Performance Analysis of MIMO STBC System in Flat Fading and Frequency Selective Fading Channels
on
Journal of Electrical, Electronics and Informatics, Vol. 3 No. 1, February 2019
19
Performance Analysis of MIMO STBC System in Flat Fading and Frequency Selective Fading Channels
Pebri Yeni Samosir1, Nyoman Pramaita2, I.G.A.K. Diafari Djuni H3, N.M.A.E.D Wirastuti4
-
1,2,3,4Electrical Engineering Department,
Faculty of Engineering, Udayana University
Bali, Indonesia
*Email : pebriyeni12@gmail.com
Abstract – Multiple Input Multiple Output (MIMO) technology is one of the technique that can be used to overcome multipath fading. The multipath fading is caused by signals coming from several paths that have different attenuations, delays, and phases. In a multipath condition, an impulse that sent by the transmitter will be received by the receiver, it is not as an impulse but as a pulse with a spread width that called delay spread. Delay spread can cause inter symbol interference (ISI) and bit translation errors from the information received. To determine the effect of delay spread on the MIMO system, the research of the MIMO systems performance on flat fading channel and frequency selective fading was using the Space Time Block Code (STBC). This research was conducted using MatLab 2018a software. The simulation results show that the MIMO STBC system performance on flat fading channels is better than the MIMO STBC system performance on the frequency selective fading channel. This result is analyzed based on the value of BER vs. Eb/No and eye diagram.
Index Terms — Delay Spread, Flat Fading, Frequency Selective Fading, MIMO, STBC.
-
I. INTRODUCTION
Wireless network communication technology has developed very rapidly, this is due to the increasing demand of users to communicate quickly with good capacity and quality of service. Therefore, wireless communication systems are required to provide high data rate services, and have reliable and efficient system. However, this is difficult to apply, because the performance of the wireless communication system is affected by the wireless channel environment that are dynamic and unpredictable. Wireless channels are the main factor that limit the performance of wireless communication systems. The varying channel conditions can cause the multipath fading. In a multipath fading situation, signals that arrive from the different path will have different attenuation and delay. In a multipath condition, an impulse that sent by the transmitter will be received by the receiver, it is not as an impulse but as a pulse with a spread width that called delay spread. Delay spread can cause inter symbol interference (ISI) and error translation bits of information received [1].
A technique that can be used to overcome multipath fading is the use of multi-antenna on the transmitter and
receiver which is often called the Multiple Input Multiple Output (MIMO) technology. MIMO technology was first introduced by Jack Winters of Bell Laboratories in 1984 with the intent to overcome multipath fading [2]. MIMO can provide diversity gain, multiplexing gain and can increase channel capacity without the need to increase bandwidth and transmit power.
To determine the effect of delay spread on the MIMO system, the MIMO system performance was measured on the flat fading and frequency selective fading channels by using the STBC coding technique. This study is used Alamouti STBC 2x2 and QPSK modulation. This research was conducted with a simulation method by using MatLab 2018a software.
-
II. LITERATURE REVIEW
-
A. Multiple Input Multiple Output (MIMO)
MIMO is one technique in wireless communication systems that use more than one antenna in the M transmitter or N receiver. The MIMO system can reduce fading, interference from other users, increase reliability, and increase throughput without the need to increase bandwidth
-
[3] . In general, the working principle of MIMO is to multiply the transmitted information signal to improve communication capabilities and reduce errors that can occur due to transmission channels [4]. MIMO can provide diversity gain and multiplexing gain. MIMO techniques use many antennas on the transmitter and receiver side, which also function as spatial multiplexing, in contrast to diversity where each diversity antenna transmits the same data, at MIMO each antenna transmits different data. MIMO and antenna systems that use spatial diversity are standard in 4G antenna systems, both standard LTE or WiMAX [5].
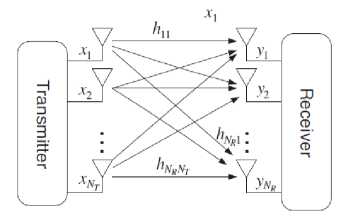
Fig. 1. MIMO Technique
-
B. Space Time Block Code (STBC)
STBC is a block coding technique in space and time. It means that the coding is composed of several symbols in one space that are sent with the space diversity technique through several periods of time. Each period of delivery will be shipped the different symbols. The STBC transmission scheme is a transmission scheme which is introduced by Siavash Alamouti in 1998. On the Alamouti STBC system, the same data stream is sent through both transmitting antennas [6]. STBC is a scheme that is used in transmit diversity techniques to achieve diversity gain in the MIMO system. The Alamouti STBC scheme is shown in Figure 2.
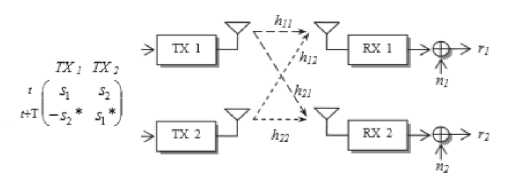
Fig. 2. Alamouti STBC 2x2 Scheme
-
C. Delay Spread
Delay spread is the pulse width of the impulses that are sent between the transmitter and receiver, which is a natural phenomenon caused by the reflection propagation and scattering in the communication channel. Delay spread can cause inter symbol interference (ISI) because each symbol will overlap each other. There are several factors in the delay spread that can be analyzed to determine the
transmission bit rate in order to avoid inter symbol interference (ISI) are The mean excess delay, maximum excess delay, and root mean square (RMS) delay spread [7].
-
a. Mean Excess Delay
Mean excess delay ( ) is the first moment of the power delay profile, that can be calculated using the equation:
∑αk ^k ∑ τ= k = k
∑ak ∑ kk
(1)
-
b. Maximum Excess Delay
Maximum Excess Delay ( ) is the delay range between the appearance of the first impulse to the last impulse in the power delay profile.
^ = max, ,∙∣τiM - τ,-(tjj
(2)
-
c. RMS Delay Spread
RMS delay spread (στ) is an important parameter that can determine the performance of a digital system, which can help identify and overcome multipath fading. By reducing the RMS delay spread the inter symbol interference (ISI) can be smaller, so that the error rate will be smaller and the data rate will increase [7]. The RMS delay spread value can be calculated using the equation:
where:
∑ak ∑ PT)
kk
-
D. Flat Fading
If the mobile radio channel has a constant gain and linear phase response over a bandwidth which is greater than the bandwidth of the transmitted signal, then the received signal will undergo flat fading. The characteristics of a flat fading channel are illustrated in Figure 3.
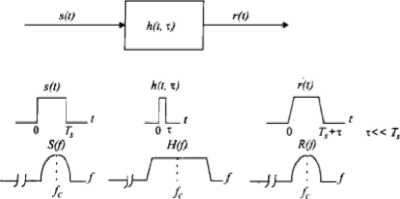
Fig. 3. Characteristics of flat fading channel
a signal undergoes flat fading if:
Bs < Bc and Ts > (5)
Where Ts is reciprocal bandwidth (symbol period), Bs is bandwidth, respectively, of the transmitted modulation,
EZ and Bc are the RMS delay spread and coherence bandwidth, respectively, of the channel [8].
-
E. Frequency Selective Fading
If the channel has coherence bandwidth that is smaller than the bandwidth of the transmitted signal, then the received signal will undergo frequency selective fading. In such conditions, the channel has a RMS delay spread that is greater than the reciprocal bandwidth (symbol period) of the transmitted message wave. When this happens, the received signal includes several versions of the wave that are transmitted with attenuation (faded) and delay, therefore the received signal is distorted [8]. This channel conditions cause inter symbol interference (ISI). A signal undergoes frequency selective fading if:
Bs > Bc and Ts < Erl (6)
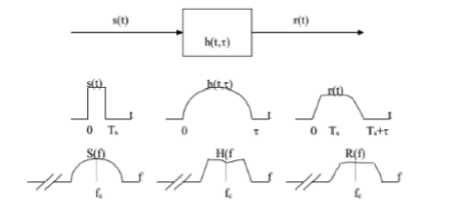
Fig. 4. Characteristics of frequency selective fading channel
-
F. Quadrature Phase Shift Keying (QPSK)
QPSK modulation is one type of Phase Shift Keying (PSK) modulation. In QPSK modulation there are four signal levels that represent four binary codes. Each level has a phase difference of 90 °. QPSK has twice the bandwidth efficiency of BPSK since 2 bits are transmitted in a single modulation symbol [8].
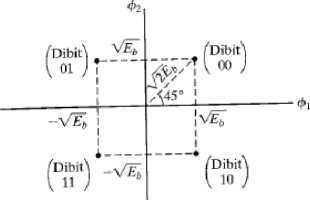
Fig. 5. QPSK Constellation Diagram
-
III. METHOD
-
A. Modeling of MIMO STBC System on the Flat Fading and Frequency Selective Fading Channels
Modeling of the MIMO STBC system in a flat fading channel is shown in Figure 6 and the MIMO STBC system modeling on the frequency selective fading channel is shown in Figure 7.
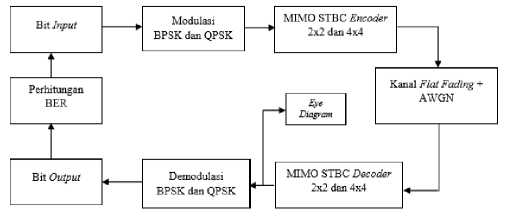
Fig. 6. Block diagram of MIMO STBC system in flat fading channel
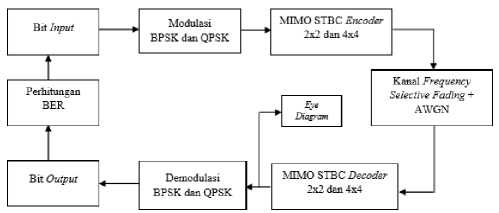
Fig 7. Block diagram of MIMO STBC system in frequency selective
fading channels
-
B. Simulation Parameters
The simulation parameters used in this study are shown in Table 1.
TABLE 1
PARAMETERS OF MIMO STBC SYSTEM SIMULATION
|
Parameters |
Parameter Value |
|
Number of bits |
1.000.000 bits |
|
Modulation |
QPSK |
|
User Type |
Single User |
|
MIMO Type |
STBC 2x2 |
|
Channel Types |
Flat Fading and Frequency Selective Fading |
|
Noise |
AWGN |
|
Fading Distribution |
Rayleigh Distribution |
|
Eb/No Value |
0 to 15 dB |
|
QPSK Symbol Period ( ) |
0.2 µs |
|
Flat Fading (FL) | |
|
Discrete path delays (µs) |
[0.0001] |
|
Average path gains (dB) |
[0] |
|
RMS Delay Spread (~) |
0 µs |
|
Frequency Selective Fading Condition 1 (FSF1) | |
|
Discrete path delays (µs) |
[0.0001 0.2 0.5 1.6 2.3 5.0] |
|
Average path gains (dB) |
[-3 0 -2 -6 -8 -10] |
|
RMS Delay Spread (~) |
1.4 µs |
|
Frequency Selective Fading Condition 2 (FSF2) | |
|
Discrete path delays (µs) |
[0.0001 0.3 1.0 1.6 5.0 6.6] |
|
Average path gains (dB) |
[-2.5 0 -3 -5 -2 -4] |
|
RMS Delay Spread ( ~ ) |
2.4 µs |
The power delay profile (PDP) model that used in the frequency selective fading study uses the PDP COST 207
model with 6 paths [9][10]. The results of the study will show the performance and comparison of the MIMO STBC system on flat fading and frequency selective fading channels by making changes to the delay spread value on the channel. The results of this study will show the effect of the delay spread value on the MIMO STBC system both based on the bit error rate value and the shape of the simulated eye diagram which is the performance parameter in this study. The MIMO STBC system simulation on the frequency selective fading channels was carried out twice with different RMS delay spread values. The first simulation on the frequency selective fading channel is named the FSF1 simulation (frequency selective fading condition 1) and the second simulation is named the FSF2 simulation (frequency selective fading condition 2).
The purpose of this study was to determine the comparison of the performance of the MIMO STBC system on the flat fading and frequency selective fading channels and to determine the effect of delay spread on the performance of the MIMO STBC system.
-
IV. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
-
A. MIMO STBC System Performance on the Flat Fading and Frequency Selective Fading Channel Analyzed Based on BER vs Eb/No
The simulation results of the MIMO STBC system on the flat fading and frequency selective fading are shown in Figure 8.
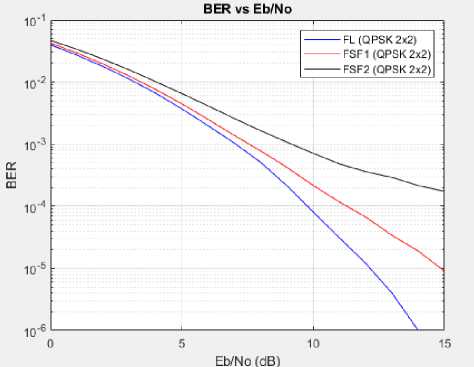
Fig. 8. Graph comparison of the performance of the MIMO STBC system on flat fading and frequency selective fading channel
FL = Flat Fading
FSF1 = Frequency Selective Fading Condition 1
FSF2 = Frequency Selective Fading Condition 2
TABLE 2
COMPARISON OF DELAY SPREAD VALUES ON FLAT FADING AND FREQUENCY SELECTIVE CHANNEL FADING
|
Parameters |
Flat Fading (FL) |
Frequency Selective Fading Condition 1 (FSF1) |
Frequency Selective Fading Condition 2 (FSF2) |
|
τ2 |
1x10-8 µs |
3.0054 µs |
11.27 µs |
|
Mean Excess Delay (τ) |
0.0001 µs |
1.03 µs |
2.28 µs |
|
RMS Delay Spread (στ) |
0 µs |
1.4 µs |
2.4 µs |
As seen in Figure 8, the simulation results show that flat fading channels have better performance than frequency selective fading channels. The BER value from the simulation on the flat fading channel is smaller than the BER value simulated on the frequency selective fading channel. This happens because the value of the RMS delay spread on flat fading channels is smaller than the value of the RMS delay spread on the frequency selective fading channel.
Based on the simulation results and can be proved theoretically by calculation using Equation (3), show that flat fading channels have a smaller RMS delay spread compared to the symbol period. While the frequency selective fading channel has a greater RMS delay spread than the symbol period. If the RMS delay spread value is small, the inter symbol interference (ISI) that occurs is also smaller, so the resulting bit error rate will be smaller in value and the data rate will increase. This causes the flat fading channel performance is better than frequency selective fading channel performance.
The purpose of this study is to determine the effect of delay spread on the MIMO STBC system. This simulation is done by comparing the performance of a flat fading channel with frequency selective fading channel, and for frequency selective fading channels there are also two variations of different RMS delay spread values with the aim to determine the effect of the value of the RMS delay spread if the value is greater against the value of the bit error rate generated. The FSF1 simulation (frequency selective fading condition 1) has a smaller RMS delay spread than the RMS delay spread in the FSF2 simulation (frequency selective fading condition 2). Based on the simulation results, the bit error rate (BER) in the FSF2 simulation is greater than the bit error rate (BER) value in the FSF1 simulation. This proves that the greater the value
of the RMS delay spread on the channel, the greater the value of the bit error rate (BER).
-
B. MIMO STBC System Performance on Flat Fading and Frequency Selective Fading Channel Analyzed Based on Eye Diagram
Eye diagram displays the signal quality by looking at the eye shape tendencies in the diagram shown. If signal quality degradation occurs, the eye diagram will tend to close and otherwise, eye diagrams will tend to open if the signal quality is good enough. In this study, the purpose of displaying an eye diagram is to determine the difference in the shape of eye diagrams on flat fading and frequency selective fading channels and to determine the effect of delay spread on the shape of eye diagrams [11][12].
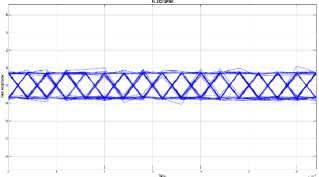
Fig. 9. The eye diagram of MIMO STBC system on a flat fading channel
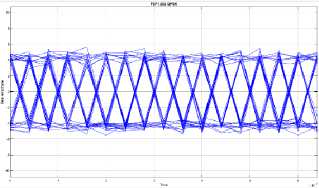
Fig. 10. The eye diagram of MIMO STBC system on frequency selective fading channel condition 1
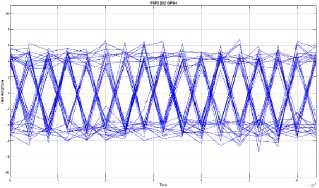
Fig. 11. The eye diagram of MIMO STBC system on frequency selective fading channel condition 2
Based on the eye diagram simulations, the performance of MIMO STBC system on flat fading and frequency selective fading channels that uses QPSK modulation shows that eye diagram on flat fading channels is better than frequency selective fading channels. The shape of the eye diagram that is simulated on the frequency selective fading channel is more irregular lines that overlap compared to the flat fading channel. The pattern of stripes is caused by jitter, this indicated that the occurrence of inter symbol interference (ISI) which still affect signal reception
in the system [11]. As previously explained, this frequency selective fading channel is a channel that has a greater RMS delay spread than the symbol period on a channel, so that the data received has a delay spread and results in inter symbol interference. The existence of inter symbol interference (ISI) can disrupt other symbols and that will cause an error.
Likewise with FSF1 and FSF2, from the simulation results, the shape of the FSF1 eye diagram is better than the FSF2. The simulation results in the form of eye diagrams are in accordance with the theory, where the delay spread on the channel will affect the shape of the eye diagram. The greater the delay spread on the channel, the more form the eye diagram will be, the more the pattern of irregular lines or worse because delay spread results in inter symbol interference (ISI).
-
V. CONCLUSION
Based on the results of this research, it can be concluded that the performance of MIMO STBC system on the flat fading channel is better than the performance of MIMO STBC system on the frequency selective fading channel. This happens because the frequency selective fading channels have a greater RMS delay spread value than the RMS delay spread value on the flat fading channels. Delay spread on the channels greatly affects the MIMO STBC system. Delay spread can cause inter symbol interference (ISI) and error translation bits of information received. By reducing delay spread the inter symbol interference (ISI) can be smaller so that the error rate will be smaller and the data rate will increase. The increase of delay spread on the channel causes the increasing value of bit error rate (BER) and the resulting eye diagram will more closed, irregular and worse.
References
-
[1] Jeruchim, et al. 2002. Simulation of Communication Systems Modeling, Methodology, and Techniques. New York: Kluwer Academic Publishers.
-
[2] Maddanaca, A. (2012). Reduksi Peak-To-Average Power Ratio Pada Sistem STBC MIMO-OFDM Dengan Metode Selected Mapping dan Partial Transmit Sequence. IncomTech Journal of Telecommunications and Computers, Vol.3, no.1.
-
[3] Hen, I. (2006). MIMO Architecture for Wireless Communication. In Intel Technology Journal, vol. 10, issue 02.
-
[4] Purwanto, T.B. (2015). Analisis Unjuk Kerja Teknik MIMO STBC dan V-BLAST Pada Sistem Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing. SPEKTRUM Journal, vol.2, no. 2.
-
[5] Wardhana, L & Makodian, N. 2010. Teknologi Wireless Communication dan Wireless Broadband. Yogyakarta: Andi Offset.
-
[6] Alamouti, S.M. (1998). A Simple Transmit Diversity Technique for Wireless Communication. IEEE Journal On Selected Areas in Communication, vol. 16, no. 8, pp. 1451-1458, Oct 1998.
-
[7] Prabowo, W.E., et al. (2014). Pengaruh Multipath Fading Terhadap Performansi Pada Downlink Jaringan CDMA2000 1X EV-DO Revision A. TEUB College Student Journal, vol. 2, no.3.
-
[8] Rappaport, T.S. 1996. Wireless Communication Principle and Practice. New Jersey: Prentice Hall.
-
[9] Cho, Y.S., et al. 2010. MIMO-OFDM Wireless Communication with MatLab. New York: John Wiley & Sons.
-
[10] Fazel, K. & Kaiser, S. 2008. Multi-Carrier and Spread Spectrum System from OFDM and MC-CDMA to LTE and WiMAX, Second Edition. New York: John Wiley & Sons.
-
[11] Hakim, M. (2017). Analisis Variasi Jumlah Antena Terhadap Unjuk Kerja Sistem Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing MIMO (Thesis). Denpasar: Udayana University.
-
[12] Seams, J. (2005). A Comparison of Resistive Terminators for High Speed Digital Data Transmission. High Frequency Electronics Journal, vol. 4, No. 10.
-
[13] Haider, D., et al. (2017). MIMO Network and The Alamouti, STBC (Space Time Block Coding). American Journal of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, vol. 5, No. 1, pp. 23-27.
-
[14] Jafarkhani, H. 2005. Space Time Coding: Theory and Practice.
Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Discussion and feedback