Expert System for Early Diagnosis of Heart Disease Using the Random Forest Method
on
Journal of Electrical, Electronics and Informatics, Vol. 3 No. 1, February 2019
15
Expert System for Early Diagnosis of Heart Disease Using Random Forest Method
I Gede Yogi Prawira Putra1*, Duman Care Khrisne 2, I Made Arsa Suyadnya3
-
1,2,3Department of Electrical Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, Udayana University Bali - Indonesia
Abstract— In Indonesia, coronary heart disease continues to grow. However, efforts to conduct testing early can still be done by diagnosing the initial symptoms caused by using an expert system. This study was designed to build an expert system application to diagnose early coronary disease by random forest methods. The application interface is built using the PHP programming language using framework bootstrap, and uses the python programming language to build a random forest. To make an early diagnosis of coronary heart disease, a decision tree was built by training data from the UCI Dataset Machine Learning Repository using the random forest method. Followed by patient classification data that has been collected through 13 questions to get the diagnosis. The diagnosis results were normal, stadium 1, stadium 2, stadium 3 and stadium 4. Based on the tests that have been carried out, the application must be able to provide results in accordance with the sample data collected using a confusion matrix resulting in an accuracy of 92.25% +/- 0.62 with 70% precision, remember 46%, which obtained a score of f0,5 72%.
Index Terms— Coronary Heart Disease, Random Forest, Confusion Matrix
-
I. INTRODUCTION1
Coronary Heart Disease (CHD) is one of the highest causes of death for all ages. Based on a survey conducted by the Indonesian Ministry of Health by conducting a Sample Registration System (SRS), CHD had increased 11.4% from 2013 to 2014. If from 2012, according to data released by the World Health Organization (WHO) showed 17, 5 million people die of cardiovascular disease, or 31% of 56.5 million deaths that occur worldwide [1].
The high mortality rate due to CHD is because people's knowledge about CHD is still very minimal. How people should pay attention to signs of heart disease, including heavy breathing, chest pain, back pain, cold sweat, fainting, trembling, and burning sensation in the chest. In addition, this disease also has characteristics including high levels of Low Density Lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol and low High Density Lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol levels [2].
The high level of people with CHD has made medical staff increase performance degradation. According to the Acute Coronary Syndrome Registry data, there are 654 patients who have ST Increased Myocardial Infarction (STMI) or heart muscle damage due to a lack of coronary blood flow, services that can be used only 59% get treatment, but can
help the faster handling of people with CHD [ 3].
The proposed expert system will carry out an initial diagnosis of heart disease using the random forest method, which is expected to reduce difficulties in applying expert rules and inferences, the combination patterns that will be carried out with the data produced by manual inference experts and expected analysis experts. (the system does not make artificial inference from expert knowledge). It is hoped that with this renewal, the results of the tests produced to diagnose coronary disease are better.
-
II. LITERATURE REVIEW
From the research that has been carried out there are several studies related to my research, such as the initial expert diagnostic system using the backward elimination and k-nearest neighbor (KNN) algorithm, the results obtained from this present have an accuracy of 89.55% +/- 6.01% and area under curve is 0.966 +/- 0.056 which is categorized as very good [4].
As for the initial expert diagnostic system established with the k-nearest neighbor method based on forward selection, the results that can be obtained from this study have an
accuracy of 91.86% +/- 0.29% and the value of Area Under Curve is 0.777 +/- 0.134 which is categorized as fair [5].
The initial expert diagnostic system was established with naïve Bayes bagging and naïve algorithm, the results that can be obtained from this study have an accuracy of 84.44% with an area under curve of 0.911 which is included in the excellent category [6].
In contrast to the research that has been done before, here I will use the random forest method by utilizing the CART and ensemble learning techniques to create quality, more forested livelihoods.
-
III. RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
This section explains the steps for making a decision tree by utilizing three methods and combining them to get a decision tree that is able to produce good predictions.
-
a. Random forest
Random forest is a classification method created from the mode of decision tree that is owned, while the value given for regression is the mean. The random forest work itself by choosing the best decision tree prediction and grouping it to be issued as a result of predictions while the bad ones will issue predictions randomly, creating many trees for each decision is very helpful in random forest methods that can prevent over fitting.[7]
-
b. Cart method
Cart used in this study aims to create a strong decision class by looking for the minimum error value of each decision class, by utilizing this impurity to get the most minimal error value from each class, to be used as a strong root so that the results obtained are maximally . In the branch produced one of the branches is pure, while the other branches will continue to be processed until there are no significant changes, at that time the process will be stopped.[8]
-
c. Ensemble learning
Utilizing the ensemble technique in this study aims to create a new line of data from test data to get richer tree rows. By utilizing bagging to overcome the instability of the ensemble, by breaking down large datasets and making them small datasets to get the most maximum results in making predictions, we use bagging because it can handle even large datasets. After the bagging process is carried out, it is continued by carrying out the boosting process to create a new subset of data from the available datasets, to add data to the training process by
combining three classifications to get the most majority votes.[9]
-
d. Receiver Operating Charactic
The ROC curve is a way to compare a plot of true positive level with a false positive level, this is seen from the area under the curve the greater the area under the curve the more accurate the test is performed [10],[11]. C-statistic or c-index is a measure of goodness of fit for binary results in the logistic regression model, in clinical studies c-statistics give the probability of patients randomly experiencing certain diseases or conditions with higher scores compared to patients who did not experience the event [12]. Tables that can be used as a reference for measuring can be seen in table 1.
Table 1 Measuring the level of truth of the diagnosis results.
|
AUROC |
CATEGORY |
|
0.9 - 1.0 |
Very Good |
|
0.8 – 0.9 |
Good |
|
0.7 – 0.8 |
Fair |
|
0.6 – 0.7 |
Poor |
|
0.5 – 0.6 |
Fail |
IV. RESULTS AND DISCUSSIONS
This experiment was carried out by collecting data from patients, by testing the training data obtained from the UCI Machine Learning Repository dataset, judging from the accuracy generated by recall and the precision obtained from testing using the Confusion Matrix, in research to predict the importance of precision from on the recall which causes to use f0,5 score.
-
A. confusion matrix testing
Testing of CHD applications using confusion matrix, can be used as much as 303 data, with 10% sample data randomly and 90% training data. The resulting graph is shown in Figure 2. From 303 data, 31 data used in this test were randomly selected. From the graph above we can see the accuracy obtained by the diagnosis made between the sample data and training data.
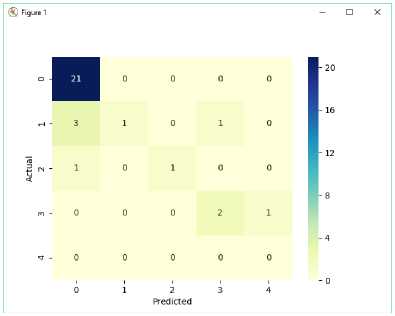
Figure 2 Display graphics from confusion matrix
In the graph above, where 21 data that is considered normal are normal predictions as many as 21, while those that should be declared 1 are found to be normal as many as 3, and which should be declared 1 but predicted 3 as many as 1. In the prediction of 2 which is declared normal as many as 1 and the one that is stated to be true is 1 piece. In predictions that must be stated 3 but stated 4 as many as 1 piece, and the correct one is as much as 2. Since the patient data is 4 little, so prediction 4 does not occur in the prediction of the graph above. In the whole confusion matrix graph can be seen the level of accuracy produced by the application is 92.25%. The sample data used by confusion matrix can be seen how many levels of accuracy, recall, precision and F0.5 score obtained from each diagnosis that can be seen in Table 2 below.
Table 2 Table of stages for each diagnosis
|
Stadium |
0 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
Rata -rata |
|
Akurasi |
0,8709 |
0,8709 |
0,9677 |
0,9354 |
0,9677 |
0.9225 |
|
Recall |
1 |
0,2 |
0,5 |
0,6 |
0.46 | |
|
Precision |
0,84 |
1 |
1 |
0,66 |
0.70 | |
|
F0.5 score |
0,868 |
0,556 |
0,833 |
0,647 |
0.7259 |
Stage one can be seen in Table 2, the level of accuracy produced at the normal stage is 0.8709, with a recall rate of 1. Precision from the results of stage one diagnosis is 0.84, indicating a value of f0.5 of 0.868. In stage one shows the resulting accuracy of 0.8709, with recall 0.2, precision of 1 and the value of f0.5 the resulting score is 0.556. In stage two of Table 2, it can be seen that the accuracy rate is 0.9677 with a recall rate of 0.5. The precision of the results of the stage two diagnosis is 1, indicating a value of f0.5 of 0.833. In stage three of Table 2, it can be seen that the resulting accuracy rate is 0.9354, while the resulting recall is 0.6, with a precision of 0.66, which produces a value of f0.5 of 0.647. In stage four of Table 2, it can be seen that the resulting
accuracy rate is 0.9677, while the results of the recall and the resulting precision are NaN, because the data possessed produces a small stage 4 value, so testing stage 4 data is not optimal. In medical problems, providing information about disease, precision is more important than recall, to find precision used f0.5 score, from the application and test data used f.05 obtained by 72%. The accuracy of the application of CHD is 92.25%, the level of AUROC measurement according to the table is the accuracy that can be achieved by the application of this initial CHD diagnosis at 0.9-1.0 (Very good).
-
V. CONCLUSION
Development of expert systems uses the python programming language using the random forest method and database system using MySQL. Random forest is a decision tree combination that was built using the CART technique to create the strongest tree trunks, CART was developed using bootstrapping aggregating to get richer decision tree variations. The decision tree that was created uses training data from 303 UCI Machine Learning Repository data, which is stored in the system database to diagnose by performing classification processes on patient data.Testing of Expert System Applications for Early Diagnosis of Heart Disease is carried out using the confusion matrix method, with the provisions of testing 303 data obtained from UCI. Tested by dividing the data as test data and training data, test data as much as 10% while 90% was used for training data. Testing is done by testing the test data on system training data using the provisions of the tree built on random forest as many as 500 decision trees, and random state is done with value 2 on the training data, while the test data gives a value of 1 in the random state. The composition used has been able to provide a diagnosis of test data by conducting classification of training data using the random forest method. The average accuracy that can be produced in measurements with confusion matrix is 0.9225 +/- 0.62, CHD applications show good accuracy results, with a recall rate of 46%, while a precision of 70%, by finding harmony between recall and precision using f0.5 72%.
References
-
[1] Sulistyowati, L. (2017, juli 29). penyakit-jantung-penyebab-kematian-tertinggi-kemenkes-ingatkan-cerdik. Retrieved from
Penyakit Jantung Penyebab Kematian Tertinggi, Kemenkes Ingatkan CERDIK: http://www.depkes.go.id/article/view/17073100005/penyakit-jantung-penyebab-kematian-tertinggi-kemenkes-ingatkan-cerdik-.html
-
[2] Santoso, L. W., Noertjahyana, A., & Leonard, I. (2013). Aplkasi Sistem Pakar Berbasis Web Untuk Mendiagnosa Awal Penyakit Jantung . Program Studi Teknik Informatika, 1.
-
[3] Tampubolon, G. S. (2017, 05 11). Infark Miokard Akut. Retrieved From Alomediaka Khusus Untuk Dokter:
https://www.alomedika.com/penyakit/kardiologi/infark-miokard-akut/epidemiologi.
-
[4] Hermawanti, L., & Rabiha, S. G. (2014). Penggabungan Algoritma Backward Elimination Dan K-Nearest Neighbor Untuk
Mendiagnosis Penyakit Jantung. Teknik Informatika,, 1.
-
[5] Safriandono, A. N. (2017). Algoritma K-Nearest Neighbor Berbasis Forward Selection Untuk Mendiagnosis Penyakit Jantung Koroner. Komputaki, 1
-
[6] Prasetio, R. T., & Pratiwi. (2015). Penerapan Teknik Bagging Pada Algoritma Klasifikasi Untuk Mengatasi Ketidakseimbangan Kelas Dataset Medis. Informatika, 395.
-
[7] Lingga P, R. D., Fatichah, C., & Purwitasari , D. (2017). Deteksi Gempa Berdasarkan Data Twitter Menggunakan Decision Tree, Random Forest dan SVM. Teknik Informatika, A-159.
-
[8] Margasari, A. (2013). Penerapan Metode Cart (Classification And Regression Trees) Dan Analisa Regresi Logistik Biner Pada
Klasifikasi Profil Mahasiswa Fmipa Universitas Brawijaya. Jurusan Matematika F.Mipa, 257 [11] Anonim. 2018. DI- Waterproof Temperature Sensor. http://www.mikron123.com. Diakses tanggal 14 april 2018
-
[9] yhat. (2013, juni 5). random forest. Retrieved from http://blog.yhat.com: http://blog.yhat.com/posts/random-forests-in-python.html.
-
[10] Hendrawati, T., & Khrisne, D. C. ASALTAG: Automatic Image Annotation Through Salient Object Detection and Improved k-Nearest Neighbor Feature Matching. Journal of Electrical, Electronics and Informatics, 2(1), 6-10.
-
[11] Khrisne, D. C., & Yusanto, M. D. (2015). Content-Based Image Retrieval Menggunakan Metode Block Truncation Algorithm dan Grid Partitioning. S@ CIES, 5(2), 79-85.
-
[12] Stephanie. (2016, Agustus 27). Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) Curve: Definition, Example. Retrieved from Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) Curve:
http://www.statisticshowto.com/receiver-operating-characteristic-roc-curve/.
Discussion and feedback