IMPLEMENTING EFFECTIVE CORPORATE INTERNAL CONTROL AND DEVELOPING GOOD CORPORATE GOVERNANCE
on
18 Jurnal Buletin Studi Ekonomi, Vol. 20 No. 1, Februari 2015
IMPLEMENTING EFFECTIVE CORPORATE INTERNAL CONTROL AND DEVELOPING GOOD CORPORATE GOVERNANCE
I Wayan Suka Negara Universitas Hindu Indonesia e-mail: wayan.negara@gmail.com
Abstract: Implementing Effective Corporate Internal Control And Developing Good Corporate Governance. Internal control and good corporate governance are acknowledged as an important component in corporation. Both concepts assist corporation to achieve its objectives. However, some people think that both concepts are different and do not have relationship each other. For this reason, this paper tries to explain what both concepts are and their relationship between them as a useful guideline for corporation to achieve its goals. Based on the analysis conducted, it is obtained the result that both internal control concept and GCG’s concept are the mutual complementary concept. The success of implementing internal control concept depends on a success of implementing GCG’s concept and vice versa.
Keywords: internal control, good corporate governance
Abstrak: Penerapan Effective Corporate Internal dan Pengembangan Good Corporate Governance. Pengendalian internal dan good corporate governance diketahui sebagai komponen yang sangat penting dalam perusahaan. Kedua konsep tersebut membantu perusahaan mencapai tujuannya. Tapi beberapa orang seringkali berpikir bahwa kedua konsep tersebut adalah berbeda dan tidak saling berhubungan satu dengan yang lain. Dengan alasan tersebut, artikel ini menjelaskan arti kedua konsep tersebut dan saling keterkaitannya sehingga bisa digunakan oleh perusahaan-perusahaan sebagai pedoman dalam mencapai tujuannya. Berdasarkan analisis yang dilakukan disimpulkan bahwa kedua konsep tersebut merupakan konsep yang saling melengkapi. Kesuksesan dalam penerapan pengendalian internal tergantung pada kesuksesan penerapan konsep good corporate governance dan sebaliknya.
Kata kunci: pengendalian internal, good corporate governance
INTRODUCTION
There are many studies that have promoted Internal Control and Good Corporate Governance (GCG) as critical component in corporation. Their roles as guidelines for corporation achieving their objectives are not doubtful. An inadequate and ineffective internal control, as one of the key reasons for most corporate failures. such as Enron, World Com, Arthur Anderson, and Tyco International Peregrine Systems (IFAC, 2007). In addition, GCG is critical component for management of corporation in developing corporate economic efficiency and growth as well as enhancing investor confidence to the corporation. Furthermore, GCG as one of key instruments to increase Indonesian company’s competitiveness (NCCG, 2001).
However, it can be inferred from many studies that between Internal Control and Good Governance are two different things. Based on Indonesian Code for Good Corporate Governance, Internal Control
makes only a small contribution to create Good Governance in corporation and Board of Directors are only element who responsible for establishing effective Internal Control. Furthermore, Mary Locatelli (2004) said that Sarbanes-Oxley Section 404 is opportunity to improve internal control, whereas Cynthia Harrington (2003) explains that this regulation is a new way of thinking about corporate governance.
Although both concepts play an important role in corporation, many people think that both concepts are different. For that reason, this paper tries to explain what they are and how they relate to one another. Understanding of both concepts will increase stakeholders’ awareness of their function in the corporation and finally it will accelerate corporation to achieve its objectives.
LITERATURE REVIEW
Internal Control
Over the last 20 years, Concept of Internal Control has experience significant changes. Before Committee
Sponsoring Organization (COSO) introduced Internal Control Comprehensive Concept in 1992, Concept of Internal Control was limited only to financial issues, internal auditor, and external auditor. However, COSO’s Internal Control assumes that Internal Control is more than that.
What is Internal Control?
Under the COSO Internal Control-Integrated Framework, Internal Control is an on going process in which all of corporation’s components take a part in achieving reasonable assurance to corporation’s objectives. From this definition, it can be seen that Internal Control is not an annual initiative but it is an embedded and on going process within corporation. Internal Control is not only responsibility of finance department and internal auditor or external auditor, but also all of levels in corporation such as Board of Director, Senior Management, and all levels of personnel have to be responsible to create effective internal control system. Although implementing of internal control does not provide absolute assurance, it provides reasonable assurance in achieving corporation’s objectives.
What are objectives of implementing Internal Control?
Based on Framework for Internal Control Systems in Banking Organizations, there are three objectives of corporation, which can be achieved through implementing of comprehensive internal control: performance objectives, information objectives, and compliance objectives. With regard to performance objective, effective internal control can encourage all of corporation’s components to effectively and efficiently use asset and other resources to achieve corporation’s objectives. Furthermore, corporation can achieve information objectives because effective internal control creates relevant, reliable, and timely information for decision maker. Lastly, through policies and procedures as components of internal control, companies can create and improve their compliances to the laws and regulations.
How does a good Internal Control create?
Creating an effective internal control system, based on COSO’s standardization, there are five interrelated elements that construct this system. They are: First of all is Control Environment. Control Environment reflects how strong boards of director commit to businesses conducts and how far managements and all of level personnel implement these businesses’ conducts in entity’s operation. Control Environment includes elements such as code
of business conducts (management’s integrity and ethical values), entity’s policies and standard operating procedures, and organization structures.
Secondly is Risk Identification. Every entity will face a variety of risks from external to internal entity that can avoid entity to achieve objectives. Effective internal control can identify and consider those risks which risks can be controllable and which are not. Thirdly is Information and Communication. An information system will be useful if this system can provide relevant, reliable, and timely information, and an effective communication is needed to create information to be more useful and to ensure that the essential information reaches the right people. Adequate information system and effective communication can create all entity’s personnel know about top management’s attitude to internal control, their roles, and their colleague’s roles. Besides that they can create a good relationship with external parties such as customers, suppliers, regulators, and shareholders. Fourthly is Control Procedures. Control Procedures, which is reflected in entity’s policies and procedures, are required to ensure that necessary actions are taken to address risks that the entity identified through risk identification process. Control procedures consist of activity controls and segregation of duties where process of authorization, verification, reconciliation, reviewing of operating performance, and security of assets are elements of these procedures. Finally is Monitoring Activities and Corrective Action. This element assesses the quality of internal control over time or on going process. Every deficiency of internal control, which was identified by business lines, Internal Auditor, and others, should be reported to appropriate management level in timely manner.
Good Corporate Governance (GCG)
Concept of Good Corporate Governance (GCG) has been known since 1992 when Cadbury Committee published report related to this issue. However, it has been hot issues again in 2002 when many big companies such as Enron, WorldCom and Arthur Anderson went bankrupt because of bad governance. What is Good Corporate Governance?
Based on definition from Cadbury Committee of United Kingdom (1992), Good Corporate Governance is a set of rules that define the relationship between shareholders, investors, creditors, the government, managers, other internal and external stakeholders in respect to their rights and responsibilities, or the system by which
companies are directed and controlled. From this definition, it can be seen that GCG involves a set of relationships between corporate managements, board of commissioners, shareholders, and other stakeholders. GCG also provides a structure for how the corporate objectives are set and how to realize these objectives. Furthermore GCG facilitates the effective monitoring of corporate operation achieving corporate objectives.
The benefits of the good corporate governance
There are some benefits that can be achieved if corporation implements GCG such as improving their business performance, easier to raise capital, and good impact on share price. With regard to improving corporate business performance, GCG encourages corporation to be effective and efficient in their operation because corporate stakeholders such as their employees and shareholders know their role – rights and liabilities – in achieving corporate objectives. In addition, based on recent survey of McKinsey & Corporation indicated that fund manager would pay 26 – 30% more for stocks companies with good corporate governance than for stocks of companies with doubtful corporate governance. It means that corporation which has good governance will have a better access to investor or creditors than those without good corporate governance. Finally, their share price would increase because many investors try to buy their shares. How to implement Good Corporate Governance
In order to create GCG, based on Indonesia’s Code of Good Corporate Governance, there are 5 (five) principles that have to implement in creating good governance in corporation. First of all is Transparency. Corporation has to provide relevant information and easily accessible by their stakeholders based on their rights. Information, which is shared, is not only mandated by laws and regulations, but also other information deemed necessary by their shareholders, creditors, and stakeholders to make decision. Secondly is Accountability. Accountability is key elements for corporation to achieve sustainable performance because it reflects a proper and measurable corporate management. Corporate must clearly define the job descriptions and responsibilities, which are in line with the vision, mission, values, and objectives of corporate from all elements of organizational structure. The qualification of all corporate organs and all their employees should be fits to their duties. In addition, corporate should have performance indicators for all their corporate elements as a guideline to implement reward and punishment
system. Thirdly is Responsibility. Maintaining longterm sustainability of corporate and recognized as a good corporate citizen, corporate must prudent in their decision-making and their actions, and ensuring their activities has already complied with laws and regulations. Fourthly is Independency. Every element of corporate have to conduct their duties based on their roles and must be free from conflict of interest and any influence or pressure. These elements must avoid the occurrence of domination by any party or shifting the responsibility from one to the other. Lastly is Fairness. Fairness principle should be considered by corporate when corporate conduct their operation. Corporate must provide an equitable treatment to their stakeholders in accordance with contribution, which they give to the corporate. Corporate must give an equal opportunity in recruitment of employees and in career development for employees.
RESULT AND DISCUSSION
Relationship between Internal Control and Good Governance
From what explained above, there are many redline that can be drawn from relationship between Internal Control and GCG, which are:
-
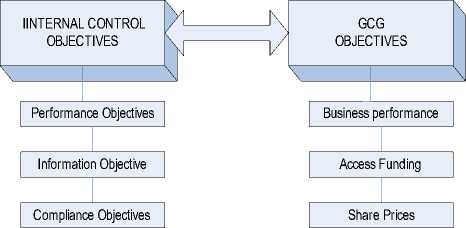
a. Same objectives
Basically both concepts have the same objectives. Corporation adopts those concepts in their operation to assist achieving their objectives. Performance objectives, information objectives, and compliance objectives are three objectives, which are wanted to achieve if the corporation has an effective Internal Control. Furthermore if those can be achieved, it automatically improves corporate business performance and increases trust among external stakeholders, which is reflected in much easier way for corporation to get funding from external parties and increasing corporate stock prices. It means that GCG’s objectives have already achieved too. Internal control objectives seem to be foundation for achieving GCG’s objectives.
-
b. Mutual Complementary Concept
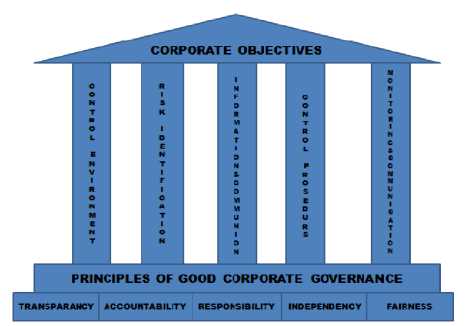
In order to construct a good internal control system, corporation has to develop and implement five interrelated elements of internal control in corporate operation. This system can be effective and efficient to achieve corporate objectives, if it is developed based on GCG’s principles. These principles can be strong foundation for five interrelated elements of internal control. If corporation can be described as a house, its foundation is constructed based on GCG’s principles, its pillars are made of internal control’s elements and its roof is the corporate objectives.
Developing Corporate Control Environment such as corporate policies and standard operating procedures (SOPs), corporation should implement GCG’s principles such as transparency, accountability and responsibility. Transparency principle reflects that these policies and SOPs are known and understood by employees and other stakeholders. Accountability and responsibility principles express that these policies and SOPs are conducted by qualified employees and comply with laws and regulations.
In addition, when company identify and consider their risks and also, this identification should be conducted based on accountability and independency principles. In Accountability principles, those risks which risks can be controllable and which are not, reflects a proper and measurable description. Furthermore, In Independency Principles, those risks must be identified and clarified by independent parties and also must be free from conflict of interest and any influence or pressure.
After that, Developing an Effective Information and Communication System should be based on transparency and fairness principles. These principles are applied to make sure that every corporate report such financial reports and operational reports is easy accessible by its stakeholders based on their rights.
In Developing Control Procedures such as activity controls and segregation of duties, the company must comply with accountability and independency principles. Accountability principles can be reflected by the qualification of all corporate organs and all their employees should be fits to their duties.
Finally, in developing Monitoring and Communication must comply with all of five GCG’s Principles, Transparency, Accountability,
Responsibility, Independency, and Fairness. Monitoring Activities and Corrective Action element assesses the quality of internal control over time or on going process based on accountability, independency and fairness principles. Every deficiency of internal control, which was identified by business lines, Internal Auditor, and others, should be reported to appropriate management level in timely manner and rely on transparency and accountability principles.
-
c. Regulate the Rights and Responsibilities of Corporate Stakeholders
GCG stresses the importance for corporation having clear guidelines for their stakeholders when they demand their rights and do their responsibilities, just as internal control does. These guidelines will encourage an effective relationship among stakeholders and will prevent the domination of one stakeholder. Every corporate stakeholder will participate in developing and assisting corporation to achieve objectives because they know that achieving corporate objectives are the responsibility of all corporate stakeholders.
CONCLUSION
Basically both internal control concept and GCG’s concept are the mutual complementary concept. The success of implementing internal control concept depends on a success of implementing GCG’s concept and vice versa. The Development of corporate internal control system has to adopt the GCG’s principles because these principles can be a strong foundation for development of internal control system. In addition, both concepts assist corporation to established strong foundation for sound and safe operation of corporation. The implement of effective
internal control and good governance can help to ensure that goals and objectives of corporation will be met, which corporation will achieve long term profitability targets, and maintain reliable financial and managerial reporting. Furthermore, both concepts can also help to ensure that corporation will comply with laws and regulations as well as policies, plans, internal rules and procedures.
REFERENCES
Bisoux, T., 2004, “What is Good Governance”, retrieved on 12 August 2008, available from http://www. aacsb. edu/publications/Archives/ Mar-Apr04/p34-36.pdf
Bank For International Settlements, 1998 “Framework for Internal Control Systems in Banking Organisations”, retrieved on 7 August 2008, available from http://www.bis.org/publ/ bcbs40.pdf.
FCGI, 2006 “What is Corporate Governance’ retrieved on 12 August 2008, available from http://www.fcgi.or.id/en/aboutgc.shtml.
Gable, J., 2006, “Compliance: Where Do We Go From Here?, Information Management Journal, May/June 2006, p. 28, retrieved on July 11 2008, available from Proquest On-line Academic Research Library, http://proqest.com/pqdauto, July 11, 2008.
Harrington, C., 2003, “The New Accounting Environment”, Journal of Accountancy, August 2003, p. 28-33, retrieved on July 11 2008, available from Proquest On-line Academic Research Library, http://proqest.com/pqdauto,.
INTOSAI, General Secretariat, 2001, “Guidelines for Internal Control Standards for the Public Sector”, retrieved on 8 August 2008, available
from http://intosai.connexcc-hosting.net/ blueline/upload/1guicspubsece.pdf.
International Federation of Accountants, 2002 “ Internal Control From Risk Based Perspective”;
KPMG, 1999, “The KPMG Review Internal Control: A Practical Guide”, retrieved on 8 August 2008, available from http://www.ecgi.org/codes/ documents/kpmg_internal_control_practical_ guide.pdf
Locatelli, M., 2004, “How Good Are Your Internal Controls…Really?, Directorship, June 2004, p. 13-17, retrieved on 11 July 2008, available from Proquest On-line Academic Research Library, http://proqest.com/pqdauto,.
Mel Gill, Synergy Associates Inc, Retrieved on 7 August 2008 “Corporate Governance after Enron and WorldCom Applying Principle of Results-Based Governance”, available from http://www.synergyassociates.ca/documents/ Corporate%20Governance%20after%20Enron %20and%20WorldCom.pdf
National Committee on Corporate Governance, 2001, “Indonesian Code for Good Corporate Governance”
OECD 2004, “OECD Principles of Corporate Governance”, retrieved on 7 August 2008, available from, http://www.oecd.org/dataoecd/ 32/18/31557724.pdf
Ramos, M., Journal of Accountancy, 2004, “Evaluate The Control Environment”, retrieved on 11 August 2008, available from http://www.aicpa.org/PUBS/ jofa/may2004/ramos.htm.
Sarah Al-Houti, “IT Governance and Security Information Trust and Compliance Issue (SOX)”, retrieved on 7 August 2008, available from http:/ /citebm.business.uiuc.edu/TWC%20Class/ Project_reports_Spring2007.
Discussion and feedback