Evaluation of Clipping and Filtering-Based PAPR Reduction in OFDM System
on
Journal of Electrical, Electronics and Informatics, p-ISSN: 2549-8304
18
Evaluation of Clipping and Filtering-Based PAPR Reduction in OFDM System
N.M.A.E.D. Wirastuti1*, N. Pramaita2, I.M.A. Suyadnya3, and D.C. Khrisne4
-
1,2Telecommunication Systems Lab., Department of Electrical Engineering
Udayana University
Badung, Bali, Indonesia
*
-
3,4Computer Lab., Department of Electrical Engineering
Udayana University
Badung, Bali, Indonesia
Abstract This paper investigates clipping and filtering techniques in reducing peak average power ratio (PAPR) of Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) system. The concept of OFDM is to split a high speed serial data into parallel data at a lower speed, then the parallel data carried by mutually orthogonal subcarriers. The high of PAPR is one of disadvantages of OFDM system. The high PAPR can damages the form of OFDM and reduces its performance. The purpose of this study is to reduce PAPR using simulation. OFDM was simulated with and without clipping filtering then compared. The methods used to reduce PAPR was clipping and filtering technique. Clipping and filtering technique operates by clipping the output of inverse Fourier transform that exceed the threshold. Graphics PAPR vs. CCDF was used to evaluate the performance of OFDM systems. PAPR for OFDM system using Fourier transform when CCDF = 10-3 is 11,2 dB, with classical clipping PAPR was 4,1 dB and PAPR 4,6 dB when with deep clipping.
Index Terms—discrete wavelet transforms, Fourier transform, PAPR, OFDM
-
I. Introduction1
OFDM has several properties which make it an attractive modulation scheme for high speed transmission. One of challenging issues in OFDM is high Peak Average Power Ratio (PAPR). The high PAPR causes the interference and degraded the performance of the system while OFDM signal pass through the amplifier [1,2]. High PAPR force the High Power Amplifier (HPA) to operate in its linear region with wide dynamic range, where the power efficiency is very poor. The poor power efficiency makes the reduction of PAPR more important in OFDM systems. So, clearly it would be desirable to have the average power and peak power values as close together as possible for achieving good performance of OFDM system. Depending upon the reduction in PAPR level and computational complexity, different techniques have been surveyed [3].
There have been many methods in which the PAPR can be reduced in OFDM system, which basically can be divided in three categories, as follows: 1) signal distortion techniques, which reduce the peak amplitudes simply by nonlinearly distorting the OFDM signal at or around the peaks, e.g. clipping and filtering, envelope scaling, peak reduction carrier, peak windowing and peak cancellation;
-
2) Signal Scrambling Techniques each OFDM symbol with different scrambling sequences and selecting the sequence that gives the smallest PAPR, e.g. Block Coding Techniques, Block Coding Scheme with Error Correction, Selected Mapping (SLM), Partial Transmit Sequence (PTS), Interleaving Technique, Tone Reservation (TR) and Tone Injection (TI); 3) coding techniques that use a special FEC code set that excludes OFDM symbols with a large PAPR [4,5].
Clipping the signal to a maximum allowed value is a simple technique used to reduce the PAPR of OFDM signals. However, this technique caused degradation of Bit Error Rate (BER) and out-of-band radiation. Clipping does not add extra information to the signal and high peaks occur
with low probability so the signal is seldom distorted. At the transmitter, filtering applied to reduce out of-band radiation. A FFT-IFFT pair can be used as filter which is easier to implement than traditional FIR filters and allows the implementation of the clip and filter set several times in order to reduce the peak regrowth that filtering introduces. At the receiver, the signal can be reconstructed for mitigating BER degradation.
The remainder of this paper is organised as follows. Section 2 presents the system model used in this study. Section 3 describes the results and analysis of the performance of OFDM system with and without clipping san filtering technique. Finally, in section 4, a conclusion is drawn.
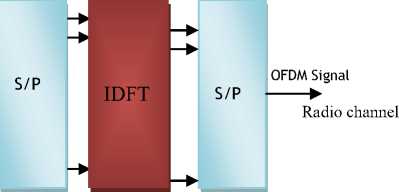
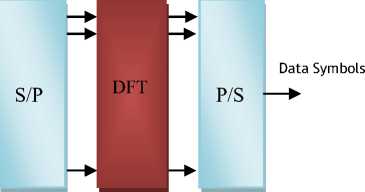
Weinstein and Ebert have shown that OFDM generation and detection can be achieved by employing an IDFT and a DFT at the transmitter and the receiver respectively [6,7]. The structure of a DFT-based base-band OFDM transmitter and receiver is shown in Figure 2. In DFT-based implementation, an OFDM symbol can be generated by taking the IDFT of the complex modulation symbols to be conveyed in each sub-channel, that is given by
N-1
x (n ) = -1 Σ X (k) ej2π^N,
Nk=0 k = 0, ……….., N – 1,
(1)
and the complex modulation symbols conveyed in each subchannel can be detected by taking the DFT of the samples as shown
N-1
X (k ) = ∑ x (n) e - j 2πknz N,
n=0 n = 0, ……….., N – 1.
(2)
Figure 1 shows the block diagram of the relationship between frequency domain and time domain in an OFDM system [8].
Frequency domain QPSK
Time domain Sum of sinusoidal
Frequency domain QPSK

Figure 2 Frequency domain and time domain in an OFDM system.
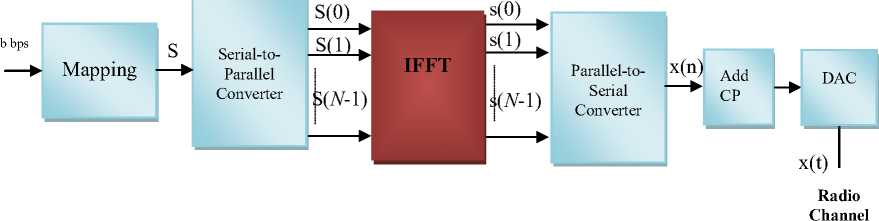
The efficient implementations of an OFDM transmitter and receiver can be constructed in practice by the IFFT and FFT, respectively, that are typically employed in the baseband OFDM basic structure [9], as shown in Figure 3. The input data stream, b bps, is modulated by a type of modulation ( M -qpsk, M -qam), resulting in an m-ary symbol stream, R, where each symbol has in-phase (I) and quadrature (q) components, each defining one out of M possible constellation points. This symbol stream is passed through a serial-to-parallel converter, which outputs a set of N parallel M-ary symbols, S(i)=S(0),S(1),…,S(N-1). These output symbols are transmitted over N sub-channels and correspond to the symbols transmitted over each of the subcarriers. The number of information bits per-OFDM block, denoted as B, depends on the number of sub-carriers, N, and the number of bits per sub-carrier, which depends on the type of modulation used. During each OFDM block, each sub-carrier transmits one symbol. Thus, the N symbols output from the serial-to-parallel converter are the discrete frequency components of the output OFDM modulator, x(n). x(n) is generated by converting its frequency components into time samples by performing an IFFT on the N sub-channels. Each sub-channel modulates a separate carrier through the IFFT modulation block, which actually generates the OFDM block, performing the multicarrier modulation [10].
ˆ
b bps


Parallel-to-Serial Converter
r(0) r(1)
Serial-to-Parallel Converter
y(n)
Remove CP

ADC
Figure 3 N-sub-carriers OFDM with IFFT/FFT implementation.
The implementation of clipping-filtering for reducing PAPR in OFDM system can be seen in Figure 4.
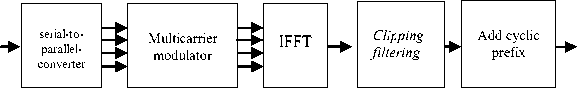
Figure 4 clipping filtering implementation in OFDM
In this research, the clipping technique was used classical clipping and deep clipping. Both types of clipping have different ways of working in clipping the amplitudes of an OFDM signal.
In classical clipping, it depends on two conditions, which are the amplitude of an OFDM signal will be passed directly when the amplitude of the signal is less than or equal to the threshold value. When signal r is greater than threshold value, signal will experiences clipping amplitude according to level of clipping ratio.
While deep clipping in the process depends on 3 conditions, which are the amplitude of an OFDM signal will be passed directly when the amplitude of the signal is less than or equal to the threshold value. When signal r in Λmox <r ≤^ A , then signal clipping process with equation A — p * (r — A) . When r > —λ , the signal amplitude will be clipped with the amplitude value "0", where p is the depth level of clipping (deep factor) that has been pre-determined.
The parameter used in the simulation can be used in Table 1.
TABLE I
Simulation Parameter
|
Parameter N frame |
Values 5000 |
|
Clipping Ratio (CR) |
Classical Clipping = 1,4 Deep Clipping = 0,6 |
|
FFT Size |
64 |
|
N of data subcarriers |
64 |
|
Guard period type |
Cyclic prefix |
|
N bits per OFDM symbol |
64 |
|
N symbol |
1 |
|
N Cyclic prefix |
¼ (N of data subcarriers) |
|
Total symbol |
N of data subcarriers + N cyclic prefix |
The simulation was based on DFT-OFDM model as seen in Figure 2. The performance of OFDM system with and without PAPR reduction scheme was described by CCDF vs. PAPR graphics. The PAPR reduction was simulated using classical and deep clipping-filtering. The three conditions were compared and analyzed.
Simulations were performed using the parameters as seen in table 1. The CCDF graph of the DFT-OFDM simulation can be seen in Figure 4.
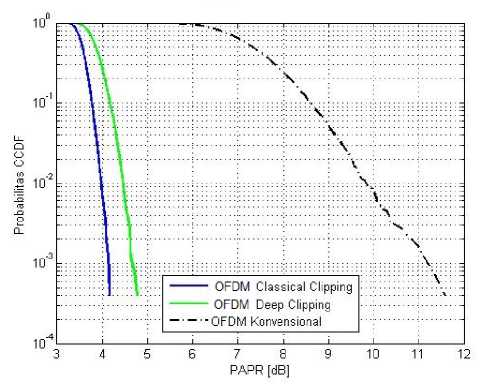
Figure 4 Comparison of CCDF using clipping and filtering method
From the result, it can be seen when CCDF 10-3, PAPR of OFDM was 11.2 dB. OFDM system using classical clipping it has a PAPR value of 4.1 dB which capable of reducing PAPR to 7.1 dB. While OFDM system with deep clipping, it has a PAPR value of 4.6 dB which able to reduce the PAPR to 6.6 dB. Classical clipping is able to reduce PAPR more the deep clipping in this simulation.
In accordance with the above simulation results, OFDM with clipping process both classical clipping and deep clipping has a lower PAPR value than OFDM without clipping. That is because in clipping process, the signal amplitude is limited by the threshold and therefore the ratio of peak amplitude to average amplitude will be smaller.
-
[4] Okello Kenneth, Usha Neelakanta, PAPR Reduction techniques in OFDM System Using Clipping & Filtering and Selective Mapping Methods, International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET), e-ISSN: 2395 -0056 Volume: 03 Issue: 12, Dec -2016. pp. 373-378.
-
[5] Suverna Sengar, Partha Pratim Bhattacharya, Signal & Image Processing: An International Journal (SIPIJ) Vol.3, No.2, April 2012, pp. 157-169.
-
[6] S. B. Weinstein, P. M. Ebert, “Data Transmission by Frequency Division Multiplexing using the Discrete Fourier Transform”, IEEE Transactions on Communications, Volume 19, No. 5, pp. 628 –634, October 1971.
-
[7] N.M.A.E.D. Wirastuti, J.M. Noras, S.M.R. Jones, Evaluation of the Very Fast Fourier Transform applied to OFDM, Proceeding of 2nd IEE/EURASIP Conference on DSPenabledRadio, London, UK, 1920 Sept. 2005, p. 12, ISBN: 0 86341 560 1.
-
[8] L. Litwin and M. Pugel, “The principles of OFDM”, RF Signal Processing, January 2001. Website:
http://voronuk.boom.ru/documents/ofdm.pdf.
-
[9] L. Hanzo, M. Munster, B. J. Choi and T. Keller, OFDM and MC-CDMA for Broadband Multi-User Communications, WLANs and Broadcasting, John Wiley & Sons., 2003.
-
[10] N.M.A.E.D. Wirastuti, J.M. Noras, S.M.R. Jones, “Performance Evaluation of G-OFDM over Multipath Fading Channels”, the fourth workshop on Signal Processing for Wireless Communication (SPWC), King’s College London, United Kingdom, 30 - 31 May 2006.
The PAPR problem is one of challenging issues in developing OFDM system. Clipping is a simple solution that results from this paper in order to reduce the effects of high PAPR in OFDM systems. At the transmitter, filtering applied to reduce out of-band radiation. By using clipping and filtering schemes, the performance of OFDM system can be improved.
Acknowledgment
The author(s) would to thank Lembaga Penelitian dan Pengabdian kepada Masyarakat (LPPM), Universitas Udayana, for their financial supports.
References
-
[1] Sandeep Bhada, Pankaj Gulhaneb , A.S.Hiwalec PAPR Reduction scheme For OFDM Procedia Technology 4(2012), 109 – 113, Elsevier.
-
[2] N.M.A.E.D. Wirastuti, Understanding Peak Average Power Ratio in VFFT-OFDM Systems, Applied Mechanics and Materials Vol 776 (2015) pp 419-424, Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland, doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.776.419.
-
[3] J. Jeevitha, Anusha Chacko, PAPR reduction techniques for performance improvement in OFDM systems. 2014 International Conference on Electronics and Communication Systems (ICECS), 13-14 February 2014, Coimbatore India
doi: 10.1109/ECS.2014.6892576.
Discussion and feedback