PROFITABLITY AND LIQUIDITY ON CORPORATE VALUE THROUGH DIVIDEND POLICY AS INTERVENING VARIABEL: EMPIRICAL STUDY ON ISLAMIC CAPITAL MARKET
on
249 Buletin Studi Ekonomi. Vol. 25 No. 2, Agustus 2020
PROFITABLITY AND LIQUIDITY ON CORPORATE VALUE THROUGH DIVIDEND POLICY AS INTERVENING VARIABEL: EMPIRICAL STUDY ON ISLAMIC CAPITAL MARKET
Sutrisno1
Bagus Panuntun2
Universitas Islam Indonesia, Yogyakarta, Indonesia1,2
Email: sutrisno@uii.ac.id1
Abstract: Profitablity and Liquidity on Corporate Value Through Dividend Policy as Intervening Variabel: Empirical Study on Islamic Capital Market. The purpose of this study is to examine the effect of profitability and liquidity on dividend policy and firm value. It also examines the role of dividend policy as an intervening variable between profitability and liquidity on firm value. The population of this study is companies registered in List of Sharia Securities consisting of more than 300 companies. Samples were taken as many as 100 companies with a purposive sampling method. The observation period is 3 years (2016-2018). To test hypotheses using multiple regression analysis. The result shows that profitability is significant and positively effect on dividend policy, while liquidity does not affect on dividend policy. Profitability and dividend policy have a positive and significant effect on firm value, while liquidity has no effect on firm value. Another result of dividend policy is able to be as an intervening effect on profitability of firm value but not as an intervening liquidity relationship to firm value.
Keywords: profitability; dividend policy; liquidity; firm value; Islamic capital market.
INTRODUCTION
The Islamic capital market is still interesting to study because of its increasingly encouraging development. Based on the Indonesia Stock Exchange data, the number of investors until the end of October 2019 reached 62,840, an increase of 41% from the position at the end of 2018 (Tari, 2019). The growth of sharia stock investors is higher than the total investor growth in the same period of 20%. This is inseparable from the role of the Indonesia Stock Exchange which continuously introduces the services, functions and role of the Islamic capital market in Indonesia. The encouragement of the stock exchange is expected to increase capital market literacy rates, particularly the Islamic capital market.
To support the development of the Islamic capital market, the Financial Services Authority (OJK) has also made a 2014-2019 Islamic capital market roadmap with the tagline ‘building synergies for a growing, stable and sustainable Islamic capital market’. The roadmap is being revised to suit current economic conditions (Kontan.co.id., February 17, 2020). Until the end of 2019, there have been 368 companies included in the Sharia Securities Register.
Companies that are included in the List of Sharia Securities are also profit-oriented, the difference is that the types of business of companies listed in sharia securities must not violate Islamic sharia. In addition, the company’s debt may not exceed 41% of its total assets. They are also demanded to be able to improve the welfare of shareholders. Thus, companies in the Islamic capital market must be able to increase the value of the company as a general corporate goal.
Company value is investors’ perception of the level of success of a company that is often associated with stock prices. High stock prices will increase investor confidence in the company’s current performance and future prospects. Fundamentally, the value of the company will be affected by the company’s financial performance (profitability), because with high profitability the company is expected to be able to pay dividends, thereby increasing share prices (Fajaria & Isnalita, 2018). Therefore, it is the duty of management to continuously improve company performance through profitability. Tahu & Susilo (2018) also revealed that profitability will increase the value of the company, because investors have more
confidence in company shares that are able to generate profits. As found by Jaara et al., (2018); Gunawan et al., (2018); Malik et al.,(2013) that profitability has a positive effect on firm value. However, different results were found by Rizkia et al., (2013); Tamrin et al., (2017); Sondakh (2019) that profitability had no effect on firm value.
Company value is inseparable from the liquidity owned by the company. Liquidity is the company’s ability to fulfill its financial obligations which must be fulfilled immediately. A company that has high liquidity is expected to be able to pay off its current debt, as well as indicate that it has funds to pay dividends (Malik et al., 2013). Liquidity must be a serious concern because it plays a very important role in maintaining company operations (Sondakh, 2019). Companies that have high liquidity are considered to have good performance by investors. This will attract investors to invest their capital in the company. Malik et al., (2013); Sondakh (2019); Gunawan & Tobing (2018) in their research found a positive and significant effect between liquidity and firm value. But there are other researchers who find that liquidity has no effect on firm value (Fajaria & Isnalita, 2018;
Tahu & Susilo, 2018).
Another factor that influences the company’s supply rate is the dividend policy. Dividend policy is a financial decision whether the profits obtained will be distributed to shareholders as dividends or retained as retained earnings. Dividend policies often lead to conflicts between company management and shareholders. This happens because company managers often have different interests from shareholders (Triani & Tarmidi, 2019). The company management considers the profits derived by the company should be used for company operations. Shareholders consider the profits derived by the company should be distributed to shareholders as dividends. Problems between management and shareholders will result in not achieving one of the company’s objectives, namely increasing the value of the company (Gunawan et al., 2018). Payment of dividends is a positive signal for investors that the company has a good performance, thus encouraging investors to buy company shares which will ultimately increase the value of the company. The results of research by Gunawan et al., (2018); Jaara et al., (2018); Triani & Tarmidi (2019) found a
positive effect on dividend policy on firm value. But the opposite results were found by Sondakh (2019); Ismawati (2018); Anggeriani et al., (2018) who found dividend policy had no effect on firm value.
Dividend policy is determined through a General Meeting of Shareholders (GMS) as the highest authority holder. The portion of the dividend distributed to shareholders is called the dividend payout ratio (DPR), which is the amount of dividend distributed divided by profit after tax. In determining the amount of dividends distributed, the company will look at several factors including profitability and liquidity. Dividends represent profits received by shareholders in exchange for the risk taken because of owning shares. The greater the profit received, the greater the expected dividends will be distributed. The results of the study by Mehta (2012); Gunawan & Tobing (2018) confirm that profitability has a positive effect on the amount of dividends paid. But the results of research by Ahmed (2015); Rizkia et al., (2013) actually found an insignificant effect on profitability on firm value.
Dividends paid also depend on the availability of funds that will be used to pay
dividends. Liquidity as a measure of the availability of current assets is a measure of the availability of these funds. Better company liquidity allows companies to pay large amounts of dividends. Malik et al., (2013) argues that large liquidity is mainly liquid assets in the form of cash, while there is no good business opportunity, there is a tendency to distribute more dividends. This is supported by the results of research by Gunawan & Tobing (2018); Ahmed (2015) who found a positive and significant effect between liquidity and dividend policy. Instead Mehta (2012) found that liquidity had no effect on dividend policy.
The effect of profitability and liquidity on company value can be directly, but also indirectly through dividend policy. Investors who buy company shares expect the company to have good performance and be able to achieve optimum profits with the hope that large profits will provide large individuals. However, this expectation could not have happened, because it was possible at the RUPS that there was a small dividend distribution decision. This is possible if there are profitable investment opportunities so that most of the profits are not distributed but to fund these investment opportunities. Such
conditions certainly disappoint investors, so it is likely that many will sell the company’s shares. As a result, stock prices can go down and company value will also go down. Ananda et al., (2018) in his research found the effect of profitability on firm value through dividend policy. Likewise, Martini (2015) found that profitability affected company value through dividend policy. In contrast, Tahu & Susilo (2018) found that dividend policy cannot moderate the effect of profitability on firm value.
Liquidity is important information for investors to assess the ability of companies to pay dividends. High liquidity allows companies to pay dividends. Thus, high liquidity will be preferred by investors if the liquidity is used to pay dividends thereby increasing share prices. Therefore, liquidity can affect the value of the company through dividend policy. Fajaria et al., (2018) also suspects dividend policy as a moderating variable on the effect of liquidity on firm value. But the results of the study Know & Susilo (2018) found that liquidity cannot be intervening the effect of liquidity on firm value.
The company’s management is chosen by the shareholders to be able to operate the company effectively and efficiently, with the
hope that the company will be able to make a profit. From this amount of profit, it will be decided how much will be distributed to shareholders as dividends and how much profit is not distributed as retained earnings. Dividend policy can be done after the company has sufficient profitability. Thus, the dividend policy will be influenced by the company’s ability to make a profit. The results of research by Gunawan & Tobing (2018); Mehta (2012) reinforce the notion that profitability influences dividend policy. Malik et al.,; (2013) also found the effect of profitability as measured by return on equity (ROE) had a positive and significant effect on dividend policy.
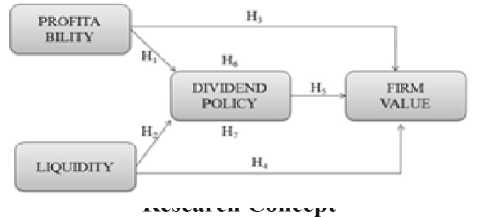
H1: Profitability has a positive effect on dividend policy
In executing the dividend policy, it is necessary to have sufficient cash flow that must be provided by the company. Availability of funds in the company will be reflected in the level of liquidity they have. If liquidity is low, the company cannot afford to pay a sufficient amount of dividends, but if liquidity is high, the company has the opportunity to pay dividends. Thus the dividend policy will be influenced by the level of company liquidity (Griffin,
2010). This is in line with research by Malik et al., (2013); Gunawan &Tobing (2018); Ahmed (2015) who found a positive and significant effect between company liquidity and dividend policy.
H2: Liquidity has a positive effect on dividend policy
The value of the company is identical to the behavior of investors on the exchange, if investors do not like stocks and sell them in large quantities, it is certain that the stock price will decrease because the supply is greater than demand. The fall in stock prices is identical to the decline in the value of the company. Profitability is information that is often used by investors to assess whether the company has good prospects, and as one of the basic decisions to buy shares. High profitability will increase investor confidence in the company’s current performance and future prospects. Management is required to continuously improve company performance through profitability. According to Tahu & Susilo (2018) profitability will increase the value of the company, because investors are more confident in company shares that are able to generate profits. This is consistent with the findings of Jaara et al., (2018); Gunawan et al.,
(2018); Malik et al., (2013) that profitability has a positive effect on firm value.
H3: Profitability has a positive effect on firm value
Liquidity shows the company’s ability to fulfill its financial obligations that must be fulfilled immediately or the obligation to pay its current debt. A company that has high liquidity is expected to be able to pay off its current debt, as well as indicate that it has funds to pay dividends (Malik et al., 2013). Liquidity must be a serious concern because it plays a very important role in maintaining the company’s operations (Sondakh, 2019). Companies that have high liquidity are considered to have good performance by investors. This will attract investors to invest their capital in the company. Malik et al., (2013); Sondakh (2019); Gunawan & Tobing (2018) in their research found a positive and significant effect between liquidity and firm value. But there are other researchers who find that liquidity has no effect on firm value (Fajaria & Isnalita, 2018; Tahu & Susilo, 2018).
H4: Liquidity has a positive effect on firm value Another factor that influences the company’s supply rate is the dividend policy. Divi-
dend policy is the company’s financial decision whether the profits obtained will be distributed to shareholders or retained as retained earnings. Dividend policies often lead to conflicts between company management and shareholders. This happens because company managers often have different interests from shareholders (Tri-ani & Tarmidi, 2019). The company management considers the profits derived by the company should be used for company operations. Shareholders consider the profits derived by the company should be distributed to shareholders as dividends. Problems between management and shareholders will result in not achieving one of the company’s objectives, namely increasing the value of the company (Gunawan et al., 2018). Payment of dividends is a positive signal for investors that the company has a good performance, thus encouraging investors to buy company shares which will ultimately increase the value of the company. The results of research by Gunawan et al., (2018); Jaara et al., (2018); Triani & Tarmidi (2019) found a positive effect on dividend policy on firm value. But the opposite results were found by Sonda-kh (2019); Ismawati (2018); Anggeriani et al., (2018) who found dividend policy had no effect
on firm value.
H5: Dividend policy has a positive effect on firm value
For investors on the Stock Exchange, profitability is an indicator of company performance but is often not used to make stock purchase decisions. This is supported by Rizkia et al., (2013) & Sondakh (2019) who find profitability has no effect on firm value. Even Tam-rin et al., (2017) found profitability to have a negative effect on firm value. Thus profitability does not directly affect the value of the company, but it does affect indirectly through dividend policy. Proditable companies do not necessarily provide dividends, thereby reducing returns for investors. This is possible if there are profitable investment opportunities so that most are not distributed but to fund these investment opportunities. Ananda et al., (2018); Martini (2015) found dividends as an intervening effect of profitability on firm value.
H6: Profitability affects the value of the company through dividend policy
High liquidity shows the company’s ability to pay, thus becoming a signal that companies with high liquidity can increase the value of the company. High liquidity does not
necessarily provide dividends, because it is
met the criteria by taking purposive sampling.
possible that the available funds will be used to
The observation period is 3 years, namely 2016
pay debts or increase investment. Sukmawardini
to 2018. The type of data needed is secondary
& Ardiansari (2018); Fajria et al., (2018) found data in the form of an annual financial statement
a negative effect of liquidity on firm value and
of the company selected as a sample. The
Tahun and Susilo found liquidity had no effect
financial statement data can be taken from each
on firm value. High liquidity if it will be used
company’s website and can also be taken from
to pay dividends will be preferred by investors
the Financial Services Authority (OJK) website
so that it will increase stock prices. Therefore,
through www.ojk.go.id or from the Indonesia
liquidity can affect the value of the company
Stock Exchange’s webside via www.idx.co.id
through dividend policy. Fajaria et al., (2018)
The research variables consist of two
found dividend policy as a moderating variable
types, the dependent variable which is the
in the effect of liquidity on firm value.
variable influenced in the form of company
H7: Liquidity affects the value of the company
value, the independent variable which is the
through dividend policy
variable that is thought to influence the dependent
RESEARCH METHODS
The population in this study are companies on the Islamic capital market which are listed on the List of Sharia Securities (DES). There are more than 300 companies in DES. The samples taken were 100 companies that
variable consisting of profitability and liquidity, and the intervening variable dividend policy. The following is the definition of variables and how they are measured.
Table 1.
Variables and Measurement
|
No |
Varables |
Measurement | |
|
( Market Value | |||
|
1 |
Tobin's Q Dividend |
TQ |
Equity+Total Debt)∕Total Assets |
|
2 |
Payout Ratio |
DPR |
Dividend paid/EAT |
|
3 |
Return on Assets Current |
ROA |
EAT/Total Assets Current |
|
4 |
ratio |
CR |
assets/Current liabilities |
To test the hypothesis a partial test (t test) will be used using a 95% confidence level or a 5% significance level. Statistical tools to test variables that affect firm value using multiple regression models with formulations as follow: Model I
Model II
TQ = α + β1ROA + β2CR + β3DPR (2)
Model III
TQ = α + β3ROA*DPR + β4CR*DPR (3)
Notation:
DPR : dividen policy
ROA : profitability
CR : liquidity
TQ : corporate value
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Descriptive statistics. Based on the results of data processing using SPSS version 21.0, an overview of the data for each variable.Based on the results of descriptive statistics, the value of
the company measured by Tobacco Q (TQ) has a very large maximum value of 23.28, a minimum value of 0.36 with an average value of 1.92%. Dividend payout ratio (DPR) paid has a very large maximum value of 830.47%, but there are also companies that adopt a policy of not paying dividends that look at a minimum value of 18.9%, with an average of 53.63%. Profitability measured by ROA has a maximum value of 92.10% with a minimum value of -5.59 %% with an average value of 8.89%. Liquidity (CR) shows a maximum value of 15.16 times and a minimum value of 0.42 times with an average value of 2.71 times.
Hypothesis Test Results. There are three models in this study, first testing the effect of profitability and liquidity variables on dividend policy, second testing the profitability, liquidity and dividend policy variables on firm value, and third testing the profitability and liquidity variables on firm value through dividend policy.
Table 2.
Descriptive Statistics
|
N |
Minimum |
Maximum |
Mean |
Std. Deviation | |
|
TQ |
300 |
.3597 |
23.2858 |
1.918864 |
2.2679897 |
|
DPR |
300 |
.0189 |
8.3047 |
.536308 |
.8141054 |
|
ROA |
300 |
-.0559 |
.9210 |
.088863 |
.0904521 |
|
CR |
300 |
.4230 |
15.1646 |
2.713835 |
1.9756476 |
|
Valid N (Iistwise) |
300 |
Source: Data processed
Table 3.
Hypothesis Result
|
Model |
TJnstandardized Coefficients |
Standardized Coefficients Beta |
t |
s⅛. | |
|
B |
Std. Error | ||||
|
Dependend Var: DPR I (Constant) |
0.171 |
0.087 |
1.956 |
0.051 | |
|
ROA |
3.132 |
0.502 |
0.348 |
6.233 |
0.000 |
|
CR |
0.032 |
0.023 |
0.078 |
1.394 |
0.165 |
|
Dependend Var: TQ II (Constant) |
0.996 |
0.211 |
4.714 |
0.000 | |
|
ROA |
15.735 |
1.287 |
0.628 |
12.230 |
0.000 |
|
CR |
-0.102 |
0.055 |
-0.089 |
-1.836 |
0.067 |
|
DPR |
0.371 |
0.143 |
0.133 |
2.587 |
0.010 |
|
III R0A*DPR |
0.543 |
0.331 |
0.109 |
1.643 |
0.049 |
|
CR*DPR |
-0.023 |
0.045 |
-0.035 |
-0.523 |
0.301 |
Source: Data attached
Profitability and dividend policy. Table 3 shows that profitability calculated by ROA results in a significance level of 0,000 greater than the significance level set at 0.05, so it can be concluded that the ROA statistically has a significant effect on dividend policy, meaning that an increase in ROA will increase the dividend policy adopted by the company. Profitability is the main indicator of financial performance, because with profitability it shows that management has put maximum effort into managing the company. Return on assets (ROA) is the company’s ability to generate profits with all assets owned, the higher the ROA is the higher the ability to generate profits. The profit obtained will be decided in the General Meeting of Shareholders (AGM) whether to be
divided as dividends or not divided as retained earnings which is used for investment (Mehta, 2012). The higher the profit, the more likely it will be distributed as a dividend. For investors, profitability is a signal that the company has a good performance which is expected to be distributed as dividends. These results are consistent with the findings of Tamrin et al., (2017), Gunawan and Tobing (2018) Ananda et al., (2018) and Mehta (2012) who found ROA to have a positive effect on dividend policy. However, the opposite result was found by Malik et al., (2013), Nasution et al., (2019) and Rizkia et al., (2013) who found no significant effect between ROA and dividend policy.
Liquidity and dividend policy. The results of the liquidity hypothesis test on the
dividend policy show a significance value of 0.165 greater than the significance level of 0.05, so it can be concluded that liquidity has no effect on dividend policy. The policy of giving cash dividends is of course very dependent on the availability of money in the company (Malik et al., 2013). Liquidity shows the ability of a company to meet its short-term financial obligations, meaning that the higher the liquidity, the more available funds for payment of short-term obligations, including to pay dividends (Ahmed, 2015). But apparently dividend payments are not based on the availability of good liquidity. This is possible because the company has good liquidity, which can be seen in the data that the average liquidity is 2.71. Thus the company in distributing dividends relies more on profitability than liquidity (Mehta, 2012). This is consistent with the results of the study by Mehta (2012) and Moradi et al., (2010) which determine liquidity has no effect on dividend policy. But the results of research by Malik et al., (2013), Gunawan and Tobing (2018), Ahmed (2015), and Khan and Ahmad (2017) determine the positive and significant effect between liquidity and dividend policy.
Company profitability and value. Hypothesis test results of the effect of profitability with firm value indicate a significance value of 0,000 smaller than 0.05, meaning that profitability has a significant and positive effect on firm value. Thus the increase in profitability will be able to increase the value of the company. According to Ehrhard and Brigham (2012) the main purpose of the company is to improve the welfare of the owner by increasing the value of the company. The value of the company measured by Tobin’s Q shows the market value of its own capital with a stock price indicator, meaning that if the stock price rises will increase the value of the company. Rise and fall of share prices will be influenced by the position of supply and demand for shares. The more shares requested the higher the price. Investors will look for companies that have good prospects, and one of the signals is profitability. The higher the profitability will affect investor interest in these shares, and the more interested in the stock will increase the stock price. Jacob and Taslim (2017) also revealed that profitability will increase the value of the company, because investors have more confidence in company shares that are able to
generate profits. As found by Jaara et al.,(2018), Gunawan et al.,(2018), Ananda et al., (2018) and Malik et al.,(2013) that profitability has a positive effect on firm value.
Liquidity and company value. Hypothesis test results of the effect of liquidity on firm value indicate a significance value of 0.067 greater than the significance level of 0.05 meaning liability does not affect the firm value. Liquidity is the company’s ability to fulfill its financial obligations that must be fulfilled immediately or the obligation to pay its current debt. In addition to paying off debt, the availability of liquidity can also be used as an indicator of ability to pay dividends. Liquidity is indeed very important for the company in order to maintain trust in its creditors. However, for investors liquidity information is not so necessary. Investors prioritize profitability information and dividend policy. Therefore liquidity has no effect on firm value. These results support the study of Tahu and Susilo (2018) which also found that liquidity had no effect on firm value. Likewise, Fajaria et al., (2018) also found that liquidity had no effect on firm value. However. Malik et al.,(2013), Sondakh (2019), Gunawan and Tobing (2018)
found a positive and significant effect between liquidity and firm value.
Dividend policy and company value. The results of the hypothesis test dividend policy on firm value produces a significance value of 0.010 smaller than the significance requirement of 0.05. Thus the dividend policy has a significant positive effect on the value of the company, meaning that the higher the dividend distributed will increase the value of the company. According to Triani and Tarmidi (2019) this dividend policy often creates conflict between management and shareholders. Management wants profits to be used to increase company funding, especially if there are profitable business opportunities, while shareholders want profits to be distributed as dividends. According to Lintner (1956) in his theory Bird in Hand said that investors preferred dividends over capital gains. Therefore, dividend policy will positively affect the value of the company. The dividend policy is a positive signal for investors that the company is in a good performance condition, therefore some companies tend to distribute dividends even though the profits are not large. The results of this study support the research of Gunawan et al.,(2018), Jaara et al.,(2018) and
Triani and Tarmidi (2019) finding a positive effect on dividend policy on firm value. But there are some researchers such as Sondakh (2019), Ismawati (2018), Anggeriani, eta.l (2018) who find dividend policy has no effect on firm value.
Profitability and company value with dividend policy as intervening. Test the dividend policy hypothesis as an intervening variable the effect of profitability on firm value produces a significance value of 0.049 smaller than the 0.05 requirement, meaning that dividend policy can be an intervening variable. These results indicate that the role of dividend policy is indeed very important. No matter how much profit the company makes, if it does not distribute dividends, it will not attract investors to buy it. Dividends are compensation for funds invested by investors through the purchase of shares. The amount of dividend will determine the amount of return received by investors and shareholders. Dividends paid are real returns for investors on the investment risk they take. While other benefits are capital gains, the difference between the selling price of shares above the purchase price, if the shares are sold, it means that there is still potential profit. These results support Septiani et al., (2018) and Jacob
and Taslim (2017) who find the dividend policy variable to be an intervening variable of the effect of profitability on firm value.
Liquidity and company value with dividend policy as intervening. Hypothesis test results of the effect of liquidity on firm value with dividend policy as an intervening variable produce a significance value of 0.301 greater than the required 0.05, meaning that dividend policy cannot be an intervening variable on the effect of liquidity on firm value. These results confirm that indeed investors in buying shares do not consider company liquidity (Malik et al.,2013; Sondakh, 2019; and Gunawan and Tobing, 2018). This also confirms this research that liquidity has no effect on dividend policy. These results support Jacob and Taslim (2017) who found dividend policy unable to be an intervening effect of liquidity on firm value. Likewise, Tahu and Susilo (2018) also found dividend policy unable to be an intervening effect of liquidity on firm value.
CONCLUSION
Based on the results of hypothesis testing using multiple regression, it can be concluded that profitability has a significant and positive
effect on dividend policy while liquidity has no effect on dividend policy. Profitability also directly influences company value. Likewise, the dividend policy also has a direct influence on the value of the company, while liquidity has no direct effect on the company’s value. Dividend policy is able to be an intervening variable on the effect of profitability on firm value, while the effect of liquidity on firm value cannot be intervened by the dividend policy.
The results of this study are expected to contribute to the company’s management in making decisions, especially in the context of increasing company value. It can also be used by investors in making investment decisions. Research is expected to be a contribution of thought to science, especially relating to dividend policy and corporate value, so that researchers can continue to be asked to develop it further, so that they can perfect the results of this study which still has many weaknesses.
REFERENCES
Ahmed, I.E,. 2015. Liquidity, Profitability and the Dividends Payout Policy. World Review of Business Research. Vol. 5(2). 73 – 85
Ananda, A.F., Sanusi, A and Harmono. 2018. Effect of Profitability of Corporate Values through Dividend Policy. Journal of Business and Management. Volume
20(7). 14-22
Anggeriani, Fachrudin, K.A and Silalahi, A.S,. 2018. The Effect Of Dividend Policy, Firm Size and Capital Structure On Firm Value with Corporate Social Responsibility As A Moderation Variable In Open Mining Companies In Indonesia Stock Exchange. Journal of Business and Management. Vol 209 (11). 70-82
Ehrhard, M.C and Brigham, E.F,. 2012. Financial Management: Theory and Practice. 14th Ed. South-Western. Cengage Learning. USA
Fajaria, A.Z and Isnalita,. 2018. The Effect of Profitability, Liquidity, Leverage and Firm Growth of Firm Value with its Dividend Policy as a Moderating Variable. International Journal of Managerial Studies and Research. Vol. 6(10). 55-69.
Griffin, C.H,. 2010. Liquidity and Dividend Policy: International Evidence.
International Business Research. Vol. 3(3). 3-10
Gunawan, I.M., Pituringsih, E and Widyastuti, E,. 2018. The Effect Of Capital Structure, Dividend Policy, Company Size, Profitability And Liquidity On Company Value (Study At Manufacturing Companies Listed On Indonesia Stock Exchange 2014-2016). International Journal of Economics, Commerce and Management. Vol. 6 (6). 405-420
Gunawan, F.S and Tobing, W.L,. 2018. The Effect Of Profitability, Liquidity And Investment Opportunities On Dividend Policy. South East Asia Journal of Contemporary Business, Economics and Law. Vol. 15(5). 189-196
Ismawati, L,. 2018. The Influence of Capital Structure and Dividends Policy to Firms Value Listed at Indonesian Stock Exchange. Proceeding. Advances in Social Science, Education and Humanities Research, volume 225. 272276
Jaara, B., Alashhab, H., and Jaara, O,. 2018. The Determinants of Dividend Policy for Non-financial Companies in Jordan. International Journal of Economics and
Financial Issues. Vol 8(2). 198-209
Jacob, J and Taslim, F.A,. 2017. The Impacts of The Ratio of Liquidity, Activity And Profitability Towards Company Value With Dividend Policy As Intervening Variables. Journal of Business and Management. Volume 19(10). 1-7
Lintner, J. 1956. Distribution of Incomes of Corporations among Dividends, Retained Earnings, and Taxes. American Economic Review, 46, 97–113
Malik, F,. Gul, S., Khan, M.T., Rehman. S., and khan, M,. 2013. Factors Influencing Corporate Dividend Payout Decisions of Financial and Non-Financial Firms. Research Journal of Finance and Accounting. Vol.4(1). 35-48
Martini, P.D. 2015. Influence PolicyAgainst Debt and Profitability Firm Value: Dividend Policy as moderating variables. Journal of Science and Accounting Research. 3 (2).
Mehta, A,. 2012. An Empirical Analysis of Determinants of Dividend Policy -Evidence from the UAE Companies. Global Review of Accounting and Finance. Vol. 3 (1). 18 31
Septiani, R,. Paramita, P.D and Ariesta, M,. 2018. The Influence Of Profitability And Debt Policy To Firm Value With Dividend Policy As Intervening Variable (A Case Study Of A Manufacturing Company In Indonesia’s Stock Exchanges 20122016). Jpurnal of Accounting. Vol 4(4). 1-17
Sondakh, R,. 2019. The Effect of Dividend Policy, Liquidity, Profitability and Firm Size on Firm Value in Financial Service Sector Industries Listed in Indonesia Stock Exchange 2015-2018 Period. Accountability Journal. Vol. 8(2). 91101
Sukmawardini, D and Ardiansari, A,. 2018. The Influence Of Institutional Ownership. Profitability, Liquidity, Dividend Policy, Debt Policy On Firm Value. Management Analysis Journal. Vol. 7 (2). 211-223
Tahu, G.P and Susilo, D.B,. 2018. Effect of Liquidity, Leverage and profitability to The Firm Value (Dividend Policy as Moderating Variable) in Manufacturing
Company of Indonesia Stock Exchange. Research Journal of Finance and Accounting. Vol. 8(18). 89-99
Tamrin, M., Mus, H.R,. Sudirman and Arfah, A,. 2017. Effect of profitability and dividend policy on corporate governance and firm value: Evidence from the Indonesian manufacturing Sectors. Journal of Business and Management. Vol. 19(10). 66-74
Triani, N and Tarmidi, D,. 2019. Firm Value: Impact of Investment Decisions, Funding Decisions and Dividend Policies. International Journal of Academic Research in Accounting, Finance and Management Sciences. Vol. 9(2). 158– 163
Tari, N.T,. 2019. Alhamdulillah, Investor Pasar Modal Syariah Tumbuh 41 Persen. Bisnis.com. November, 21, 2019
Attachment:
Attach 1. Determinat factors of dividend policy(DPR)
|
Model |
Unstandardized Coefficients |
Standardized Coefficients |
T |
Sig. | ||
|
B |
Std. Error |
Beta | ||||
|
1 |
(Constant) |
.171 |
.087 |
1.956 |
.051 | |
|
ROA |
3.132 |
.502 |
.348 |
6.233 |
.000 | |
|
CR |
.032 |
.023 |
.078 |
1.394 |
.165 | |
|
a. Dependent Variable: DPR | ||||||
|
Attach 2. Determinat factors of Γιrm value (TQ) | ||||||
|
Unstandardized Coefficients |
Standardized Coefficients | |||||
|
Model |
B |
Std Error |
Beta |
T |
Sig. | |
|
1 |
(Constant) |
.996 |
.211 |
4.714 |
.000 | |
|
ROA |
15.735 |
1.287 |
,628 |
12.230 |
.000 | |
|
CR |
-.102 |
.055 |
-.089 |
-1.836 |
.067 | |
|
DPR |
.371 |
.143 |
.133 |
2.587 |
.010 | |
|
a. Dependent Variable: TQ | ||||||
|
Attach 3. Determiuat factors of DPR as intervening variable | ||||||
|
Unstandardized Coefficients |
Standardized Coefficients | |||||
|
Model |
B |
Std Error |
Beta |
t |
Sig- | |
|
1 |
(Constant) |
1.916 |
.149 |
12.833 |
.000 | |
|
ROA+DPR |
.543 |
.331 |
.109 |
1.643 |
.050 | |
|
CR+DPR |
-.023 |
.045 |
-.035 |
-.523 |
.301 | |
|
a. Dependent Variable: TQ | ||||||
Discussion and feedback