FEASIBILITY STUDY BASED ON ECONOMIC PERSPECTIVE OF COBALT NANOPARTICLE SYNTHESIS WITH CHEMICAL REDUCTION METHOD
on
Cakra Kimia (Indonesian E-Journal of Applied Chemistry)
Volume 7 Nomor 1, Mei 2019
FEASIBILITY STUDY BASED ON ECONOMIC PERSPECTIVE OF COBALT NANOPARTICLE SYNTHESIS WITH CHEMICAL REDUCTION METHOD
Fira Nandatamadini, Suci Karina, Asep Bayu Dani Nandiyanto* Departemen Kimia, Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia, No. 229 Setiabudhi Street, 40154, Bandung, West Java, Indonesia
ABSTRACT: Cobalt nanoparticle powder is synthesized by chemical reduction method. Cobalt nanoparticle powder is synthesized through reduction of aqueous solution of Co ions by NaBH4 using cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) as cationic surfactant. Cobalt nanoparticles have many applications, especially in the field of technology. The successfulness of a project will produce opportunities that make it possible to advance technology in developing countries. For this reason, a feasibility study for the synthesis of cobalt powder nanoparticles is needed. This project has estimated ideal conditions for bad cases that will occur in production by adding several parameters which are raw materials and sales. This feasibility study was using two parameters which were economic analysis and evaluation techniques including Gross Provit Margin (GPM), Cumulative Net Present Value (CNPV), Break Even Poit (BEP), Payback Period (PBP). These parameters were to show potential profitability for the project. Although the IRR value of this project was not very promising, all other parameters had positive impacts. The project that used a reducing metal salt method which is an easy process and purchased relatively inexpensive equipments will provide benefits and attrac investors of this project.
Keyword: Cobalt nanoparticles, Reduction, Mass balance, Economic evaluation, Feasibility study
Cobalt (Co) is a chemical element in Period 4, Group 9, block D element, with an atomic mass of 58,933195. The cobalt atom has a radius of 125 pm and the Van Der Waals radius of 192 pm. In its elemental form, cobalt is gray and shiny. Cobalt releases blue pigments and have been used in a long time for paint and glass colours. Cobalt is a ferromagnetic metal, used in the production of very hard and magnetic superalloys [1].
Co nanoparticle powders were synthesized through chemical reduction methods by several researchers [2]. Reducing cobalt (II) by a chemical reduction reaction, adding sodium borohydride at a controlled rate, with a concentration of NaOH which varies in reducing solution. The synthesized particles are about 20-100 nm in size [3]. Some applications of Co nanoparticles including in the field of separation technology, information storage systems, catalysis, and biomedicine [4] require discrete nanoparticles, identical in shape and size, and uniform in composition and crystal structure [5]. However, the formation of nanoparticles that meets these requirements has proved to be difficult due to their high surface energy, intrinsic magnetic properties, and available inherent limitations [6]. So far, the liquid phase synthesis route is the most successful in preparing of monodisperse Co nanoparticle. Examples of liquid phase processes are metal salt reduction, reverse micelles, and thermal decomposition of organometallic precursor. Among these methods, the method chosen in this study was the reduction of direct metal salt in solution because it is the simplest, fastest, and cheapest method, desired in large-scale production [7].
The economic evaluation analysis is used to analyze the feasibility study of cobalt powder nanoparticle synthesis using chemical reduction. The economic evaluation of the chemical industry is a form of quantitative assessment of what is expected and desired by the community to carry out the investment process in a
project [8]. This evaluation uses several parameters such as Gross Profit Margin (GPM) calculation which is the first analysis to determine the level of profitability of a project from economic conditions; then the Internal Rate of Return (IRR) calculation to ensure economic conditions; Break Even Point (BEP) calculation that states the drinking capacity where the project is not beneficial. This BEP is an important factor to avoid the project experiencing losses; then the calculation of the Payback Period (PBP) to predict of how long it takes for an investment to be able to return the initial total expenditure [8]; The calculation of Commulative Net Present Value (CNPV) to predict the condition of the project as a function of the production year or CNPV can be obtained as the number of cumulative financial flows each year; and calculation of the Profitability Index (PI) to obtain information about profits.
Data for chemicals, equipment specifications and labor are needed to support economic evaluation analysis. Then the data was calculated to analyze the industrial feasibility study of making cobalt nanoparticles powder which was designed to meet the feasibility test or not to be established. So from this industry feasibility study is very important to support how to optimize the project to benefit economic growth at this time.
Cobalt nanoparticles are needed especially in technological applications, for example as medical sensors; biomedicine as a contrast agent for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI); coatings, plastics, nano fibers, nanowires, textiles, high-performance magnetic recording materials; magnetic fluids-made of iron, cobalt, nickel and mixed nanoparticles; and as microwave absorbing material [9]. Therefore the successfulness of this project will create job opportunities that have a direct impact on reducing poverty and application of advancing technologies, especially in developing countries.
All calculations in economic evaluation research were carried out in ideal conditions. The additional variables were
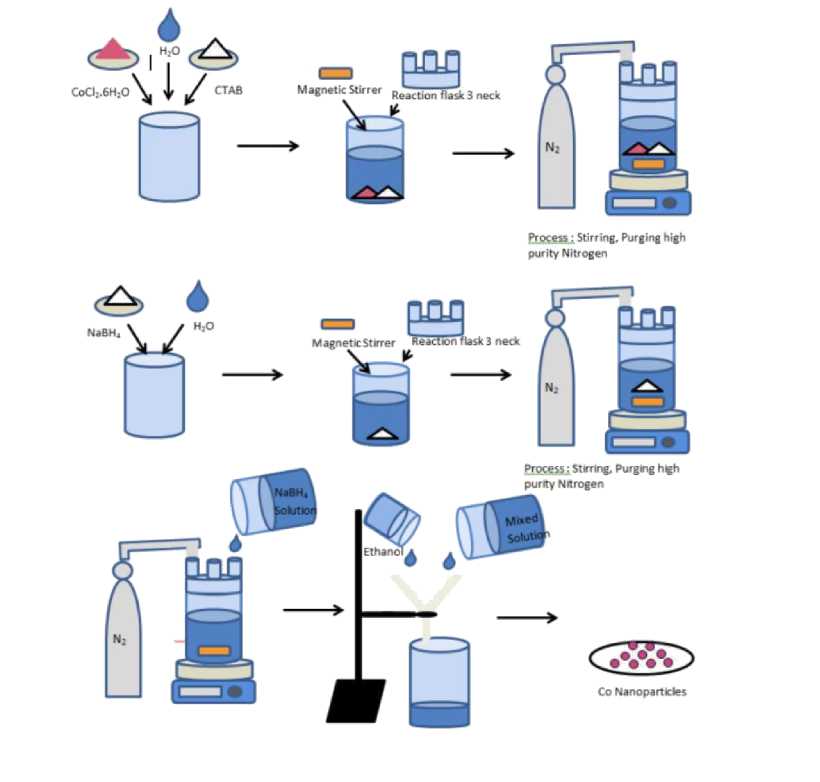
Figure 1. Flowchart of the Co nanoparticle synthesis process
added to calculations such as raw materials, product sales, and CNPV analysis based on changes in Variable Cost.
Co nanoparticle production was carried out based on the literature [3]. The most successful route of liquid phase synthesis in the preparation of nanoparticles Co is monodispers. An example of a method in the liquid phase is the reduction of metal salt. The method of reducing metal salts directly in solution is chosen because of the simplest, fastest, and cheapest method.
The systematics of the process carried out in this economic feasibility study is shown in Figure 1. The steps for the synthesis of Co nanoparticles were as follows: A total of 23.76 g cobalt (II) chloride hexahydrate with 97% purity were added to the reaction flask beaker and 9.12 g CTAB with 99% purity were added. CTAB is a cationic surfactant (surface active agent) and is added because its addition is expected to facilitate pore formation. Then 1 L of distilled water was added and the beaker reaction flask was closed using a 3-neck reaction flask. Stir the mixture using a magnetic stirrer while being purged with high purity nitrogen gas. A total of 37.84 g sodium borohydride (NaBH4) solids with 98% purity used as reducing agent was also dissolved in 1 L of distilled water in the beaker reaction flask, which was also fed with high purity 63
nitrogen gas. Then, the reducing solution (NaBH4) was added slowly to a solution containing a solute to prevent a sudden reaction since CTAB can cause boiling over. During this process, nitrogen gas was purged continuously. After the reaction was completed, the resulted solid was filtered and washed with distilled water and ethanol to prevent oxidation. The prepared powder was then dried. The following is the Co nanoparticle formation reaction mechanism using chemical reduction:
4Co2+ + BH4- + 8OH- → 4Co + BO2- + 6H2O
The economic feasibility study method is used to analyze the price, components, and specification of equipment obtained from Sigma-Aldrich and other online shopping webs such as alibaba. Data were obtained later with mathematical analysis to obtain economic evaluation parameters such as GPM, IRR, PBP, CNPV, BEP and and PI sales to investment. Economic evaluation parameters are calculated based on literature [3]. Calculations use the following formula:
-
(1) GPM is calculated by reducing the costs of raw material and sales results.
-
(2) PBP is a calculation to predict the length of time which takes an investment to be able to return the initial total expenditure. In short, PBP is calculated based on when CNPV reaches zero for the first time.
-
(3) IRR was from the following equations:
n⅛⅛2:
Where Co and Ct are the total investment costs and the net cash inflow during the t period, respectively. t is time (as year). r is the discount rate.
-
(4) CNPV is a value obtained from net present value (NPV) at a certain
time. CNPV is obtained with adding of the NPV value from the beginning of the project. NPV is calculated by multiplying cash flows by a discount factor.
-
(5) Calculating BEP by dividing fixed costs and profits.
-
(6) Estimating the PI by dividing the CNPV with the sales or total investment cost, based on profit on sales or the type of PI profit for investment, respectively.
When evaluating the economic feasibility, various conditions were tested such as changes in raw materials, sales capacity and Variable Cost variations.
As shown in Figure 1, the yield of the production has been calculated by stoichiometry based on 24 L of cobalt solution, with the following assumptions:
-
(1) All compositions of chemicals used such as cobalt (II) chloride hexahydrate, CTAB, and sodium borohydride used for the synthesis of cobalt nanoparticles are based on the literature[3].
-
(2) The rate of conversion of nanoparticle Co formation is 90%
-
(3) Losses caused by washing with ethanol are 10%.
Based on the assumption above, it takes 570.24 g of cobalt (II) chloride hexahydrate, 218.88 g of CTAB, 908.16 g of sodium borohydride, ethanol, and water to produce 543 g Co nanoparticles in a day. Co nanoparticles production is obtained every day which is 108 products (per 5 grams), so that in one year it will produce as many as 32400 nanoparticle Co products (per 5 grams).
In this study, we made several assumptions. Those several assumptions were made to look at the economic perspective in this study:
-
(1) Materials used in the production nanoparticles Co were estimated
2.300,00
1.800,00
1.300,00
800,00
300,00
Oq (200,00) 0
O
O
O
O
Q
O
O
.∙∙∙β
O
O
5
10
Economic evaluation parameters
GPM/y
GPM/pack
PBP
BEP
Break Even Capacity
IRR
last CNPV/total investment
PI profit-to-sales
PI profit-to-TIC
15
20
value
111.867,59 USD/y
345,27
2,01 years
8,10 process
970,27%
15,00% %
102.553,53%
4,20% %/year
588,55% %/year
25
LIFETIME (YEAR)
Figure 2. The ideal condition of the CNPV under various indicators of economic evaluation
3.1.1 Ideal Condition
based on the stoichiometrical calculation.
-
(2) The process neglected other supporting fees such as plant startup, instrumentation, and electrical-
[10] related component
.
-
(3) Calculations using IDR
(Indonesian currency). Then, the value is converted to USD with a
fixed value of 1 USD = 10000
IDR
-
(4) Prices of commercial raw materials obtained from available online sites. The price of cobalt
-
(II) chloride hexahydrate is 1.5247 USD / gram, CTAB
2.4526 USD / gram, and sodium borohydride 1.3297 USD / gram
-
(5) The raw materials used for productionarecalculated according to stoichiometric calculations.
-
(6) The electricity price is 24.9375 USD / day.
-
(7) Labor is paid at 8 USD / day
-
(8) The duration of the project is 20 years.
The CNPV curve with economic evaluation indicators that vary in ideal conditions is presented in Figure 2. The analysis results show that the synthesis of Co nanoparticles from cobalt (II) chloride hexahydrate is quite profitable. Technical analysis explains that the preparation can be improved using currently available technology, with equipment that is reasonably priced. The results of the economic evaluation also showed very promising results, because of the positive value of the economic parameter values. However, to return the initial total expenditure on the project, it takes around 2 years.
-
3.1 .2 Effect of Raw Material and Sales Figure 3 shows the effect of raw material prices and sales on the GPM, where GPM is calculated by reducing sales revenue and production prices. The most influential indicator in the raw material of this project is sodium borohydride because it has the highest prices compared to other raw materials. Sodium borohydride is an important factor in the method used for the synthesis of nanoparticles Co as a reducing
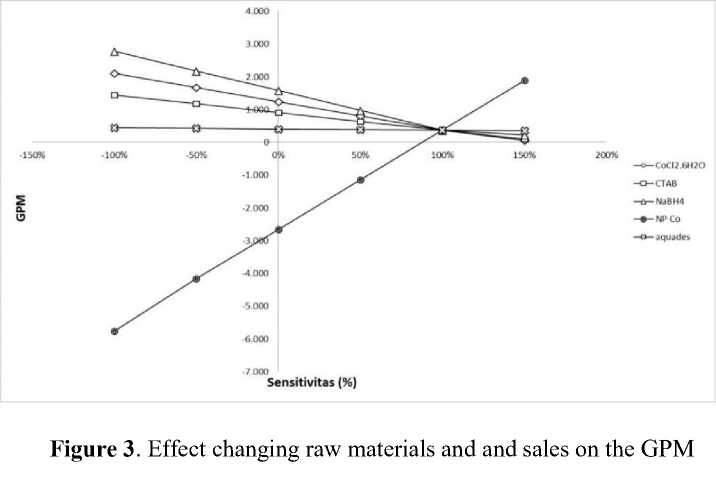
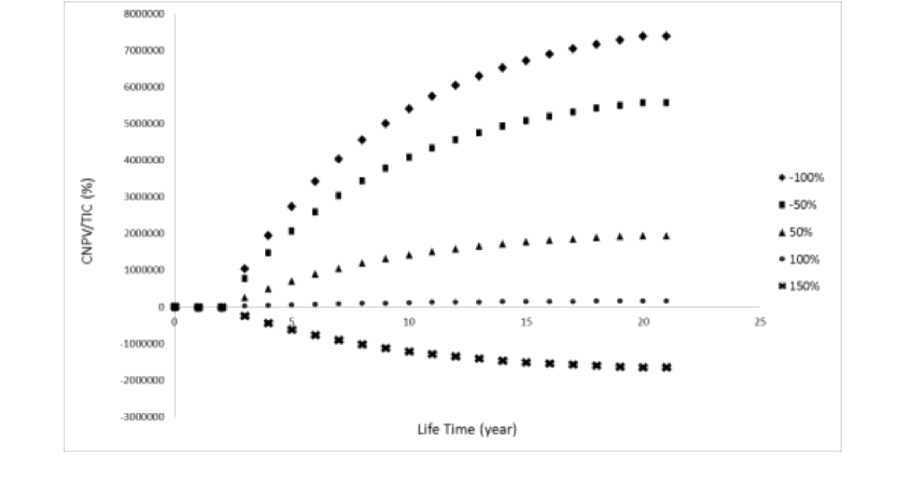
Figure 4. CNPV curve below the various Variable Cost values
agent and more needed raw materials. The curve analysis in Figure 3 shows that the higher the price of raw materials, it will have a negative impact on the project because it produces a low GPM value, which means it produces fewer sales that will be loss to the project. Otherwise, if the price of raw materials is lowered and the value of GPM is high, it will produce more sales that will benefit the project. On the sale of nanoparticles Co it will be profitable
if the sales price is increased by more than 100% because it shows a positive GPM value, which means the project is feasible to run.
CNPV analysis based on changes in Variable Cost is shown in Figure 4. The Variable Cost in analysis result plays an important role in profits, which the decrease in Variable Cost affects the high value of final CNPV. Related to increasing Variable Cost, the project will suffer losses.
Table 1. The Estimate of Gross Profit Margin on Nanoparticle Co production
Nanoparticle Co
28
Table 2. Economic Parameters for The Production of Nanoparticle Co
|
Product |
Profit-to- Investment |
Payback Periode (Years) |
IRR (%) |
BEP (cycle) |
Last CNVP/TIC |
|
(%) |
(%) | ||||
|
Nanoparticle Co |
588,55 |
2 |
15 |
8,90 |
102.533,53 |
But when using a lower Variable Cost value, the project will be more effective in producing more profits. When using production that is more than 100% Variable Cost, minimum PBP cannot be achieved. In fact, this can make the project unprofitable. The maximum value in varying sales must be less than 100% of the estimated value, in order to support the project.
In terms of engineering, it can be seen the possibility in the scaling up process. This is because the scaling up process can be applied using generally available and cheap equipment. Plans suggested in the future with a project that has 28800 cycles per year is to produce nanoparticles Co of 171,072 Kg from an amount of 163,1232 Kg cobalt (II) chloride hexahydrate per year. In ideal conditions, the project can reach 28800 cycles per year, which can produce 163,1232 Kg of nanoparticle Co per year. By calculating the length of the project for 20 years, the results show that the entire project can produce an amount of 3.262464 tons products in ideal conditions.
Based on the analysis of the data produced, the project is feasible to run in ideal conditions. However, the project will be profitable under certain conditions if there are changes in certain situations so the project can no longer be run. So the specific conditions based on the analysis of economic feasibility studies can be explained, namely the project will be profitable if the increase in raw material costs is less than 150% of the estimated raw material costs, the impact of the GPM value of each raw material in the synthesis of Co nanoparticles varies. The indicator of the most influential raw material is sodium borohydrate. To keep the project running, product sales must be as high as possible. However, the increase in sales must keep optimized because of its relationship with other costs. When there are conditions to reduce sales, sales must remain higher than 100% of the estimated value. Otherwise, the project will be failed. This is because the minimum costs for production cannot be obtained if sales are too low. In addition to the economic outlook, a project feasibility analysis also needs to be carried out. In this project, GPM in Table. 1 and BEP Table. 2 shows a positive value, which means that this project is feasible to run.
Another economic analysis factors such as PBP, and CNPV provide highly profitable prospects from investors. PBP analysis shows that investment will be
profitable after more than 2 years. It could be that this project can be competed with PBP capital market standards because the investment will return in a short period of time.
Regarding the parameters, the IRR in Table.2 value shows 15% for 20 years project life. This value gives a relatively of low yield per year. This IRR value indicates that this project is not promising. However, based on the final CNPV parameters, the value is quite high for projects with 20 years of life time. This result is also reinforced with the relatively high values for PI. Of course, this typical long-term investment will provide a very interesting perspective for investors.
This study shows the engineering perspective and economic evaluation in production of Co nanoparticles. PBP analysis shows that investment will be profitable after more than 2 years. It could be that this project can compete with PBP capital market standards because the investment will return in a short period of time. It can be seen from the IRR value of this project that it is not very promising, but there are other parameters that have a positive impact on attracting investors in this project. Some of the things that affect these benefits include using a chemical reduction method, because this method is very easy and cheap. From this analysis of economic evaluation, we can conclude that this project is feasible to run.
-
[1] N.N. Cobalt Nanoparticles.
https://www.americanelements.com/cobalt-nanoparticles-7440-48-4.
Accesed on December 2018.
-
[2] Lu, J., Dreisinger, D. B.,, and Cooper, W. C. 1997. Cobalt precipitation by reduction with sodiumborohydride. Hydrometallurgy, 45 (3): 305-322
-
[3] Hong, S. H., Jin, Y.,M., Kim, K., T.,
Ahn, C., W., Park, D.,S., Song, W,. Y. 2014. Synthesis of Nanocobalt Powders for an Anode Material of Lithium-Ion
Batteries by Chemical Reduction and Carbon Coating. Journal of Nanomaterials, 2014: 8 pages
-
[4] Kodama, R. H. 1999. Magnetic
Nanoparticle. Journal of Magnetism and MagneticMaterials, 200: 359-372
-
[5] Cao, G. 2002 Nanostructures and Nanomaterials: Synthesis,
Properties, Aplication. Imperial College Press.
-
[6] Balela, M.D. l., 2008. Cobalt
Nanoparticles Prepared by LiquidPhase Reduction. Malaysia: University Sains Malaysia
-
[7] Curcin, V., Guo, Y. 2002. Scientific Workflow Applied to Nano- and Material Science. Imperial Collage London
http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/378103
-
[8] Nandiyanto, A.B.D., and Ragadhita, R., 2018. Evaluasi Ekonomi
Perancangan Pabrik Kimia. Bandung UPI Press.
-
[9] N.N. Cobalt Nanoparticles-properties, Applications. Available online at: https://www.azonano.com/article.as Accesed on December 2018.
-
[10] Ragadhita, R, Nandiyanto, A.B.D., Maulana, A.C., Oktiani, R., Sukmafitri, A., Machmud, A., Surachman, E. 2019. Techno-Economic Analysis for The Production of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticle Produced by LiquidPhase Synthesis Method. Journal of Engineering Science and Technology, 14 (3): 1639 - 1652
68
Discussion and feedback