC8 with the organizational commitment variable with a value of 0.062 for the OC7 correlation and 0.289 for the OC8 correlation. This shows that the indicator is not significant in building the organizational commitment construct, so it must be eliminated. After conducting re-analysis on the measurement model by eliminating two indicators that have a low correlation to the relevant variables, the indicators are OC7 and OC8, can be seen in Figure 2.
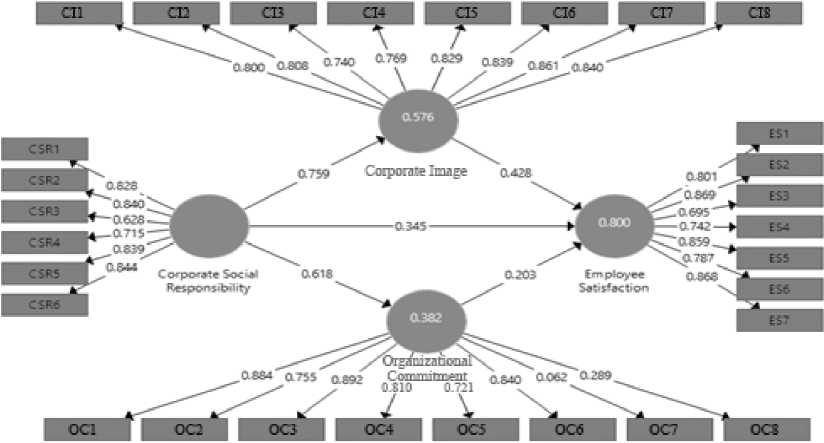
Figure 1. Full Model Structural (Pre Elimination)
Source: Processed Data, 2019
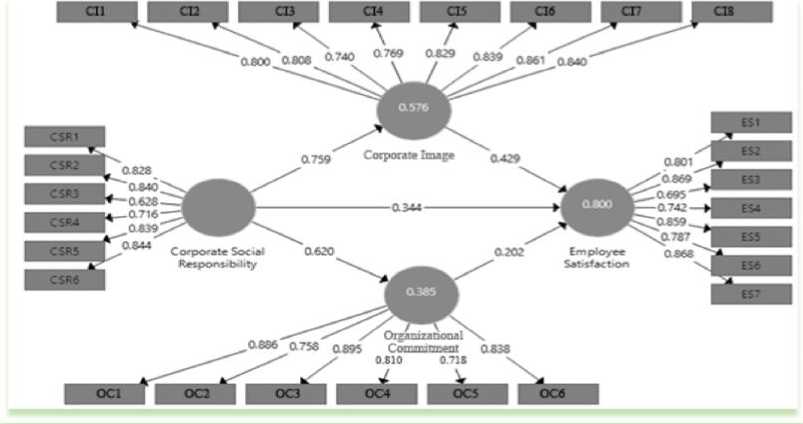
Figure 2. Full Model Structural (Post Elimination)
Source: Processed Data, 2019
In Figure 2. shows all indicators have a correlation of more than 0.70 to each variable concerned. High or low validity of an indicator shows the extent to which the indicator can explain the variable in question.
Convergent Validity. Test of convergent data validity in this study using software SmartPLS version 3.0 with the rule of thumb used for convergent validity is outer loading > 0.70, communality > 0.50, and Average Variance Extracted (AVE) > 0.50. Of all the indicators there are 2 indicators that still have a loading factor below 0.70, namely the CSR3 indicator with a loading factor value of 0.628 and ES3 with a loading factor of 0.695. Ghozali (2015) states that the value of outer loading can be tolerated up to 0.50 and if it is below 0.50 new deletion is carried out on the related indicators. From these recommendations, the researchers finally decided to maintain the CSR3 and ES3 indicators to be included in the next analysis. Besides seeing the loading factor, it can also be seen by looking at the average variance extracted (AVE) value. A construct is said to have convergent validity if it has a value of AVE > 0.50. The AVE value can be seen in Table 1.
From the average variant extracted (AVE), none of the AVE values of latent variables in this study showed a value < 0.50. This shows that each construct has a good validity value from each dimension. For AVE the highest value is in the organizational commitment construct (0.672) and the lowest is in the CSR construct (0.619). Discriminant validity is related to the principle that verifiers on different variables should not be highly correlated.
Table 1. Value of Average Variance Extracted (AVE)
|
Average Variance Extracted (AVE) |
Details | |
|
Corporate Image |
0.659 |
Valid |
|
CSR |
0.619 |
Valid |
|
Employee Satisfaction |
0.649 |
Valid |
|
Organizational Commitment |
0.672 |
Valid |
Source: Processed Data, 2019
Table 2. Value of AVE and Root of AVE
|
Average Variance |
Root of Average Variance | |
|
Extracted (AVE) |
Extracted (AVE) | |
|
Corporate Image |
0.659 |
0.812 |
|
CSR |
0.619 |
0.787 |
|
Employee Satisfaction |
0.649 |
0.805 |
|
Organizational Commitment |
0.672 |
0.820 |
Source: Processed Data, 2019
In the discriminant validity there is an evaluation of the discriminant validity through the cross-loading value, with the acceptance criteria of cross loading value > 0.70 in one variable. The cross loading value shows that all have values > 0.70 (see appendix 2), it can be concluded that each indicator that constructs latent variables has a cross loading value that is different from indicators on other variables, and has a high cross loading value in its own construct. After evaluating the discriminant validity through cross loading values, it was still necessary to evaluate by comparing the value of the AVE root with the correlation of latent variables, and recommended the AVE root must be more than the correlation value of the latent variable in order to meet the
discriminant validity criteria. The comparison between AVE roots and latent variable correlation values illustrated in Table 2.
The root value of the average variance extracted (Table 2.) is greater or higher than the correlation value of the latent variable (Table 3.). So, it can be concluded that the dimensions used in this study have met the criteria of discriminant validity that have been set.
Reliability, in addition to the validity test also carried out a reliability test aimed at showing the consistency, accuracy, and accuracy of a measuring instrument in making measurements. The reliability test was carried out using two methods, namely the Cronbach's alpha method and composite reliability. The rule of thumb for the Cronbach's alpha value must be greater than 0.600 while for composite reliability it must be greater than 0.700. The Cronbach's alpha value is in accordance with predetermined criteria which is more than 0.600 for each latent variable. The value of the Composite variable of each latent variable also shows the value above the predetermined criteria, which is > 0.700 (Table 4.). Structural Model (Inner Model), discusses the correlation of each independent variable to the dependent variable. Structural models will also show the indirect effect between independent and dependent variables through the mediating role of intervening variables.
Table 3. Correlation of Latent Variables
|
Corporate CSR Employee Organizational Image Satisfaction Commitment | |
|
Corporate Image CSR Employee Satisfaction Organizational Commitment |
1.000 0.759 1.000 0.859 0.796 1.000 0.833 0.620 0.774 1.000 |
Source: Processed Data, 2019
Table 4. Cronbach’s Alpha Value and Composite Reliability
|
Cronbach's Alpha |
Composite Reliability |
Details | |
|
Corporate Image |
0.926 |
0.939 |
Reliable |
|
CSR |
0.874 |
0.906 |
Reliable |
|
Employee Satisfaction |
0.908 |
0.928 |
Reliable |
|
Organizational Commitment |
0.901 |
0.924 |
Reliable |
|
Source: Processed Data, 2019 | |||
The R-square value of each endogenous (dependent) variable in this study, the construct of corporate image has a value of R2 0.576 which means that the CSR variable as an independent variable is able to explain the corporate image variable by 57.6%. In addition, CSR can also explain employee satisfaction by 80%, and explain the variable organizational commitment by 38.5% (Table 5.). In addition to viewing the R-square value, the PLS model was evaluated using the Q-square predictive relevance to measure how well the observed values generated by the model and estimation parameters.
The result of Formula (1) shows the Q-square value of 0.948, and it can be seen that the value > 0 and close to 1. This shows that 94.8% of the variation in employee satisfaction variables is explained by the variables used in the model. Whereas 5.2% is explained by other factors which are outside this research model. Thus, from these results the research model can be stated to have good goodness of fit.
Corporate social responsibility affects employee satisfaction. The results show that CSR has a positive effect on employee satisfaction. Because it has a significance value < level value of the test that is equal to 0.000 (0.000 < 0.05) so the first hypothesis is accepted. These results are in line with Agler (2013), Barakat et al. (2016), which states that, corporate CSR has a positive and significant relationship to employee satisfaction. Besides that, Raihan & Al Karim (2017) also states that there is a positive and significant influence of CSR on employee satisfaction. The involvement of companies in CSR activities can build perceptions when companies try to develop and carry out social responsibility, company employees will also feel satisfied with the implementation of social responsibility. This is because they feel identified as being part of the company with social care. In addition, employee satisfaction with CSR carried out by their company can be built if the CSR is also carried out on the company's employees, by giving the rights that they must get in the implementation of work for the company.
Corporate social responsibility affects the corporate image. The results show that CSR has a positive and significant effect on corporate image. Because it has a significance value < level value of the test that is equal to 0.000 (0.000 < 0.05) so the second hypothesis is accepted. These results are in line with previous studies by Kartikasari et al. (2017), Maruf, (2013), Prasiska et al. (2017), Famiyeh et al., (2016) which reveal a positive and significant influence among aspects of CSR in the study of the corporate image.
Table 5. Value of R-square
|
R Square |
Details | |
|
Corporate Image |
0.576 |
Strong |
|
Employee Satisfaction |
0.800 |
Strong |
|
Organizational Commitment |
0.385 |
Strong |
|
Source: Processed Data, 2019 | ||
Table 6. Path Coefficient (Mean, STDEV, T Statistics)
|
T Statistics (|O/STDEV|) |
P Values |
Details | |
|
CI-> ES |
4.496 |
0.000 |
Significant |
|
CSR -> CI |
13.966 |
0.000 |
Significant |
|
CSR -> ES |
3.863 |
0.000 |
Significant |
|
CSR -> OC |
8.353 |
0.000 |
Significant |
|
OC -> ES |
2.685 |
0.008 |
Significant |
Source: Processed Data, 2019
CSR is a way to form positive perceptions in society so that it will form a positive corporate image as well. CSR provides a variety of positive things that can bring the company to their goals. CSR policies and programs can be used as a means of collecting and realizing the company's attention to the environment. Corporate social responsibility affects organizational commitment. The results show that CSR has a positive and significant effect on organizational commitment. Because it has a significance value < level value of the test that is equal to 0.000 (0.000 < 0.05) so the third hypothesis is accepted. These results support previous research conducted by Hamdani & Awatara (2016), Prutina (2016), Huang (2016) and Nejati & Ghasemi (2013) who also state that CSR had a positive and significant effect on organizational commitment.
On the social implications that have been found, displaying the firmness that employees will show high commitment when working in companies with good social responsibility. Corporate image influences employee satisfaction. The results show that corporate image has a positive and significant effect on employee satisfaction. Because it has a significance value < level value of the test that is equal to 0.000 (0.000 < 0.05) so the fourth hypothesis is accepted. These results reinforce previous research conducted by Alniacik et al. (2011) which state that corporate image has a positive effect on job satisfaction (employee satisfaction). The better and high corporate image will affect the increase in employee satisfaction (employee satisfaction). The presence of a positive corporate image will immediately give a good effect for employees. As happy as an inseparable part of the company, employees will be directly related to the company's development towards a positive thing that will be made proud and satisfied if the company can form a good image in the eyes of the community. Employees will be satisfied to be part of a company with a good corporate image in the eyes of the community and other stakeholders.
Organizational commitment has a positive effect on employee satisfaction. The results show that organizational commitment has a positive and significant effect on employee satisfaction. Because it has a significance value < level value of the test that is equal to 0.008 (0.000 < 0.05) so the fifth hypothesis is accepted. In a previous study conducted by Hartono & Setiawan (2013), Taufik et al. (2018) explain that there is a significant positive effect between organizational commitment to job satisfaction. In theory, high organizational commitment due to the ability of employees to complete their work properly with all the capabilities they have and with the conditions of a very comfortable work environment can build satisfaction within employees. Employees with high organizational commitment tend to be reluctant to leave their company. Job satisfaction will be better if in a company the employees have high organizational commitment, so they can work together well and comfortably.
Table 7. Indirect Effect
|
T Statistics (|O/STDEV|) |
P Values |
Details | |
|
CSR-> CI -> |
4.070 |
0.000 |
Significant |
|
CSR ->OC - |
2.326 |
0.020 |
Significant |
Source: Processed Data, 2019
Based on indirect effects (Table 7.) which explain the magnitude of T-statistics and p values that can be used to measure the support of hypotheses, can be obtained as follows:
Corporate social responsibility has an effect on employee satisfaction mediated by the corporate image. The results show that corporate social responsibility has a positive and significant effect on employee satisfaction with the corporate image as a mediator. Because it has a significance value < level value of the test that is equal to 0.000 (0.000 < 0.05) so the sixth hypothesis is accepted. Maria (2014) states that the formation of CSR will increase employee job satisfaction because the company has been able to improve the corporate image. The corporate image as mediating the relationship between CSR and employee satisfaction is also strengthened by the results of previous studies conducted by Barakat et al. (2016) which reveal that the existence of CSR-oriented activities carried out by the company would lead to a better corporate image, thereby increasing employee job satisfaction. The mediating role given by the corporate image can help the relationship between CSR and employee satisfaction. That is, if the corporate image increases due to or caused by CSR run by the company, then the improvement of the corporate image should also increase employee satisfaction with their organization.
Corporate social responsibility has an effect on employee satisfaction mediated by organizational commitment. The results show that corporate social responsibility has a positive and significant effect on employee satisfaction with organizational commitment as a mediator. Because it has a significance value < level value of the test that is equal to 0.020 (0.000 < 0.05) so the sixth hypothesis is accepted. Corporate social responsibility can be an impetus for the formation of organizational commitment for company employees. Companies with CSR practices can make their employees continue to side with the company and maintain its membership in the organization. Employees with strong organizational commitment tend to get satisfaction at their jobs and companies. Therefore, the higher the CSR practices carried out by the company, can form employee commitment that can increase the level of perceived satisfaction. Although no literature has been found that shows the mediating role of organizational commitment on the influence of CSR on employee satisfaction, the results of the study provide evidence that there is an indirect effect of CSR on employee satisfaction through organizational commitment.
Table 8. Direct Effect Test Results
|
Original Sample (O) |
Sample Mean (M) |
Standard Deviation (STDEV) |
T Statistics (|O/STDEV|) |
P Values | |
|
CSR -> ES |
0.796 |
0.800 |
0.026 |
30.514 |
0.000 |
Source: Processed Data, 2019
Analysis of Mediation Effects. In testing the mediation effect, the output of parameter of the significance test is seen in the total effect table not in the coefficient table. But before testing the mediation effect, it must be proven first that the main effect (the influence of CSR on employee satisfaction) is significant, to meet the rules. Baron & Kenny, (1986).
As Table 8. has shown, the direct effect of CSR on employee satisfaction is significant with a T-statistics value of 30.514 with p values < 0.01. Therefore, it can be continued by testing on the mediating effect.
As can be seen that the value of T-statistics in the path coefficient (Table 8.) shows the same value as the T-statistics in the total effect table (Table 9.), but has different aims and objectives. The T-statistics in the path coefficient table (Table 8.) are used to determine the path coefficient between variables in the study. Whereas the T-statistics in the total effect table (Table 9.) can be used to help determine the mediating effects contained in this study. As is known in this study there are two mediating variables that provide a mediating effect on the influence of CSR on employee satisfaction, namely corporate image and organizational commitment.
For mediation by corporate image, it can be seen that the value of T-statistics on the influence of CSR on corporate image is 13.966 > 1.96 with a significance level < 0.01. And the influence of corporate image on employee satisfaction 4.496 with a significance level < 0.05. So, it can be concluded that the corporate image mediates partially (partial mediating) on the influence of CSR on employee satisfaction.
For mediation by organizational commitment, it can be seen that the value of T-statistics on the influence of CSR on corporate image 8.353 > 1.96 with a significance level < 0.01. And the influence of corporate image on employee satisfaction 2.685 with a significance level < 0.05. So, it can be concluded that organizational commitment partially mediates on the influence of CSR on employee satisfaction.
That is, the corporate image as a mediating variable in this study succeeded in mediating the relationship between CSR and employee satisfaction. Similarly, organizational commitment also succeeded in mediating the relationship between CSR and employee satisfaction. This shows that when CSR policies and activities in a company will have an impact on the corporate image, and this impact will indirectly affect employee satisfaction. As well as organizational commitment, when CSR has an influence on employee organizational commitment, then this will also affect employee satisfaction indirectly.
So, it is expected that the company or organization will always improve the implementation of CSR activities that will have a positive impact on all aspects of the company, and most importantly, ensure the survival of the company.
Table 9. Mediation Effect Test Results
|
Original Sample |
Sample Mean |
Standard Deviation |
T Statistics |
P Values | |
|
CI -> ES |
0.429 |
0.438 |
0.095 |
4.496 |
0.000 |
|
CSR -> CI |
0.759 |
0.760 |
0.054 |
13.966 |
0.000 |
|
CSR -> ES |
0.344 |
0.335 |
0.089 |
3.863 |
0.000 |
|
CSR -> OC |
0.620 |
0.626 |
0.074 |
8.353 |
0.000 |
|
OC -> ES |
0.202 |
0.206 |
0.075 |
2.685 |
0.008 |
Source: Processed Data, 2019
Conclusion
Referring to the results of testing and discussion, it was concluded that Corporate Social Responsibility, company image and organizational commitment had a positive effect on employee satisfaction. Likewise, Corporate Social Responsibility had a significant positive effect on company image and organizational commitment. Therefore, the company must maintain and develop CSR practices that can support the continuity and sustainability of the company's life and as a key to establishing good relationships between the company and the environment and society. The results of intervening variables indicated that corporate image and organizational commitment can mediate the influence of corporate social responsibility on employee satisfaction.
This research faced several limitations that could affect the conditions of the research conducted. The limitations include: First, there were still answers to the questionnaire that were inconsistent according to the observations of researchers. This could be due to respondents being less careful about the statements that were so inconsistent in answering the questionnaire. Therefore, it is expected that further research can make sentences in questionnaires that are easily understood by respondents. secondly, the object of research was only focused on one of the companies that won the 2017 CSR TOP, so it was still not enough to describe the condition of other companies' CSR in other categories that also won the 2017 CSR TOP. Therefore, for further research it is expected to use companies TOP CSR winners as a population, should take several companies from several categories to be the object of research, so that respondents from several sample companies and are expected to provide competent results. Finally, there were several variables that affect employee satisfaction that had not been included in this study, so it is hoped that further research considers other variables such as organizational culture and work motivation.
References
Agler, J. R. (2013). Employee satisfaction as it relates to corporate social responsibility: a quantitative study [University of Phoenix]. In Published by ProQuest LLC. https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9781107415324.004
Aguilera, R. V., Rupp, D. E., Williams, C. A., & Ganapathi, J. (2007). Putting the S Back in Corporate Social Responsibility. Academy of Management Review.
https://doi.org/10.5465/amr.2007.25275678
Al Mubarak, Z., Ben Hamed, A., & Al Mubarak, M. (2018). Impact of corporate social responsibility on bank’s corporate image. Social Responsibility Journal, 15(5), 710– 722. https://doi.org/10.1108/SRJ-01-2018-0015
Alniacik, U., Cigerim, E., Akcin, K., & Bayram, O. (2011). Independent and joint effects of perceived corporate reputation, affective commitment and job satisfaction on turnover intentions. Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2011.09.139
Arifah, D. A., & Romadhon, C. (2015). Pengaruh Komitmen Organisasi, Komitmen Profesional Dan Gaya Kepemimpinan Terhadap Kepuasan Kerja Dengan Motivasi Sebagai Variabel Intervening. Journal of Visual Languages & Computing, 2(1), 357369.
Arslan, M., & Roudaki, J. (2017). Corporate Governance, Socio-Economic Factors and Economic Growth: Theoretical Analysis. International Journal of Accounting and Financial Reporting, 7(1), 311. https://doi.org/10.5296/ijafr.v7i1.11279
Barakat, S. R., Isabella, G., Boaventura, J. M. G., & Mazzon, J. A. (2016). The influence of corporate social responsibility on employee satisfaction. Management Decision. https://doi.org/10.1108/MD-05-2016-0308
Famiyeh, S., Kwarteng, A., & Dadzie, S. A. (2016). Corporate social responsibility and reputation: some empirical perspectives. Journal of Global Responsibility, 7(2), 258–274. https://doi.org/10.1108/jgr-04-2016-0009
Ferreira, P., & de Oliveira, E. R. (2014). Does corporate social responsibility impact on employee engagement? Journal of Workplace Learning.
https://doi.org/10.1108/JWL-09-2013-0070
Freeman, R. E., & Dmytriyev, S. (2017). Corporate Social Responsibility and Stakeholder Theory: Learning From Each Other. Symphonya. Emerging Issues in Management, 1, 7. https://doi.org/10.4468/2017.1.02freeman.dmytriyev
Hamdani, A., & Awatara, I. G. P. D. (2016). Pengaruh Tanggung Jawab Sosial Perusahaan terhadap Komitmen Organisasi dan Kinerja Karyawan. Jurnal Aplikasi Manajemen, 14(2), 201-208. https://doi.org/10.18202/jam23026332.14.2.02
Hartono, B., & Setiawan, R. (2013). Pengaruh Komitmen Organisasional Terhadap Kepuasan Kerja Karyawan Paparonâs Pizza City of Tomorrow. Agora, 1(1), 1–8.
Huang, C.-C. (2016). Employees’ Perception of Corporate Social Responsibility: Corporate Volunteer and Organizational Commitment. International Business Research. https://doi.org/10.5539/ibr.v9n9p142
Kartikasari, N., Hidayat, K., & Yulianto, E. (2017). Pengaruh Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) Terhadap Citra Perusahaan Multinasional (Survei pada Konsumen Unilever di Indonesia Mengenai Program âProject Sunlightâ PT Unilever Indonesia Tbk.). Jurnal Administrasi Bisnis S1 Universitas Brawijaya, 44(1), 8–16.
Kartini, D. (2009). Corporate social responsibility: transformasi konsep sustainability management dan implementasi di Indonesia. Refika Aditama.
Low, M. P., Ong, S. F., & Tan, P. M. (2017). Positioning ethics and social responsibility as a strategic tool in employees’ affective commitment. Annals in Social Responsibility. https://doi.org/10.1108/asr-12-2016-0013
Marnelly, R. (2012). CORPORATE SOCIAL RESPONSIBILITY (CSR): Tinjauan Teori dan Praktek di Indonesia. Jurnal Aplikasi Bisnis, 2(2), 49–59.
https://www.academia.edu/30213987/Akuntansi_Pertanggungjawaban_sosial_Cor porate_sosial_Responbilitty_
Maruf, A. A. (2013). Corporate Social Responsibility And Corporate Image. Transnational Journal of Science and Technology, 3(8), 29–49.
https://doi.org/10.4324/9781351282642
Nejati, M., & Ghasemi, S. (2013). Corporate social responsibility and organizational commitment. Journal of Global Responsibility, 4(2), 263–275.
https://doi.org/10.1108/jgr-01-2013-0001
O’Donovan, G. (2002). Environmental disclosures in the annual report: Extending the applicability and predictive power of legitimacy theory. Accounting, Auditing & Accountability Journal, 15(3), 344–371.
https://doi.org/10.1108/09513570210435870
Parimita, W., Larasati, D., & Handaru, A. W. (2014). Pengaruh Motivasi Dan Komitmen Organisasional Terhadap Kepuasan Kerja Pada Pegawai Tata Usaha (Studi pada Tujuh Fakultas di Universitas Negeri Jakarta). Jurnal Riset Manajemen Sains Indonesia (JRMSI), 5(1), 123–146.
Pearce, John A. & Robinson, R. (2009). Strategic Management: Formulation, Implementation, and Control. (Eleventh E). New York: McGraw-Hill.
Prasiska, Y. V., Pertiwi, B., Nabila, Y. ., Indah, K., & Safitri, D. (2017). CSR dan Citra Perusahaan. Jurnal Bisnis Dan Ekonomi, 24(1), 43–49.
Prutina, Ž. (2016). The effect of corporate social responsibility on organizational commitment. Management (Croatia), 21, 227–248.
Purwanto, A. (2011). Pengaruh Tipe Industri, Ukuran Perusahaan, Profitabilitas, Terhadap Corporate Social Responsiblity. Universitas Diponegoro, 8(1), 12–29.
Rahman, S., Haski-Leventhal, D., & Pournader, M. (2016). The effect of employee CSR attitudes on job satisfaction and organizational commitment: Evidence from the Bangladeshi banking industry. Social Responsibility Journal, 12(2), 228–246. https://doi.org/10.1108/SRJ-10-2014-0139
Raihan, T., & Al Karim, R. (2017). CSR and Employee Job Satisfaction : a Case From MNCs Bangladesh. Global Journal of Human Resource Management, 5(April 2017), 26-39.
Rupp, D., Skarlicki, D., & Shao, R. (2013). The Psychology of Corporate Social Responsibility and Humanitarian Work: A Person-Centric Perspective. Industrial and Organizational Psychology, 6. https://doi.org/10.1111/iops.12068
Sarjono, H., & Julianita, W. (2015). Struktural Equqtion Modeling (SEM), Sebuah Pengantar, Aplikasi untuk Penelitian dan Bisnis (R. Aryanto (ed.)). Salemba Empat.
Tanwar, K., & Prasad, A. (2016). The effect of employer brand dimensions on job satisfaction: gender as a moderator. Management Decision.
https://doi.org/10.1108/MD-08-2015-0343
Taufik, M. H., Sjahruddin, H., & Razak, N. (2018). Pengaruh Pemberdayaan Terhadap Kepuasan Kerja Melalui Komitmen Organisasional. Jurnal Organisasi Dan Manajemen, 1(1), 82–98. https://doi.org/10.31227/osf.io/rfsyx Issue
Tuzcu, A. (2014). The Impact of Corporate Social Responsibility Perception on The Job Satisfaction and Organizational Commitment. Journal of The Faculty of Economics and Administrative Sciences, 4(1), 185–202.
Walton, S. B. (2010). Do the right thing: Measuring the effectiveness of Corporate Social Responsibility. Public Relations Tactics.
Yenti, A. (2013). Pengaruh Penerapan Program Corporate Social Responsibility Terhadap Citra Perusahaan PT. Semen Padang. In Fakultas Ekonomi Universitas Negeri Padang.
-
Appendix 1: Outer Loading (Pre Elimination)
Corporate Image_
Corporate Social Responsibility_
Employee Satisfaction
Organizational Commitment
CI 1
0.800
CI 2
0.808
CI 3
0.740
CI 4
0.769
CI 5
0.829
CI 6
0.839
CI 7
0.861
CI 8
0.840
CSR1
0.828
CSR2
0.840
CSR3
0.628
CSR4
0.715
CSR5
0.839
CSR6
0.844
ES1
0.801
ES2
0.869
ES3
0.695
ES4
0.742
ES5
0.859
ES6
0.787
ES7
0.868
OC1
0.884
OC 2
0.755
OC 3
0.892
OC 4
0.810
OC 5
0.721
OC 6
0.840
OC 7
0.062
OC 8
0.289
-
Appendix 2: Outer Loading (Post Elimination)
Corporate Image
Corporate Social Responsibility_
Employee
Satisfaction
Organizational Commitment
CI1
0.800
CI 2
0.808
CI 3
0.740
CI 4
0.769
CI 5
0.829
CI 6
0.839
CI 7
0.861
CI 8
0.840
CSR1
0.828
CSR2
0.840
CSR3
0.628
CSR4
0.716
CSR5
0.839
CSR6
0.844
ES1
0.801
ES2
0.869
ES3
0.695
ES4
0.742
ES5
0.859
ES6
0.787
ES7
0.868
OC 1
0.886
OC 2
0.758
OC 3
0.895
OC 4
0.810
OC 5
0.716
OC 6
0.838
-
Appendix 3: Cross Loading (Post Elimination)
Corporate Image
Corporate Social Responsibility_
Employee
Satisfaction
Organizational Commitment
CI1
0.800
0.701
0.740
0.614
CI2
0.808
0.585
0.692
0.682
CI3
0.740
0.520
0.622
0.628
CI4
0.769
0.583
0.587
0.629
CI5
0.829
0.540
0.655
0.688
CI6
0.839
0.720
0.733
0.647
CI7
0.861
0.587
0.755
0.786
CI8
0.840
0.657
0.764
0.733
CSR1
0.634
0.828
0.663
0.538
CSR2
0.640
0.840
0.690
0.524
CSR3
0.452
0.628
0.505
0.390
CSR4
0.512
0.716
0.527
0.336
CSR5
0.634
0.839
0.664
0.507
CSR6
0.676
0.844
0.678
0.587
ES1
0.689
0.626
0.801
0.676
ES2
0.727
0.736
0.869
0.639
ES3
0.560
0.493
0.695
0.483
ES4
0.681
0.582
0.742
0.589
ES5
0.705
0.672
0.859
0.629
ES6
0.649
0.647
0.787
0.556
ES7
0.805
0.701
0.868
0.754
OC1
0.719
0.553
0.691
0.886
OC 2
0.596
0.458
0.594
0.758
OC 3
0.784
0.614
0.731
0.895
OC 4
0.655
0.491
0.600
0.810
OC 5
0.555
0.386
0.475
0.716
OC 6
0.755
0.514
0.674
0.838
Jurnal Ilmiah Akuntansi dan Bisnis, 2020 | 251
Discussion and feedback