CONCORDANCE OF PROCALSITONIN LEVEL USING ELECTROCHEMILUMINESCENCE IMMUNOASSAY (ECLIA) METHOD AND FLOURESCENCE IMMUNOASSAY (FIA) METHOD AT SANGLAH HOSPITAL DENPASAR
on
ISSN: 2597-8012
JURNAL MEDIKA UDAYANA, VOL. 8 NO.10,OKTOBER, 2019
DIRECTORY OF
OPEN ACCESS
JOURNALS
DOAJ

AGREEMENT OF PROCALCITONIN EXAMINATION USING ELECTROCHEMILUMINESCENCE IMMUNOASSAY (ECLIA) METHOD AND FLOURESCENCE IMMUNOASSAY (FIA) METHOD AT SANGLAH HOSPITAL DENPASAR
Endrawati KJ1 ,Wiradewi Lestari AA2, Wande IN2
-
1) Clinical Pathology Trainee/Faculty of Medicine, Udayana University /Sanglah Hospital Denpasar
-
2) Clinical Pathology Departement/Faculty of Medicine, Udayana University / Sanglah Hospital Denpasar
*juwitaendrawati@gmail.com/081236281480
ABSTRACT
INTRODUCTION. Sepsis is one of cause mortallity in critical patients. The use of biomarkers such as procalcitonin is helpful to choose the right diagnosis and treatment. Procalcitonin (PCT), is a prohormone of the calcitonin hormone and is produced during the inflammatory process related to bacterial endotoxins and inflammatory cytokines. There are several methods for PCT examination such as Electrochemiluminenscence Immunoassay (ECLIA) and Flourescence Immunoassay (FIA).
PURPOSE. This study purpose is to determine whether there are differences value in PCT examination between ECLIA method and FIA method.
METHOD. The study was using a cross sectional analytic of PCT refference using the ECLIA method on Cobas e601 Roche devices, and the FIA method on Nano Entek FREND devices. Bivariate analysis using paired T test with P <0.05.
RESULTS. Data analyzed using SPSS 17 version, study was conducted at the Clinical Pathology Laboratory at Sanglah Hospital from February-April 2019 and obtained a median value procalcitonin level with the ECLIA method of 0.52 (0.03-129.6)ng/mL and the FIA method of 0.78 (0.07-32)ng/mL. The Spearman correlation test within two method, r 0.973, p 0,000. The Bland-Altman test with degree of suitability p = 0.326.
CONCLUSION. There is no difference results of procalcitonin level between ECLIA method and FIA method.
Keywords: procalcitonin, ECLIA, FIA
ABSTRAK
LATAR BELAKANG. Sepsis merupakan penyebab kematian terbesar pada pasien kritis. Penggunaan biomarker seperti procalcitonin sangat membantu penegakan diagnosis dan pemberian terapi yang tepat. Procalcitonin (PCT), merupakan prohormon dari hormon calcitonin dan dihasilkan selama proses inflamasi terkait endotoksin bakteri dan sitokin inflamasi. Ada beberapa metode pemeriksaan procalcitonin, seperti metode Electrochemiluminenscence Immunoassay (ECLIA) dan Flourescence Immunoassay (FIA).
TUJUAN. Penelitian ini bertujuan mengetahui apakah terdapat perbedaan hasil pemeriksaan PCT antara metode ECLIA dan metode FIA.
METODE. Data dianalisis dengan menggunakan SPSS versi 17, dilaksanakan dengan rancangan penelitian analitik potong lintang (cross sectional) dari pemeriksaan PCT dengan metode ECLIA pada alat Cobas e601 Roche, dan metode FIA pada alat Nano Entek FREND. Analisis bivariat menggunakan Uji T berpasangan dengan P<0,05.
HASIL. Penelitian dilakukan di Laboratorium Patologi Klinik RSUP Sanglah pada Februari-April 2019 mendapatkan nilai median kadar procalcitonin dengan metode ECLIA 0.52 (0.03-129.6)ng/mL dan metode FIA sebesar 0.78 (0.07-32)ng/mL.
Ditemukan korelasi positif kuat antara kedua metode menggunakan Uji korelasi spearman
DOAJ

r 0,973 dengan p= 0,000. Uji kesesuaian Bland-Altman didapatkan derajat kesesuaian antara metode ECLIA dengan FIA p = 0.326.
SIMPULAN. Tidak terdapat perbedaan bermakna dari hasil pemeriksan PCT menggunakan metode ECLIA dengan metode FIA.
Kata Kunci: procalcitonin, ECLIA, FIA.
Introduction
Sepsis is the biggest cause of death in critical patients. Delay in the diagnosis and treatment can increase mortality. However, clinicians have difficulty distinguishing sepsis triggered by infection or non-infection in SIRS (Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome), this is especially the case for critically ill patients who can experience SIRS conditions due to other causes .1,2 The mortality rate associated with bacteremia is very high in patients with systemic clinical symptoms. Therefore, immediate handling of patients is necessary. The use of biomarkers such as procalcitonin is very helpful in establishing the diagnosis and providing appropriate therapy 3.
Procalcitonin (PCT) with a protein content of 13 kDa, is a prohormone from the hormone calcitonin and is produced during the inflammatory process associated with bacterial endotoxins and inflammatory cytokines. PCT is produced by two mechanisms, the direct pathway induced by liposaccharides (LPS), while the second pathway is an indirect pathway induced by several inflammatory mediators such as IL-6 and TNF-α 4.
Procalcitonin examination in the Clinical Pathology Laboratory of Sanglah Hospital using the
Electrochemiluminenscence Immunoassay (ECLIA) method with the Cobas e601 Roche tool requires a relatively long examination time, whereas with the Flourescence Immunoassay (FIA) method using the Nano Entity FREND tool can shorten the examination time. The purpose of this study was to determine the suitability of the ECLIA method with the FIA. It is hoped that the results of this research can be a reference for writers, laboratories in determining the method used for PCT examination
This study aims to determine the suitability of Procalcitonin examination results with the ECLIA method with the FIA method.
METHOD
This research was carried out with a cross sectional analytical study design from
PCT examination using ECLIA method using Cobas e601 Roche method and FIA method by using Nano Entek FREND tool with 48 samples obtained from the remaining serum of examination from samples examined by PCT levels. The study was conducted from February to April 2019 at the Clinical Pathology Laboratory of Sanglah Hospital Denpasar.
ECLIA Automatic Methods
PCT examination on COBAS e601 Roche uses the two-step two-site sandwich electrochemiluminescence immunoassay (ECLIA) principle, using PCT specific antibodies labeled with biotin and PCT specific monoclonal antibodies labeled with ruthenium complexes. 30 µL samples labeled with antigens and anti-PCT antibodies labeled biotin and ruthenium were incubated at 37oC to form a sandwich complex. Second incubation, streptavidin-coated microparticles were added which bind the complex through biotin-streptavidin interactions. The reaction mixture is aspirated into a cell meter where the microparticles are captured magnetically on the surface of the electrode. Unbound substances are removed by washing and continued by induction of chemiluminescence and measured by photomultiplier.5,12
FIA Automatic Method
Nano Entek FREND PCT uses the 'sandwich' quantitative rapid immunoasai method. Nanoparticles are used to measure PCT concentrations.
35µL sample is then taken into a PCT FREND cartridge hole, the sample will interact and mix with the dry reagent in the cartridge. One of the reagents contains the fluorescent nanoparticle conjugate antibody, which will form an immune complex with PCT in the patient sample. Then capillary movement will occur, to detect PCT nanoparticle antibodies. PCT concentrations are calculated automatically with the FREND system. The results are then calculated using information stored on a specific lot of FREND PCT chip code and then displayed on the FREND system screen. 6
DOAJ

The total concentration of the sample analyzed by FREND PCT in the FREND system is directly related to the intensity of fluorescence, the higher the concentration of PCT, the flourescent ratio increases. This tool can detect PCT concentrations with a mean of 0.07ng / mL to 32ng / Ml.6
Analytical Statistics
The research data was processed using IBM SPSS software version 17. Before conducting the suitability test normality tests were done using Saphiro Wilk. The Wilcoxon test was performed to determine differences in the two devices, p values <0.05 indicating a difference. The Spearman correlation test and the Bland-Altman test were also carried out to determine the level of compatibility between the two devices.
RESULTS
Study participants as many as 48 people got a median WBC value of 11.06 103 / µL (0.66-32.16) with a differential count value: a median neutrophil value of 7.45% (2.04-32.4), a median value of lymphocytes 1.72% (0.09-22.68), median monocyte value 0.7% (0.14-5.77), median eosinophil value 0.13% (0.1-1.15), median value basophils
0.09% (0.02-1.73). All remaining serum
samples were measured by procalcitonin values by the ECLIA method with the Cobas e601 Roche automatic device and the FIA method by the automated Nano Entek FREND tool. All remaining blood samples examined had a median value at ECLIA 0.52 and a median value, at an FIA of 0.78.
Table 1. Results PCT with Metode ECLIA methods and FIA methods.
|
Procalcitonin (ng/mL) |
Median (Minimum Maximum) |
Standard Error |
r |
P-value |
|
ECLIA |
0,52(0,03-129,6) |
88,58 |
0,973b |
0,086a |
|
FIA |
0,78(0,07-32) |
0,000b |
a Wilcoxon test : no difference if P<0,05
b Spearman Correlation : no difference if P<0,05 r : Coefficient correlation
Wilcoxon test results showed that the two methods did not have significant differences with a value of P> 0.086 (a). Table
1 also shows that the two methods have a strong correlation with the correlation coefficient r of 0.973 using the Spearman test.
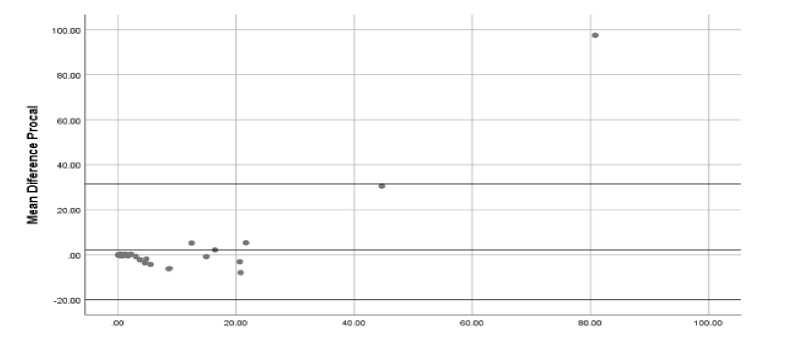
Figure 1. Bland Altman Correlation with ECLIA and FIA Methods.
The results of the study of 48 samples obtained a very good suitability between the Roche Cobas e601 tool and FREND Nano Entek. This compatibility is seen with the Bland Altman graph in Figure 1.
DISCUSSION
This study examined procalcitonin levels in 48 patients treated in intensive care, obtained a median PCT value using the ECLIA
DOAJ

method of 0.52 ng / mL (0.03-129.6) and of 0.78ng / mL (0.07-32 ) using the FIA method. This result is in accordance with the study of Harbarth et al, which obtained a median PCT level on arrival in the intensive room of 0.6 (05.3) ng / ml in SIRS patients, 3.5 (0.4-6.7) ng / ml in sepsis patients 6.2 (2.2-85 ) ng / ml in severe sepsis patients and 21.3 (1.2-654) ng / ml in sepsis shock patients (p <001). This Harbarth et al study examined PCT levels using immunoassays with the sandwich method and chemiluminenscence detection system in accordance with manufacturing protocols.7 Research conducted at Sanglah Hospital did not distinguish between samples diagnosed with Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome (SIRS) or sepsis.
Research by Ahmed et al. In this hospital in Pakistan obtained a median PCT level of 1.5 µg / L with 79% of patients having a PCT level> 0.5 µg / L. PCT levels with a median of 2.14 µg / L were found in the group of patients with positive culture results and this value was significantly higher than patients with negative blood cultures (p <0.01).8 Ahmed et al's research is similar to the results of this study, except that this study does not look for the results of blood culture research samples.
Several immunoassays for assessing PCT levels are commercially available and are based on sandwich immunoassays developed by BRAHMS GmbH Germany. Rascher et al, assessed PCT levels using various types of immunoassays such as the following: PCT with LIA obtained a range of values from 0.1 to 500 ng / mL, using Liason obtained a range of values from 0.1 to 500 ng / mL, Sensitive Kryptor obtained a range of 0.02-50 ng / mL, ADVIA Centaur obtained levels of 0.02-75 ng / mL, Elecsys with a range of values of 0.02100 ng / mL, VIDAS obtained a range of values of 0.09-200 ng / mL.9
Research conducted at Sanglah Hospital obtained a median PCT value using the ECLIA method of 0.52 ng / mL (0.03-129.6) and 0.78 ng / mL (0.07-32) using the FIA method. Wilcoxon test for PCT values using the ECLIA method with the FIA method did not show significant differences (p = 0.086).
Meta analysis conducted by Cabral et al. Obtained several studies using different methods of measuring PCT levels such as PCT-Q, PCT Lumi test, ECLIA, and sandwich immunoassay and fluoresencence techniques (VIDAS). Different methods produce different measurement values for PCT levels, so a mean
cut value of about 1.59 ng / mL is obtained in establishing a diagnosis of sepsis.10
Research that distinguishes
measurement of PCT levels using the ECLIA method with the FIA method that has been conducted by Fernandes et al. Shows the same results as this study, namely there is no significant difference between the ECLIA method with the Kryptor Compact plus (Thermo Fisher) automatic device and FIA with an automatic tool AFIAS 6.11
Bland Altman suitability test for Procalcitonin examination between the ECLIA method and the FIA method in this study with a mean differential PCT of 2.138 ± 14.93, 95% CI (-2.198-6474) (P = 0.326). This indicates that both ECLIA and FIA methods show the same results, it can be seen in the graph that almost all plots are located within 1.96 times the standard intersection means that these observations have in common with other words not as outliers, this is supported by the results (P> 0.05) and confidence interval confidence that is in the 95% CI range.
CONCLUSIONS AND SUGGESTIONS
In this study no significant differences were found between the ECLIA and FIA methods. Both methods also show a very strong level of correlation and a good level of conformity.
Suggestions for further research need larger samples.
REFERENCES
-
1. Dae Young Hong, Sang O Park, Jong Won Kim, Kyeong Ryong Lee,kwang Je Baek, Ji Ung Na, Pil Cho Choi, Young Hwan Lee. 2016. Respiration Procalcitonin in Critical Illness. 2092:241–251.
-
2. Fatema H. Ashour, Hend M. Maghraby, AsmaaS. Hassan.
2017.Procalcitonin as A Diagnostic and Prognostic Marker of Sepsis in Critically Ill Patients in Intensive Care Unit.
-
3. Caspar Corti, Markus Fally, Andreas Fabricius-Bjerre, Katrine Mortensen, Birgitte Nybo, Jensen Helle F Andreassen, Celeste Porsbjerg, Jenny Dahl Knudsen, Jens-Ulrik Jensen. 2016. Point-of-care procalcitonin test to reduce antibiotic exposure in patients hospitalized with acute exacerbation of COPD. International Journal of COPD 2016:11 1381–1389. Denmark.
DOAJ

-
4. Vijayan, Vanimaya, Shilpa
Ravindran, R. Saikant, S. Lakshmi, R. Kartik and Manoj. G. 2017. Procalcitonin: a promising diagnostic marker for sepsis and antibiotic therapy. Journal of Intensive Care 5(51), 1-7. India
-
5. Anonim. 2018. Elecsys Brahms PCT (PCT) Diagnostics Roche. Available http://e-labdoc.roche.com.Germany
-
6. Anonim. 2018. Nano Entek. Insert kit FREND PCT Procalcitonin. Korea
-
7. Harbarth, S., Holeckova, K., Froidevaux, C., Pittet, D., Ricou, B., Grau, G.E., Vadas, L., Pugin, J., and the Geneva Sepsis Network. 2001. Diagnostic Value of Procalcitonin, Interleukin-6, and Interleukin-8 in Critically Ill Patients Admitted with Suspected Sepsis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med Vol 164. pages 396–402.
-
8. Ahmed, S., Siddiqui, I., Jafri, L.,Hashmi, M., Khan, A.H., Ghani, F. 2018. Prospective evaluation of serum procalcitonin in critically ill patients with suspected sepsis- experience
from a tertiary care hospital in Pakistan. Annals of Medicine and Surgery 35 180–184.
-
9. Rascher, D., Geerlof, A., Kremmer,E., Krämer, P., Michael, S., Hartmann, A., Rieger, M. 2014. Total internal reflection (TIRF)-based quantification of procalcitonin for sepsis diagnosis – A point-of-care testing application. . Biosensors and Bioelectronics 59 :251–258.
-
10. Cabral, L., Afreixo, V., Almeida, L., Paiva, J.A. 2016.The Use of Procalcitonin (PCT) for Diagnosis of Sepsis in Burn Patients: A MetaAnalysis. PONE 22: 1-16.
-
11. Fernandez R.M, E. Fernández, O. Espanyol, L. Macias, X. Filella. 2019.
Evaluation of procalcitonin in a fluorescent immunoassay AFIAS-6 analyzer. Clinica Chimica Acta 493, S643–S672. Hospital Clínic de Barcelona, Spain.
-
12. Meisner M. 2000.
Procalcitonin(PCT)- A New
Innovative Infection Parameter, Biochemical and Clinical Aspects. ISBN : 3-131055503-0. Thieme,
Stuggart. New York.
Discussion and feedback