Recreation Opportunity Spectrum Analysis of Strategic Area Tourism Destination Pelang Region
on
E-Journal of Tourism Vol.8. No.2. (2021): 172-183
Recreation Opportunity Spectrum Analysis of Strategic Area Tourism Destination Pelang Region
Herlina Suksmawati, Leily Suci Rahmatin*, Praja Firdaus
Universitas Pembangunan Nasioanal “Veteran” Jawa Timur, Indonesia
*Corresponding Author: leily.suci.par@upnjatim.ac.id
DOI: https://doi.org/10.24922/eot.v8i2.77562
Article Info
Submitted:
August 20th 2021.
Accepted:
September 18th 2021.
Published:
September 30th 2021
Abstract
Tourism planning and development should be adjusted based on regional characteristics and applicable policies, but over time, tourism planning often pays less attention to the carrying capacity of the region. So there is a need for an analytical study of tourism planning that is tailored to the characteristics of the region to create sustainable tourism. This research was conducted at the Pelang Regional Tourism Destination, Trenggalek Regency using Recreation Opportunity Spectrum Analysis and the concept of Attractions, Amenities, Access, Ancillary to see tourism potential. The research methodology used is Qualitative Description with the methods of collecting observation data, documentation studies and indepth interviews. Tourism development in the Pelang Regional Tourism Destinations based on regional tourism development planning is included in the concept of natural tourism development with collaborative management between stakeholders, but in the current development implementation when viewed from the Recreation Opportunity Spectrum analysis there is no clear management system and the Pelang Tourism Destinations are classified as the characteristics of semi-primitive areas have not paid attention to aspects of appropriate land use functions, especially in the development of tourism supporting infrastructure.
Keywords: ROS, DPD, Tourism Potential
INTRODUCTION
Tourism is an industry that does not merely produce the usual formal production with real products, tourism is often an activity that is supported by the same sector in each region, although with different supporting components (Lickorish, 1997). Tourism is one of the supporting industries for economic, cultural and environmental development, not only globally but at the regional level as well as a promising industry (UNWTO, 2005). The supporting
aspects of the tourism sector that rely on human movement and travel between regions are located in the transportation, accommodation and supporting infrastructure sectors for the sake of achieving travel. Tourism creates products that can only be obtained by traveling and visiting activity producers, landscapes that cannot be found in the area of origin are the driving force for travellers, Rojek (in Franklin 2003) tourism is not only in the form of literature and writings about regional landscapes but also physical visits to enjoy the scenery and tou-
rism potential of a tourism destination area. The main function of the tourism industry is to serve tourists, all forms of activity in tourism are related to service products and are tangible (Camilleri, 2018). Tourism destinations are the center of activities in the tourism industry, in tourism destinations a network of systems is formed that can have an impact on other supporting sectors, both positive and negative , so that it is necessary to have tourism planning and management wrapped in the concept of sustainability (Cooper, 2016).
Regional planning and development is important to adjust land use, so that integrated development in an area creates memorable tourism, development management provides identification of opportunities for development more sustainable tourism Development planning will provide a match between tourist expectations and the availability of potential developed in tourism activities In its development aspects of ROS (Recreation Opportunity Spectrum) Analysis makes management development aspects based on regional characteristics so that they are integrated (Brown, 1982).
Tourism development is also formed based on tourism potential which is currently not only about luxury and modern services, but also as a fulfillment of people’s curiosity about activities in certain places so that they can gain new experiences in the midst of post-modern community trends (Page, 2019). New experiences are the main goal of visiting destinations with uniqueness, beauty, and value in the form of a diversity of natural, cultural, and manmade wealth that is the target or purpose of tourist visits (Tourism Law, 2009). In the development of tourism activities, various innovations in planning and developing tourist destinations have become important, to improve the quality of tourist attractions. Regional characteristics, the availability of accommodation, access, facilities and infrastructure for attractions that are
different from each region and good management will make tourism an industry that is not only of economic value. Tourism is expected to be sustainable for the natural and social resources of local communities in tourism areas (Newsome, Moore and Dowling, 2013). It is the same thing that is now starting to be realized by stakeholders in Pelang District, the potential for areas with coastlines to become opportunities for tourism development.
Purpose of the research is to analyze the potential development planning of the Pelang Regional Tourism Destination area, the characteristics of the area with hilly and coastal landscapes have the opportunity to become superior tourism, but over time there needs to be a balance between the usability of the area and the value of the area designation, especially in tourism, so that tourism becomes a priority. sustainable industry. The analysis of regional characteristics will be a guideline for the development and planning of tourism areas, especially in determining aspects of supporting tourism activities, tourism transportation, tourism accommodation and other tourism supporting infrastructure.
Purpose of the research is to analyze the potential development planning of the Pelang destination area by using a tourism planning analysis that is adapted to the characteristics of the region, in order to create sustainable tourism both in terms of natural resources, economy and socio-culture of the local community. Thus, tourism development planning is no longer based on the interests of certain stakeholders.
LITERATURE REVIEW
Tourism Destinations
A geographical area located in one or more administrative areas in which there are tourist attractions, public facilities, tourism facilities, accessibility, and communities that are interrelated and complement
the realization of tourism (Tourism Law, 2009). Tourism destinations are areas that are limited by administration, which can be in the form of regions, countries, islands, cities and villages, where tourists spend at least one night in the area using tourism supporting products, tourism resources and enjoying the attractions found in tourism destinations. Tourism destinations are also limited based on their management to increase marketability and the target market that is expected to come to visit (UNWTO, 2002). Destination analysis is important to determine the potential of the Pelang tourism area, supporting sectors and other industries in the implementation of tourism.
Regional Tourism Strategic Areas Tourism
destination areas that have the main function of tourism with planning and development according to their potential in one or more aspects so as to have an impact on other sectors, such as economic, social and cultural growth, empowerment of natural resources, and environmental carrying capacity. Regional Strategic Areas are defined as tourism destinations that are superior to certain regions in increasing tourism development, the KSPD referred to in this study is the Plang KSPD which is a tourism area with a natural concept with collaborative management. This analysis is used to see the suitability of the area designation with the regional planning and development policies of Trenggalek Regency so as to make sustainable tourism.
Recreation Opportunity Spectrum
As a concept used in developing a planning framework for outdoor recreation areas, ROS is used to be able to define the characteristics of the area and the suitability of land use and transportation patterns as well as other tourism supporting facilities. Clark and Stankey (1979) describe the most specific arrangement of factors that influen-
ce the development of tourism areas. Implying that six basic factors are used to define ROS namely access, use of resources outside of tourism, tourism management, social interaction, acceptance of visitor impacts, and other acceptable impacts. Brown (1982) details 6 (six) physical characteristics of the region in determining planning and development opportunities for tourism areas, Primitive Destination Setting, which is characterized as an area where human activity is very rare except for those who expect tranquility to blend with nature, the use of modern transportation is not allowed, primitive destinations are destinations that do not prioritize facilities. Semi-Primitive is divided into semi-primitive with motorized vehicles and without motorized vehicles. Characteristics of destinations with minimal provision of facilities as a safe limit both against environmental damage and visits, management control may be found in the area but is very low, if semiprimitives are motorized, it is possible to use vehicles motorized but very low, and vice versa if the semi-primitive area is non-motorized then the use of motorized vehicles is not allowed but there is still management control that is different from primitive where all forms of activity are only with nature without any mixing of activities outside the destination. Next, Roaded Natural is a destination with the characteristics of a natural area but with facilities developed outside the tourism destination area to provide comfort, tourist attractions are still in the form of natural landscapes with limited management, activities outside of tourism can also be found in this area but are still very rare. Characteristics of rural areas of destinations with facilities that have been developed to be able to receive visits, modification of renewable resources and the development of other supporting facilities have begun to increase. Availability of trails, motorized transportation, accommodation and arrangement of the physical
environment in order to develop tourism activities. Urban Characteristics of destinations with modern facilities, infrastructure facilities are provided in large numbers with emphasis on comfort and fulfillment capacity with the number of visits mass, the convenience factor takes precedence over the physical character of the environment. ROS analysis is used to identify the Pelang Regional Tourism Destinations and the suitability of tourism planning development to the physical environment of the region. Especially in determining the characteristics and classification of tourist attractions that are designated as Tourism Strategic Areas for Pelang Beach and Kili - Kili Beach Regions.
Aspect 4A
Formation of tourism destinations that can attract tourist visits cannot be separated from aspects of 4A (Attractions, Amenities, Access, Ancillary) (Cooper, 2016). Tourist attraction is anything that has uniqueness, beauty, and value in the form of a diversity of natural, cultural, and man-made wealth that is the target or purpose of tourist visits. Amenities are all forms of activities and services provided to meet the needs of tourists during their visit to travel, both accommodation facilities, food and beverage services, souvenirs, banking and other additional facilities. Access is often interpreted as road facilities available in tourism destinations, access is also about transportation networks and transport capacity in meeting the needs of moving between areas of origin to tourist destinations, including the availability of land terminal infrastructure, air and rail lines, in the research on Sustainable Development Strategy For Ecotourism at Tangkahan, North Sumatra by Wi-ranatha (2015), access indicators in tourism are considered important by visitors both in terms of means of communication and transportation, but from the results of research access to tourist attractions is inadequa-
te. Ancillary is a destination management organization or management system that exists in tourism destinations, management can be in the form of formal and informal organizations, national or regional as well as the public or private sector.
METHODS
research was conducted at Pelang Regional Tourism Destinations, Trenggalek Regency in two tourist attractions namely Kili - Kili beach and Pelang beach, data was collected through observation and documentation related to supporting Pelang tourism planning and development. Indepth interviews were conducted to obtain information about the development stages currently in the DPD Pelang. This research approach uses a qualitative approach with a qualitative descriptive method, looking for an overview of the research data, comparing the data obtained and looking for the relationship between each data obtained.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Tourism development is inseparable from the wealth of resources that can be potential in determining each attraction that will be a factor attracting tourists to visit a tourism destination (Boniface, Brian and Cooper, 2014). Tourist attraction itself is defined as an activity that is unique and can provide a value experience for visiting tourists, the existence of a leading destination in Trenggalek Regency, which is one of the regencies that is included in strong economic development in the Wilis circle area. The Panggul KSPD Destination is a regional tourism planning and development area.
The potential of tourism destinations is also supported by four aspects of tourism, the nature of tourism that demands collaboration between every aspect of the organization and product so as to produce
an integrated network of tourism activities, both in the form of tourist attractions, supporting facilities and management (Cooper, 2016). Potential 4A (Attractions, Amenities, Access, Ancillary) Pelang Regional Tourism Destinations.
Attractions, all forms of activities that can be enjoyed and carried out by tourists while doing tourism are very important, various forms of tourist attractions or tourist attractions are the leading tourist destinations in the Pelang area which are superior in regional tourism development. The combination of types of attractions is a potential in the development of regional tourism, several tourist attractions are found in tourism destinations in the Pelang area.
Natural tourist attractions, attractions whose sources come from natural wealth, ownership of attractions are often disguised as administrative areas or local ownership, these attractions are classified as resource-based tourist attractions thus the characteristics of the area become important to the selling value of attractions. The attractions of DPD Pelang are resource-based, Pelang beach which is located in the southern region is approximately 1.5 hours to 2 hours drive from the city center of Trenggalek district, white sand beach with a direct boundary to the Indian Ocean, the uniqueness of Pelang beach is also found in the presence of a waterfall. The characteristics of the hilly area make it an added value. Kili-Kili Beach, is a beach that is still in the same line as Pelang beach but is separated from Bukittinggi, the characteristics of Kili-Kili beach are more of a turtle conservation area, the activities that are the main attraction on Kili-Kili beach are mostly turtle conservation activities. tourists who come have the characteristics of special interest tourists.
An artificial tourist attraction, this attraction was originally not there because of tourism activities but functioned for other activities, but there are also tourist attrac-
tions that are deliberately made to fulfill the wishes of tourists (Cooper, 2016). Tourist attractions made by DPD Pelang include heritage areas, both historical and cultural heritages, as well as the planning process for developing a culinary center that will become an additional attraction so that it will become a new value in the introduction of local culinary that is not only different from other regions but also has history.
The existence of natural and artificial tourist attractions in the Pelang DPD is a potential tourism development that is interesting to visit, the location of tourist attractions in one area and a short travel time are the choices for tourists visiting various types of attractions.
Amenities, most tourist activities are carried out in tourist destinations, the needs needed during tourism will be important to be available in the area, the provision of facilities shows the multi-sectoral nature of tourism supply and interdependence between various sectors ranging from the provision of physical facilities to the need for service products hospitality (Cooper, 2016). The availability of additional facilities and hospitality provides an opportunity to increase regional income if every available facility is local and under regional ownership, the expenditures made by tourists will directly become income for the region (Cooper, 2016). The availability of hospitality services in the form of lodging and food and beverage services from DPD Pelang is more for MSMEs, the added value of facilities with management from MSMEs makes strengthening the local economy, local cultural values and the introduction of local culinary delights will be an attraction for tourists to choose to use services provided locally. However, what is often an obstacle in the development ofservices hospitality which also includes food and beverage services regarding management in services is the conformity of expectations to be obtained while using the available services, as
well as minimum standard of facilities that can provide comfort in using both in terms of hygiene, sanitation and decent conditions. use.
Access, access is defined as the availability of supporting facilities and infrastructure to and while in tourism destinations, not only as the provision of connecting roads, terminals, but also transportation networks that support tourism which is an activity of moving from the area of origin to the destination. The convenience and diversity of transportation modes and supporting infrastructure during the trip is an experience for tourists when going to tourist destinations, traveling from one area to another will not be easy and efficient if it is not supported by the availability of adequate transportation support facilities and infrastructure, both in terms of numbers availability with the capacity of the facility as well as the feasibility of the transportation network to be used (Boniface, Brian and Cooper, 2014). DPD Pelang does not yet have an integrated transportation system, the procurement of public transportation in the form of a transportation network is not well organized, the types of public transportation that can be used are limited with operating hours and the range of service areas for tourism locations can only be reached by private vehicles. In addition, several accesses to tourist attractions to the dominant beach in the area behind the hills are in poor condition.
Ancillary, is another aspect that must exist in tourism destinations, management organizations or in tourism are known as Destination Management Organizations (DMOs) (Pike and Page, 2014). DMOs or organizations that manage tourism can be formal or non-formal, in tourism in DPD Pelang management is intertwined with the division of obligations in every tourism development, both at the district, sub-district and village levels. The management of each tourist attraction in the Pelang DPD
consists of the local government, local communities and contributions from conservation activists, especially for the Kili-kili beach whose main attraction is turtle conservation. However, often the effectiveness of various tourist attraction managers becomes an obstacle in developing better tourism services, sectoral ego becomes an important issue, especially related to user fees and the provision of tourism supporting infrastructure development. This can also be an obstacle if coordination between stakeholders is not well established, as is what is happening in the Pelang DPD, there is a collaboration gap between relevant stakeholders in tourism development and marketing at the district, sub-district and village levels. build collaborative coordination among stakeholders.
Recreation Opportunity Spectrum, planning for tourist destinations that are used to analyze the character of tourist destinations to be able to provide diverse marketing opportunities, ROS planning framework in research aims to see land management and suitability (Brown, 1982). As in this paper, the existence of tourist attractions in the strategic area of the Pelang tourism destination makes this area with a hilly structure an opportunity to become an outdoor tourist attraction, with a unique landscape that is different from the surrounding area with coastal tourist attractions. Development planning in the form of existing systems in tourism, management arrangements and supporting industry support to make tourism activities develop sustainably, the existence of a tourist attraction in the Pelang area managed by various stakeholders has its own challenges, both in the form of policies and regulations, administrative boundaries and management authorized to carry out regional planning and development in the form of tourism supporting infrastructure and other 4A aspects. Such characteristics must of course also be a benchmark in making further
tourism development decisions.
The planning of the Pelang Beach and Kili - Kili KSPD which is a form of outdoor tourism activity and comes from the existence of resources makes the tourist attraction area unique and has a marketing selling value. The factors that influence the development of the Kili - Kili and Pelang Beach areas seen from the characteristics of the area that have been adopted from (Clark and Stankey in Sarbanes, 2011) provide an overview of the factors that influence tourism development seen from various aspects of supporting the tourism industry. Analysis of ROS characteristics provides guidance for relevant stakeholders regarding regional development so that it can guide policy making and regional planning decisions. Clark and Stankey provide an overview of how the benefits of ROS in analyzing the characteristics of the area so that it can provide convenience and assist in the formulation of appropriate management objectives, for example an area that cannot receive noise, namely the Primitive area, of course, developed using the concept of special interest tourism that only certain people only hope for peace in the journey undertaken.
The aspect that was seen during the research on the Pelang KSDP, especially the Kili - Kili beach and the first Pelang beach in the form of access, was divided into three basic components in looking at the characteristics of the region, including:
Ease of reaching tourism destinations, Pelang KSPD especially Pelang Beach and Kili - Kili which are the mainstay of tourism. Natural tourist attraction located in an area with a hilly landscape and not on the main road connecting the regions makes access to the location a fairly long time allocation, taking less than 2 - 3 hours drive from the city center of Trenggalek Regency. However, the availability of directions makes it easier to find the location of tourist attractions. The design of the ease of reach-
ing the area is one of the determining factors for regional development, determining the right development concept to have a sustainable impact on tourism destinations.
The access system to tourism destinations is one of the factors in planning and developing tourism destination areas, the suitability of road facilities and the transportation used will have an impact on regional functions, the readiness of the region to accept noise with the construction of road facilities and transportation routes is an important aspect that must be considered. In the table above, the Pelang KSPD, especially the Kili-Kili and Pelang beaches, which are behind the hills, makes land use for road infrastructure development important, adapted to semi-primitive areas, especially with hilly landscapes, regional resilience and regional acceptance capacity will be important when there is a change in the concept of tourism development, KSPD Pelang which in this case the Kili - Kili and Pelang beaches are two tourist attractions with the concept of nature, but the characteristics of the 2 beaches have differences, especially attractions and activities that tourists can do for Kili - Kili beach tourism activities designed not for mass tourism and not with modern transportation routes and facilities, this is because the area is a conservation area, in contrast to Pelang beach which is designed to accept tourists without special interests. However, when viewed from the Pelang beach area, aspects of transportation routes and road facilities, especially in tourist attractions, are no longer semi-primitive areas, it is also a note in this study that it is important in tourism sustainability to pay attention to land use and land use in accordance with the characteristics use in the development of tourism facilities and infrastructure. Access to the area is still largely constrained by the quality of roads and lanes, inadequate roads and well-designed transportation routes.
Mode of Transport, the provision of
adequate transportation facilities will make the image of a tourist destination better, the importance of the role of transportation is now also a global issue, especially regarding the safety and comfort of transportation users, therefore the establishment of policies regarding the development and procurement of mass transportation supporting tourism activities is very important. Important in its implementation, the policy of using transportation can also support activities, especially tourism with the concept of nature that prioritizes hospitality and tourism sustainability. At the outset, it is easy to assume that each form of transport is very different. In fact, all systems share some common characteristics, which have important practical implications. As Burkart and Medlik stated more than 25 years ago: ‘Transportation systems can be analyzed in three parts: Paths or routes, Means used, and Infrastructure or terminals’ (Burkart and Medlik, in Middleton, 2009). Modern transportation is a factor that reduces the motivation of visits to tourist attractions, but there are some exceptions to this, in the development of Pelang KSPD tourism which is an area with a natural landscape describing the development of transportation facilities that are not environmentally friendly, the use of transportation facilities is more important towards regional access. The lack of environmentally friendly mass transportation such as a well-systemized transportation network makes this area a semi-primitive area characteristic with motorized transportation support, but in some areas it is still considered a semi-primitive area without motorized transportation, this is because the area was developed as a conservation area. turtles so that the area’s entry point to the location of a tourist attraction is without the use of transportation modes. The available mode of transportation is limited to land transportation, and only in the form of buses between cities within the province and village transportation, but
cannot directly reach tourist destinations. The lack of development and provision of transportation means a minus in tourism development when viewed from the satisfaction of tourists to enjoy a comfortable and safe travel atmosphere.
Utilization of Resources Outside of Tourism Activities, the design in the development of areas that are adapted to the needs of the population who resides permanently in the tourism destination area becomes important as tourism develops, the availability of resources will become economic goods for local communities if there is no control in planning and developing tourism. Every resource is basically the property of the local community, there must be an evaluation in the use and utilization of resources so that they do not become scarce goods. Utilization of resources outside of tourism activities usually occurs due to the high number of visits to tourism destinations, causing high competitiveness between tourists and local communities. The existence of the Pelang KSPD tourism destination in an unspoiled area requires planning and development of nature-based tourism by taking into account sustainable resources. sustainable development is designed to meet the needs of the present without eliminating its existence in the future, but several aspects that occur in tourism development in the Pelang KSPD area regarding the development of permanent facilities that eliminate the main functions of nature-based tourism areas, such as the provision of permanent footpaths, stairs to the hills , and several irrigation lines and artificial ponds. So with the characteristics of areas with semi-permanent landscapes, attention is needed, especially in developing and procuring infrastructure to support sustainable tourism activities. Ecologically sustainable, namely: tourism development does not cause negative effects on the local ecosystem. In addition, conservation is a necessity that must be pursued to protect
natural resources and the environment from the negative effects of tourism activities. 2. Socially acceptable, namely: refers to the ability of local communities to absorb tourism activities without causing social conflict. 3. Culturally adaptive, meaning that local communities are able to adapt to a quite different tourist culture (tourist culture). 4. Economically profitable, meaning: the benefits derived from tourism activities can improve the welfare of the community (Arida and Sunarta, 2017).
Availability of Tourism Destination Managers, in tourism management there are many models that can be applied in planning and building the management of tourism destinations, especially to increase demand (Sharma, 2014), but there is often a mismatch between the expectations of the stakeholders who are responsible for a particular tourism destination. Strategic mechanisms are often needed in achieving management conformity, Hall and Mcarthur in Newsome convey several examples of management in conservation areas with regional zoning, every aspect of zoning is developed according to the function of the area, especially towards the procurement and improvement of facilities and infrastructure. The conservation area is prohibited from having permanent buildings, and no activities are allowed during the period of environmental restoration for some time in order to maintain the balance of the ecosystem. similar to the management contained in the development of the Pelang KSPD area, the priority of management becomes important when the area is included in the conservation area, namely the Kili -Kili coast, the manager becomes the main door in enforcing development and conservation policies, understanding the process in conservation and the vulnerability of the area will become important aspect in maintaining the sustainability and sustainability of tourism. However, a collaborative management system is also another option to
create a balance in management by involving every tourism stakeholder, both local governments, local communities, and conservation observers. In contrast to Kili-kili beach, Pelang beach dominates the role of local government under the district tourism office, every aspect of development and planning is managed by the dina, with the involvement of local communities who are semi-involved. The characteristics of management in the development and planning of the Pelang KSPD tourism are far from balanced collaboration, the dominance of several parties who are still strong tends to hinder tourism development, the readiness of each tourism stakeholder in terms of resources is still very limited so that it can be categorized as an area with semi-primitive characteristics with limitations. the use of technology in the process of managing tourist attractions, especially in terms of entry fees and networks between tourist attractions in recording the number of visits at a certain time.
Social interaction is defined as a dynamic relationship between individuals and individuals, between individuals and groups or between groups and groups in the form of cooperation, competition or conflict. Social interaction is an orderly relationship in the form of actions based on social values and norms prevailing in society. Social interaction is not enough just to be explained as a reciprocal relationship between humans based on certain patterns, because social interaction is still based on certain characteristics or characters. In order to be categorized as a form of interaction, the reciprocal relationship between humans must have certain criteria such as, there must be more than one actor, there is communication between actors, there is a time dimension and there are certain goals (Setiadi and Kolip, 2011). In social interaction there are also elements, namely: social action; This action is understood as an act, behavior or action taken by humans to
achieve certain goals. social contacts; individual or group action in the form of a sign that has meaning for the perpetrator, and the recipient responds to the action with a reaction. social communication; interpreted as a process of giving mutual interpretation to or from between parties who are in a relationship and through that interpretation the parties who are interconnected manifest behavior as a reaction to the intent or message intended by the other party (Setiadi and Kolip, 2011). Social interactions that occur in the community in the Pelang KSPD area, between the community and tourists are not enough to just be explained as reciprocal relationships. Rather, it is based on several elements, so that it can be categorized as a form of interaction. The elements contained in social interaction are social action, social contact and social communication. So, with the fulfillment of elements in social interaction, the relationship that exists in tourism activities between the community and tourists as well as within the community can be said to be social interaction. Social action, in this case the local community as the host, has not really formed the level of frequency in the reciprocal relationship of activities carried out in tourism, enough between buyers and sellers, not as hosts in service activities. Social conflict occurs only for a moment without any follow-up and gives the impression that it is not optimal in the field of tourism hospitality services, and social communication that occurs is limited to relationships in economic transactions without any impression that continues as a story that will be carried after the tour is over. Semi-primitive characteristics are very clearly visible in the Panggul KSPD area, but the need to increase tourism awareness from local communities will be an added value in tourism development and planning.
The impact of tourist visits seen from the level of impact and the extent of the impact is still not widely seen, this is also
because the number of visits is still limited to special interest tourists and local tourists but not yet mass. However, the problem of household waste and waste is something that deserves attention in order to maintain sustainability and comfort during tourism activities, it is necessary to treat household waste and waste that is not easily decomposed so that the problem of waste and waste can turn into other positive things if the management is applied properly, both in the recycling process and in the utilization of biogas from recycled waste. This is something that is now being designed by stakeholders so that the waste problem is no longer a contributor to environmental destruction.
The level of regional resilience seen from the location of the southern coastal area makes the Pelang area prone to earthquakes and tsunamis, building structures and evacuation routes are important in planning the development of tourism areas. In addition, the landscape of hilly areas that tend to be prone to landslides requires that land use in development must pay attention to the border areas of ravines and cliffs. The development of tourism that is not yet mass in nature, provides an opportunity for the Pelang KSPD area to be able to provide prevention in the fulfillment of infrastructure facilities that are adapted to regional characteristics. Environmentally friendly and sustainable infrastructure facilities will be an important aspect in fulfilling the hospitality services of the Pelang KSPD, and become a supporting element for sustainable tourism. The characteristics of the Pelang Coastal and Kili-Kili KSPD areas which are adapted to the determination of the characteristics of the ROS area based on the explanation above are described in table 1 Characteristics of the Pelang Coastal Area (Adopted from Clark and Stankey, 1979). The results of the observation and study of documentation are detailed in the table below regarding the regional analysis
based on the influencing factors.
Table 1. Characteristics of the Pelang
Coastal Area
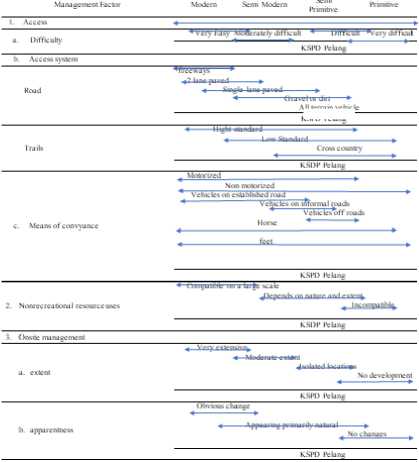
KSH> HeUns
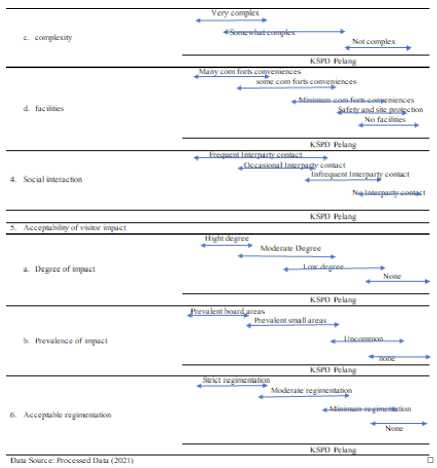
Characteristics of the Semi Primitive Region of the Pelang KSPD Area for Pelang Beach and Kili - Kili Tourist Attractions, development planning that needs to be adjusted includes the use of resources outside of tourism activities which should pay attention to local aspects so that the level of competition between local communities and tourists will not cause negative impacts in the future, In addition, the existence of
disaster-prone areas requires a more planned development concept, especially in the feasibility study of disaster-prone areas in tourism development.
CONCLUSION
Analysis of potential 4A of the Pelang Tourism Destination has opportunities in increasing regional tourism, especially the diversity of tourist attractions. however, in terms of access and amenities, improvements are needed both in terms of the availability of transportation and supporting infrastructure, as well as hospitality services in the form of lodging, food and beverage services which are not widely available. Management and collaboration between stakeholders has not been well organized and there is no special tourism organization within the local community to create tourism awareness.
In terms of analyzing the characteristics of the Pelang DPD area, it is included in the character of a semi-primitive area with several supporting characteristics such as access to tourism destinations, land use functions outside of tourism activities which are still dominated by green areas, as well as the impact of tourism activities on the environment and socio-cultural surroundings. still relatively low. Stakeholder participation and collaboration is needed to create sustainable tourism, planning and development that is prepared by adjusting the characteristics of the region will minimize the negative impact of tourism.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
To all tourism stakeholders of Trenggalek Regency, especially in the Pelang KSPD area, research team colleagues and faculty leaders who have given research permits, university level leaders who have provided funding support and trust to the research team to carry out one form of tri
dharma with research.
REFERENCES
Arida, I. N. S. and Sunarta, N. (2017) Pariwisata berkelanjutan. Bali: Cakra Press.
Boniface, Brian and Cooper, C. (2014) Worldwide Destinations: The Geography of Travel and Tourism Fifth Edition. Elsevier Ltd.
Brown, P. J. (1982) ‘Recreation opportunity spectrum with implications for wildlife-oriented recreation’.
Burkart, A. J. and Medlik, S. (1974) ‘Tourism: Present, Past, and Future’. London: Heinemann.
Camilleri, M. A. (2018) Travel marketing, tourism economics and the airline product: An introduction to theory and practice. Springer.
Cooper, C. (2016) Essentials Of Tourism Second Edition Edition Second. Pearson Education Limited.
Lickorish, L. J. (1997) ‘Travel statistics—
the slow move forward’, Tourism Management, 18(8), pp. 491–497.
Newsome, D., Moore, S. A. and Dowling, R. K. (2013) Natural Area Tourism Ecology, Impacts and Management 2nd edition. Channel View Publications.
Page, S. J. (2019) Tourism Management. Routledge.
Setiadi, E. M. and Kolip, U. (2011) Pengantar sosiologi: pemahaman fakta dan gejala permasalahaan sosial: teori, applikasi dan pemecahannya. Kencana.
Sharma, K. (2014) Introduction to Tourism Management. Tata McGraw-Hill Education.
UNWTO (2005) Making Tourism More Sustainable - A Guide for Policy Makers.
Wiranatha, A. S. (2015) ‘Sustainable Development Strategy For Ecotourism at Tangkahan, North Sumatera’, E-Jour-nal of Tourism, 2(1), pp. 1–8.
http://ojs.unud.ac.id/index.php/eot
183
e-ISSN 2407-392X. p-ISSN 2541-0857
Discussion and feedback